Interpreting SARS-CoV-2 evolution
Jesse Bloom
Fred Hutch Cancer Center / HHMI
These slides at https://slides.com/jbloom/sars2evol

The Faroe Islands


"Measles had not prevailed on the Faroes since 1781, then it broke out early in April 1846."
"Of the 7782 inhabitants, about 6000 were taken with measles."
"Of the many aged people still living in the Faroes who had measles in 1781, not one was attacked the second time."
Panum was describing immune memory, which provides lifelong protection from measles


What was reason for thinking coronavirus immunity would not be affected by viral mutations?
Coronaviruses have lower mutation rate than other RNA viruses
Coronaviruses are only RNA viruses with proofreading activity in their polymerase, and so have ~5- to 10-fold lower mutation rate than influenza virus
The average single-nucleotide mutation to SARS-CoV-2 had occurred >10,000 independent times in human-transmitted SARS-CoV-2 by third year of the pandemic.
But evolution of SARS-CoV-2 is not mutation-limited
Evolution is not just mutation: also involves selection on phenotypic effects of mutations

My group studies virus evolution at the level of phenotype
... atg ttt gtt ttt ctt gtt ...
... atg ttt ctt ttt ctt gtt ...
... atg ttt gtt tat ctt gtt ...
17,052,049 SARS-CoV-2 sequences are currently available
But what do they mean?
CoV-229E causes common colds and has been circulating in humans for a long time.
How do human coronaviruses evolve?
Evolution of CoV-229E spike

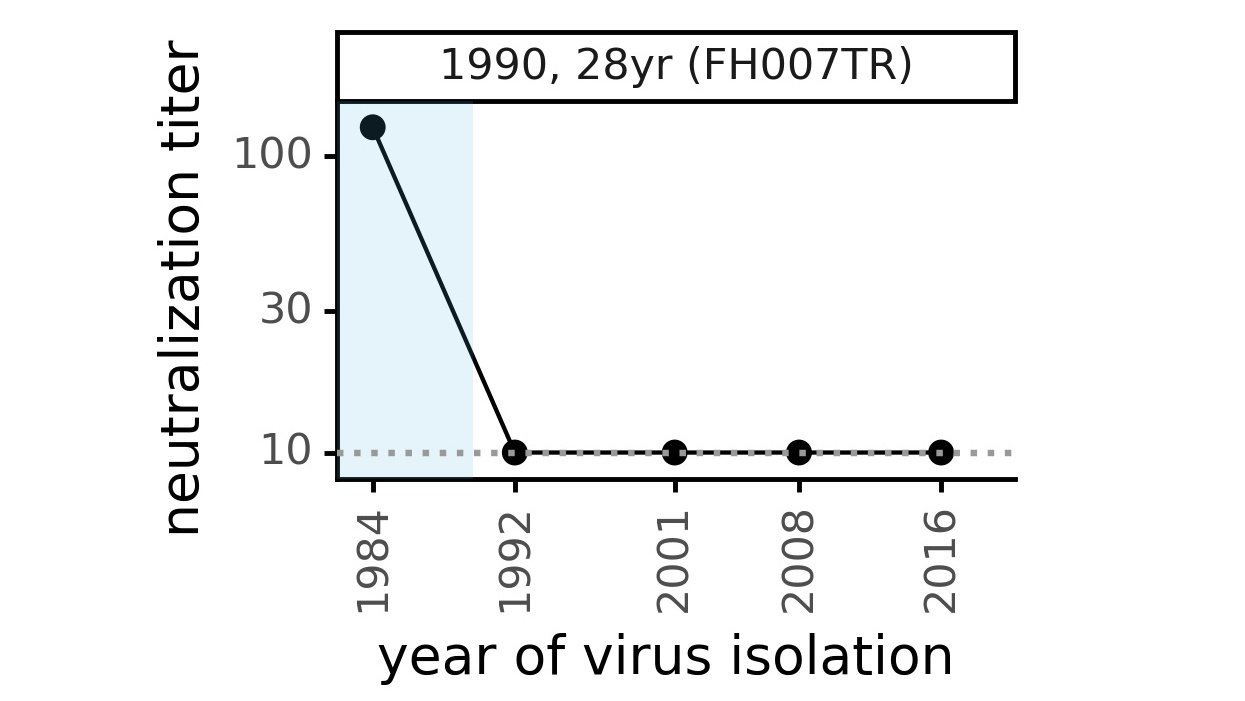
We experimentally generated CoV-229E spikes at ~8 year intervals to study in the lab:
- 1984
- 1992
- 2001
- 2008
- 2016
Evolution of CoV-229E spike erodes neutralization by human serum antibodies

Ideally vaccines would elicit evolution-resistant antibodies (like those made by person at right) rather than evolution-sensitive antibodies (like those made by person at left)
Evolution erodes neutralization by sera from different people at different rates
We now know SARS-CoV-2 evolves to erode neutralizing antibodies, just like CoV-229E
neutralization from original COVID-19 vaccine
Original vaccine induced high neutralizing antibody titers against early viral strains
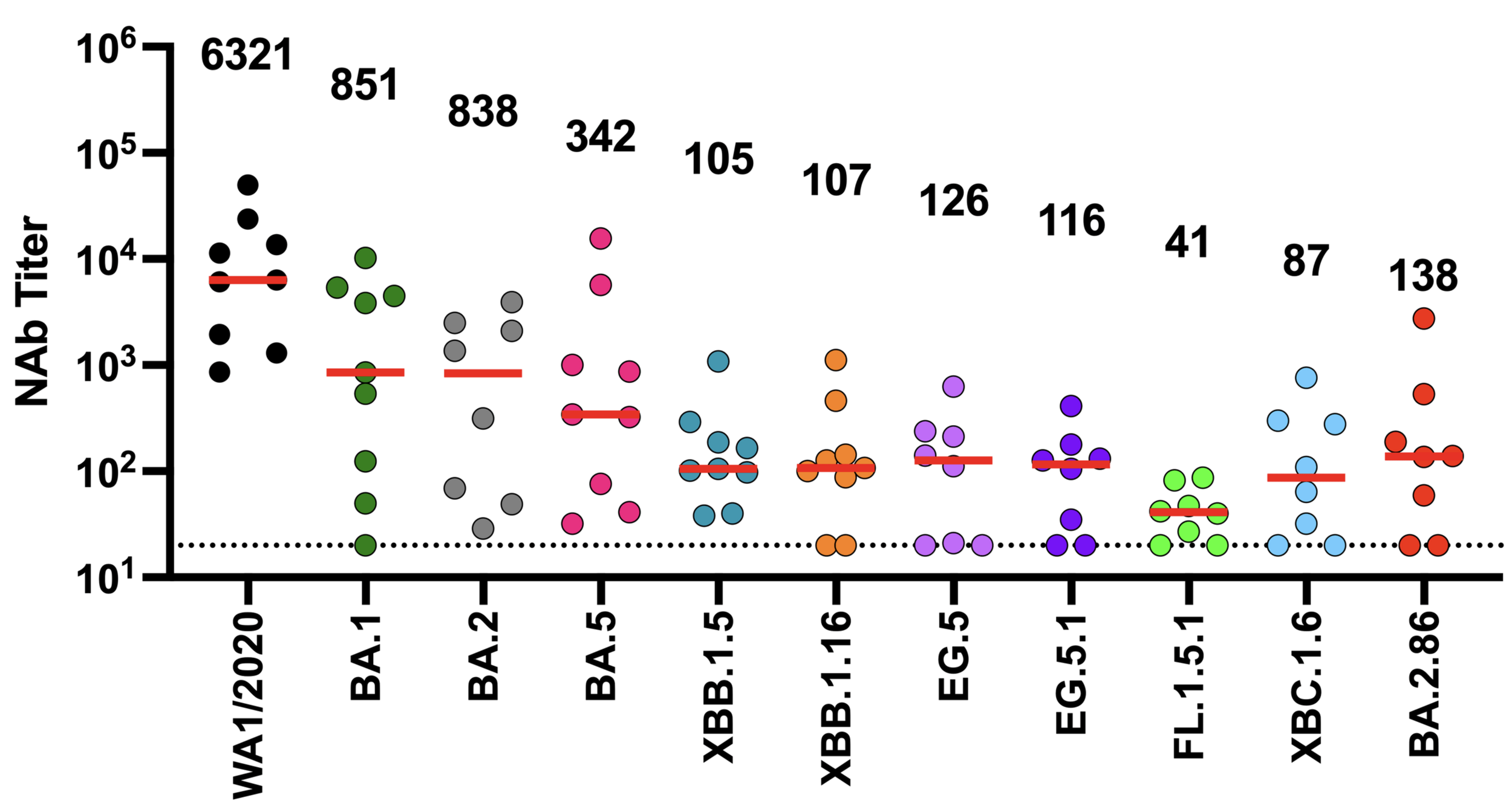
We now know SARS-CoV-2 evolves to erode neutralizing antibodies, just like CoV-229E
newer viral variants
neutralization from original COVID-19 vaccine

