
BHEX Mini
Direct Imaging Black Holes from LEO
Ref Bari, Brown University



- 🎯 Introduction
- 🔭 Event Horizon Telescope
- 📻 BHEX (Black Hole Explorer Satellite)
- 🕰️ BHEX Mini
- 🕒 BHEX Mini Timeline
- 💰Funding Deadlines
BHEX Mini



- 🎯 Introduction
- 🔭 Event Horizon Telescope
- 📻 BHEX (Black Hole Explorer Satellite)
- 🕰️ BHEX Mini
- 🕒 BHEX Mini Timeline
- 💰Funding Deadlines
BHEX Mini


Ref Bari
Physics MS, Brown
-
Analysis of Binary Black Holes via Neural Networks (under Prof. Brendan Keith, Brown)
-
Funded under NSF Neural DynAMO Grant
-
-
“Nitrogen Outgassing from Water Worlds” (R.Bari et. al., under review, The Astrophysical Journal 2025)
-
“Reflection from Relativistic Light Sails” (R. Bari, The Astronomical Journal 2024)
-
“Simulating the Action Principle in Optics” (R. Bari, The Physics Teacher 2023)
-
Spin Qubit CNN Researcher at the Meriles Condensed Matter Lab
-
“A Path Integral Derivation of Hawking Radiation” (MS Thesis)

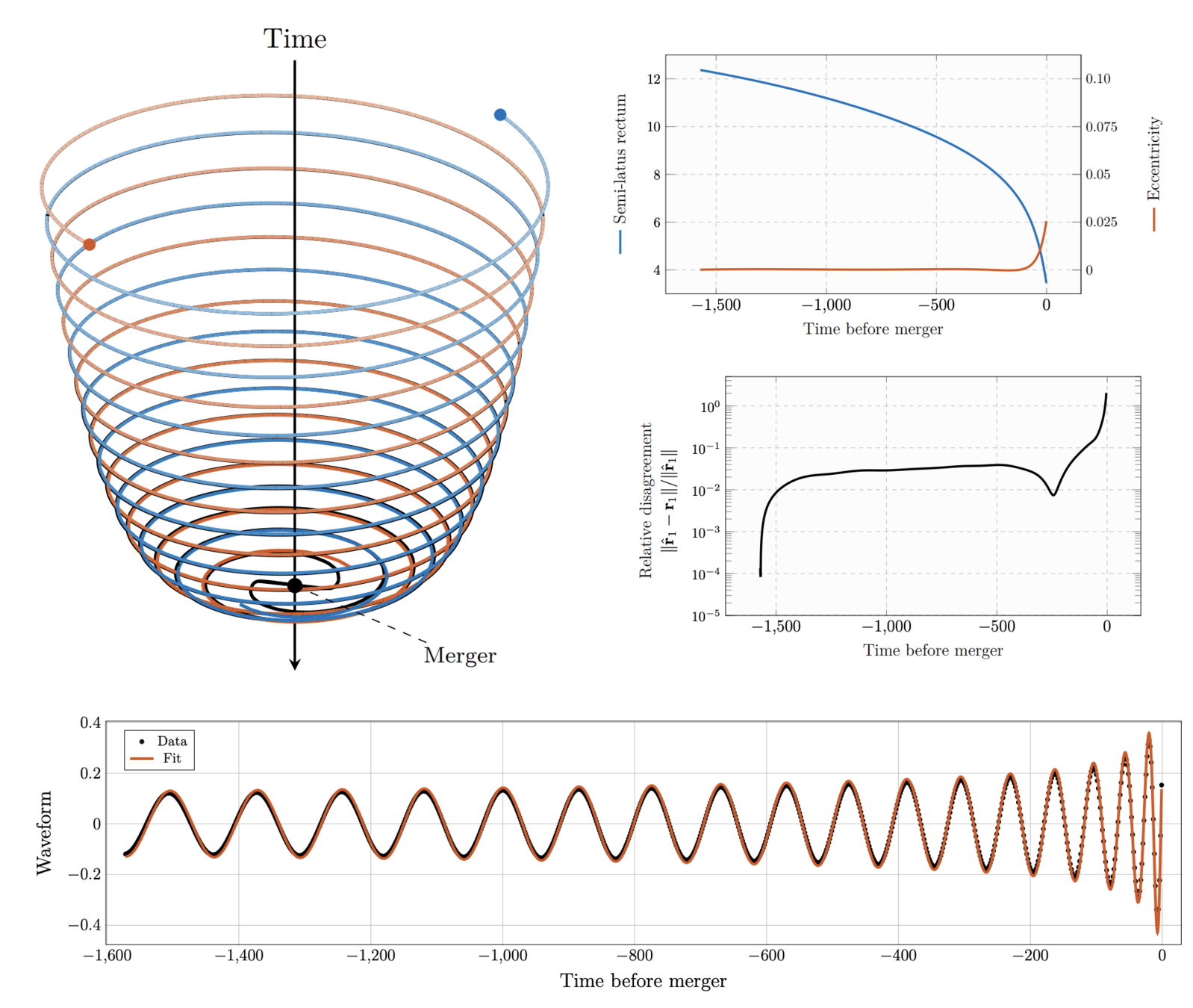
Binary Black Holes
Physics MS, Brown
-
Analysis of Binary Black Holes via Neural Networks (Prof. Brendan Keith, Brown)


Brown Space Engineering


Spaceflight Heritage


EQUiSat
SBUDNIC
PVDX


Spaceflight Heritage

SBUDNIC
PVDX


- 1U CubeSat (1.3 kg, 10x10x10 cm)
- Payload: High-Power LED Array + LiFePO4 Batteries (<6 kg)
- ADCS: Passive Magnetic Atitude Control System
- Power Generated: 1.3W (Top+Bottom Panels) & .7W (Side)
-
Total Cost: $5000
- All components built in-house at Brown Engineering Lab

EQUiSat
- 3U CubeSat (3 kg, 30x10x10 cm)
- Payload: Ham Radio Transceiver, 2 Cameras, Arduino Nano
- ADCS: Spring-Loaded + Aerodynamic Drag Sail
- Power Generated: 1.3W (Top+Bottom Panels) & .7W (Side)
-
Total Cost: $10,000
- 3D-Printed Components at BDW
- 3U CubeSat (~6 kg, 30x10x10 cm)
- Payload: Perovskite Solar Panels + Robotic Arm + Digital Display
- ADCS: Magnetorquers
-
Total Cost: ~$30,000
- 3D-Printed Components at BDW
- CUBECOM S-Band Transceiver ($10,000)


- 🎯 Introduction
- 🔭 Event Horizon Telescope
- 📻 BHEX (Black Hole Explorer Satellite)
- 🕰️ BHEX Mini
- 🕒 BHEX Mini Timeline
- 💰Funding Deadlines
BHEX Mini


