Building cool stuff together.

TELL YOUR STORY WITH METRICS
@authors Matt Turner & Alejandro Varela
A Picture Says 1,000 Words
But today, we’re not painting happy little trees. We’re painting happy little metrics.

Before you realize the metrics...
You are failing to capture your true value
When you look closely...
Your landscape conveys a narrative
Define the that matter...

" Every angle tells a slightly different story. The theme is always captured value." - Not Bob Ross
METRICS
" Numbers are like brushstrokes. Alone they’re fine, but together they tell a story." - Not Bob Ross
Showcase your team's
VALUE
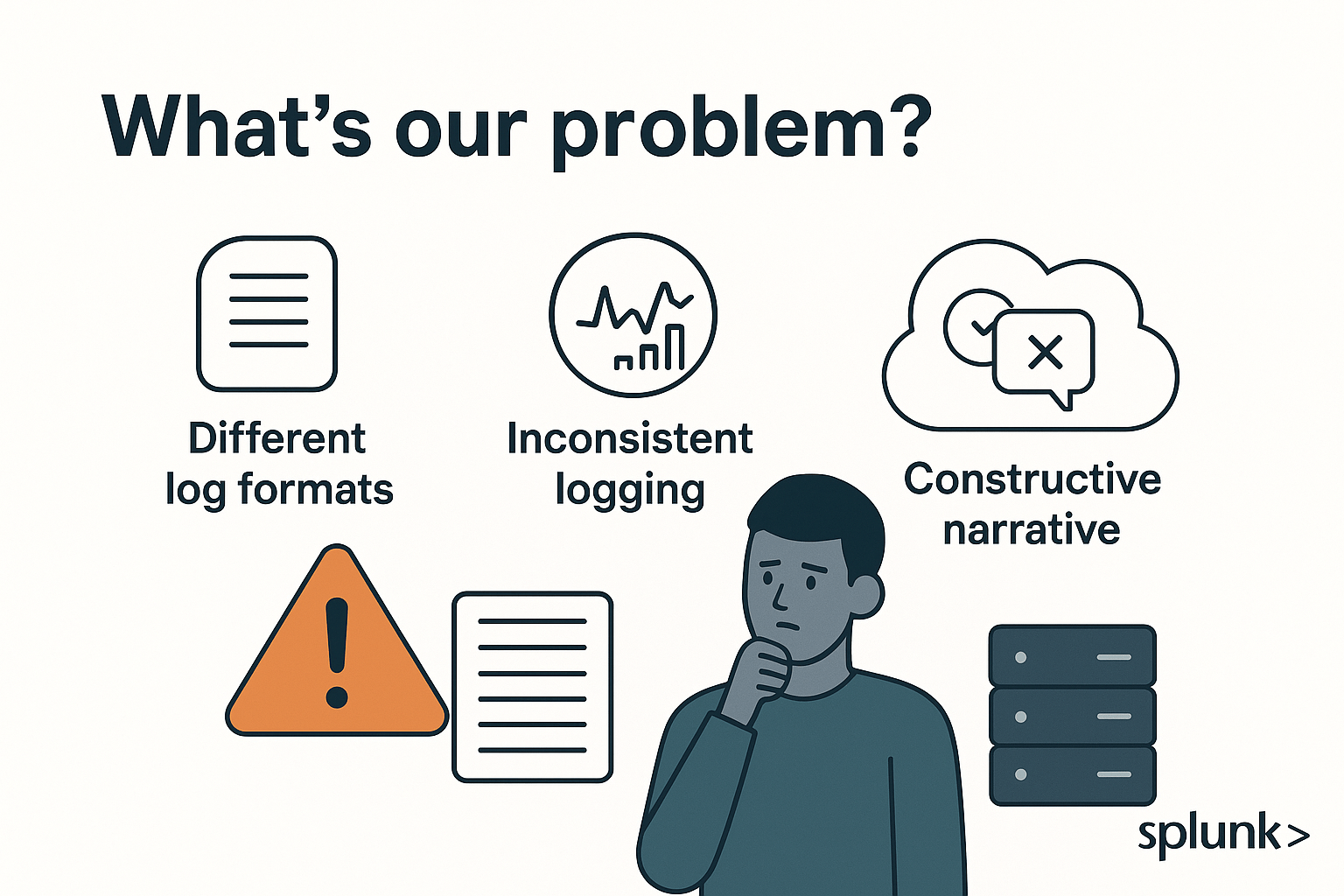
What's the big deal?