New variants (with more antibody escape) replace old ones in SARS-CoV-2 evolution
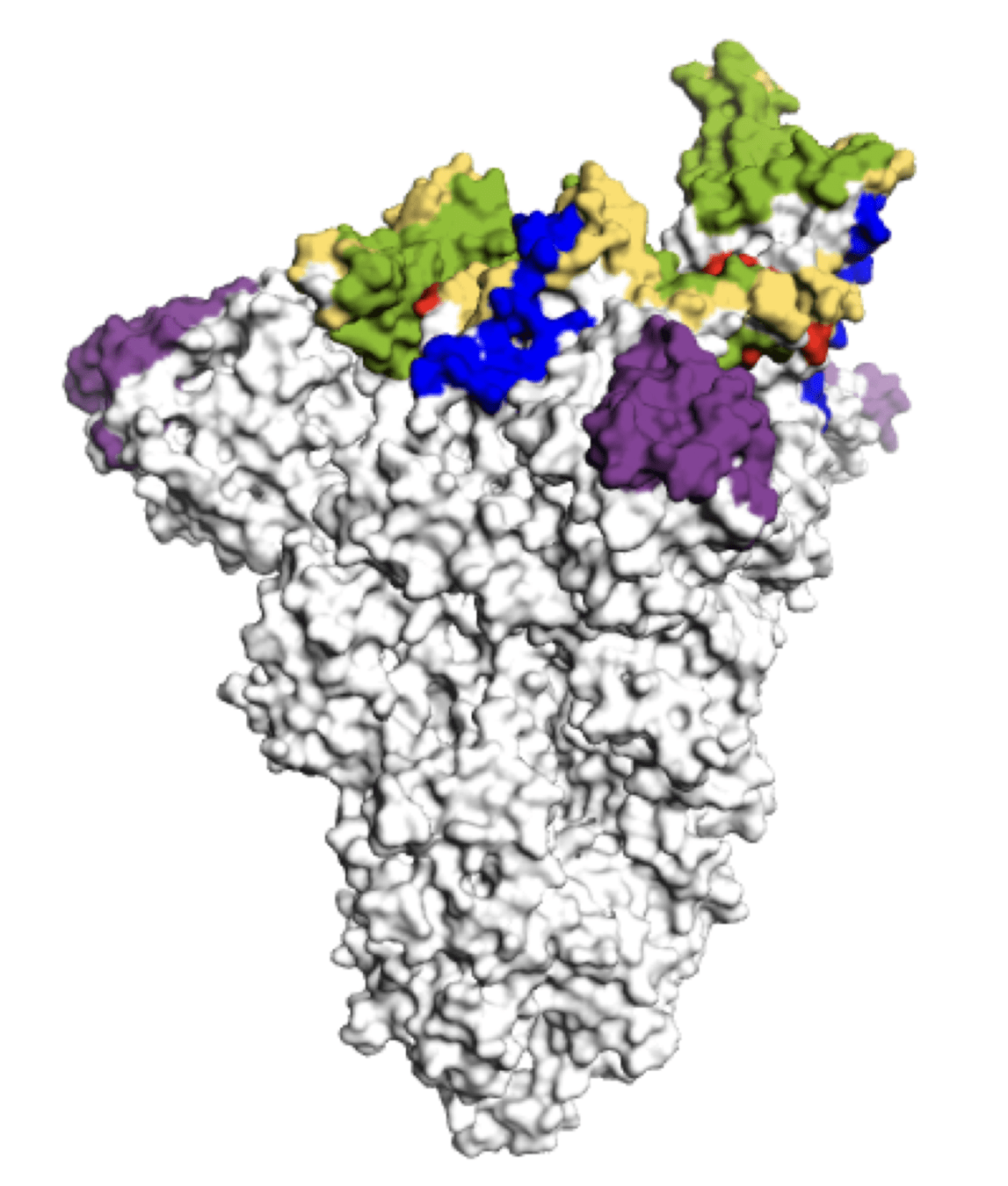
Main regions where neutralizing antibodies bind
Molecular basis of this antigenic evolution?

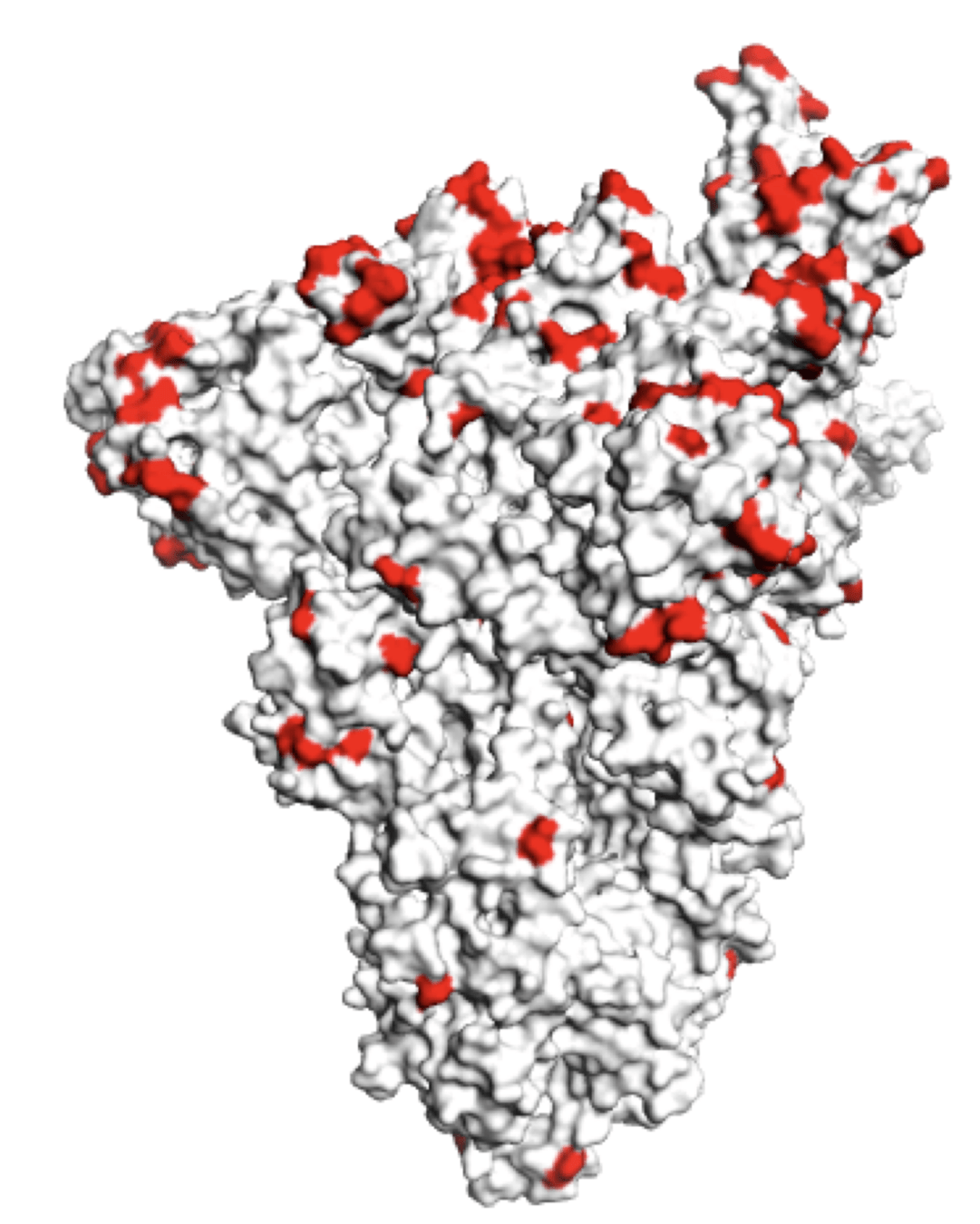

Molecular basis of this antigenic evolution?Mutations where antibodies bind
Main regions where neutralizing antibodies bind
Sites of mutations in recent (BA.2.86) SARS-CoV-2 strain relative to early 2020 strain
Can we predict evolutionary success of new viral variants?
SARS-CoV-2's spike binds receptor and mediates viral entry
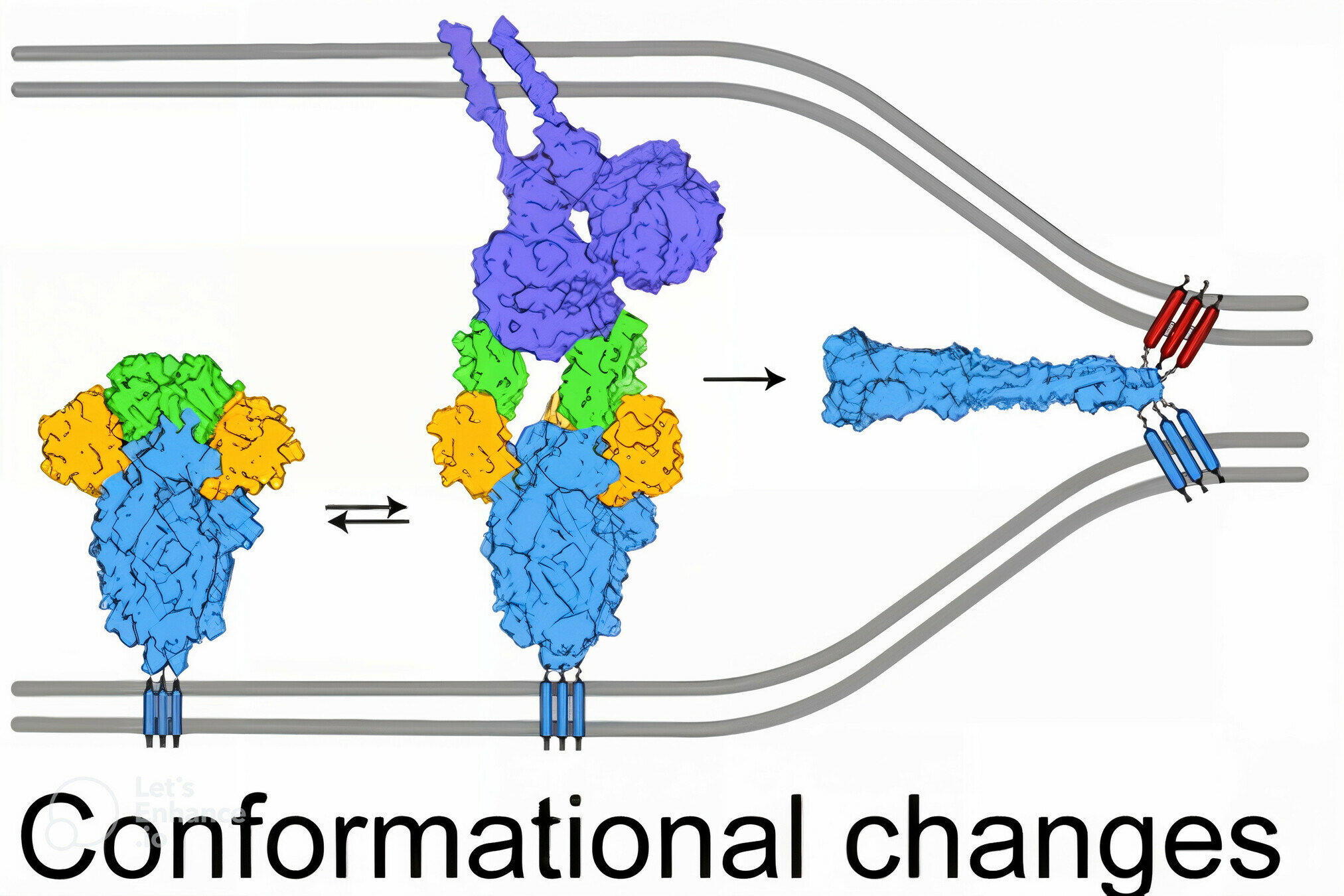
viral membrane
cell membrane
spike
spike conformational change
Image adapted from here
ACE2