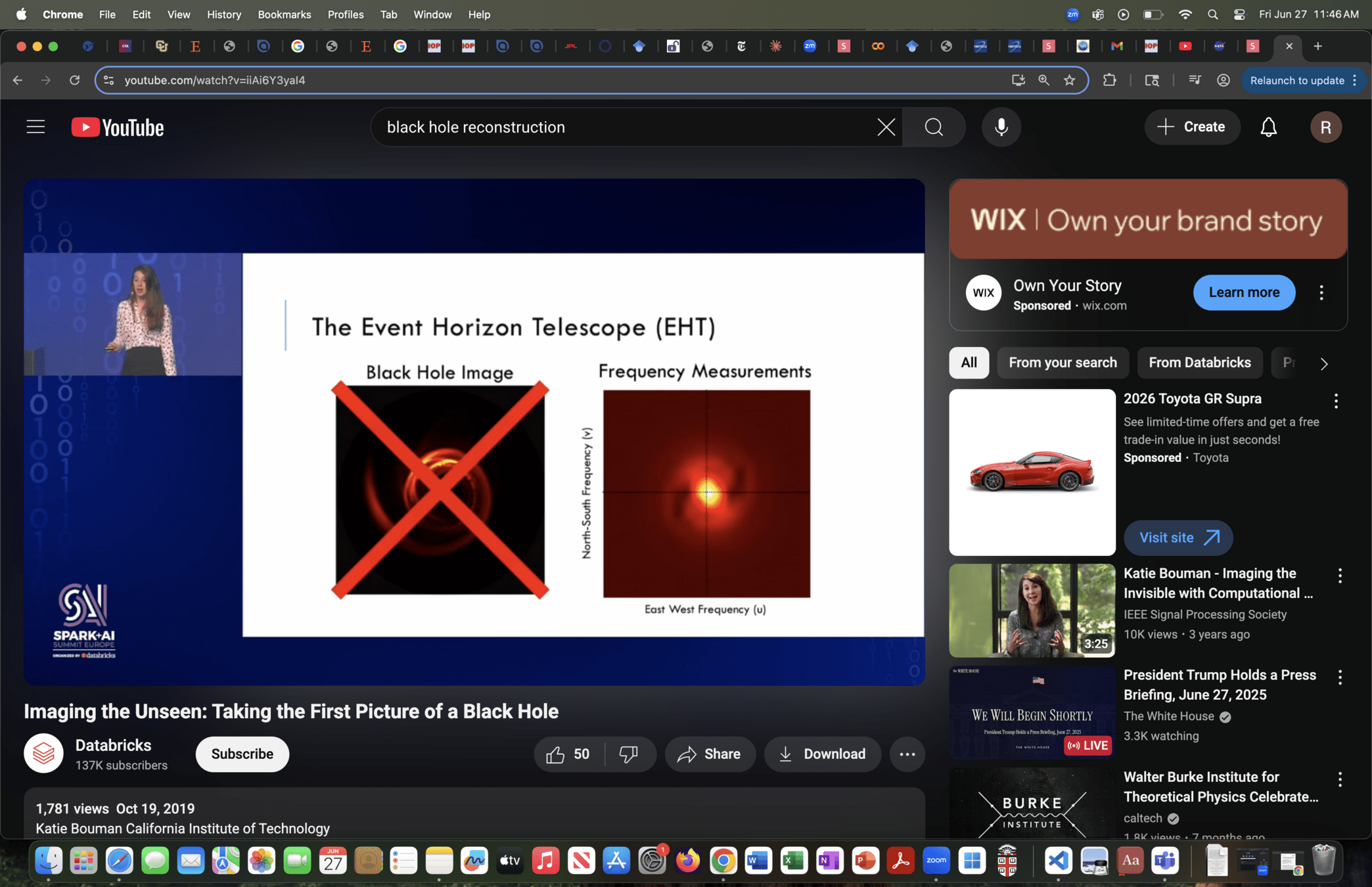
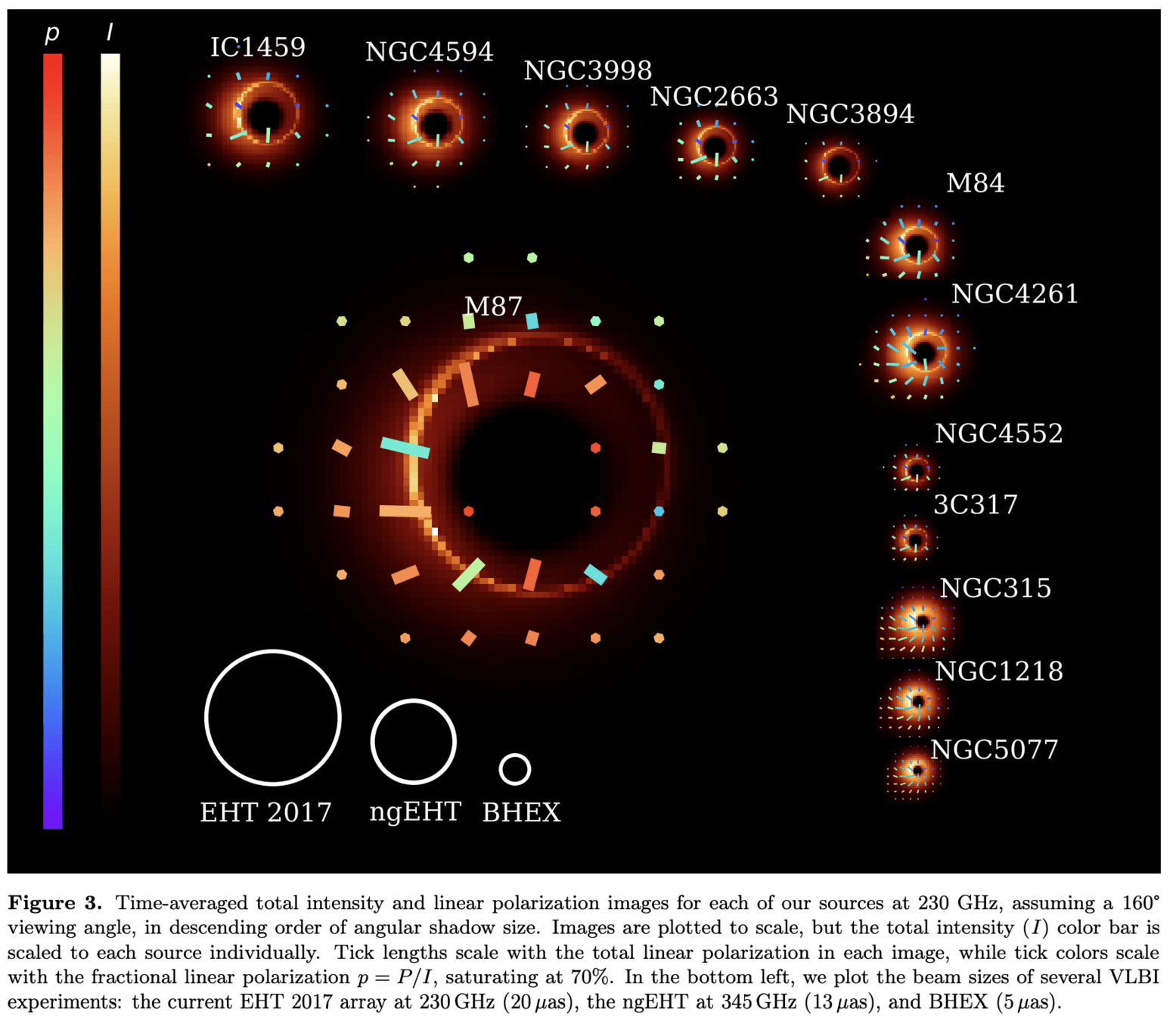
Black Hole (M87)

Event Horizon Telescope
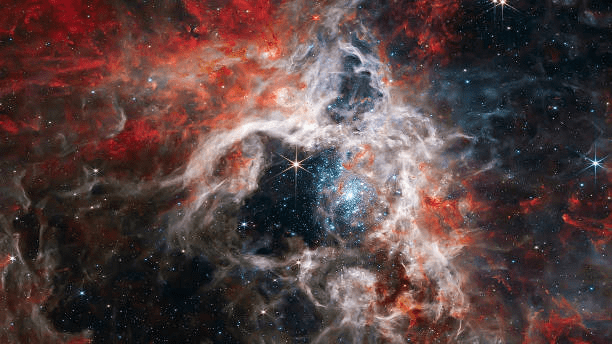

(2019)
Event Horizon Telescope (EHT)
Event Horizon Telescope
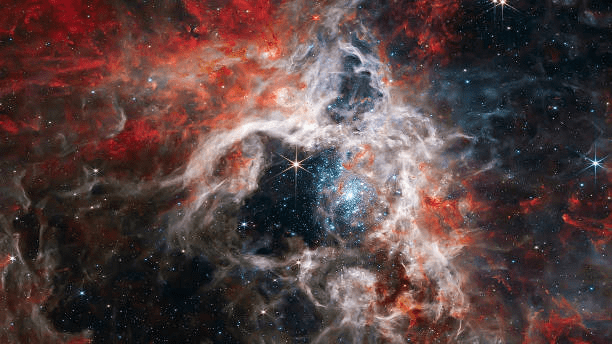


(2019)
Event Horizon Telescope (EHT)

- 🎯 Introduction
- 🔭 Event Horizon Telescope
- 📻 BHEX (Black Hole Explorer Satellite)
- 🕰️ BHEX Mini
- 🕒 BHEX Mini Timeline
- 💰Funding Deadlines
BHEX Mini