-
Showcase value to business leaders
-
Enhance application support exeperience
-
Prioritize features that matter most
-
Realize the business impact of your application(s)
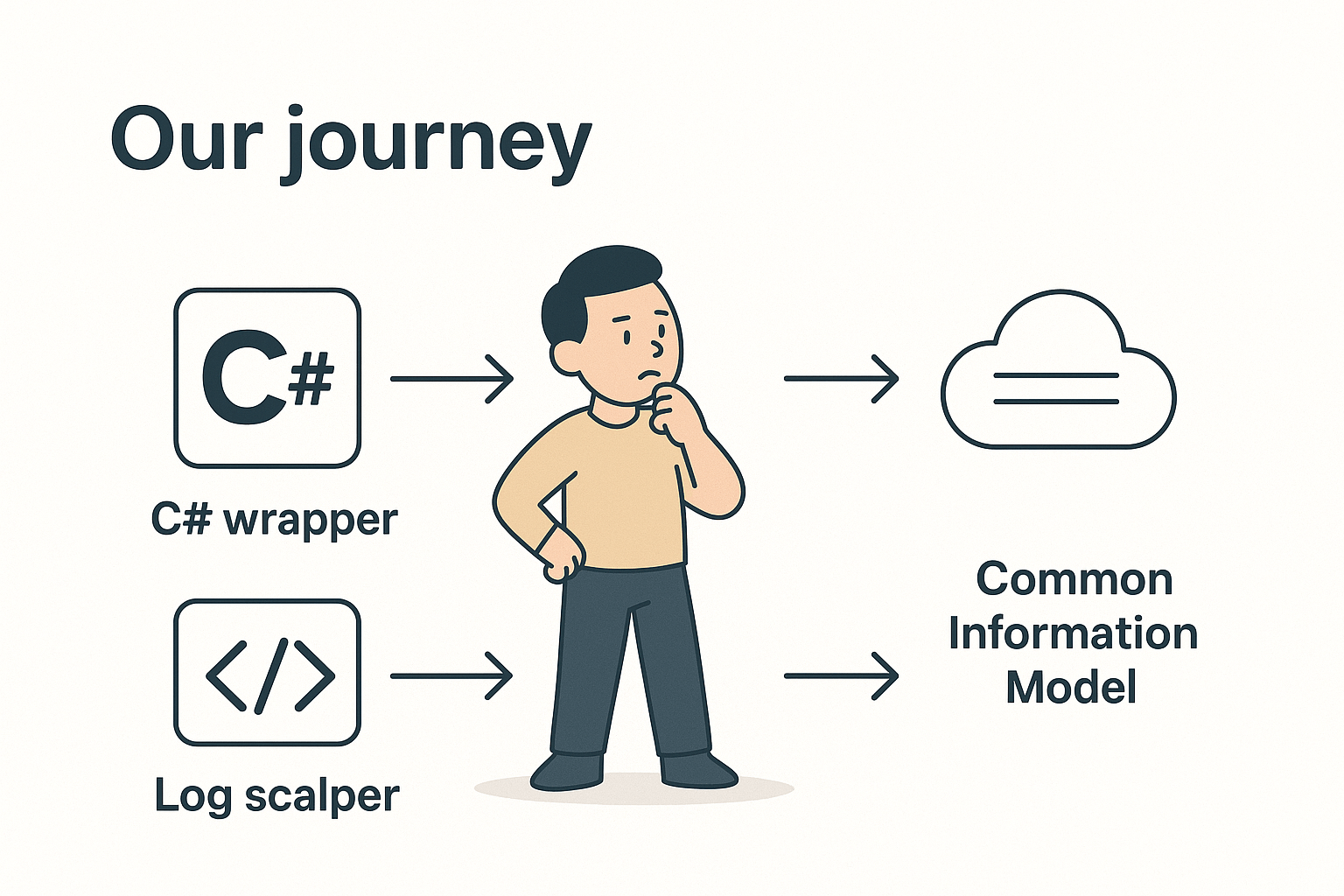
Proposed Solution
Adopt Splunk's Common Information Model to standardize logging across the enterprise.