antibody
Image adapted from here
SARS-CoV-2's spike binds receptor and mediates viral entry
Deep mutational scanning to measure effects of mutations
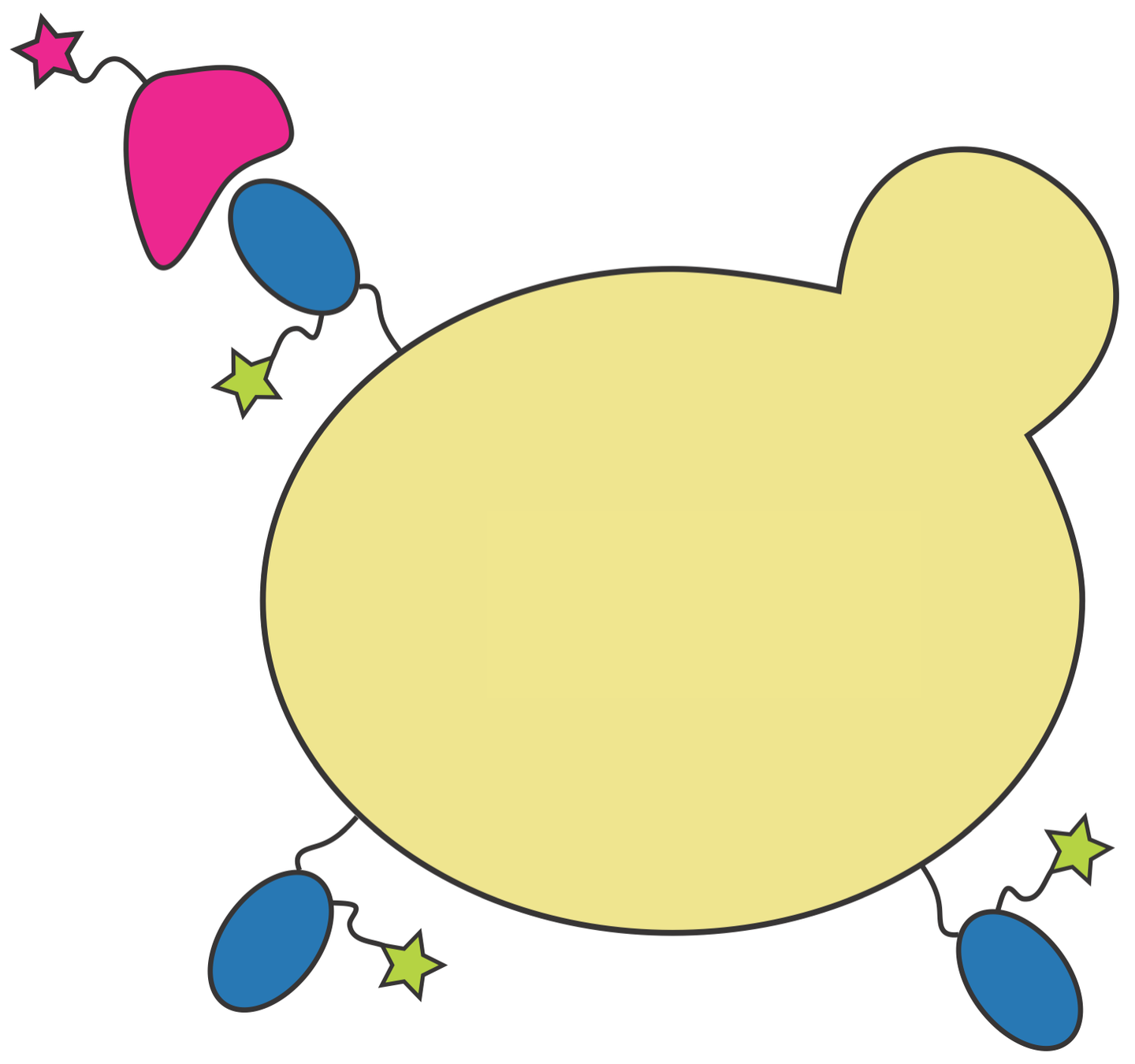
RBD
fluorescent ACE2
yeast
fluorescent tag on RBD
Yeast display of spike receptor-binding domain (RBD) to measure ACE2 binding

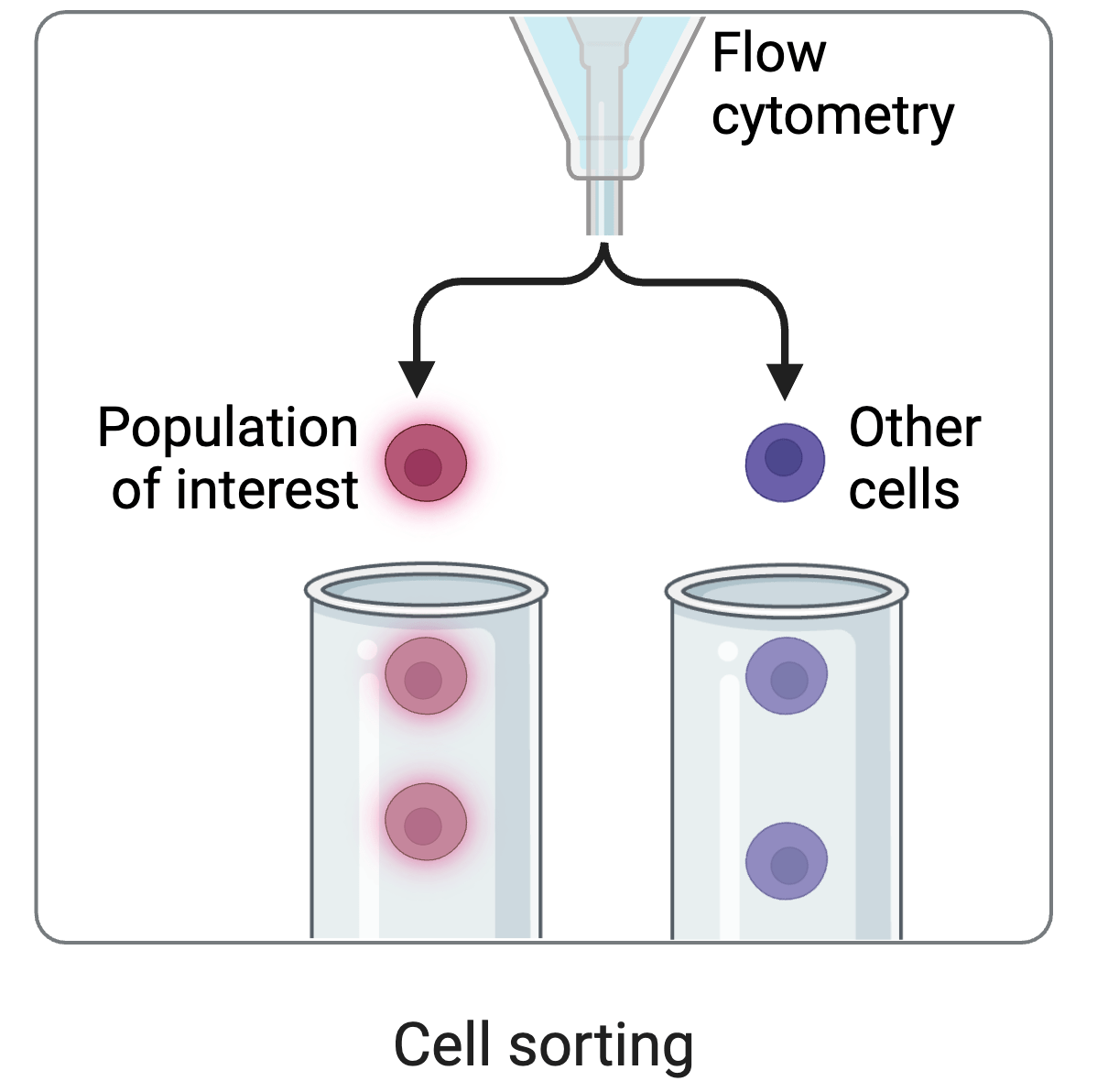
cell sorting
Deep mutational scanning: selections on libraries of mutants, read out by sequencing
Experiments identified N501Y as a mutation that increases ACE2 binding
RBD
fluorescently labeled antibody
yeast
fluorescent tag on RBD
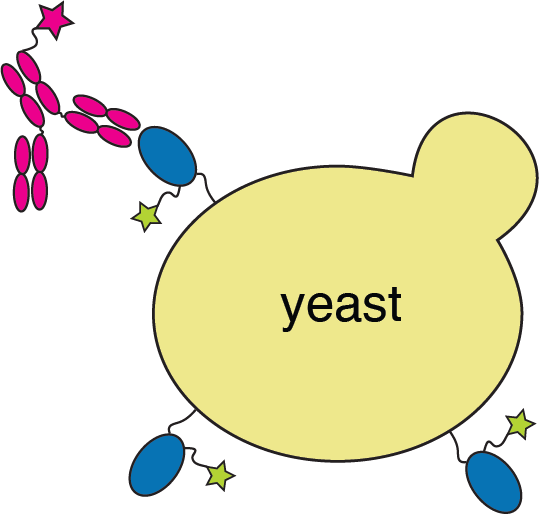
Yeast display to measure how all RBD mutations escape antibody binding

site in RBD
antibody escape
Experiments identified mutations at E484 as causing most antibody escape
484
These anecdotes suggest experiments can identify mutations subsequently selected by evolution

Yeast display only measures binding, which is just part of spike's biological function


cell sorting
Viral infection is more biologically relevant measure of mutation effects

However, we are cognizant of biosafety concerns of mutating actual virus

actual SARS-CoV-2 virion: pathogen capable of spread in humans
pseudotyped lentiviral particle: not a pathogen, cannot spread in humans

actual SARS-CoV-2 virion: pathogen capable of spread in humans
pseudotyped lentiviral particle: not a pathogen, cannot spread in humans
Therefore we use pseudoviruses rather than actual replicative SARS-CoV-2
Pseudoviruses are modified viruses that can only undergo single round of infection