Event Horizon Telescope


(2019)
Event Horizon Telescope (EHT)
Black Holes: An Intro
(2031)
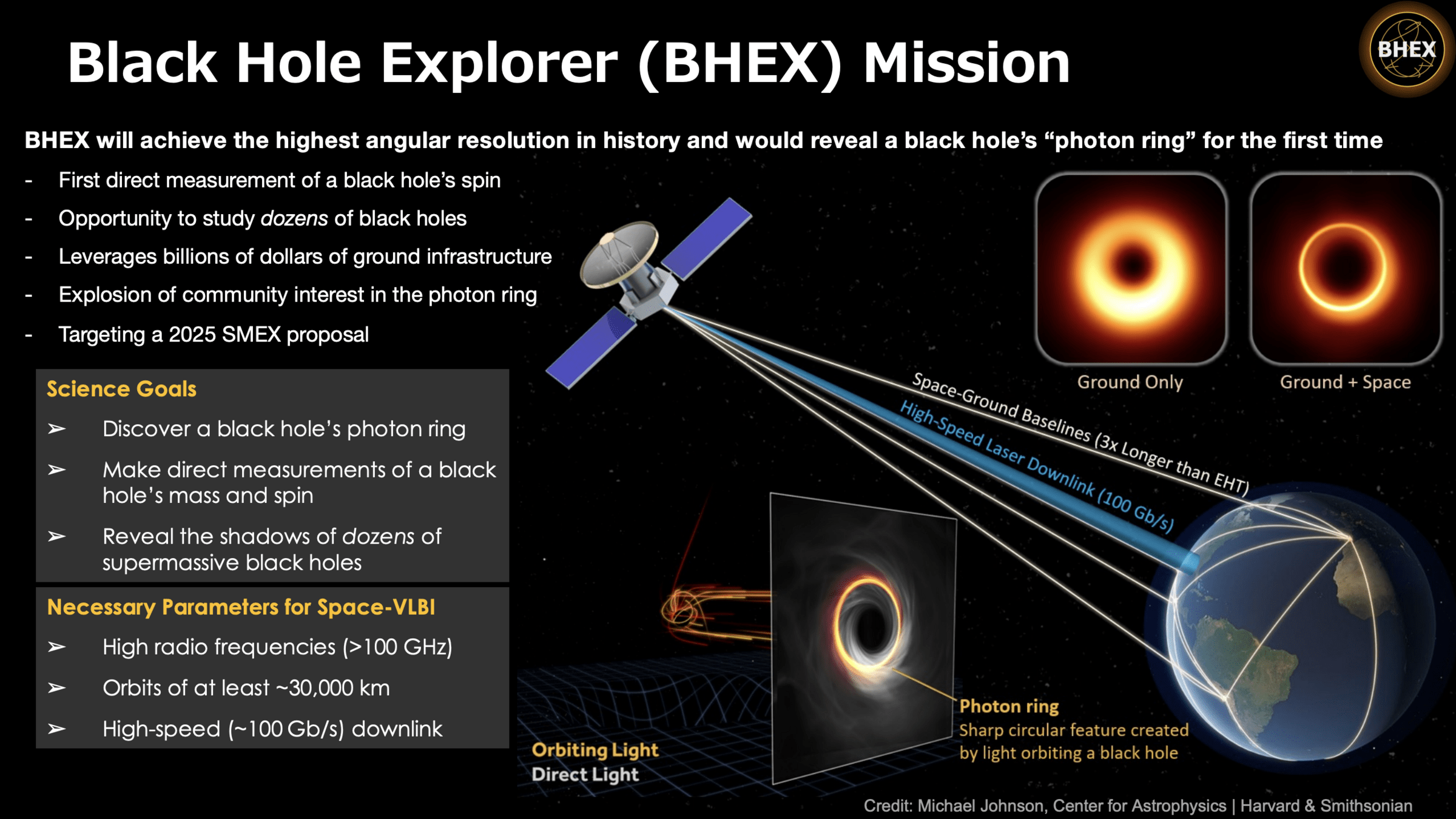
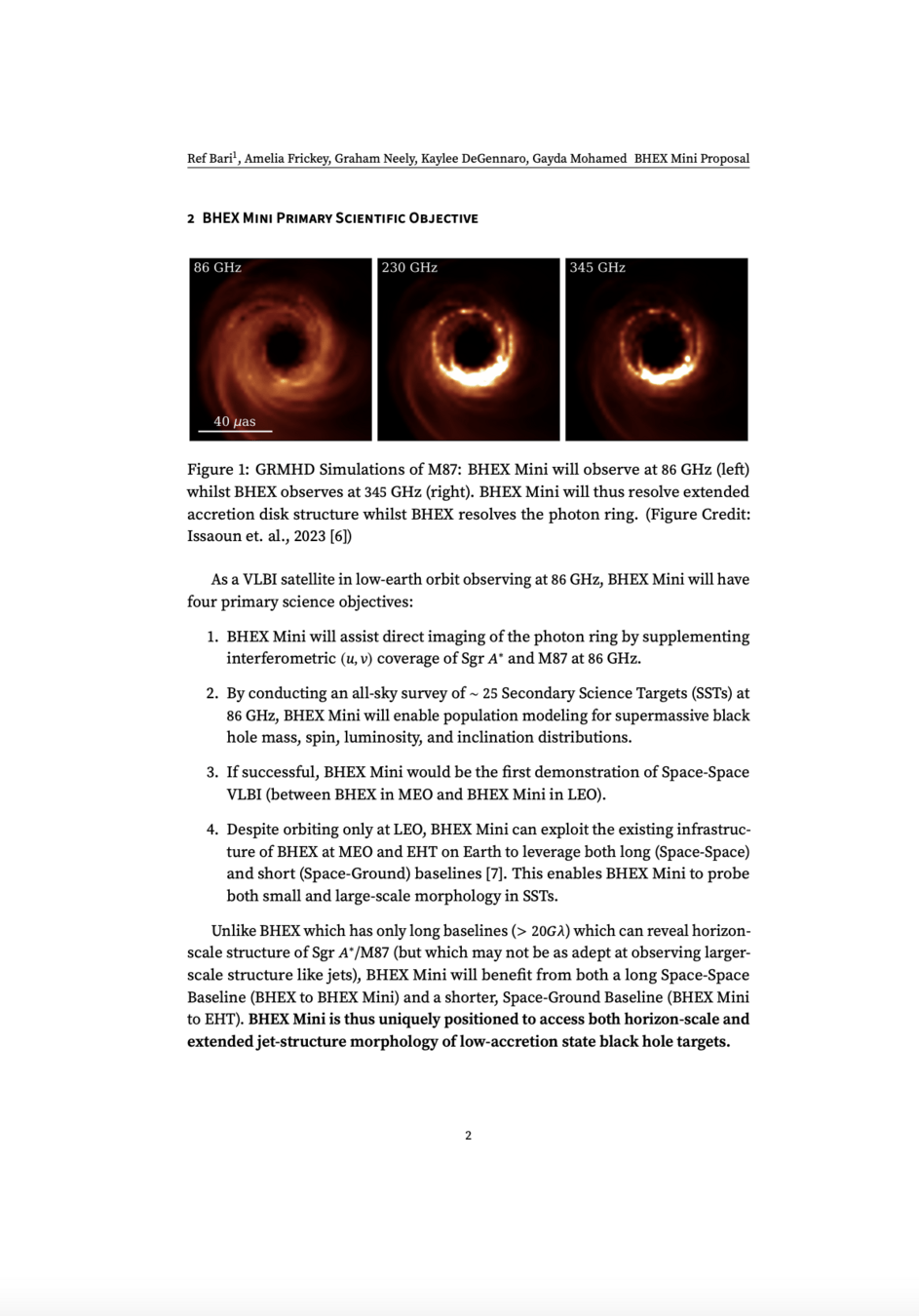
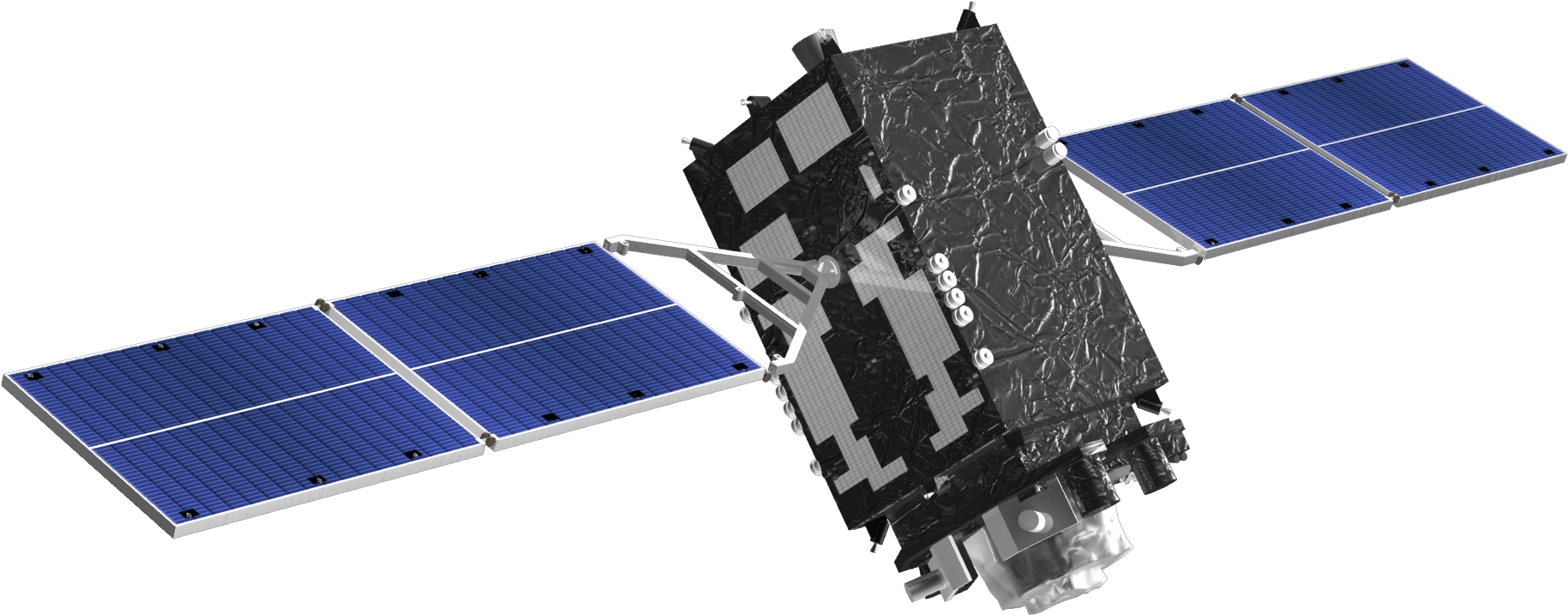
Black Hole Explorer Satellite (BHEX) Mission