Introducing Splunk's Common Information Model
What is CIM?
Splunk’s Common Information Model is a semantic model focused on extracting value from data.
- Normalize and standardize logs
- Uses consistent field names and data types
- Applies semantic meaning to log content
- Ensures that all logs follow the same structure:
- e.g.,
clientIP→src_ip
- e.g.,
Benefits of CIM
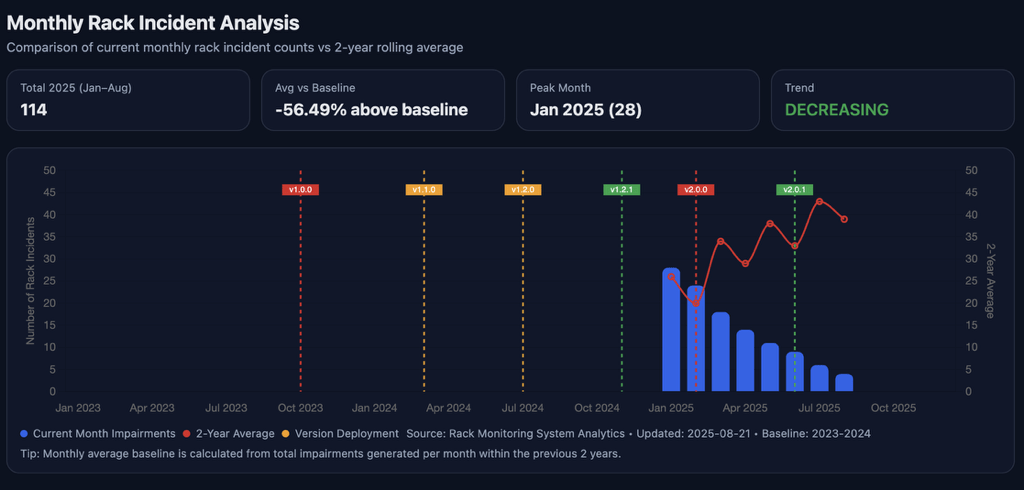
- Identify your application trends
- Proactively avoid application incidents
- Enhance your application support experience
- Showcase the business value that your application brings to the table
- Understand your application's impact with an elevated perspective
Implementation...
Planning & Design
- Review Splunk CIM documentation
- Define event types (e.g., logins, errors)
- Map your app events to existing CIM models
Phase 1
Field Mapping in Splunk
- Ingest logs as-is (JSON recommended)
-
Configure Splunk field aliases:
clientIP→src_ipuserId→user
Phase 2
Build Awesome Dashboards
- Translate the data into a language understood by our business leaders.
- Visualize the trending patterns.
- Enhance application support experience.
Phase 3
Selling the pitch...
Splunk's common information model isn’t just structure!
It’s strategy, scalability, and smarter operations.
Understand Your Impact
Visualize Your Metrics
Showcase Your Value

Questions?
CodeCommIT - Splunk CIM
By Matt Turner
CodeCommIT - Splunk CIM
Introducing Slides AI, an innovative tool that will streamline the way you create presentations. Powered by OpenAI GPT.
- 103