We need to link phenotype (spike mutant) and genotype (sequence encoded by virus)
To link genotype to phenotype, we encode spike in viral genome with barcode
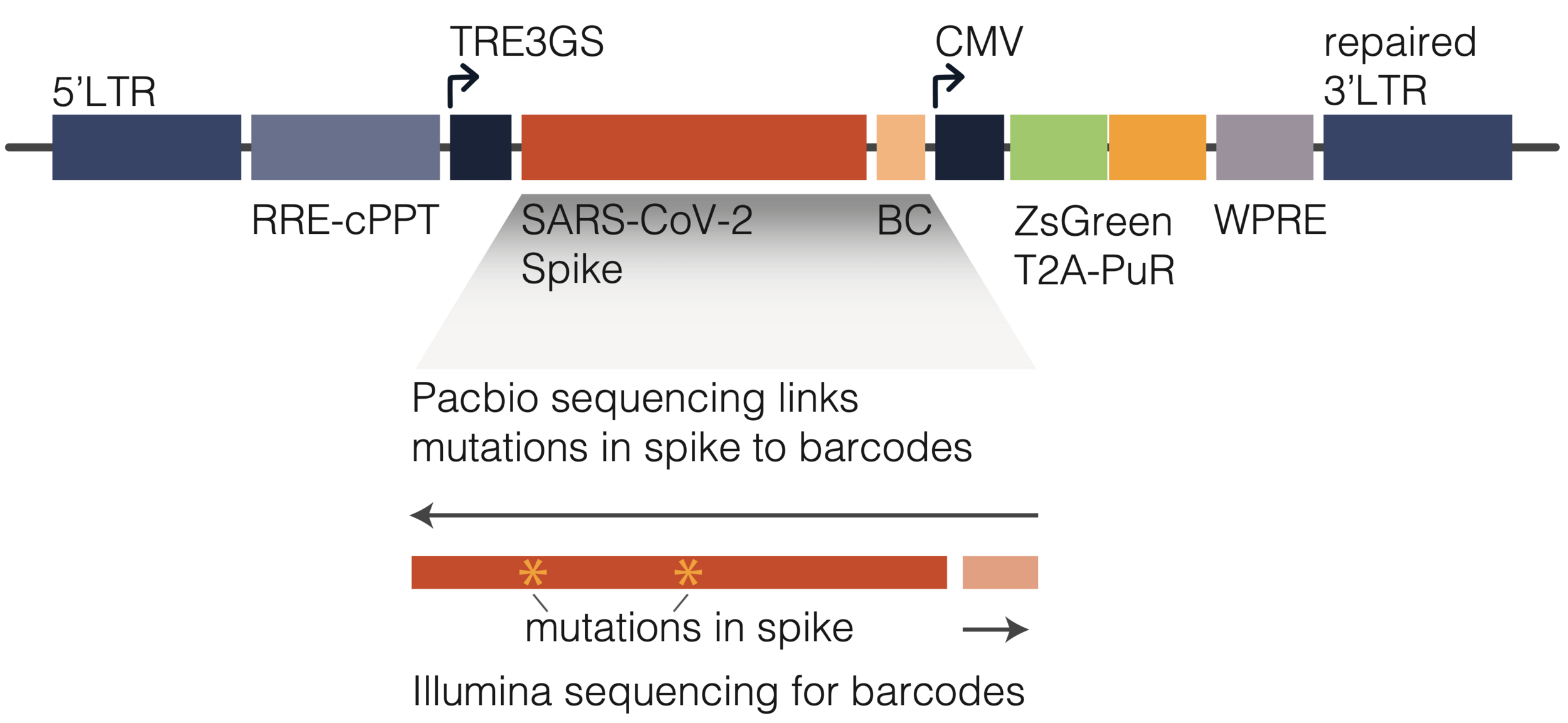
We then create genotype-phenotype linked libraries by two-step process
Result is library of spike mutant pseudoviruses with identifying barcodes
- Captures full cell-entry function of spike
- Each mutant identified by short barcode
- Pseudoviruses safe at biosafety-level 2
- Broadly applicable to viral entry proteins
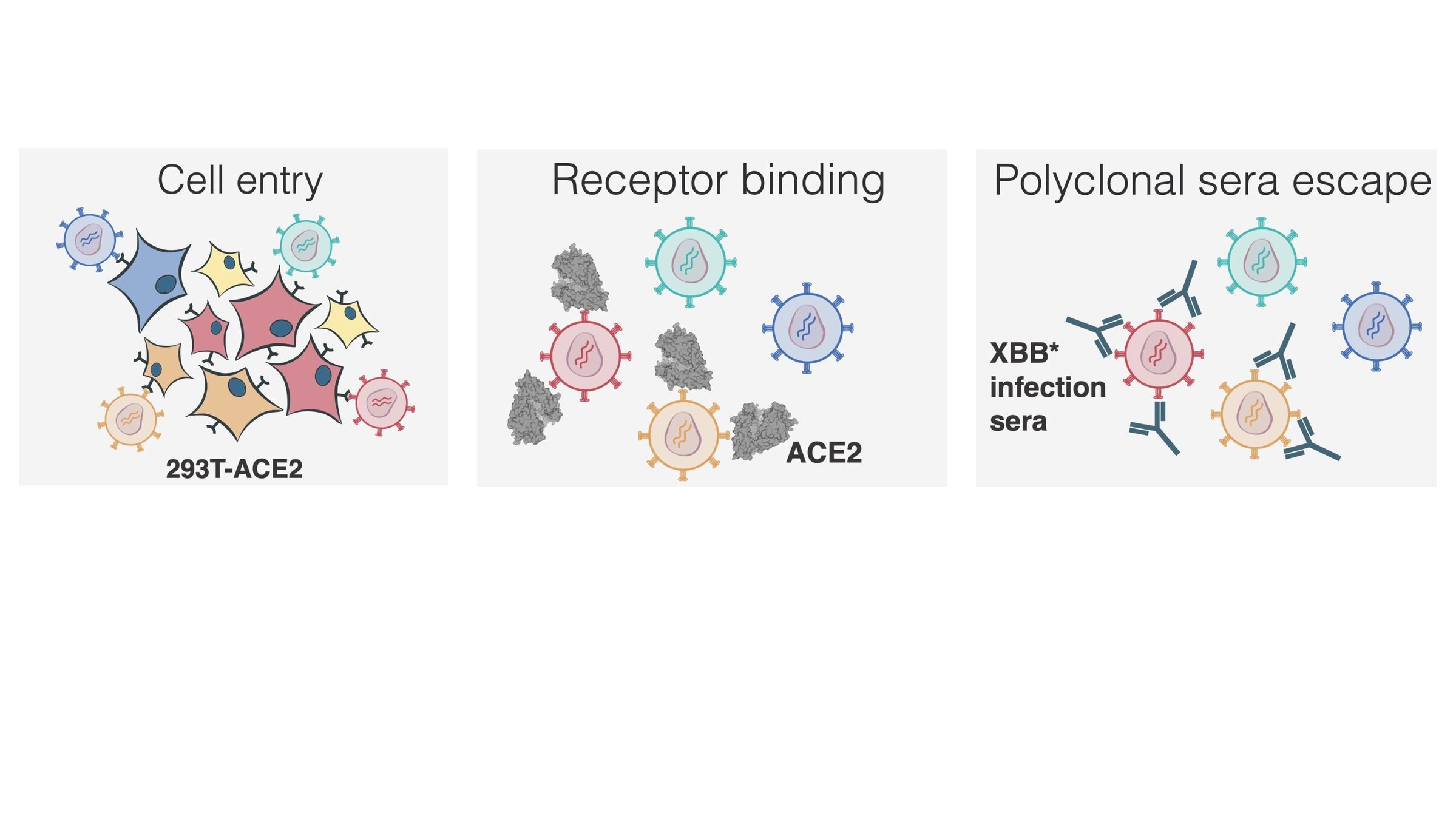
Measured how spike mutations affect three molecular phenotypes

Measured how spike mutations affect three molecular phenotypes

Measured how spike mutations affect three molecular phenotypes
Neutralization by soluble ACE2 is proportional to ACE2 binding affinity
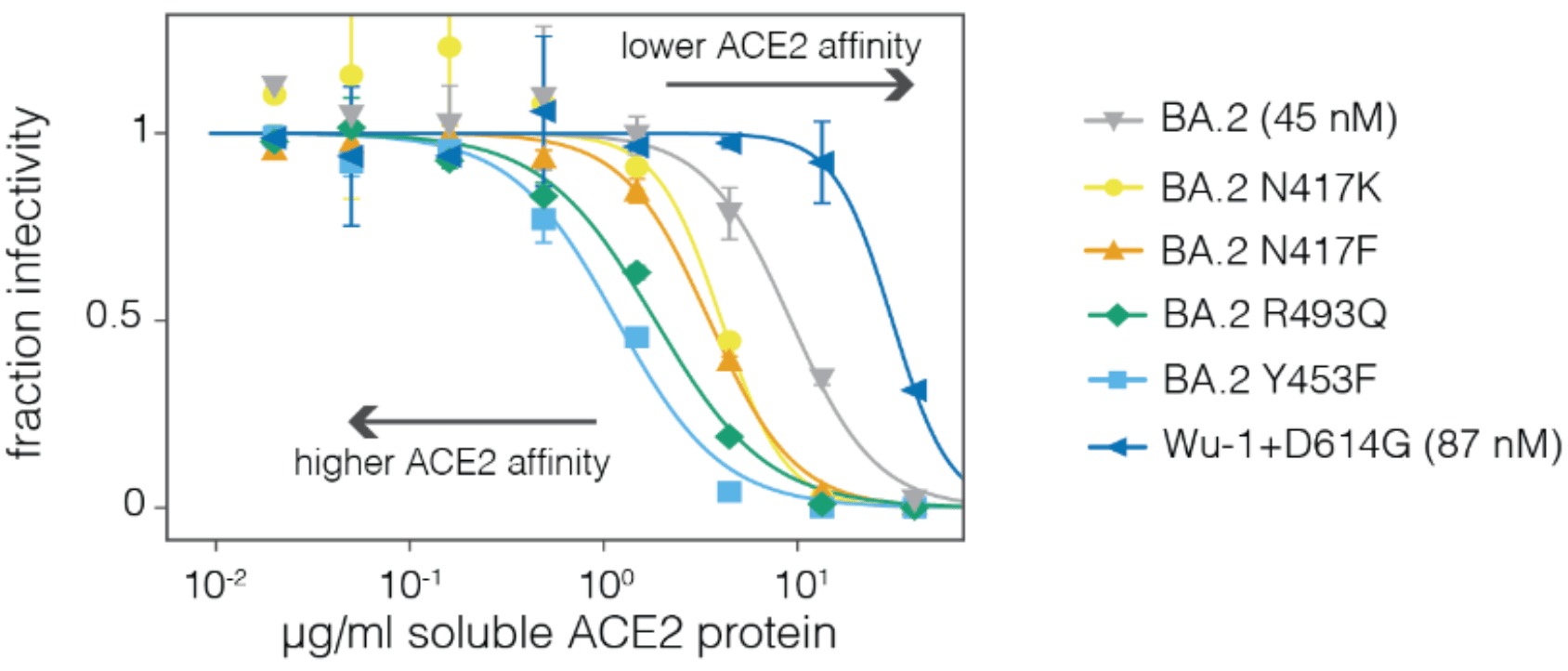
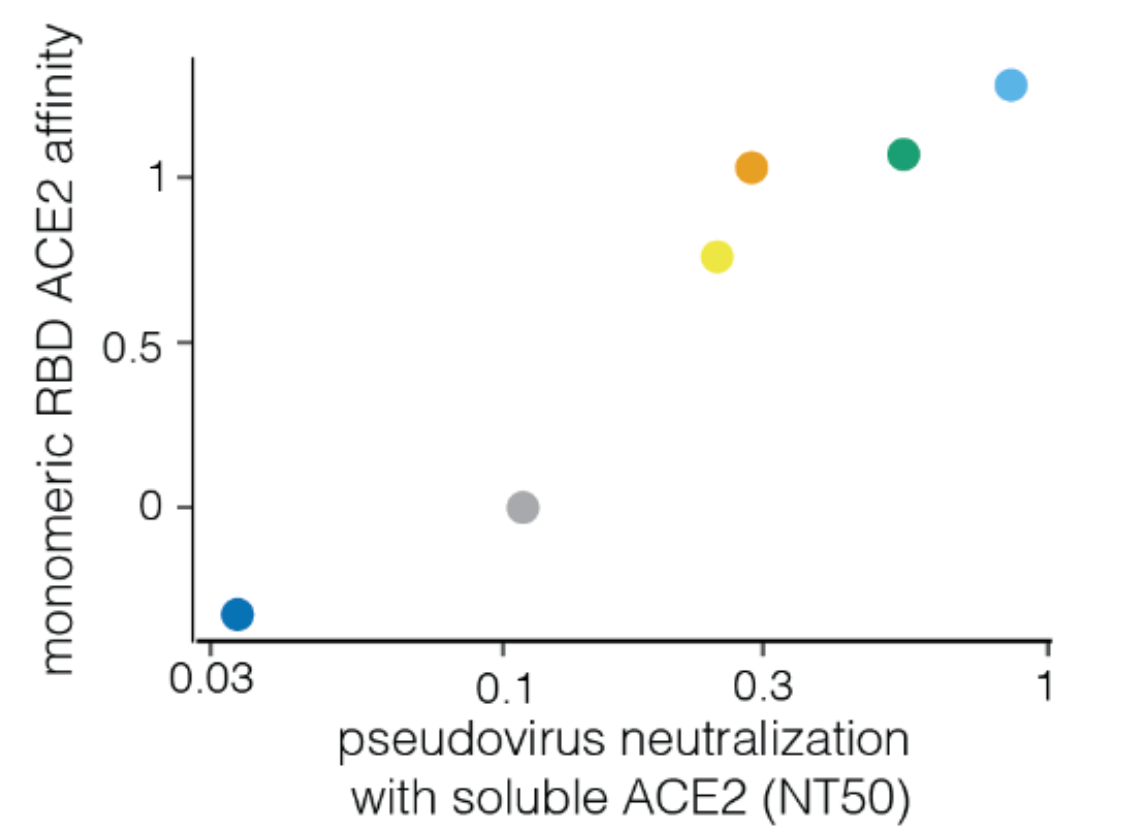