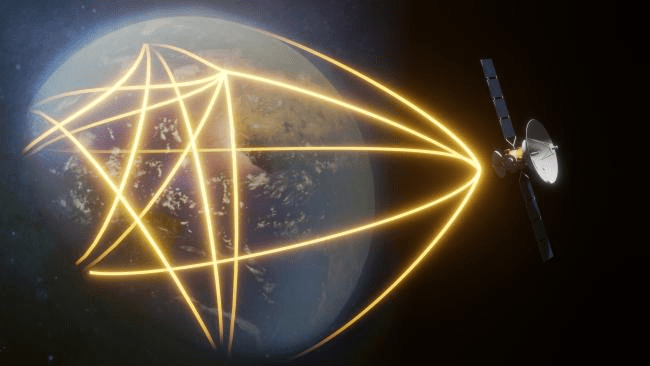


Imaging a Black Hole

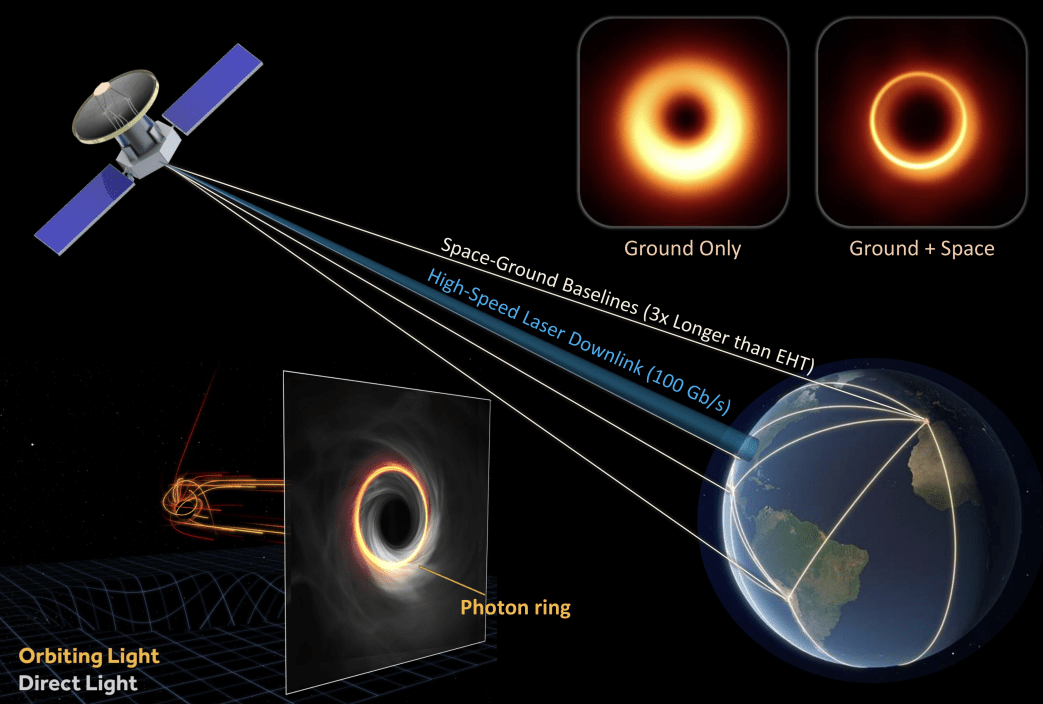
(The black hole explorer: Motivation and vision, Johnson et. al., 2024)

- 🎯 Introduction
- 🔭 Event Horizon Telescope
- 📻 BHEX (Black Hole Explorer Satellite)
- 🕰️ BHEX Mini
- 🕒 BHEX Mini Timeline
- 💰Funding Deadlines
BHEX Mini


