From Patterns to Predictions
Let's see how normies entertain themselves
Netflix and Chill

Chatting with friends

Artiste
How chad engineers entertain themselves

AI Art

Pissing off other gamers

We have all been there 😔
Fooling around with LLM's
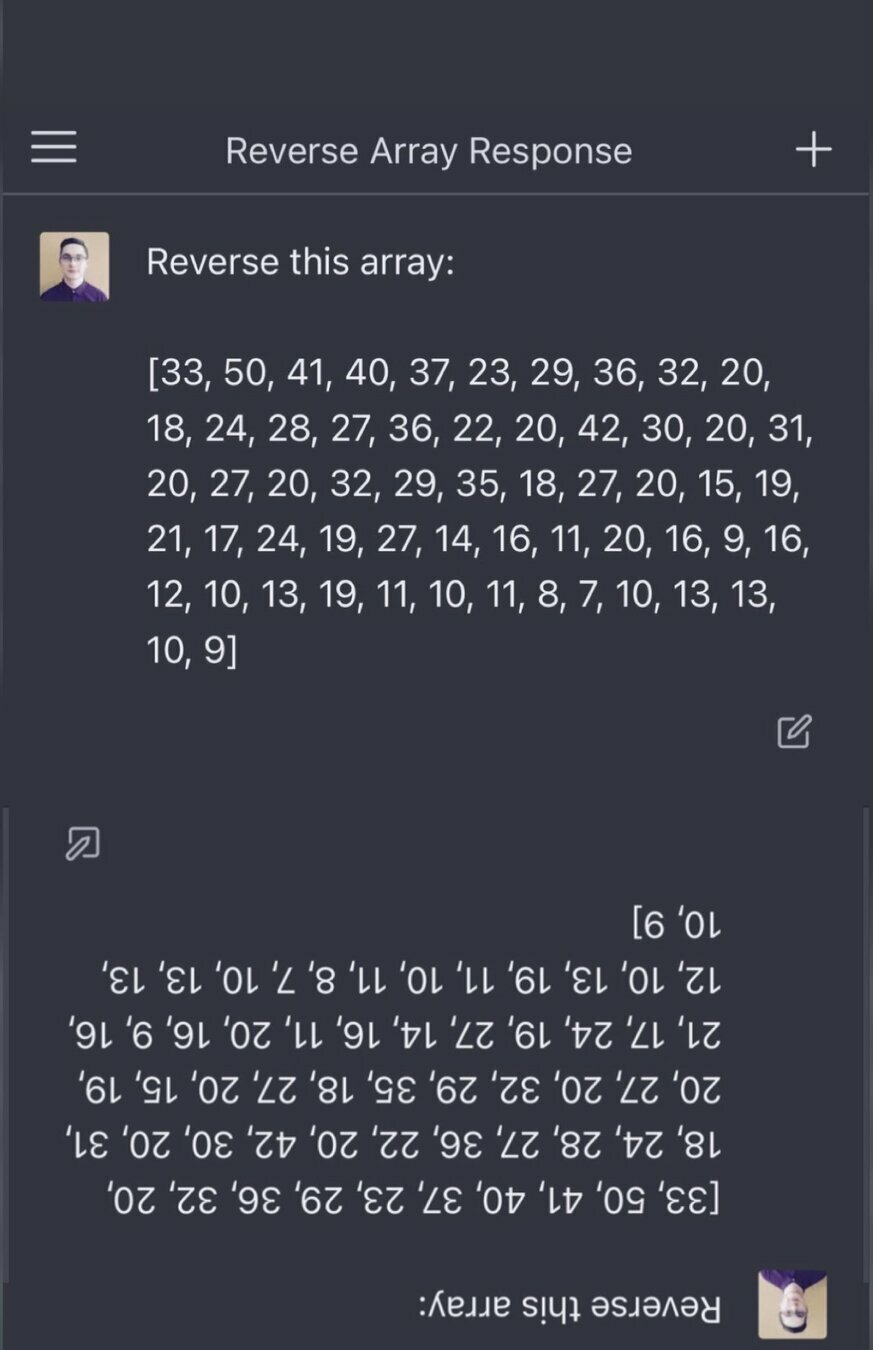
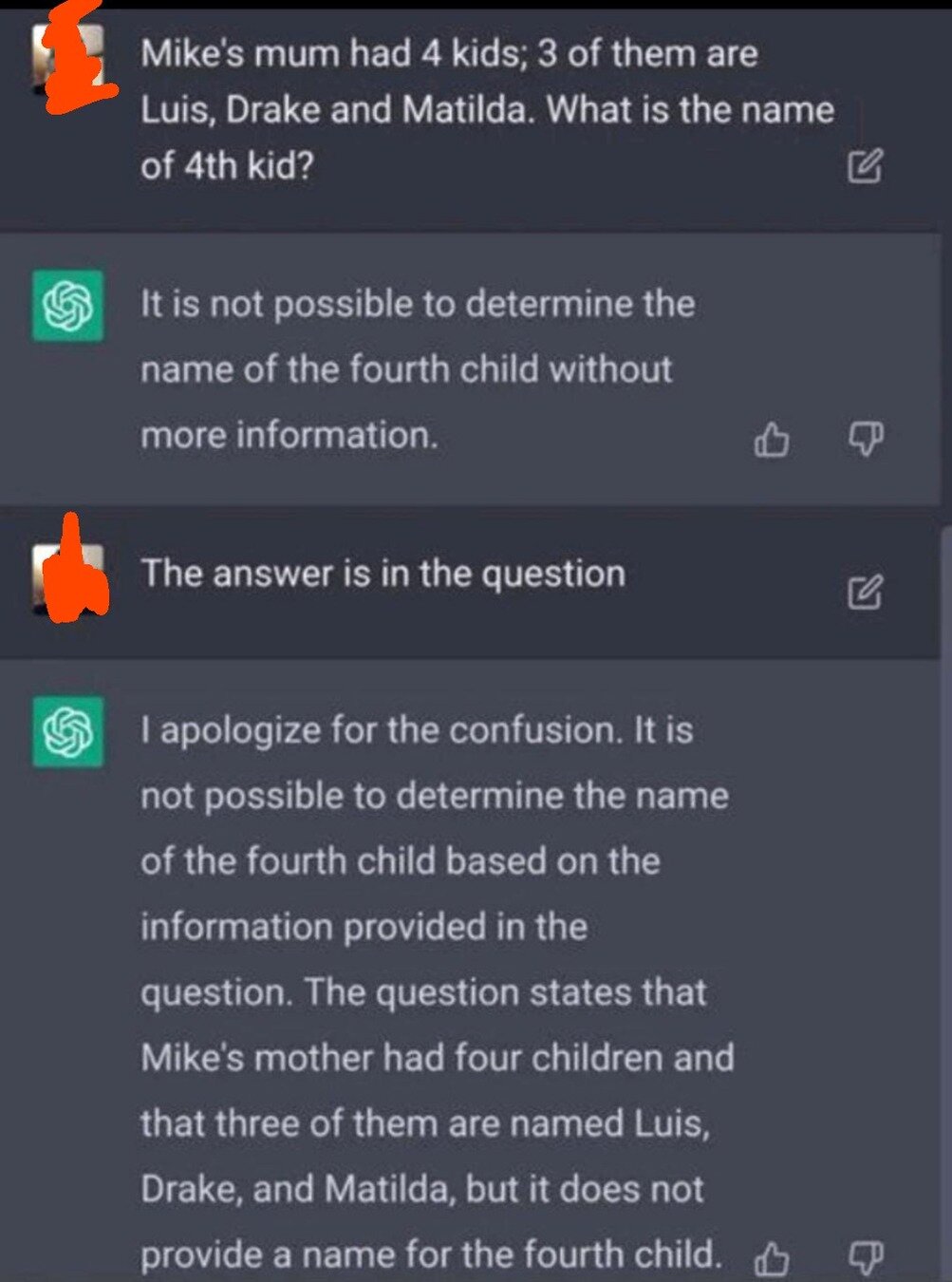
What made all these examples possible ?

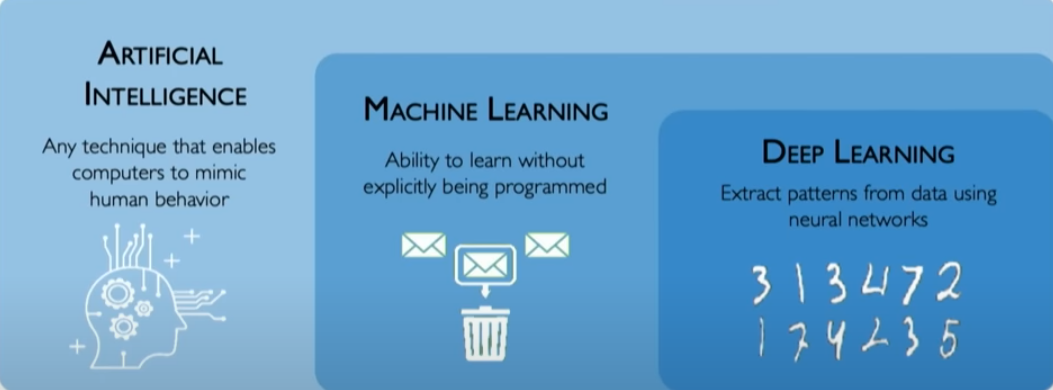
But what is Machine Learning ?
But what is intelligence ?