Measured how spike mutations affect three molecular phenotypes
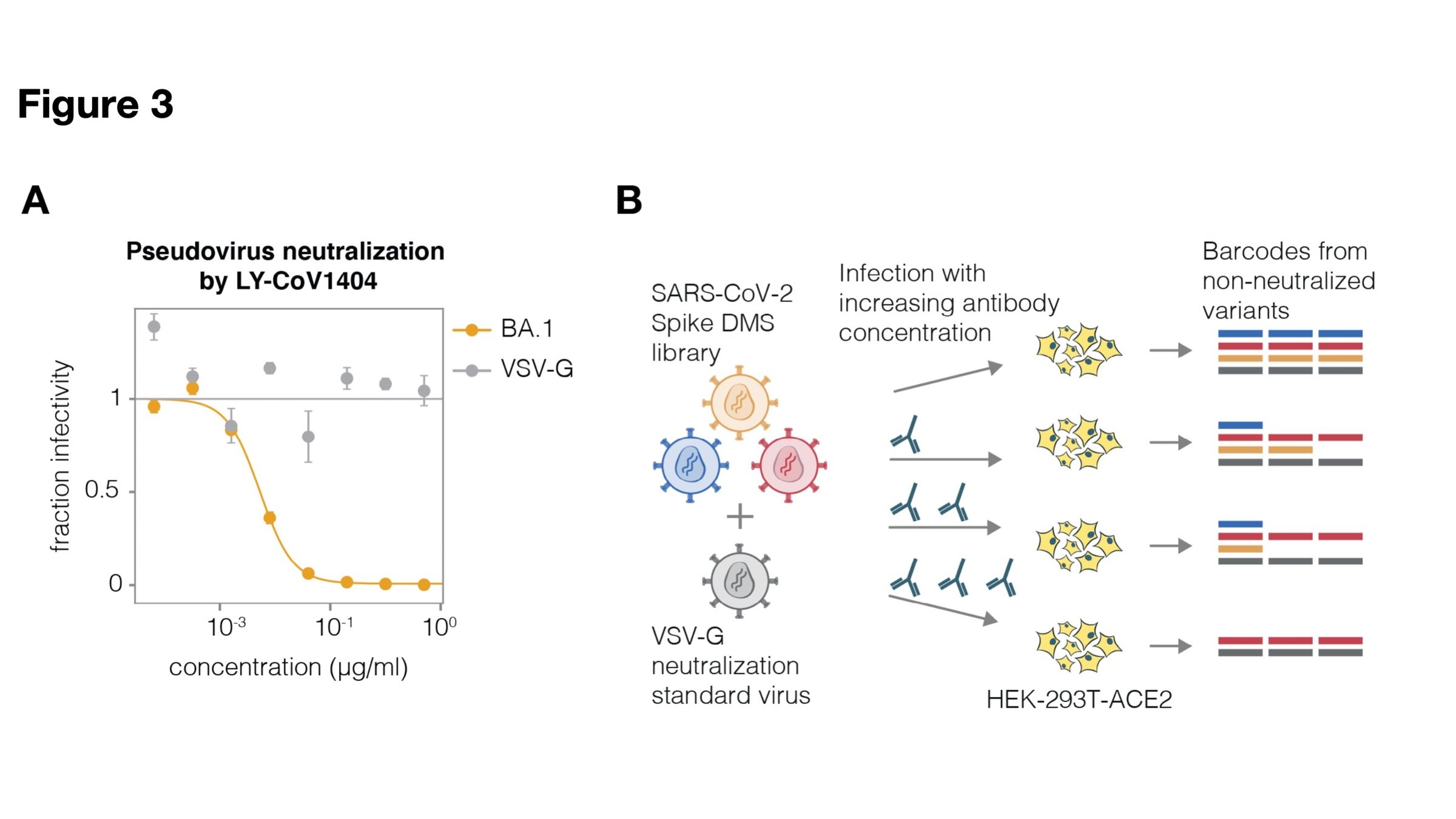
Full workflow to measure effects of mutations on antibody neutralization
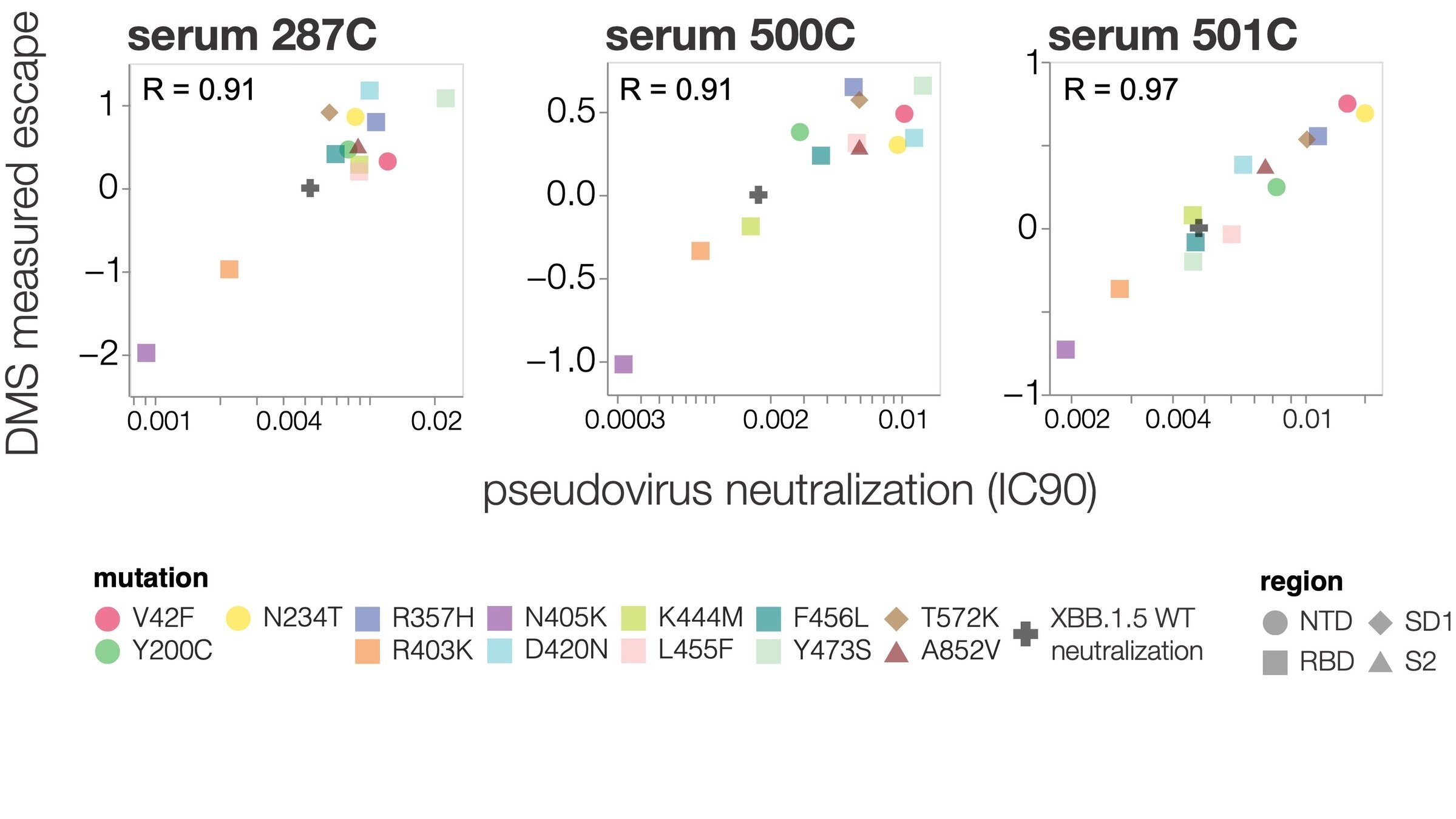
Deep mutational scanning correlates well with traditional neutralization assays
How do these experimental measurements relate to actual evolution?
Estimating variant fitness (multinomial logistic regression)
With Trevor Bedford & Ben Murrell
With Trevor Bedford & Ben Murrell
Estimating variant fitness (multinomial logistic regression)
We analyze changes in clade growth rather than raw clade growth
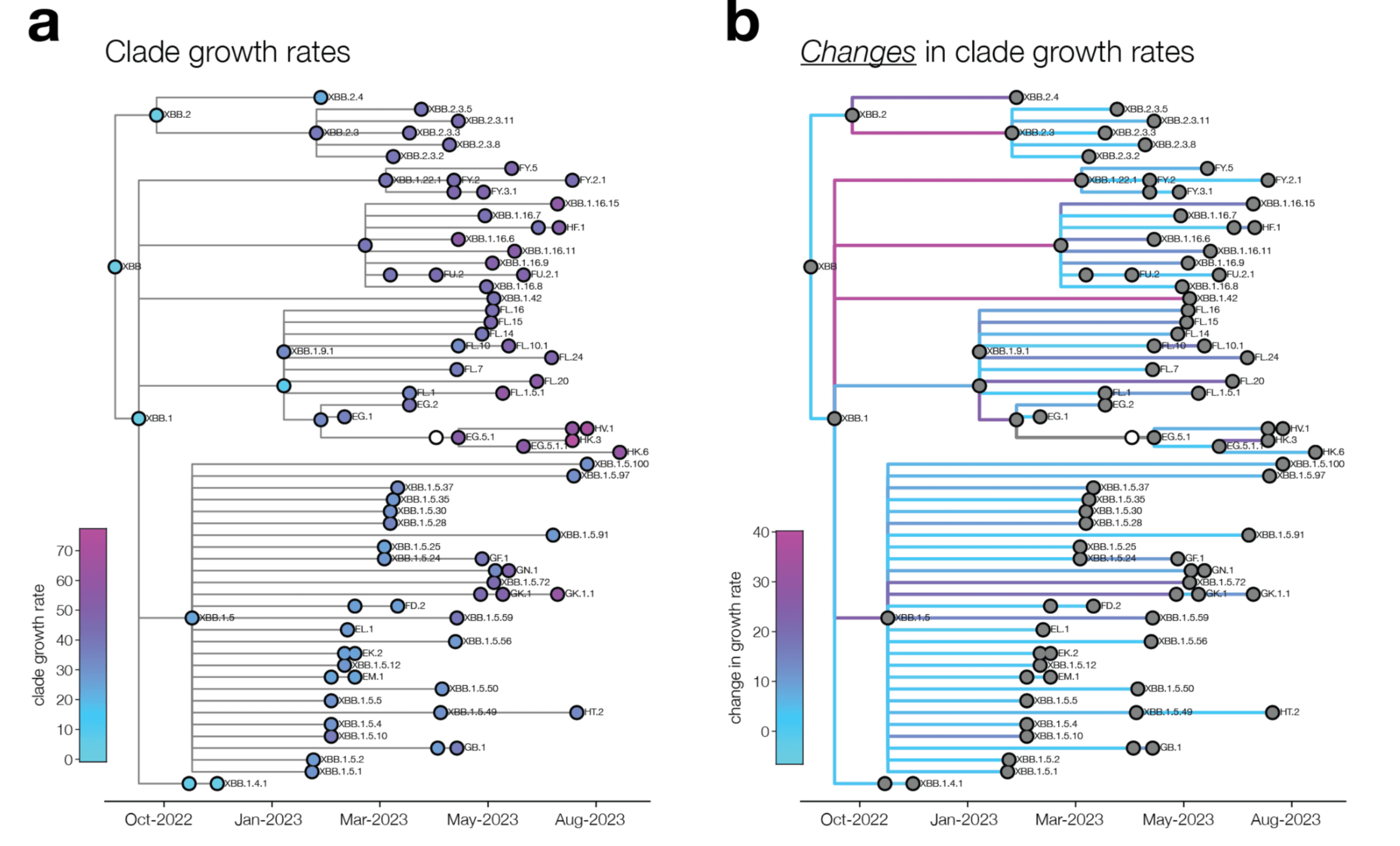
change in clade growth
clade growth
Deep mutational scanning measurements correlate with SARS-CoV-2 variant fitness
Combining phenotypes offers best predictions (because mutations can involve tradeoffs)
We can explain ~55% of the variance in growth of different clades, with largest fraction of variance uniquely explained by sera escape.
Can partially predict outcome of real-world evolutionary competition from experiments!
But human population in which SARS-CoV-2 evolves is changing...
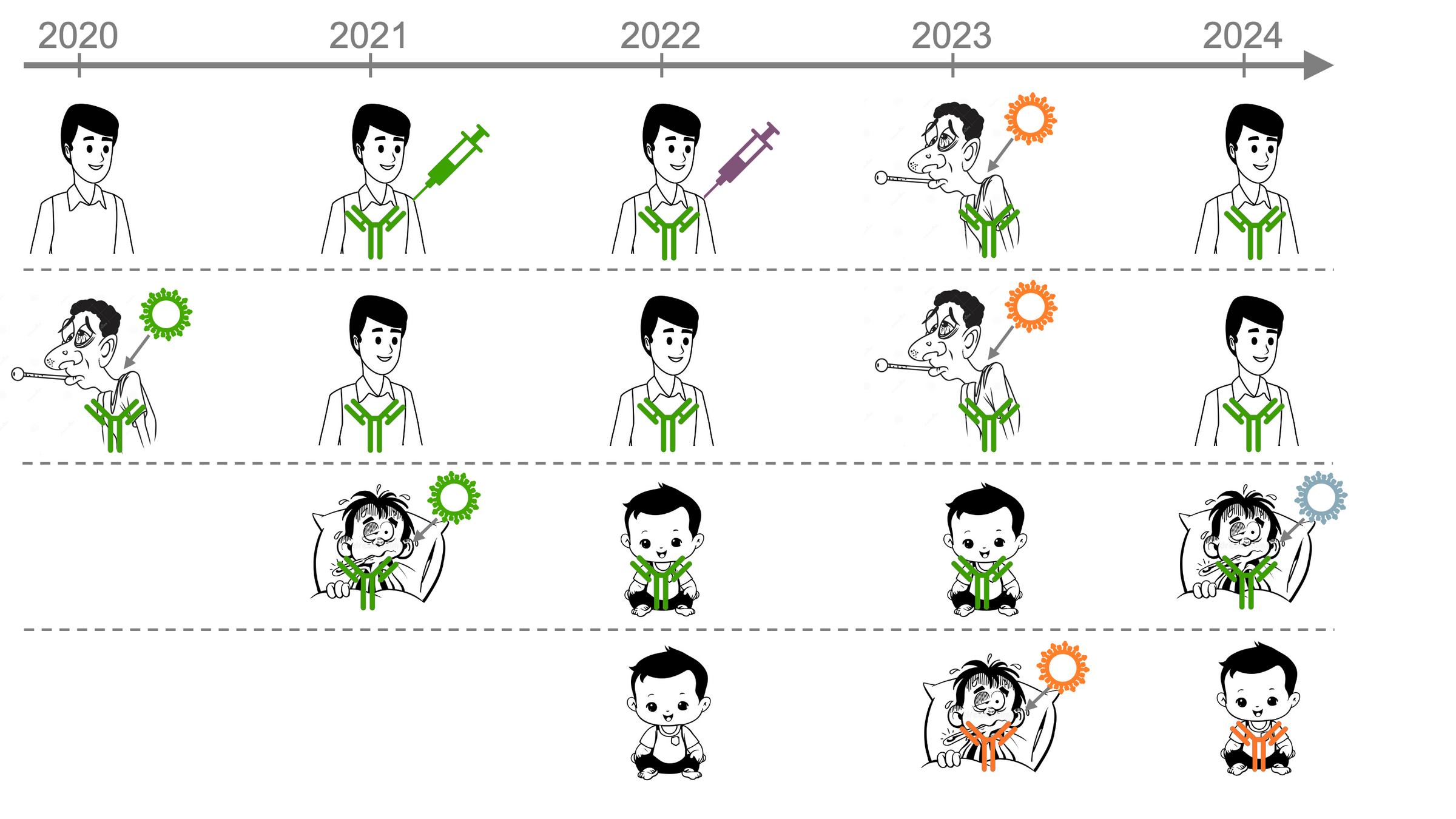
Initially, most people were exposed to early strain, imprinting antibody response ( )
First exposed to early strain in original vaccine
First infected by an early strain (pre-Omicron)