Spaceflight Heritage


EQUiSat
SBUDNIC
PVDX


Spaceflight Heritage

SBUDNIC
PVDX



EQUiSat
BHEX Mini


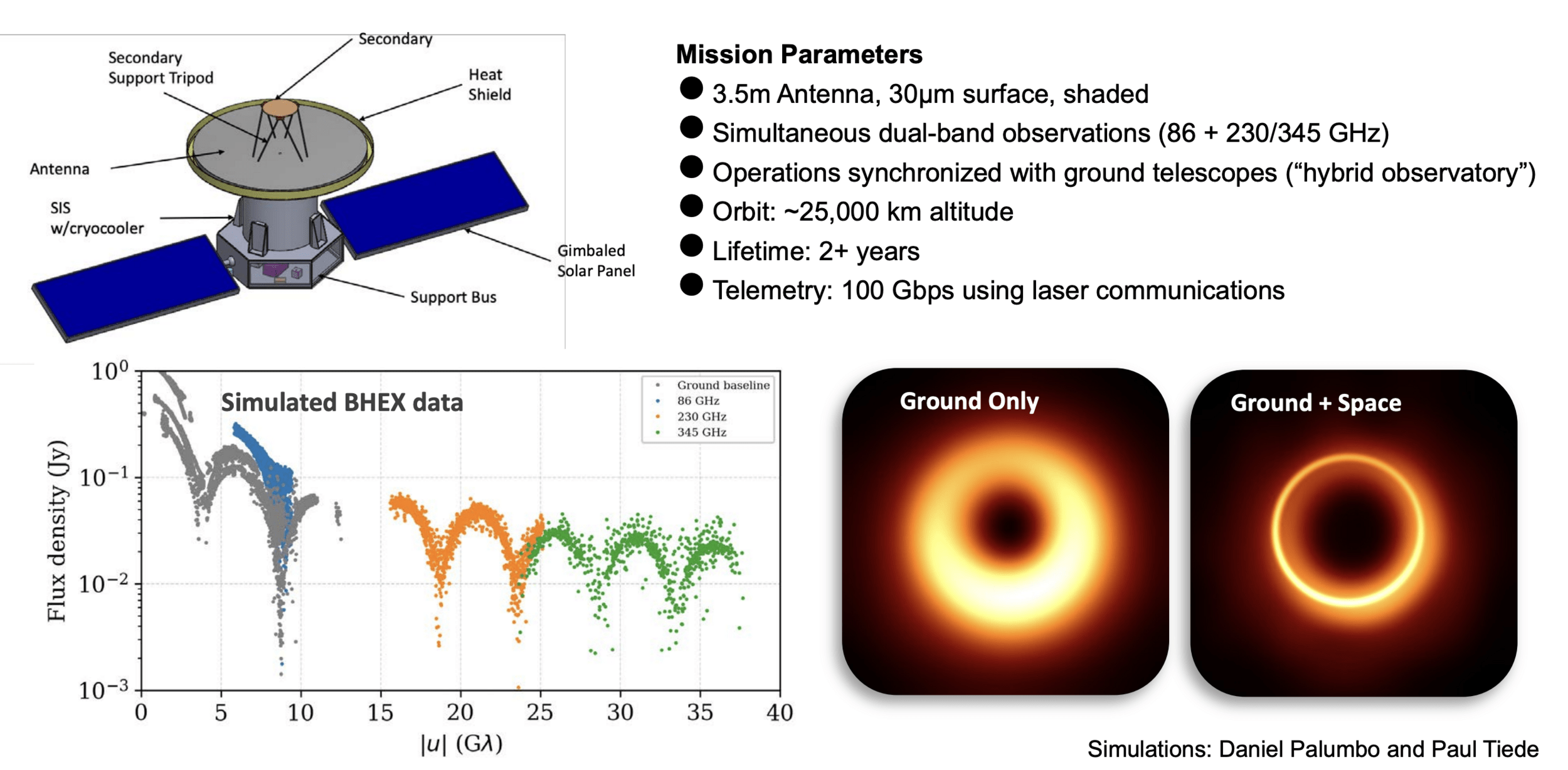
BHEX Mini


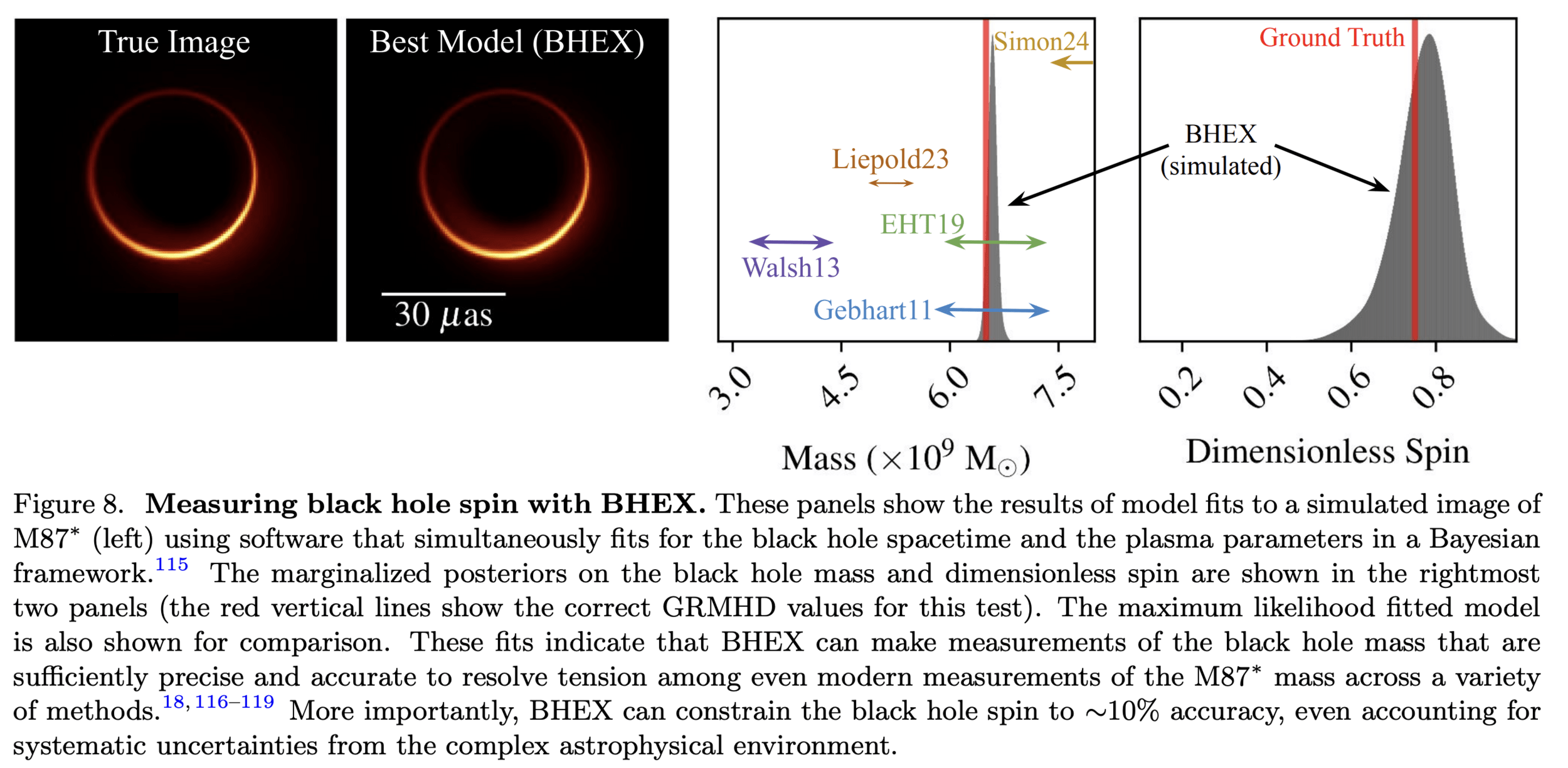
Imaging a Black Hole



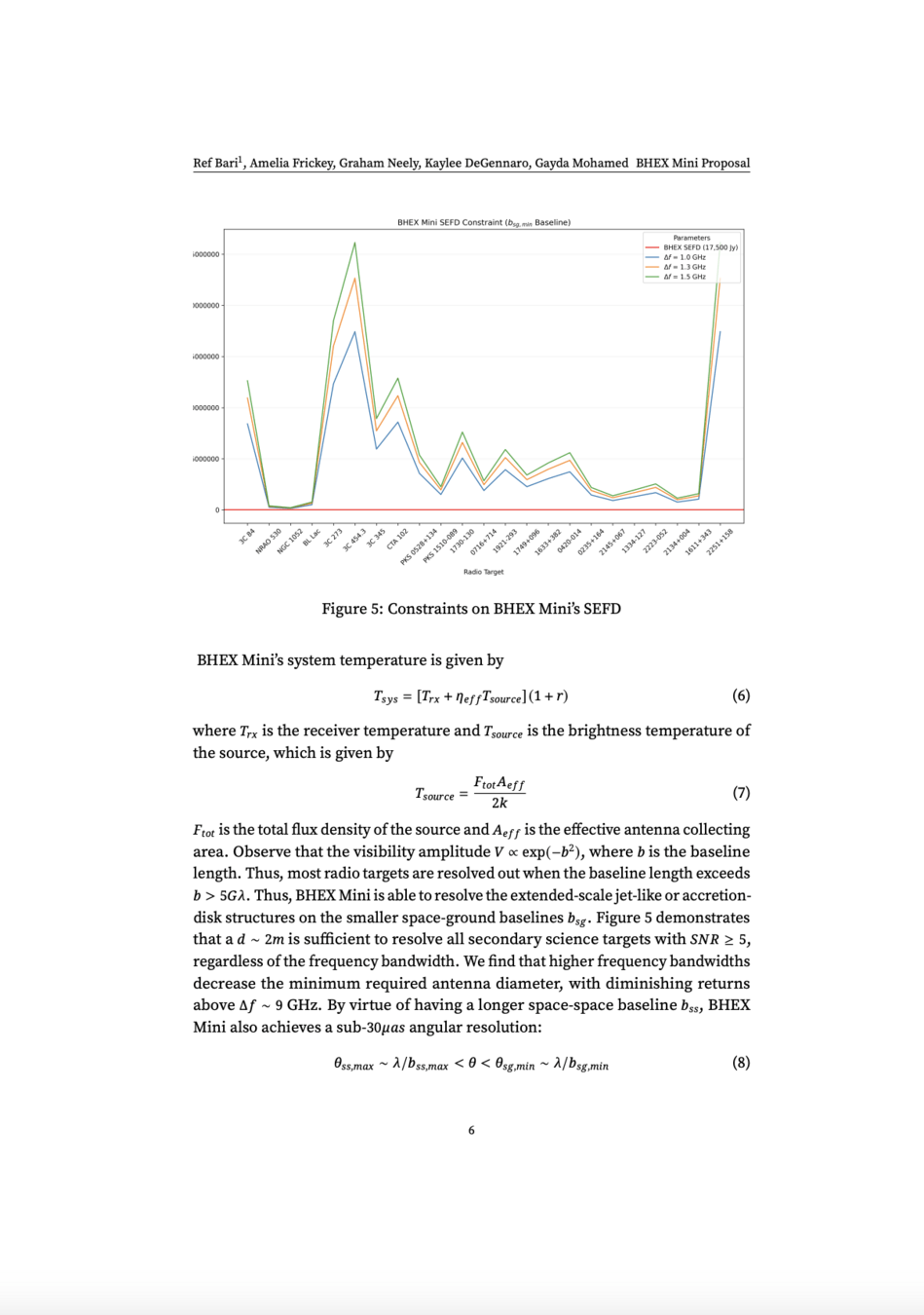










Todd Ely
Joseph Lazio
Eric Burt
Ben Hudson
Luke Anderson
Rick Fleeter
BHEX Mini


Partner Satellite to BHEX

Stand-alone Satellite

Pathfinder Mission


BHEX Mini

Partner Satellite to BHEX