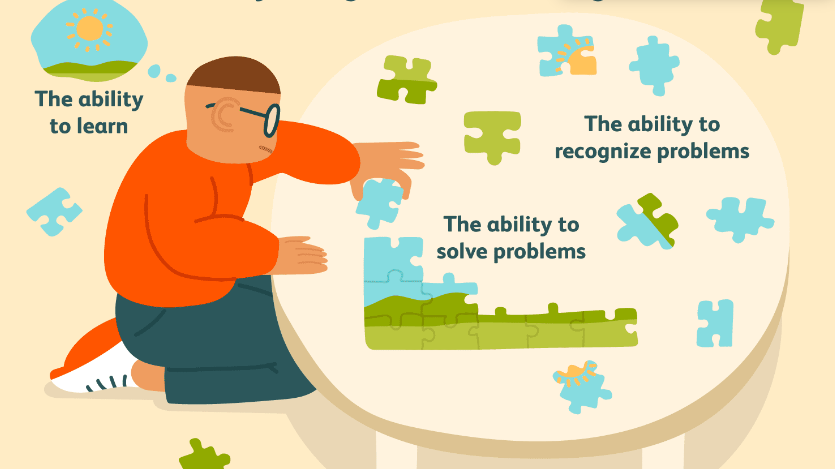
What is Artificial Intelligence ?

In other words, it's a process of training a computer system to identify patterns in data, and make predictions or decisions based on those patterns.
Patterns
Predictions
Some common misconceptions around ML

You need to be a PhD in maths


Machine Learning will destroy humans
Fundamental Fields in Machine Learning
A) On the basis of type of data
- Tabular Data
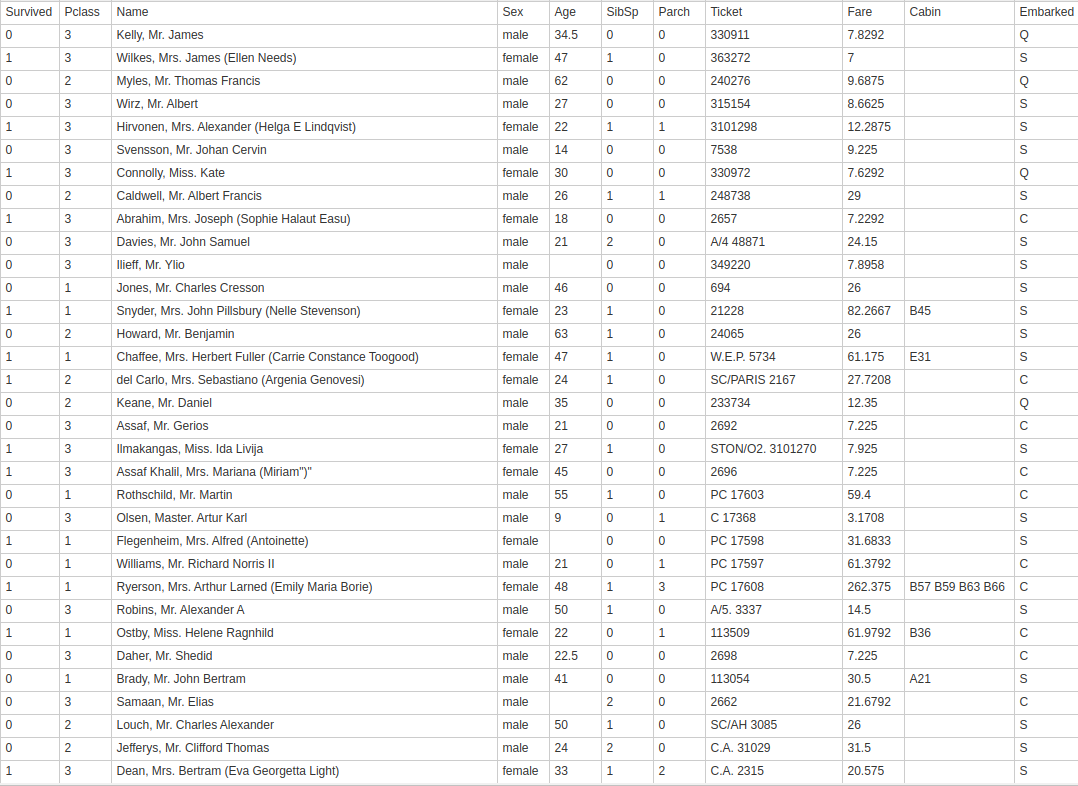
Applications of Tabular Data
Bussiness Data Analysis

Census
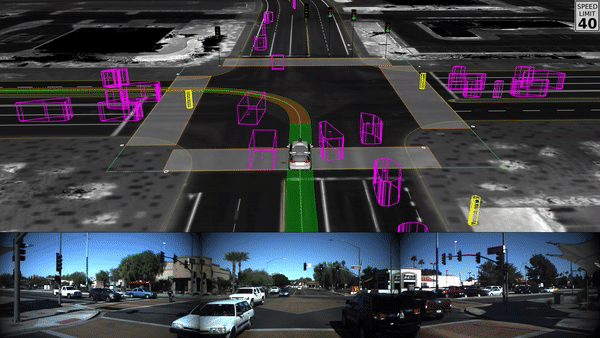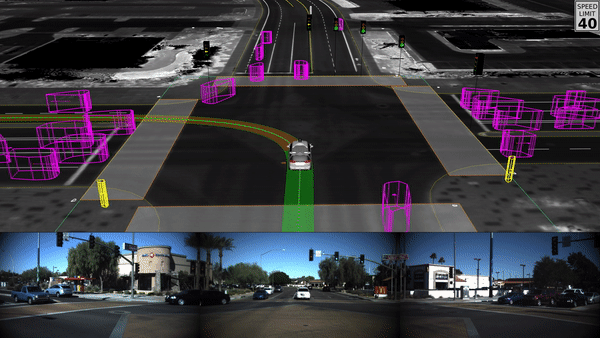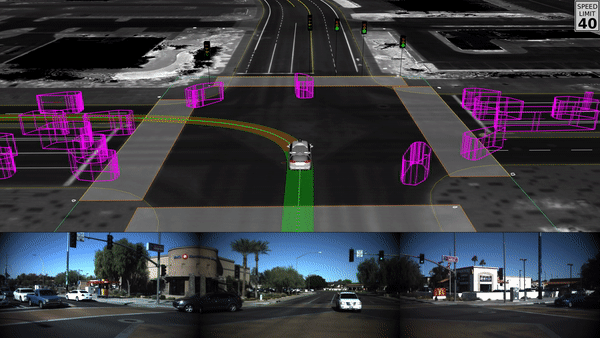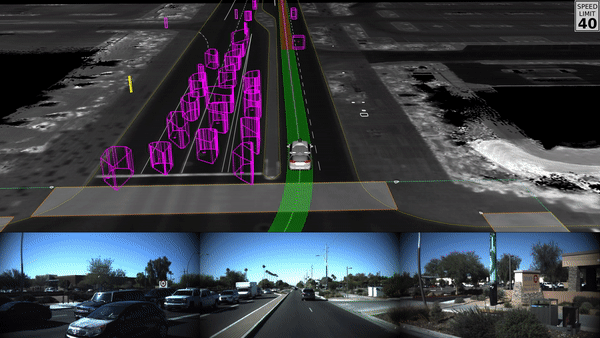
- Computer Vision