Imprinting to early strain continues to shape antibody response after later exposures

But antibody response of infants is imprinted by more recent strain
Imprinted by recent strain

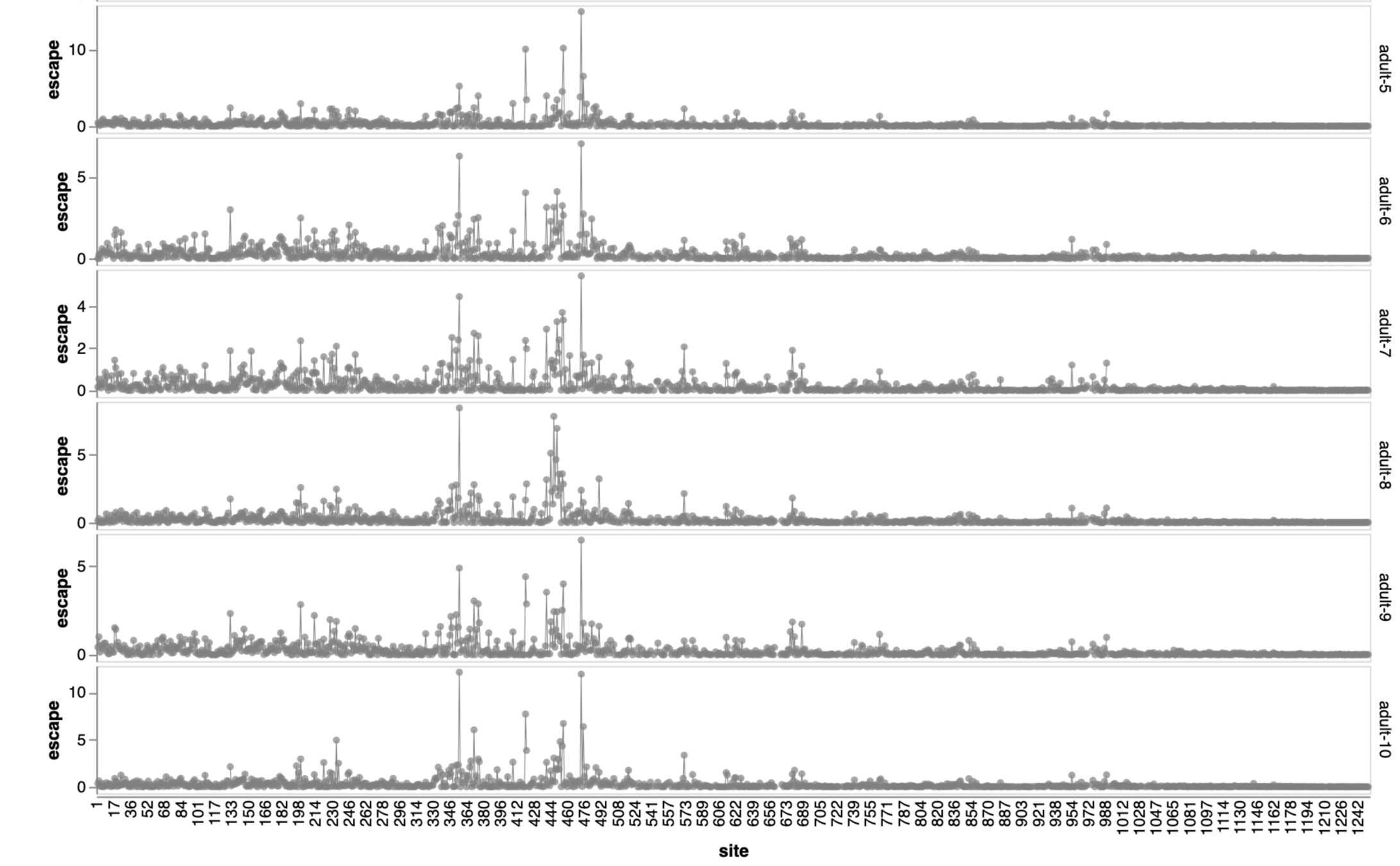
We measured which spike mutations erode neutralization by antibodies from people imprinted with different strains