Stand-alone Satellite

Pathfinder Mission
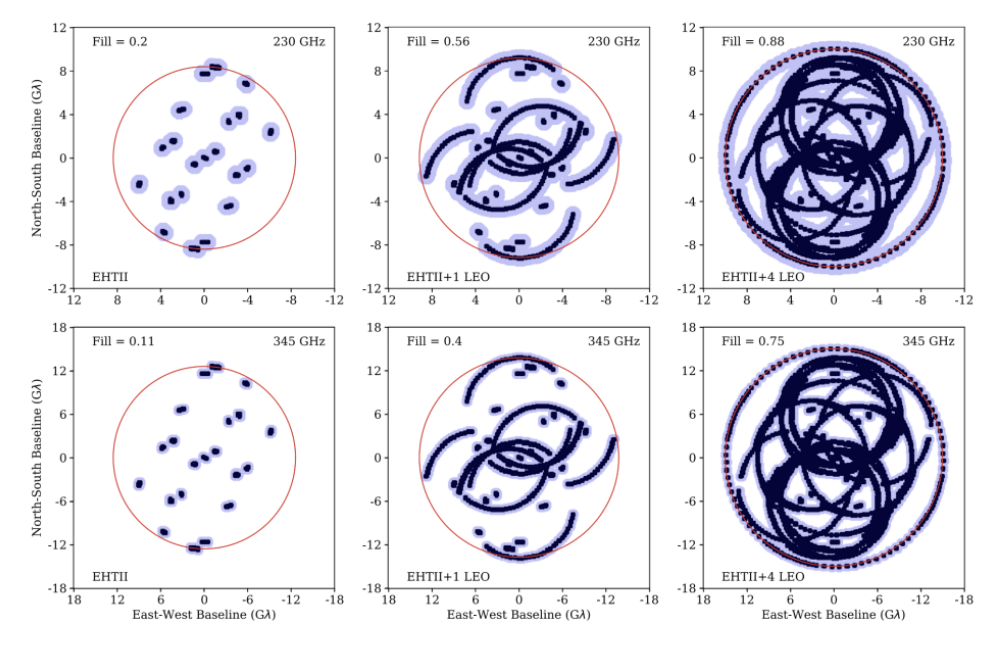
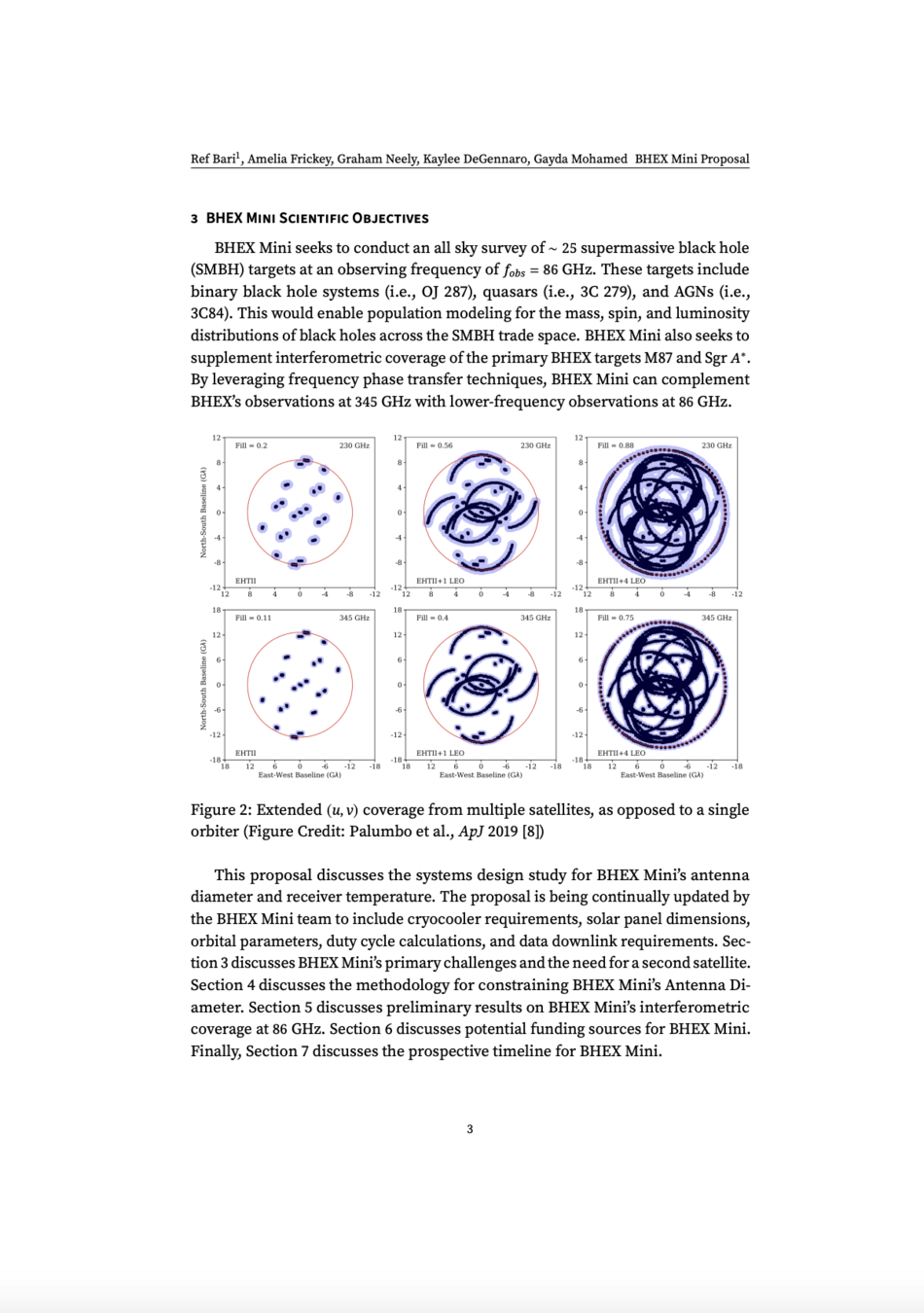
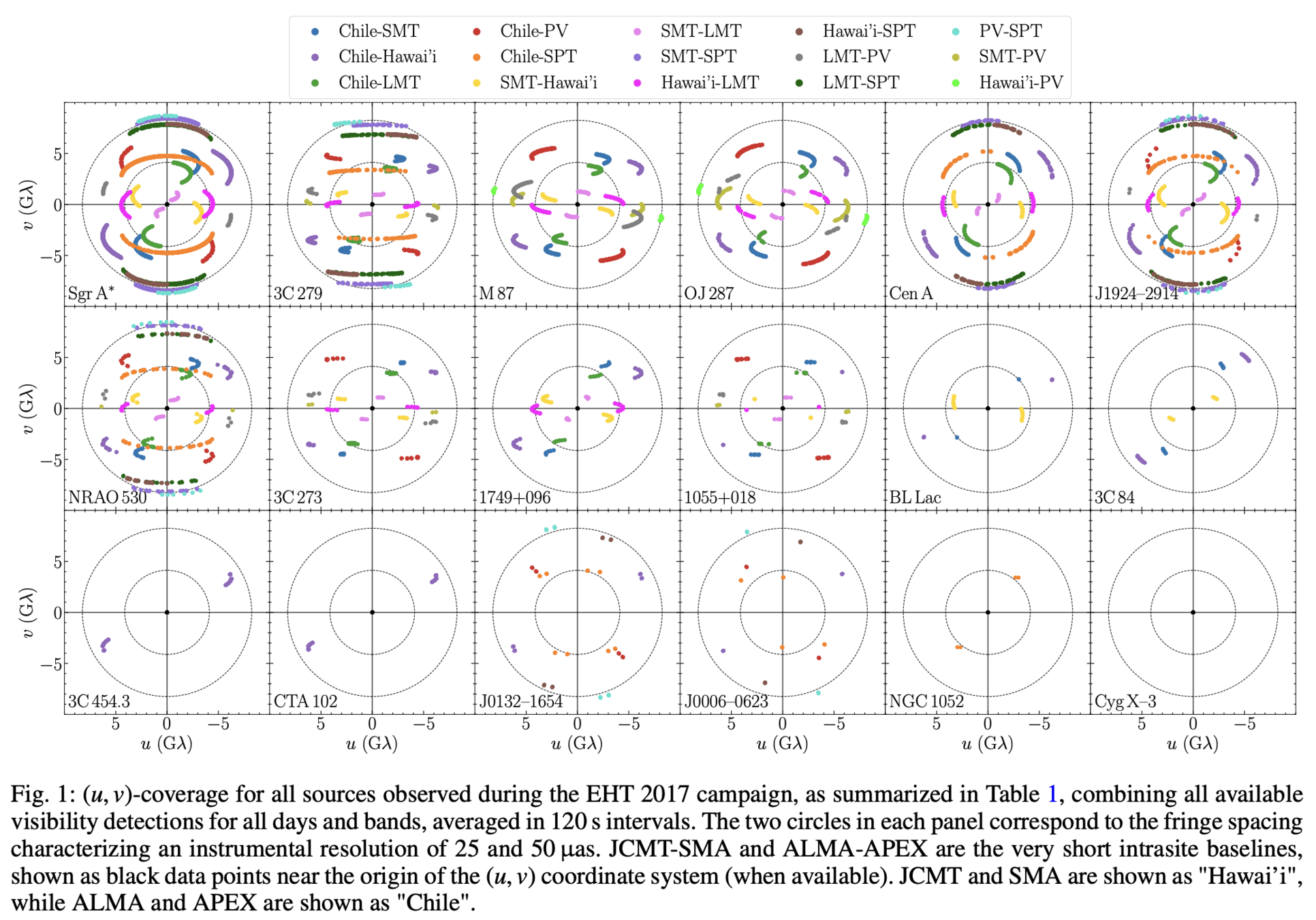
Supplement (u,v) coverage at 86 GHz
Enable parameter estimation of Sgr A*/M87
Achieve Space-Space VLBI




BHEX Mini

Partner Satellite to BHEX

Stand-alone Satellite

Pathfinder Mission
Supplement (u,v) coverage at 86 GHz
Enable parameter estimation of Sgr A*/M87
Achieve Space-Space VLBI