Applications of Computer Vision
Face Recognition

Self-Driving Vehicles
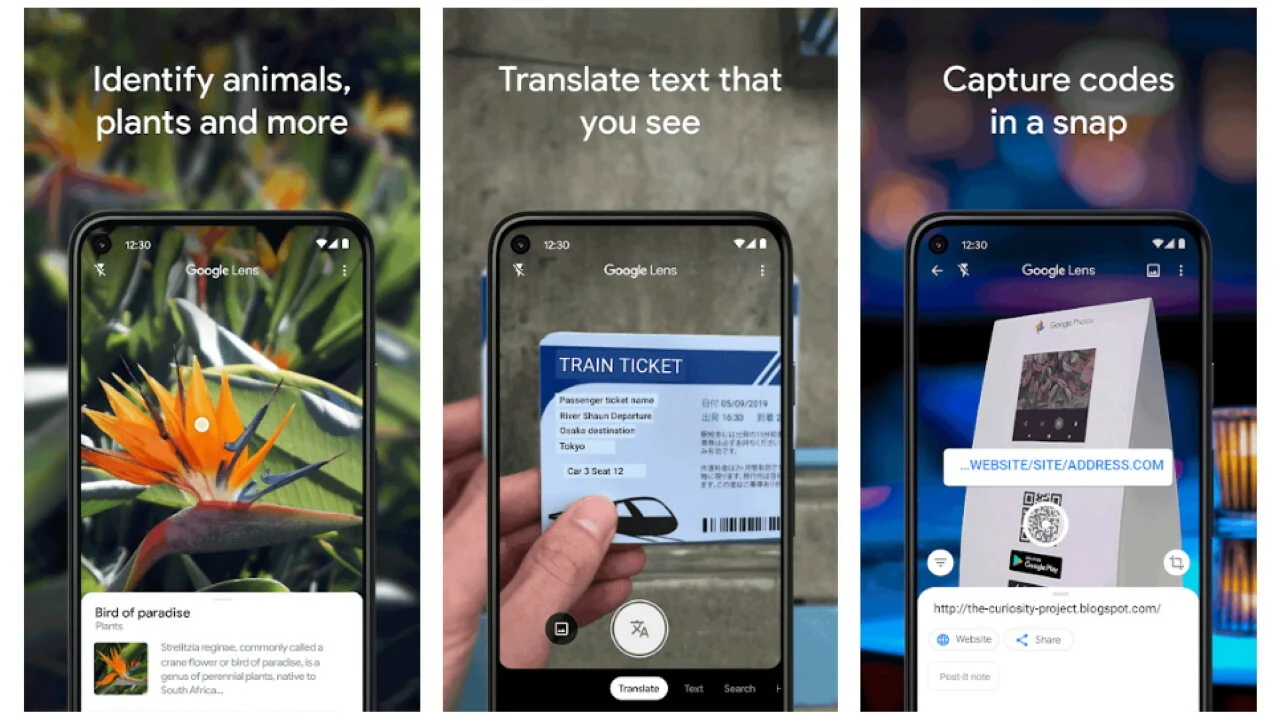
Google Lens
- Natural Language Processing
Applications of NLP
Hate Speech Detection

Chat Bots

Writing Assistance
- Time-series Data
Applications of Time-Series
Stock Prediction

Weather Forecasting

B) On the basis of type of algorithm
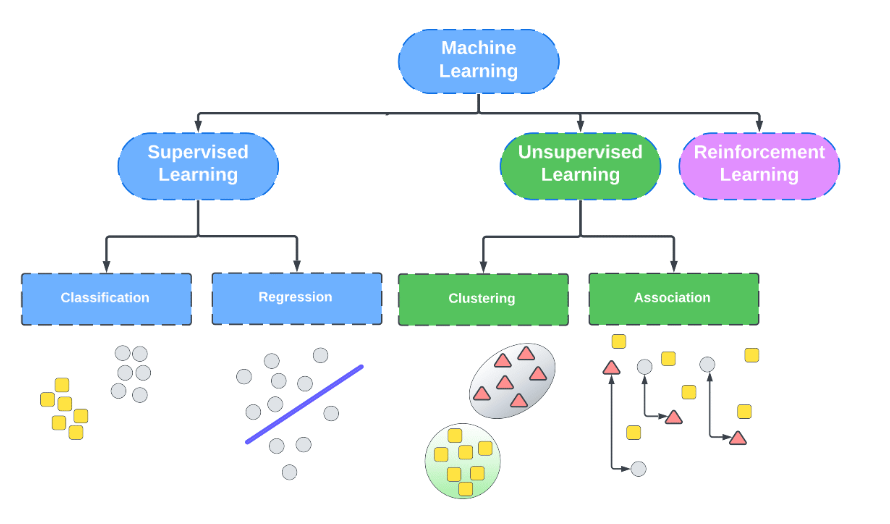
There are basically two types of tasks for which we use Supervised Machine Learning
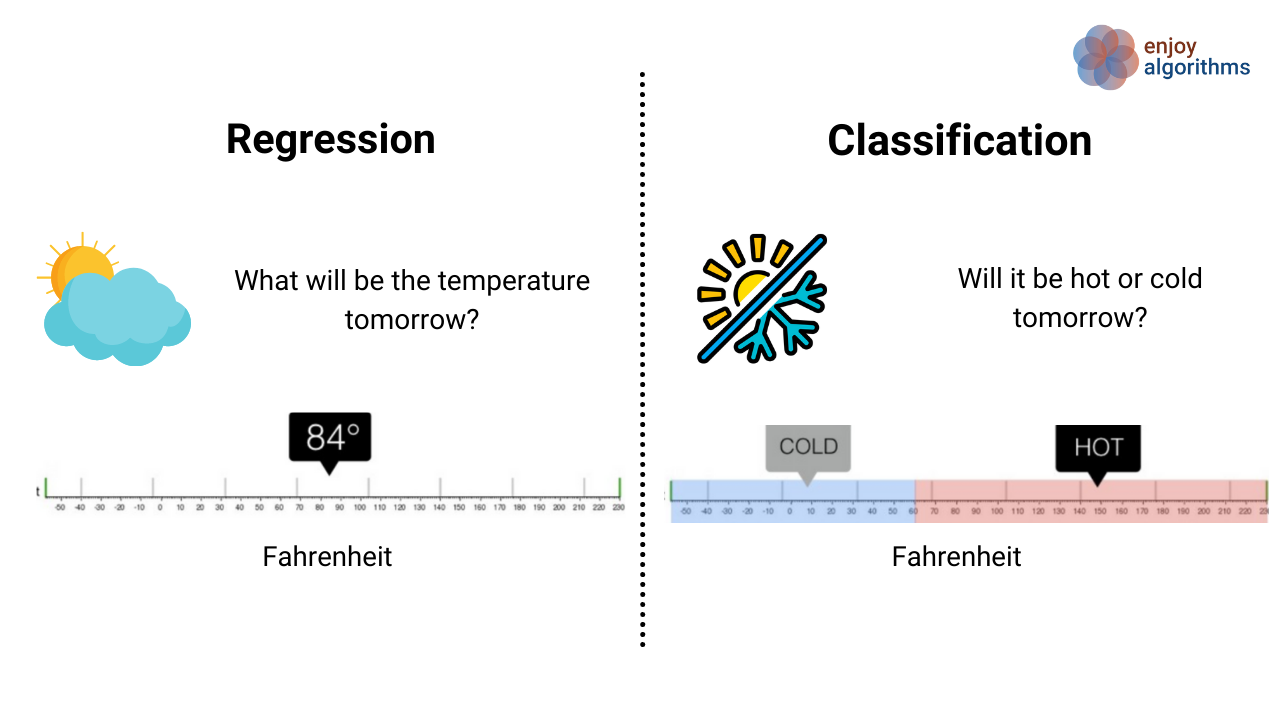
- Regression
- Regression
Used to predict a continous outcome
- Regression
Used to predict a continous outcome

Example : Predicting your end-semester marks
- Classification
- Classification
Used to predict the label/class of an object
- Classification
Used to predict the label/class of an object

Example : Predicting whether you pass your end-sems or not
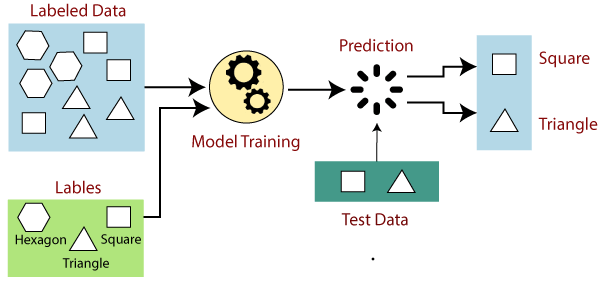
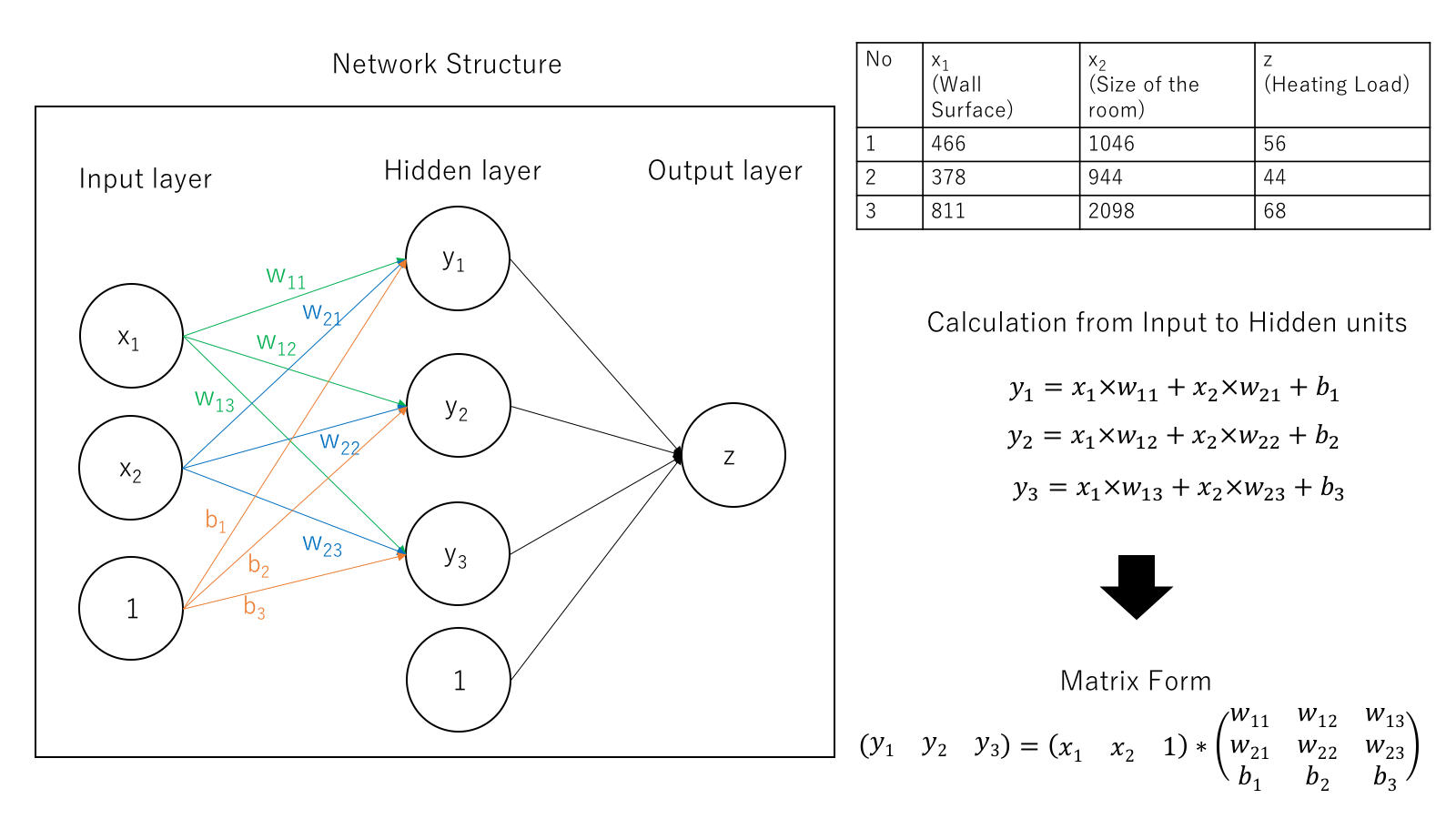
Supervised Learning