Adults vaccinated with original strain followed by various exposures
Adult sera from Helen Chu's HAARVI study; infant sera from Mary Staat's IMPRINT cohort
6-12 month infants first infected by XBB*
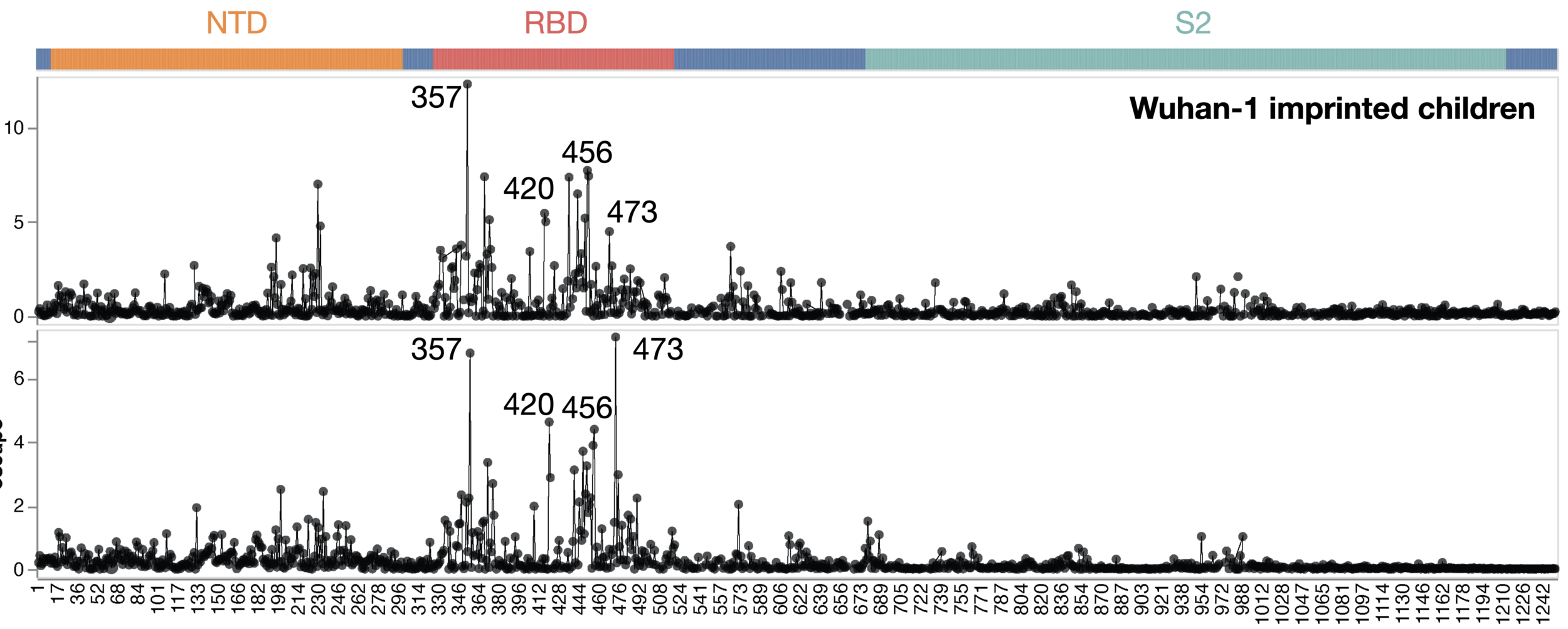
Adult sera have similar escape (mostly in RBD)

site in spike
escape caused by mutations at site
Sites of escape from sera of adults imprinted with original vaccine, then exposed to various infections and vaccinations.
adult 1
adult 2
adult 3
adult 4
adult 5
adult 6

2021
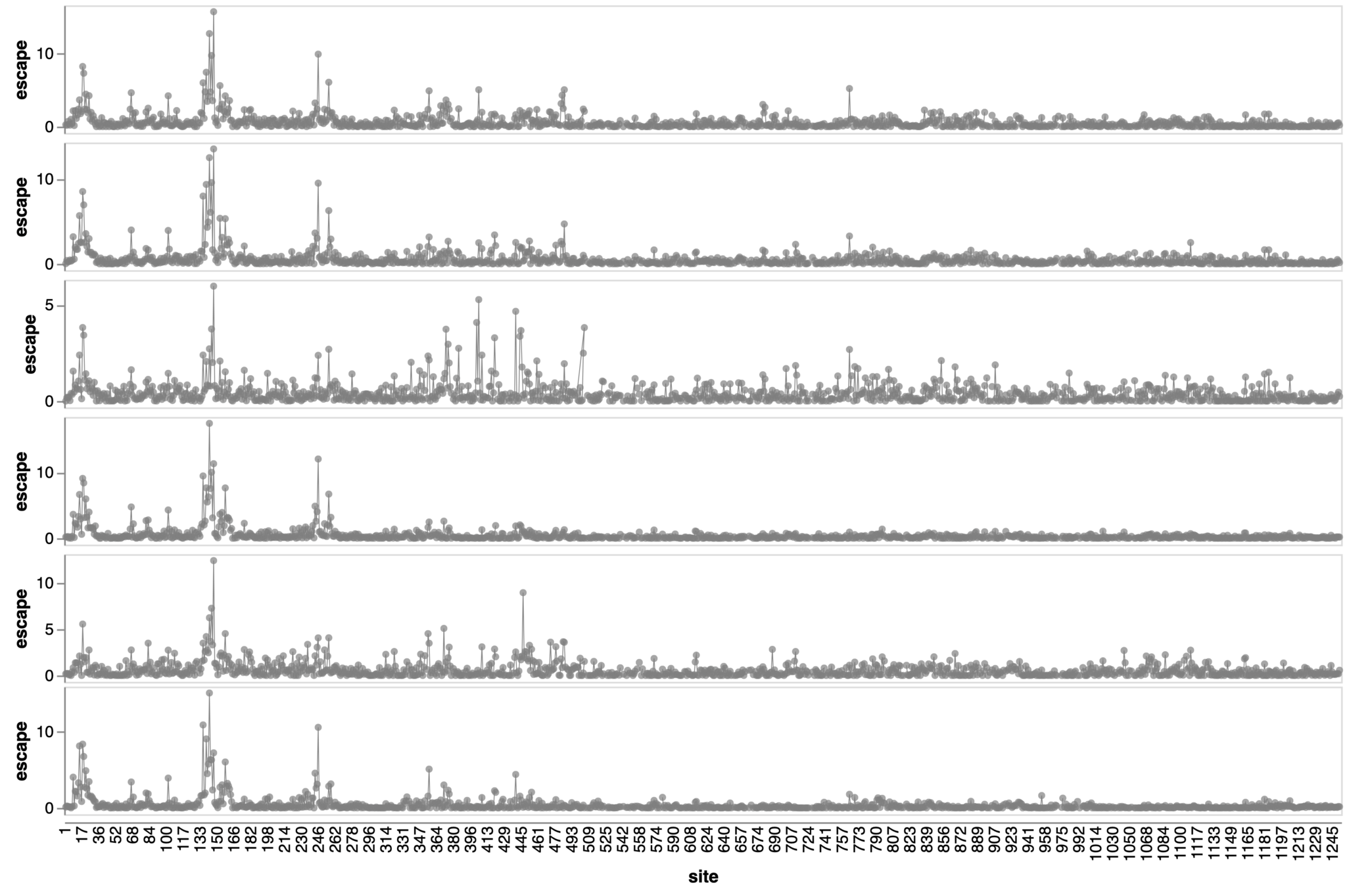
site in spike
escape caused by mutations at site
Sites of escape from infants with only single infection with XBB*
infant 1
infant 2
infant 3
infant 4
infant 5
infant 6



2023
Infant sera have similar escape (mostly in NTD)
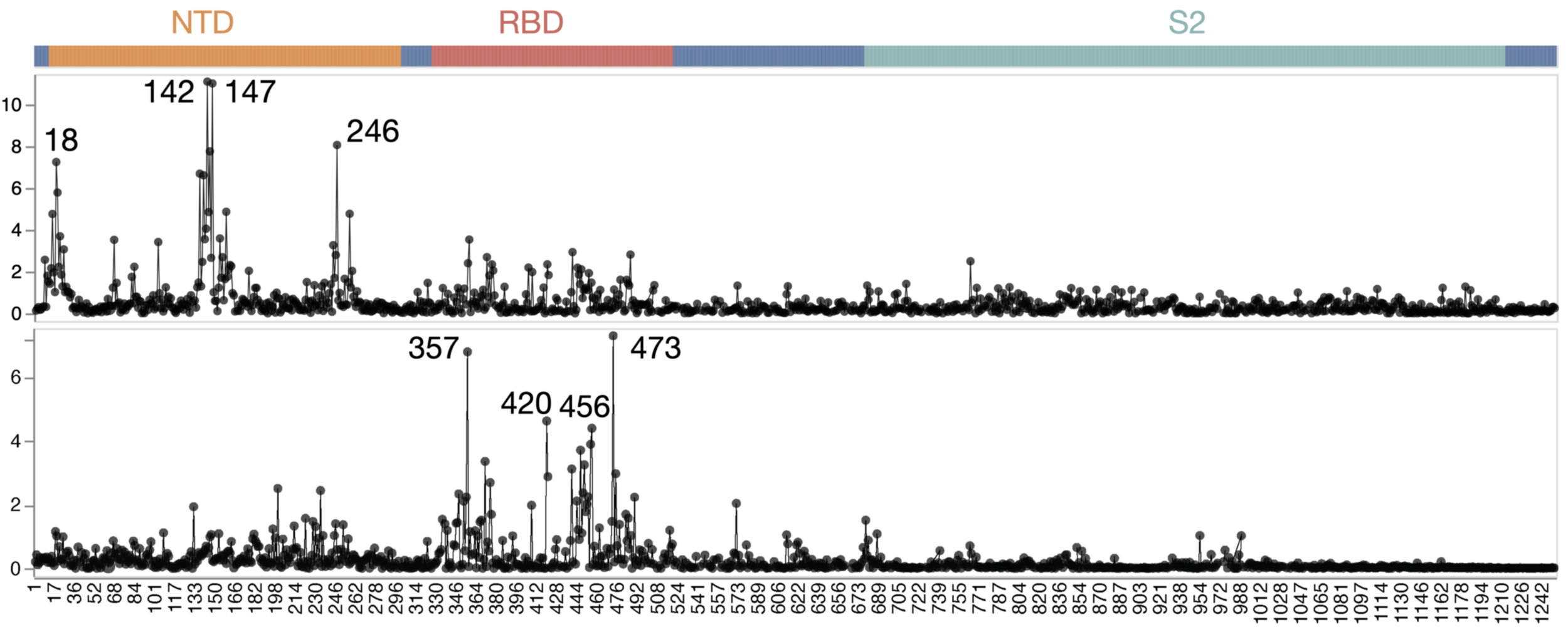
There are dramatic differences in sites of escape from adult versus infant sera