BHEX Mini

Pathfinder Mission


Partner Satellite to BHEX

Stand-alone Satellite
Supplement (u,v) coverage at 86 GHz
Enable parameter estimation of Sgr A*/M87
Achieve Space-Space VLBI
Supplement (u,v) coverage at 86 GHz
Enable parameter estimation of Sgr A*/M87
Achieve Space-Space VLBI
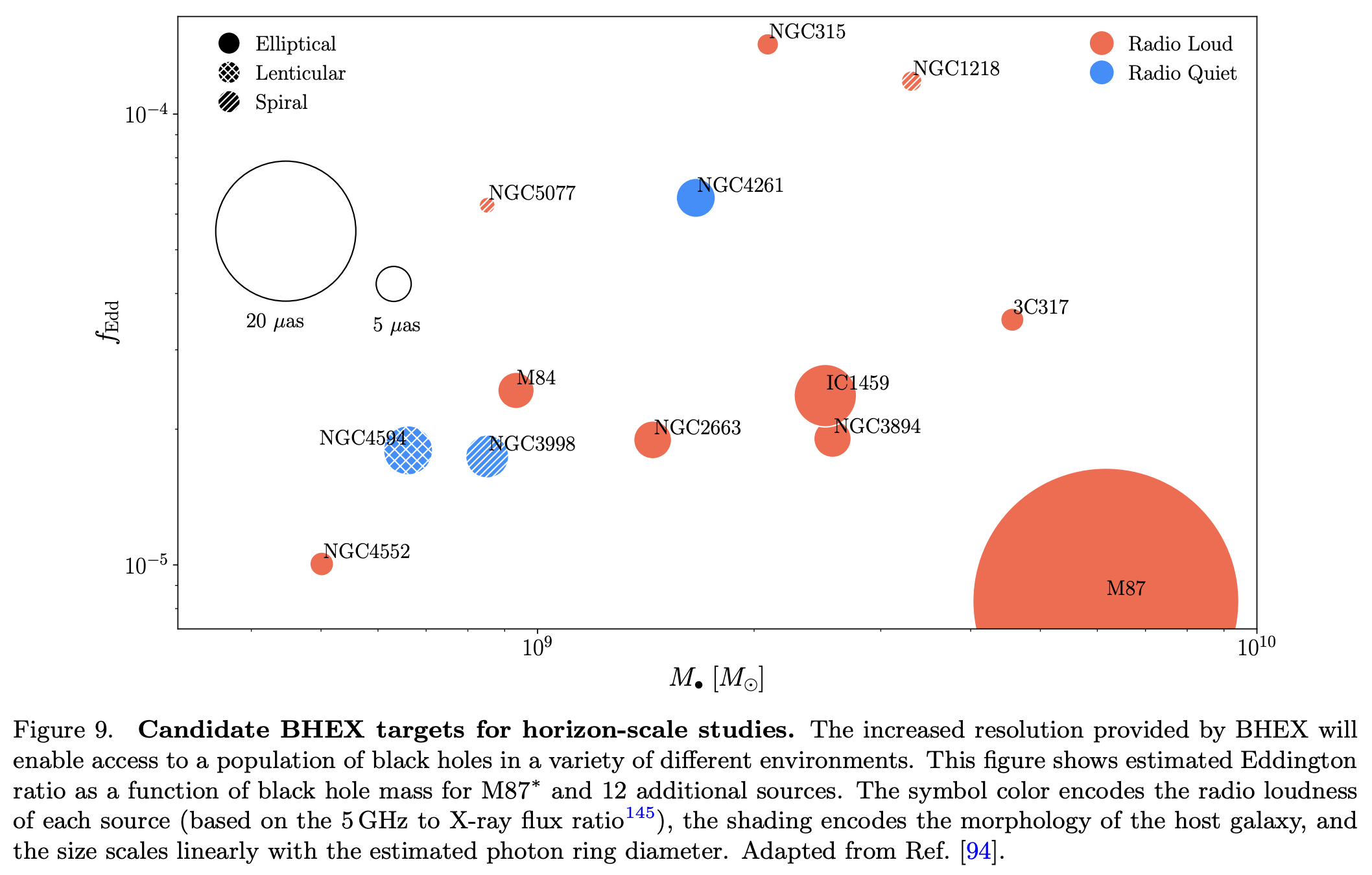
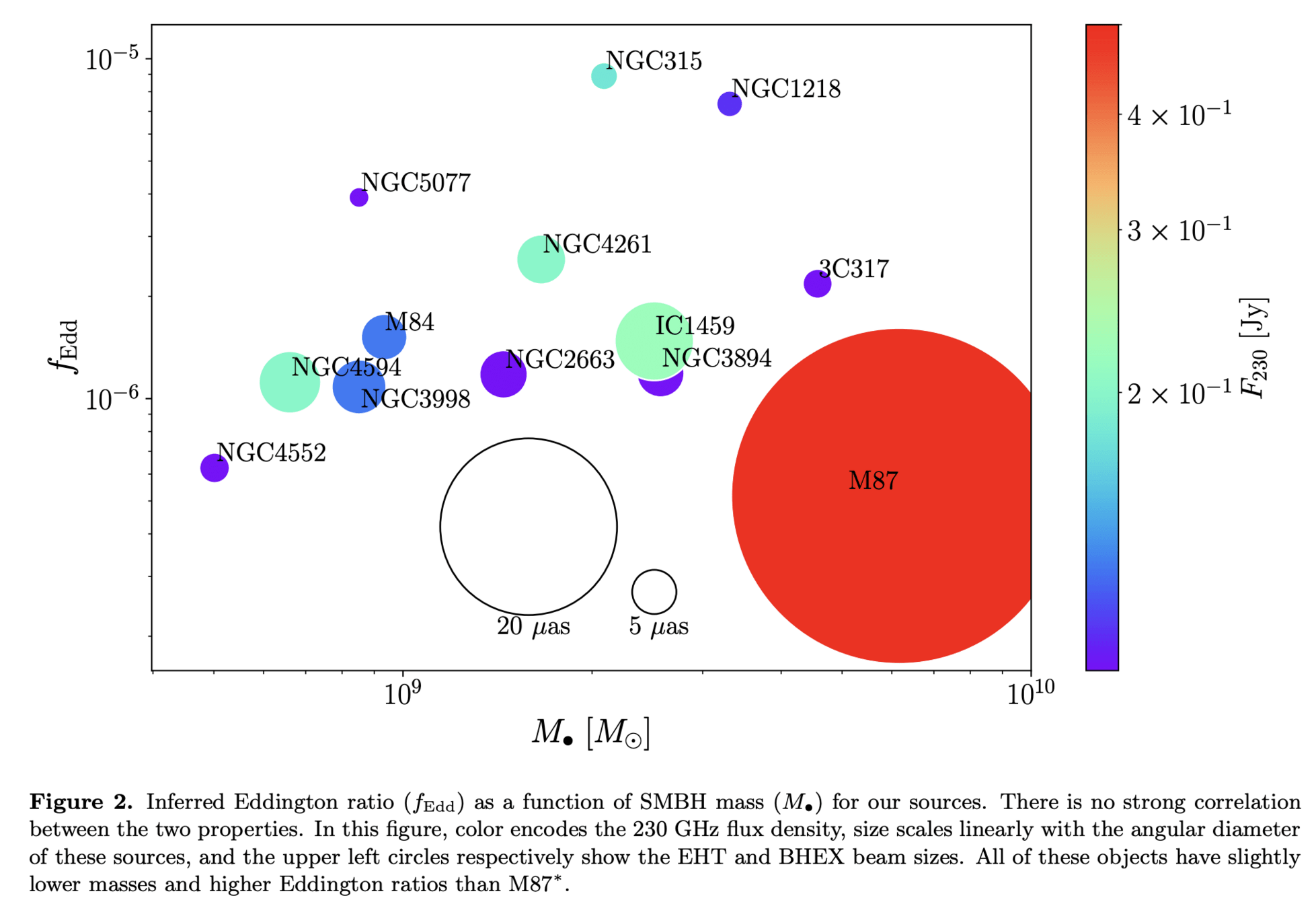
Survey of >25 AGN+BH Targets @86 GHz
Enable Population Modeling of SMBHs
Enable real-time imaging of dynamical accretion disk around Sgr A*
Enable multi-messenger gravitational astronomy w/ LIGO + LISA
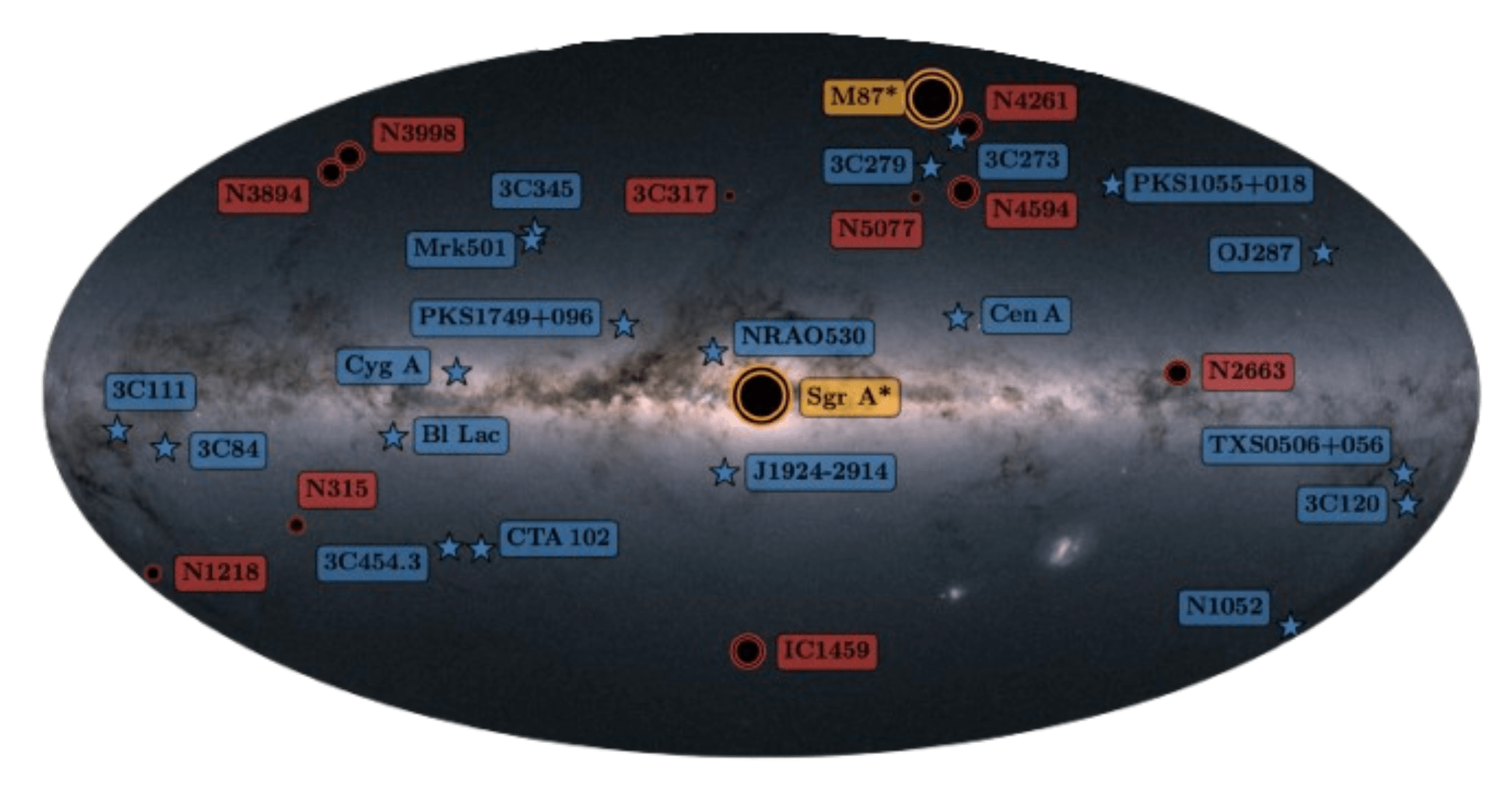