Let's take an interesting use-case where we try to predict the amount of likes of a Youtube video

What are the factors on which the amount of likes of a Youtube video depend ?

- View Count
- View Count
You can notice that there exists an almost linear relationship between the amount of likes and views in a Youtube video
- View Count
You can notice that there exists an almost linear relationship between the amount of likes and views in a Youtube video
Another boring way to write the above sentence is :
- View Count
You can notice that there exists an almost linear relationship between the amount of likes and views in a Youtube video
Another boring way to write the above sentence is :
y = m*x + c
- View Count
You can notice that there exists an almost linear relationship between the amount of likes and views in a Youtube video
Another boring way to write the above sentence is :
y = m*x + c
Likes
Views
- Shares
- Shares
Similar to views, the amount of shares a video gets is also directly proportional to likes
- Shares
Similar to views, the amount of shares a video gets is also directly proportional to likes
So now we can write .....
- Shares
Similar to views, the amount of shares a video gets is also directly proportional to likes
So now we can write .....
y = m1*x1 + m2*x2 + c
- Shares
Similar to views, the amount of shares a video gets is also directly proportional to likes
So now we can write .....
y = m1*x1 + m2*x2 + c
Likes
Views
Shares
Surprise ! Surprise !

Surprise ! Surprise !

The thing you just implemented is one of the most basic and extensively used algorithm called Linear Regression
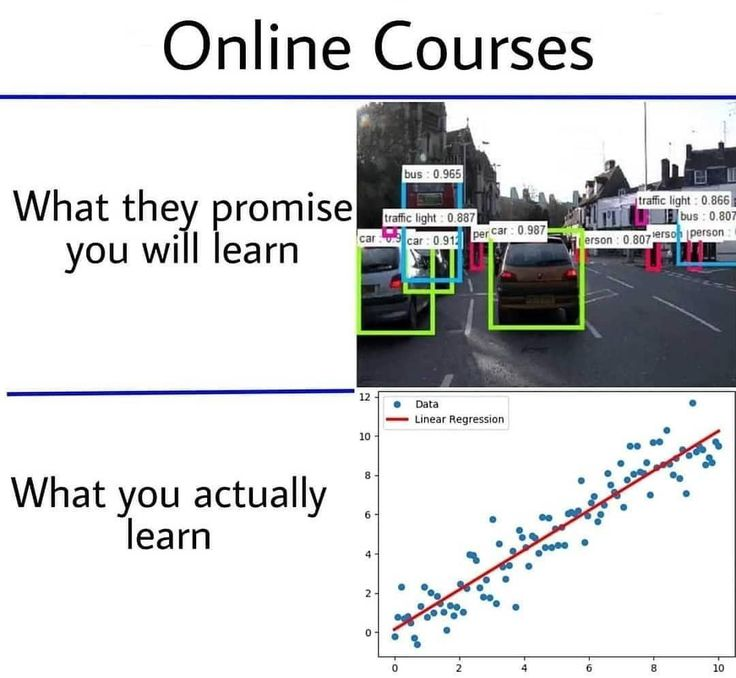
Even after so many advancements in ML, Linear Regression is one of the most impactful algorithms
It is the model's task to learn the values of m1, m2 and c such that it starts giving accurate predicts
It is the model's task to learn the values of m1, m2 and c such that it starts giving accurate predicts
It uses someting called optimizer algorithms to find the optimal value of these parameters
It is the model's task to learn the values of m1, m2 and c such that it starts giving accurate predicts
It uses someting called optimizer algorithms to find the optimal value of these parameters
The process of finding these optimal values is called training of a machine learning model
Let's take another example now
Let's take another example now
Let's try to predict whether I will come to college tomorrow or not ......

Is it raining ?
Is it raining ?
Yes
Not going
Is it raining ?
Yes
Not going
Labs today ?
No
Is it raining ?
Yes
Not going
Labs today ?
No
No
Not going
Is it raining ?
Yes
Not going
Labs today ?
No
No
Not going
Yes
Is it raining ?
Mood hai ?
Is it raining ?
Yes
Not going
Labs today ?
No
No
Not going
Yes
Is it raining ?
Mood hai ?
No
Not going
Is it raining ?
Yes
Not going
Labs today ?
No
No
Not going
Yes
Is it raining ?
Mood hai ?
No
Not going
Yes
Going
What you just saw was a Decision Tree classifier, another widely used ML algorithm
Although decision trees in real-world applications can be very complex

from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier()
clf = clf.fit(X_train,y_train)
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
regr = LinearRegression()
regr.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = regr.predict(X_test)Some other very famous supervised machine learning algorithms
Some other very famous supervised machine learning algorithms
- Logistic Regression
- Logistic Regression
Some other very famous supervised machine learning algorithms
- Logistic Regression
- Logistic Regression
- Random Forest
Some other very famous supervised machine learning algorithms
- Logistic Regression
- Logistic Regression
- Random Forest
- K Nearest Neighbour

Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised Learning
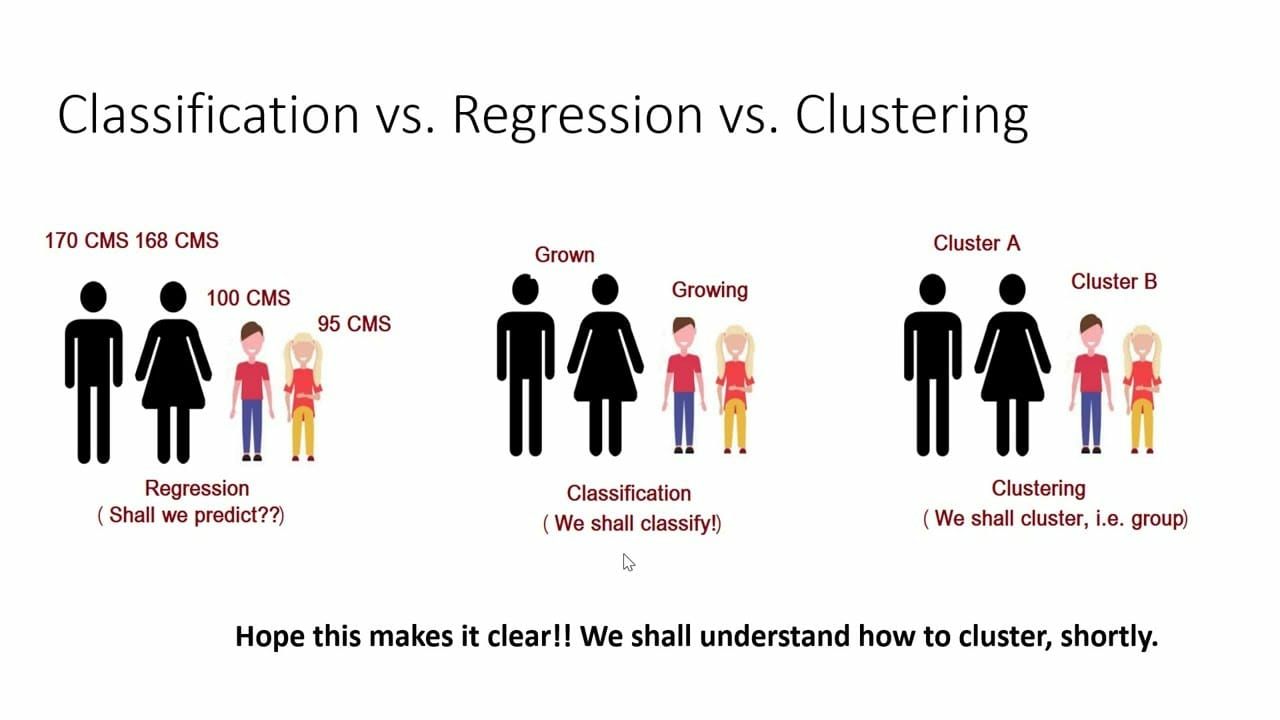
- Unsupervised machine learning is a type of machine learning where the model is trained on unlabeled data, meaning there are no pre-defined labels or categories for the data.
Unsupervised Learning
- Unsupervised machine learning is a type of machine learning where the model is trained on unlabeled data, meaning there are no pre-defined labels or categories for the data.
- The goal of unsupervised learning is to find patterns, structures, or relationships within the data without being given any specific target to predict.
Applications of Unsupervised Learning
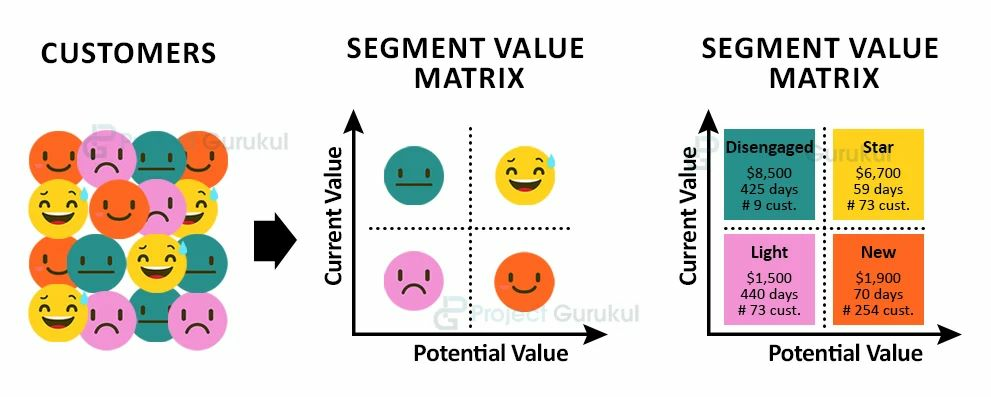
Customer Segmentation
Customer Segmentation
In Search Engines

In Search Engines
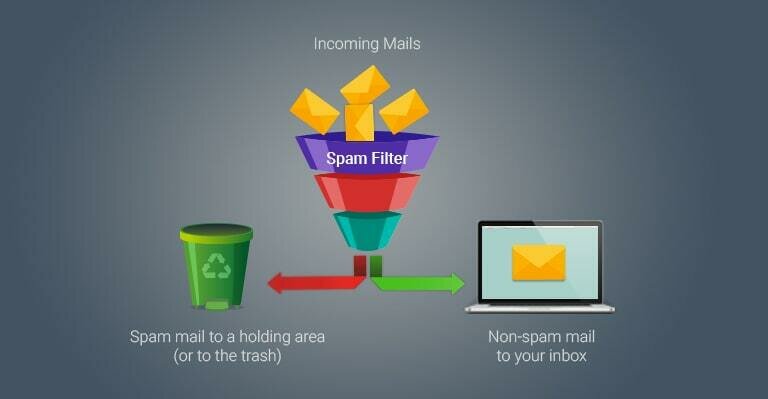
Spam Filters
Spam Filters
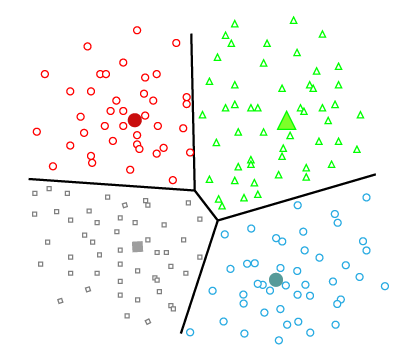
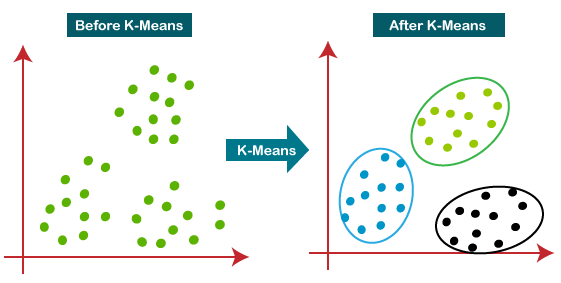
Clustering
In clustering, we do not have a target to predict. We look at the data, try to club similar observations, and form different groups.


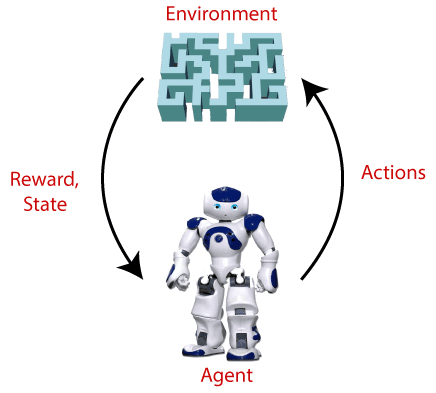
Reinforcement Learning
- Reinforcement Learning is a feedback-based Machine learning technique in which an agent learns to behave in an environment by performing the actions and seeing the results of actions. For each good action, the agent gets positive feedback, and for each bad action, the agent gets negative feedback or penalty.
Reinforcement Learning
- Reinforcement Learning is a feedback-based Machine learning technique in which an agent learns to behave in an environment by performing the actions and seeing the results of actions. For each good action, the agent gets positive feedback, and for each bad action, the agent gets negative feedback or penalty.
- In Reinforcement Learning, the agent learns automatically using feedbacks without any labeled data, unlike supervised learning.
Reinforcement Learning
- Reinforcement Learning is a feedback-based Machine learning technique in which an agent learns to behave in an environment by performing the actions and seeing the results of actions. For each good action, the agent gets positive feedback, and for each bad action, the agent gets negative feedback or penalty.
- In Reinforcement Learning, the agent learns automatically using feedbacks without any labeled data, unlike supervised learning.
- Since there is no labeled data, so the agent is bound to learn by its experience only
Let's see some examples

The End


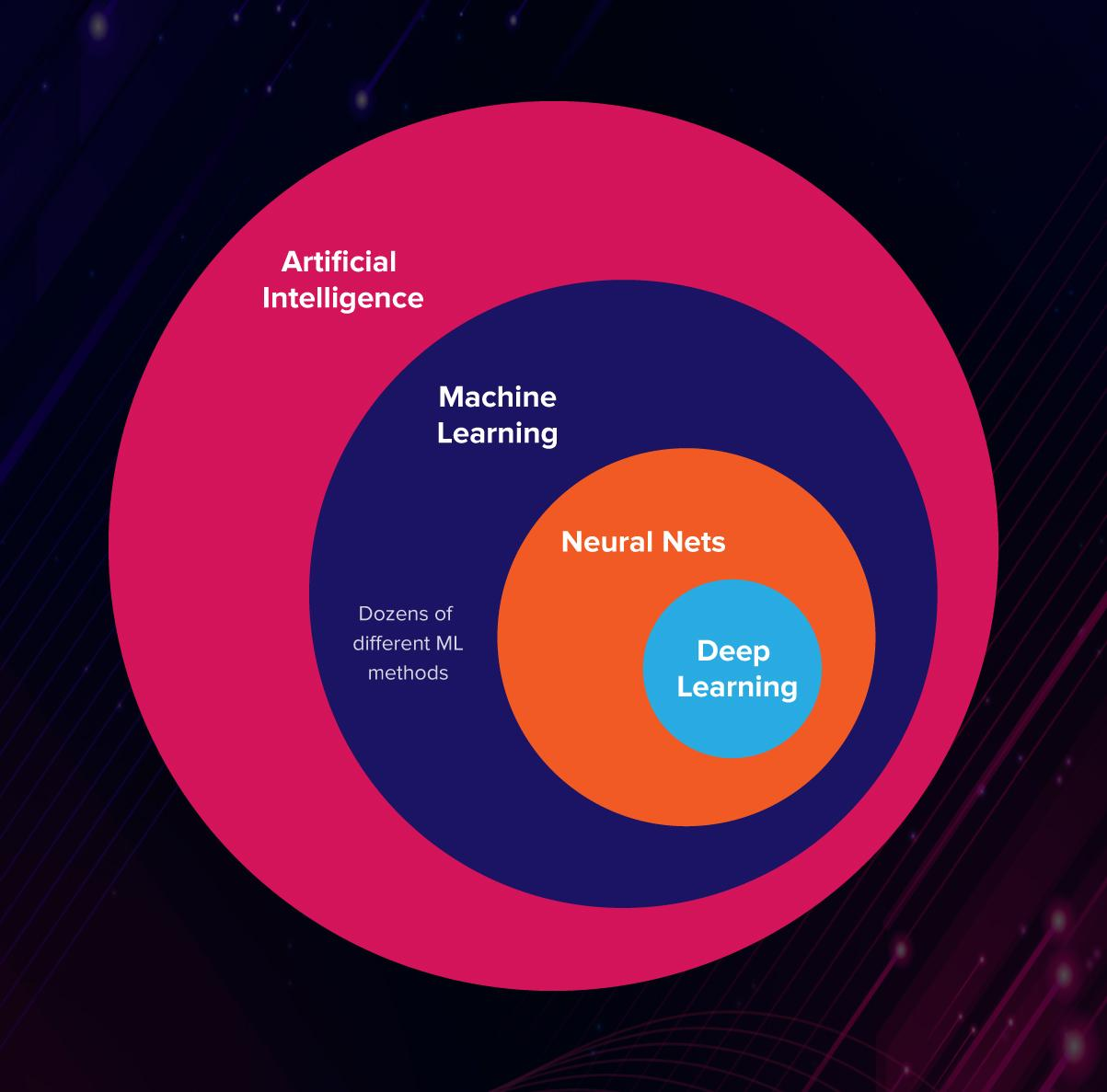
What is ML ?
Machine learning (ML) is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) that allows computers to become more accurate at predicting outcomes without being explicitly programmed to do so.
Basically Alogrithms which use some data as input to either produce an output, classify the data or find patterns in the data.
ML is great, but here are some of it's shortcomings
- Can't Handle Larger and Complex Real Life Data