escape caused by mutations at site
site in spike
Average of sera from six infants with only a single infection by XBB* in 2023
Average of sera from ten adults imprinted by original vaccine in 2021
Implications of population immune heterogeneity
How does it impact viral evolution when an antibody-escape mutation only affects the immunity of some individuals in the population?
How do different age groups contribute to driving viral evolution?
How much does person-to-person variation in impacts of viral mutations shape disease susceptibility?
Important questions related to population immune heterogeneity
How does it impact viral evolution when an antibody-escape mutation only affects the immunity of some individuals in the population?
Which are the key age groups for driving viral evolution?
How much does person-to-person variation in impacts of viral mutations shape disease susceptibility?
We recently developed new method to measure neutralization of ~100 of influenza strains by 100s of human sera
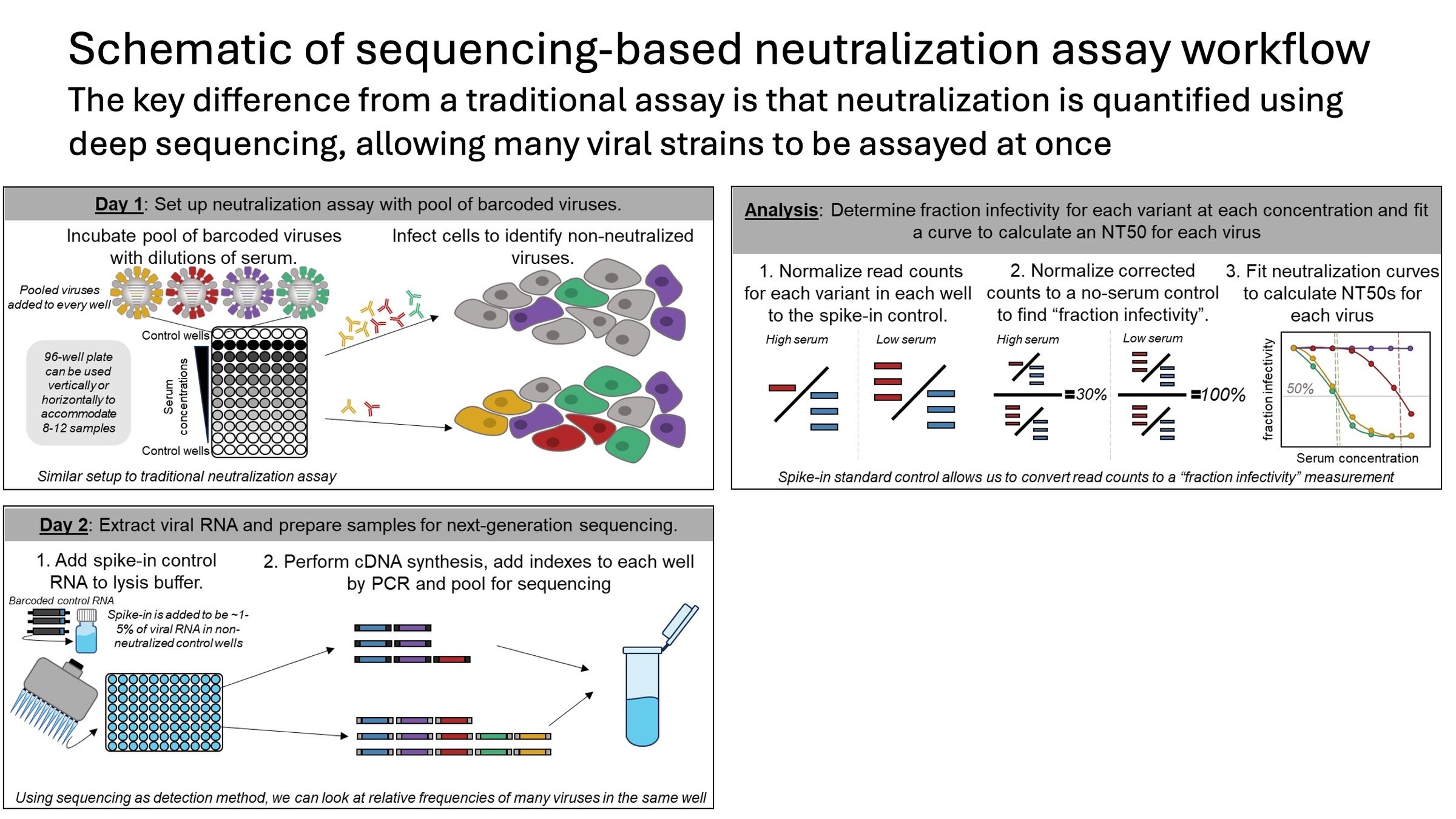
Sequencing-based neutralization assays
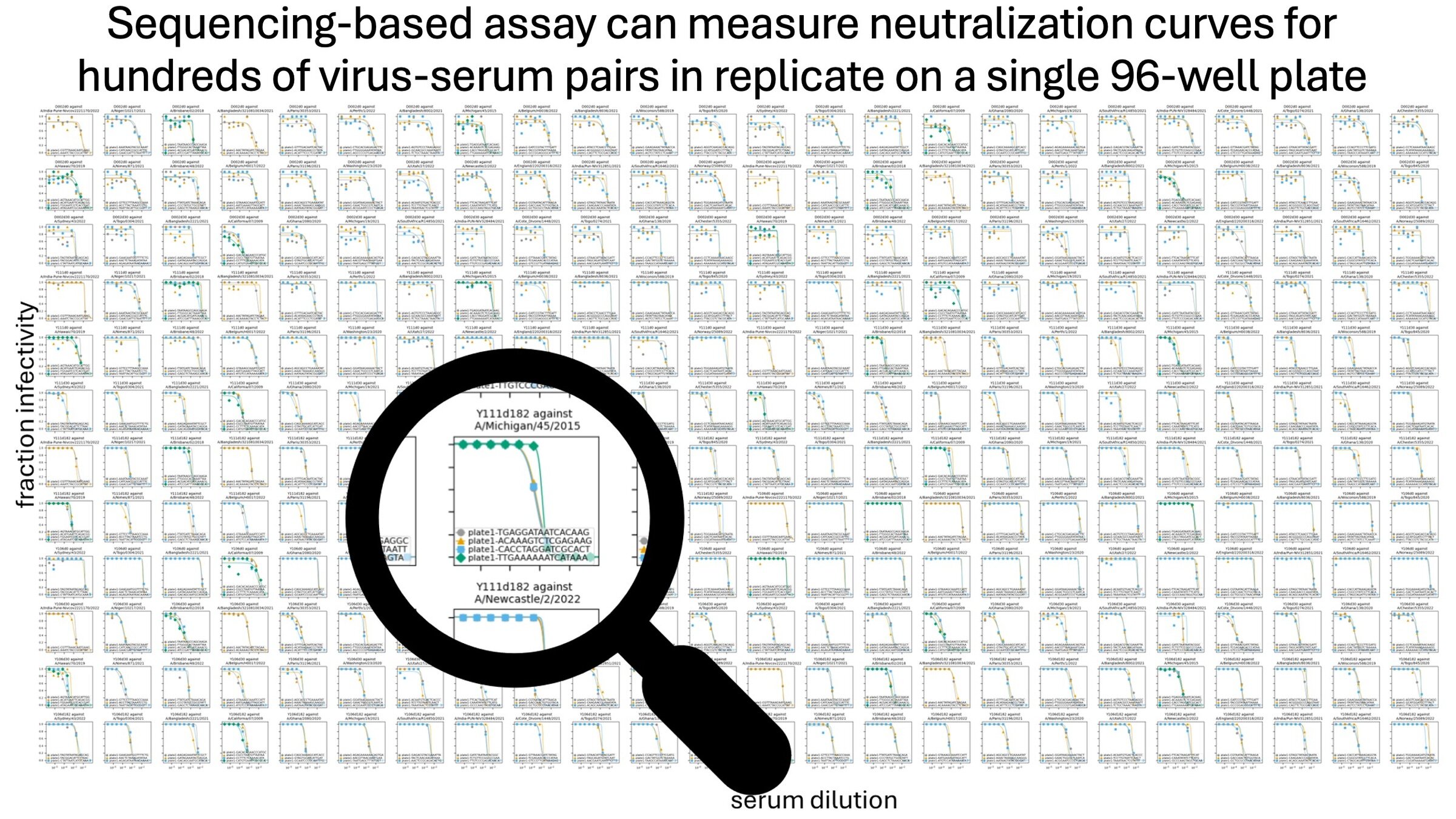
A single 96-well plate can measure ~3,000 curves (~1,000 titers in triplicate)
Unpublished data available here


We measured neutralization of many influenza strains by large set of human sera
sera from 95 individuals of different ages





Measured neutralization by each individual serum
Unpublished data available here




We measured neutralization of many influenza strains by large set of human sera
sera from 95 individuals of different ages






Measured neutralization by each individual serum

Measured neutralization by pool of all sera
Success of influenza strains correlates to fraction sera with low titers, not titer of sera pool
This result underscores importance of population immune heterogeneity in viral evolution
The approaches we have developed are applicable to many other viral entry proteins
- influenza hemagglutinin (Dadonaite et al, 2024)
- HIV envelope protein (Radford et al, 2023)
- Lassa virus glycoprotein (Carr et al, 2024)
- Nipah virus RBP and F proteins (Larsen et al, 2024)
- RSV G and F proteins
- Rabies G protein
- Chikungunya virus E proteins

Interpreting viral evolution
... atg ttt gtt ttt ctt gtt ...
... atg ttt ctt ttt ctt gtt ...
... atg ttt gtt tat ctt gtt ...
Lots of viral sequences
But what do they mean?
Bloom lab




These slides: https://slides.com/jbloom/sars2evol
Thanks


Fred Hutch Cancer Center
Trevor Bedford
University of Washington
Helen Chu and HAARVI cohort
Neil King
David Veesler
Cincinnati Children's Hospital
Mary Staat
David Haslam
Allie Burrell


Tyler Starr (now at Utah)
Allie Greaney (now at UCSF)
Kate Crawford
William Hannon
Caelan Radford
Brendan Larsen


Bernadeta Dadonaite
Rachel Eguia