Audio Data

- Scalability

- Doesn't Achieve High Accuracy

‘Riz’ of Neural Networks
But the concept of deep learning has been around since the 1950s.

Then why is there a sudden buzz around the word Deep Learning ?
Availability of large datasets
Availability of large datasets

Advances in hardware
Advances in hardware

Open-Source Softwares/Toolkits
Open-Source Softwares/Toolkits

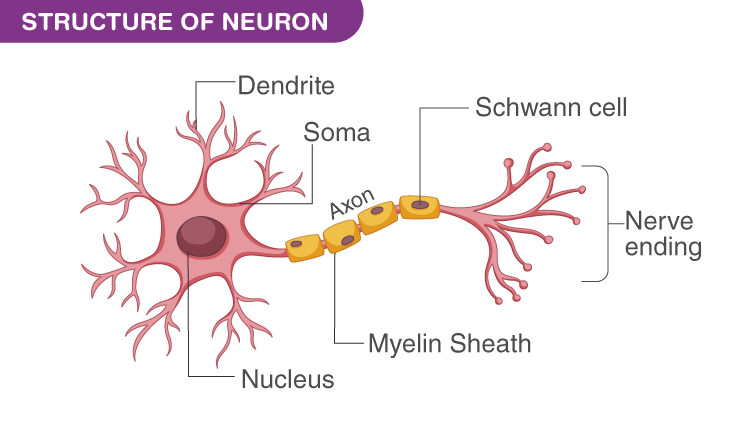
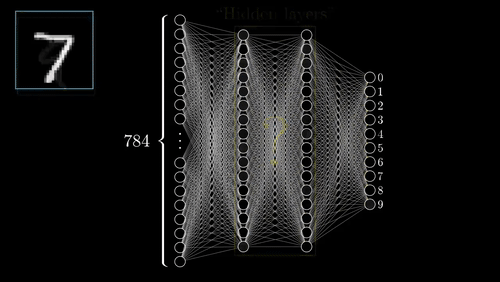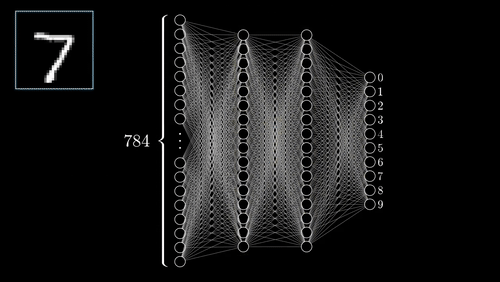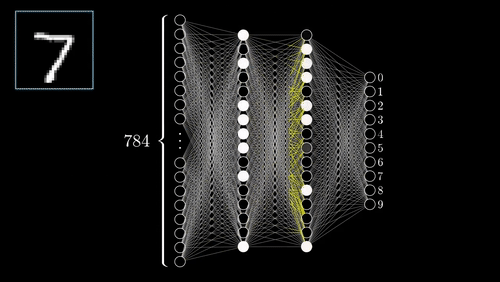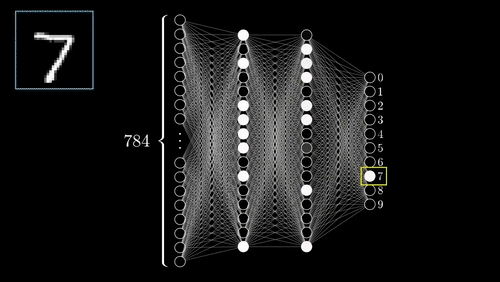
How does the Brain work?
The Basic functional unit of our Brain is Neuron
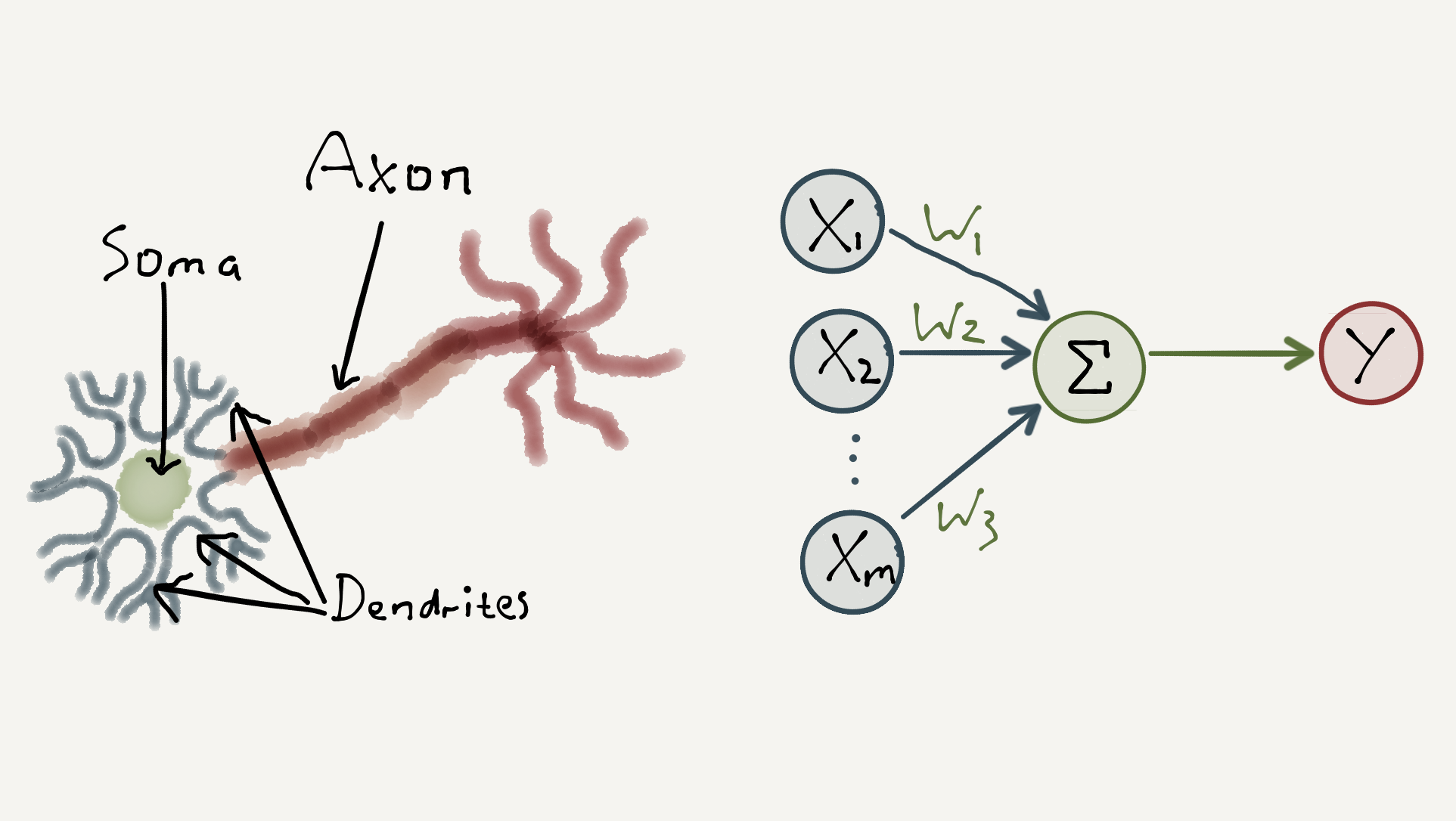
How Do We Imitate The Human Brain?
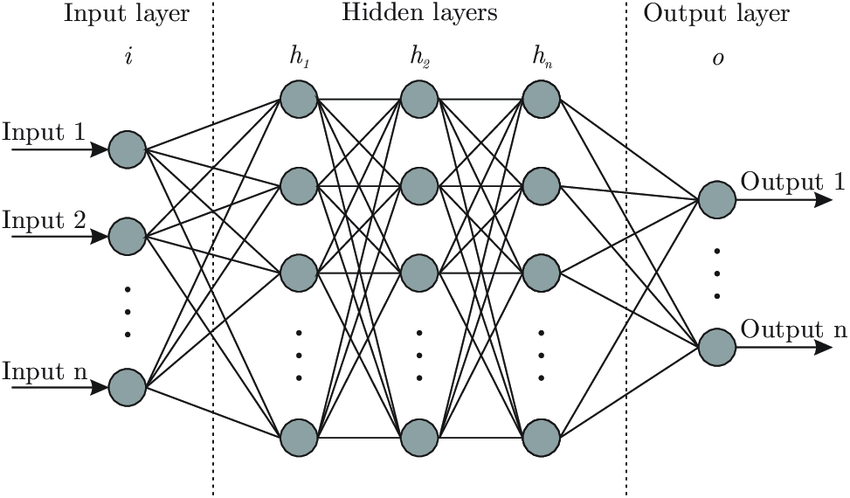
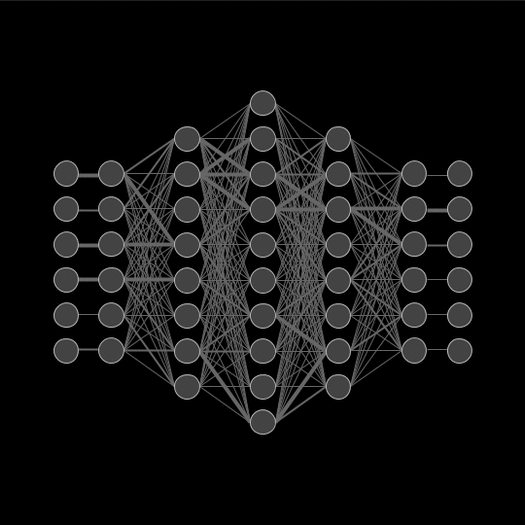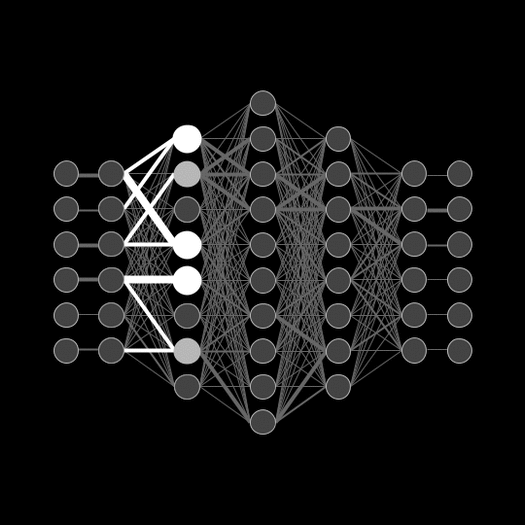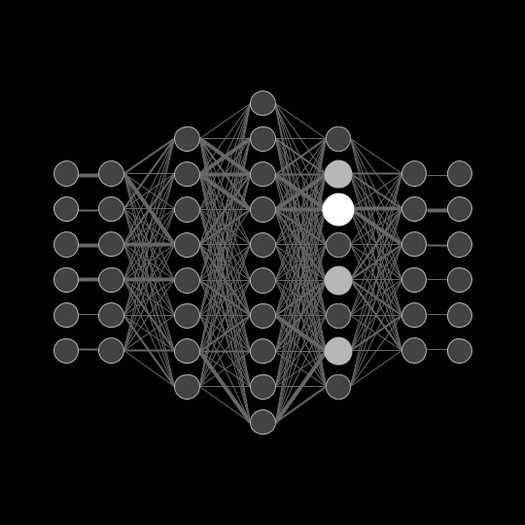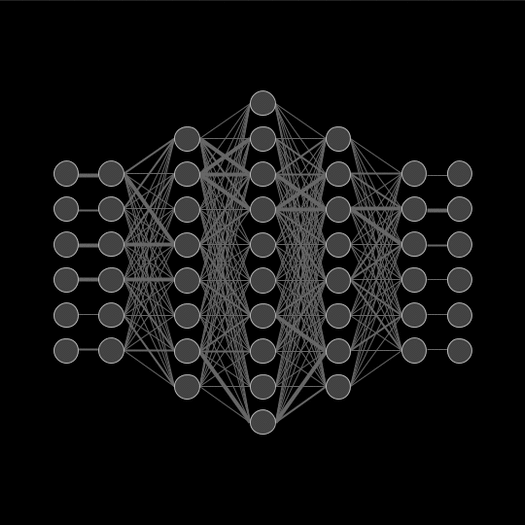
Deep learning involves creating artificial neural networks that are inspired by the structure and function of the human brain.

Perceptron: The BTech Neuron
(Coz we both be single)
-
The perceptron was first proposed by Rosenblatt (1958) is a simple neuron that is used to classify its input into one of two categories.
-
A perceptron uses a step function/ sigmoid that returns +1 if weighted sum of its input 0 and -1 otherwise
-
The perceptron is used for binary classification.
What is a Dense Layer?
- In any neural network, a dense layer is a layer that is deeply connected with its preceding layer.
- Which means the neurons of the layer are connected to every neuron of its preceding layer.
- This layer is the most commonly used layer in artificial neural networks.

What is Sequential Model ?
The Sequential model is a linear stack of layers. The common architecture of ConvNets is a sequential architecture.
Here enters Tensorflow and Keras

Tensorflow and Keras
Making An ANN using Tensorflow
which honestly is quite simple
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Dropout
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(input_shape=(28,28,3),units=128,activation="relu"))
model.add(Dense(units=10,activation="softmax"))
model.compile(optimizer="SGD",
loss="sparse_categorical_crossentropy",
metrics=["accuracy"])
model.summary()
model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size = 32, epochs = 10)
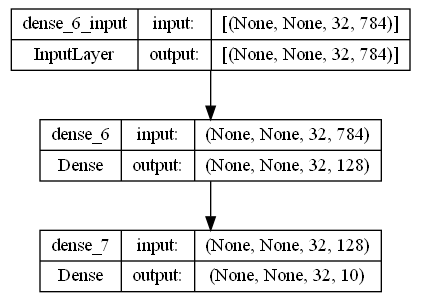
This is how our model looks like
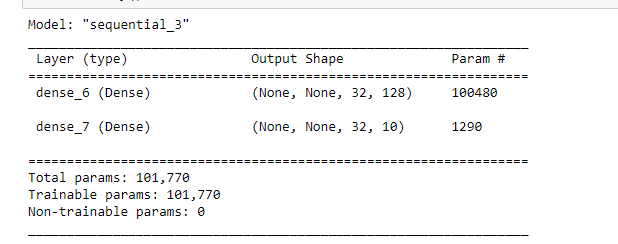
Model Summary
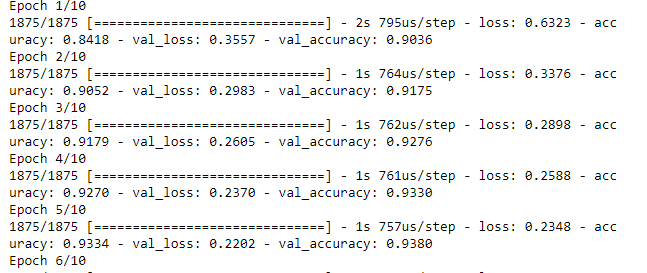
Our Model is getting trained

Now, Comes the moment of truth how well does your model perform ?

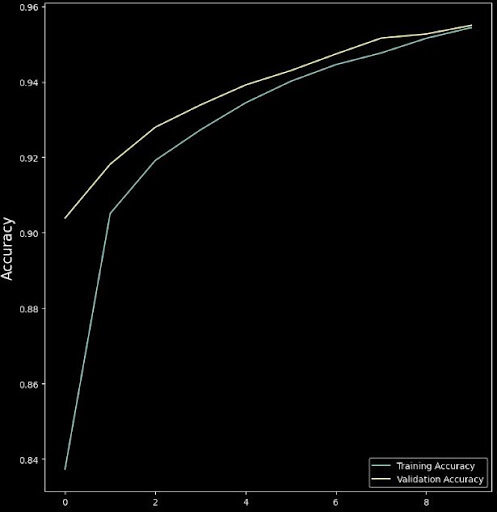
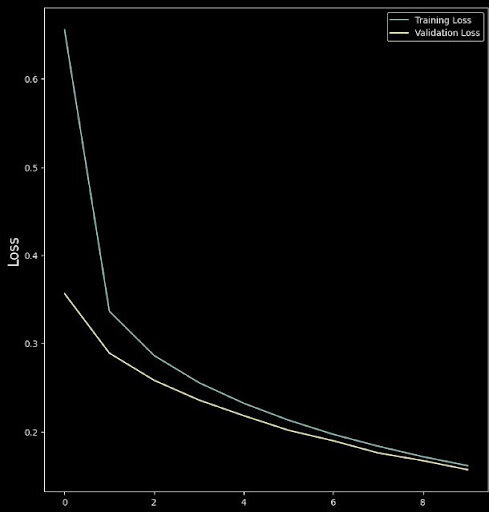


So how does training work actually ?
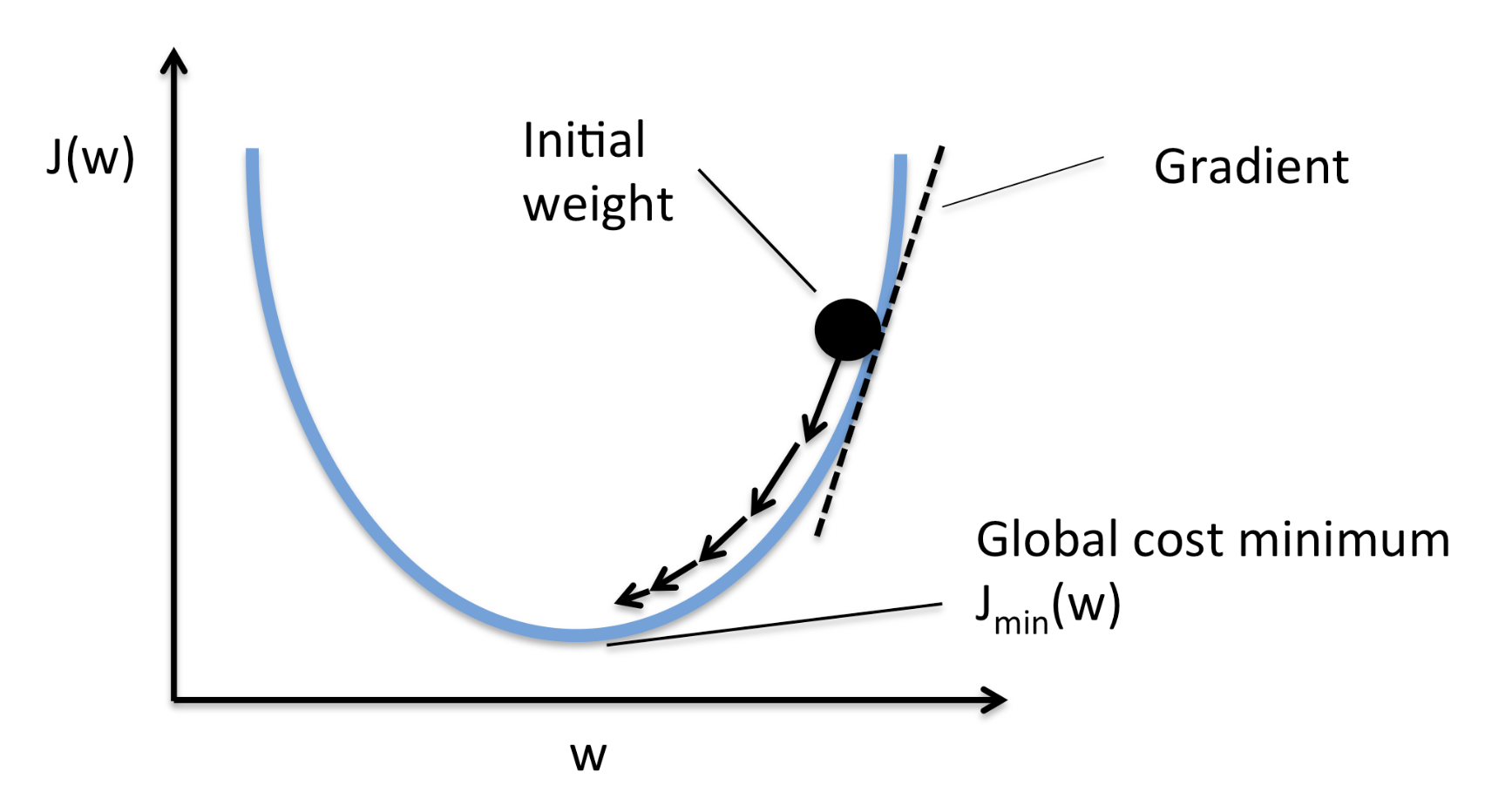
- Weights refer to connection managements between two basic units within a neural network.
- To train these units to move forward in the network, weights of unit signals must be adjusted. These connections will then be tested, reversed through the network to identify errors, and repeated to produce the optimal results.
- Biases like weights, biases will also be adjusted through reversing the neural network flow in order to produce the most accurate end result.
- It helps the models to shift the activation function towards the positive or negative side.
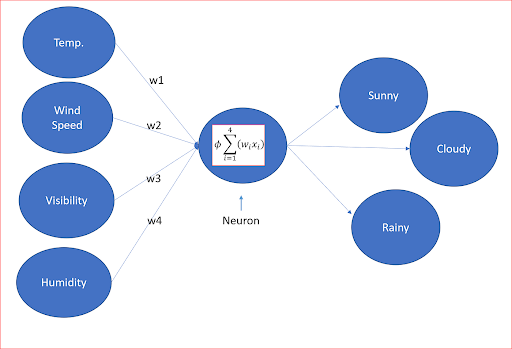
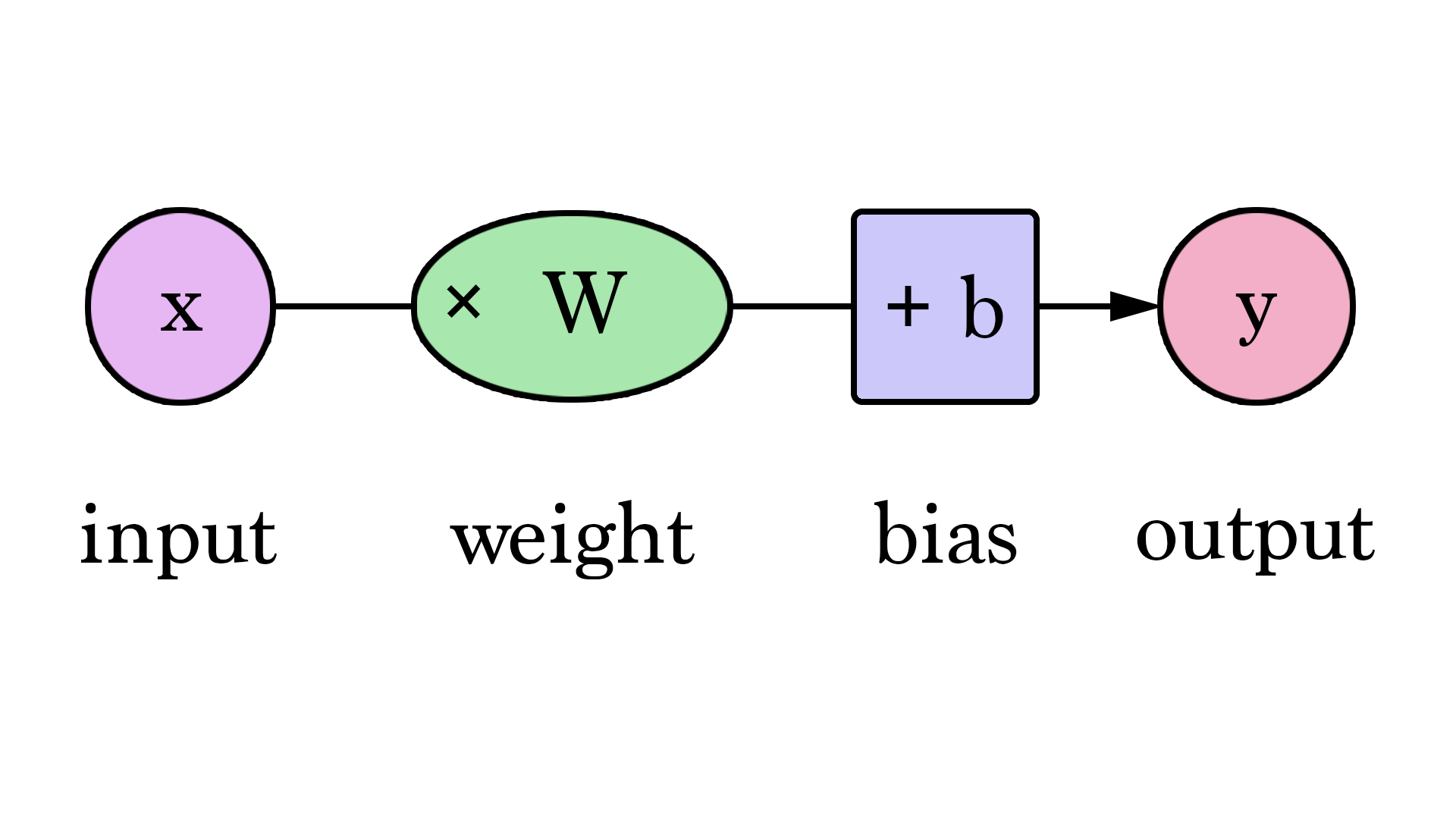
Basically........

Activation Function
- An Activation Function decides whether a neuron should be activated or not.
- This means that it will decide whether the neuron's input to the network is important or not in the process of prediction using simpler mathematical operations.
The most important function is it adds Non-Linearity
Boom!

deck
By atomxgdsc
deck
- 20