BHEX Mini

BHEX Mini

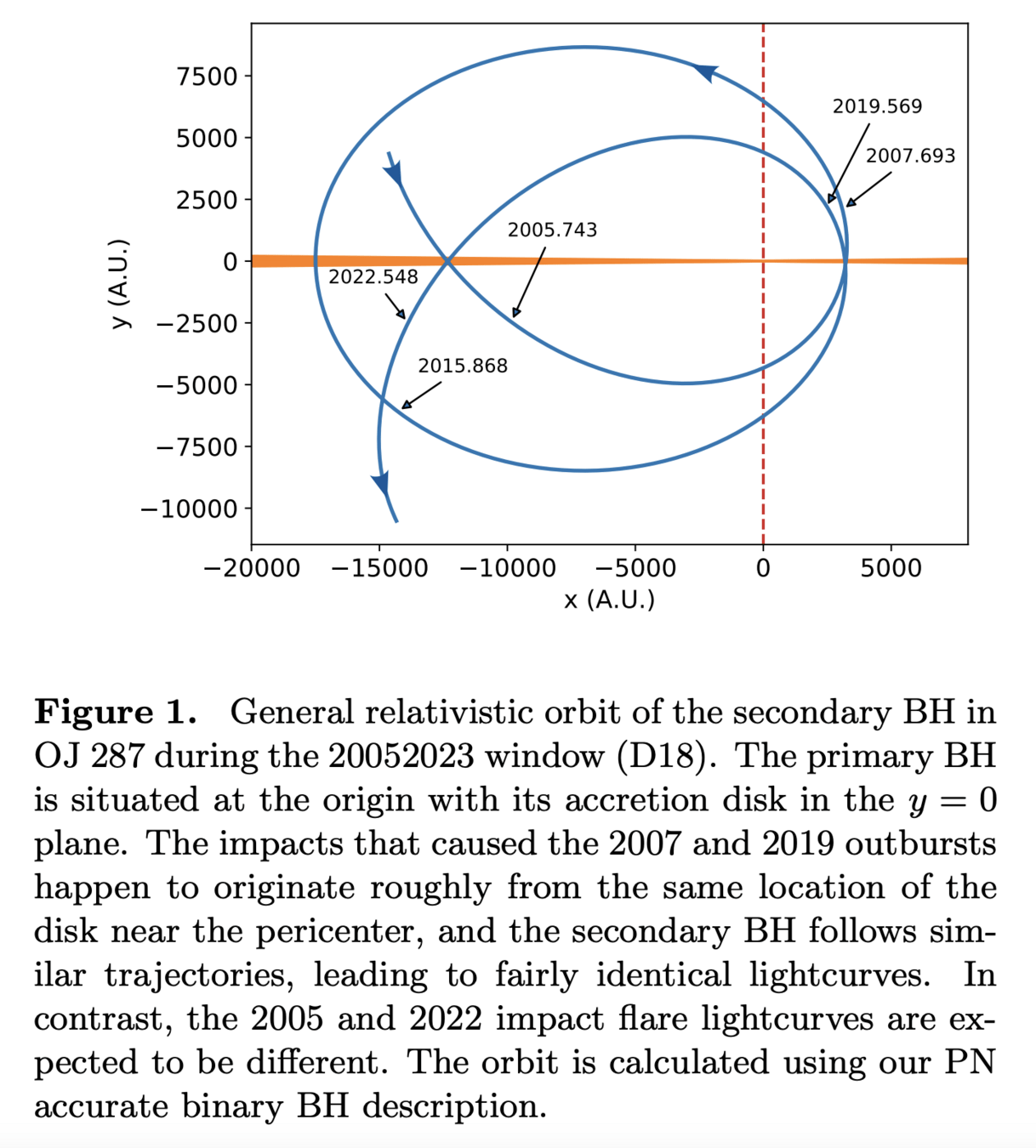
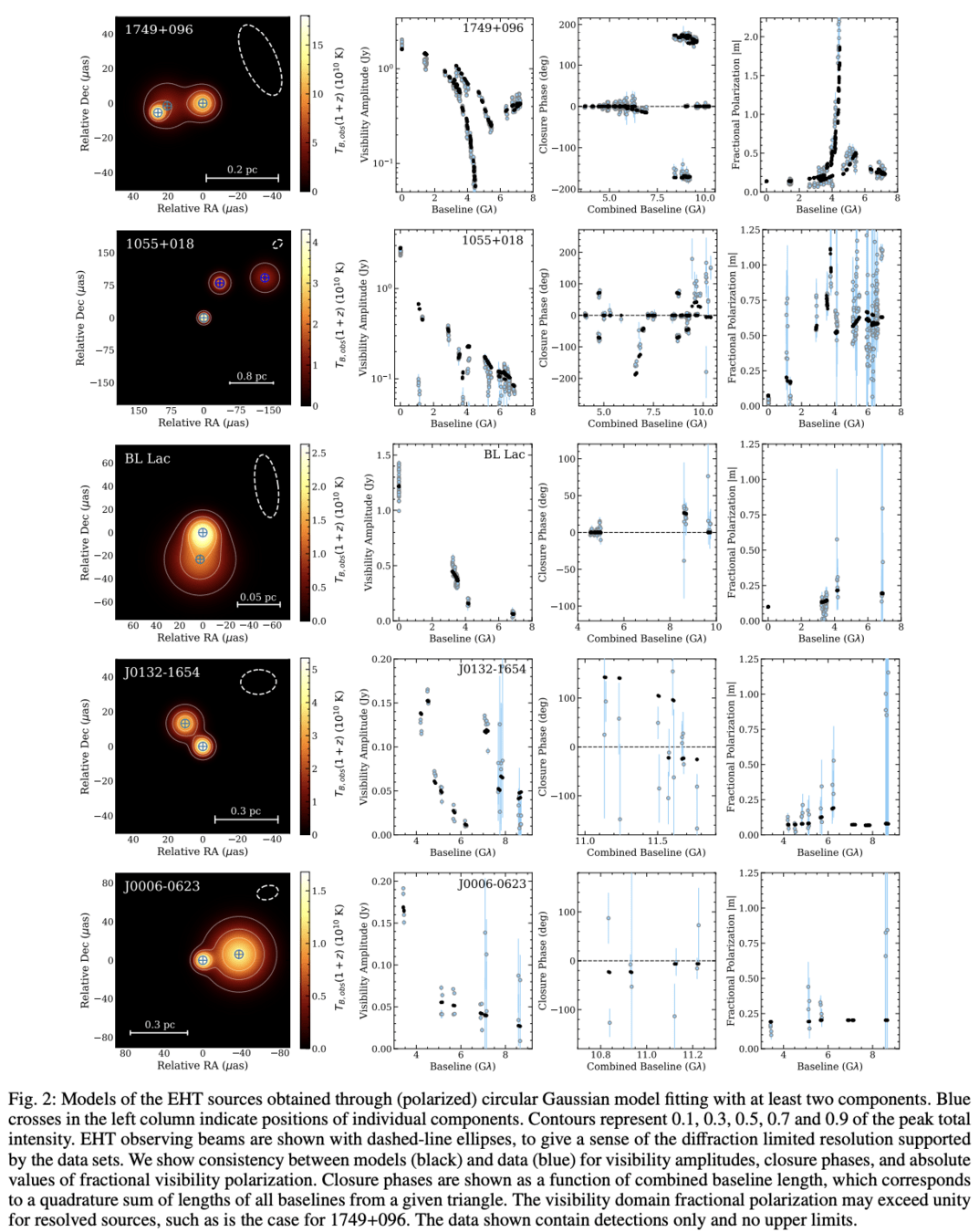
OJ 287

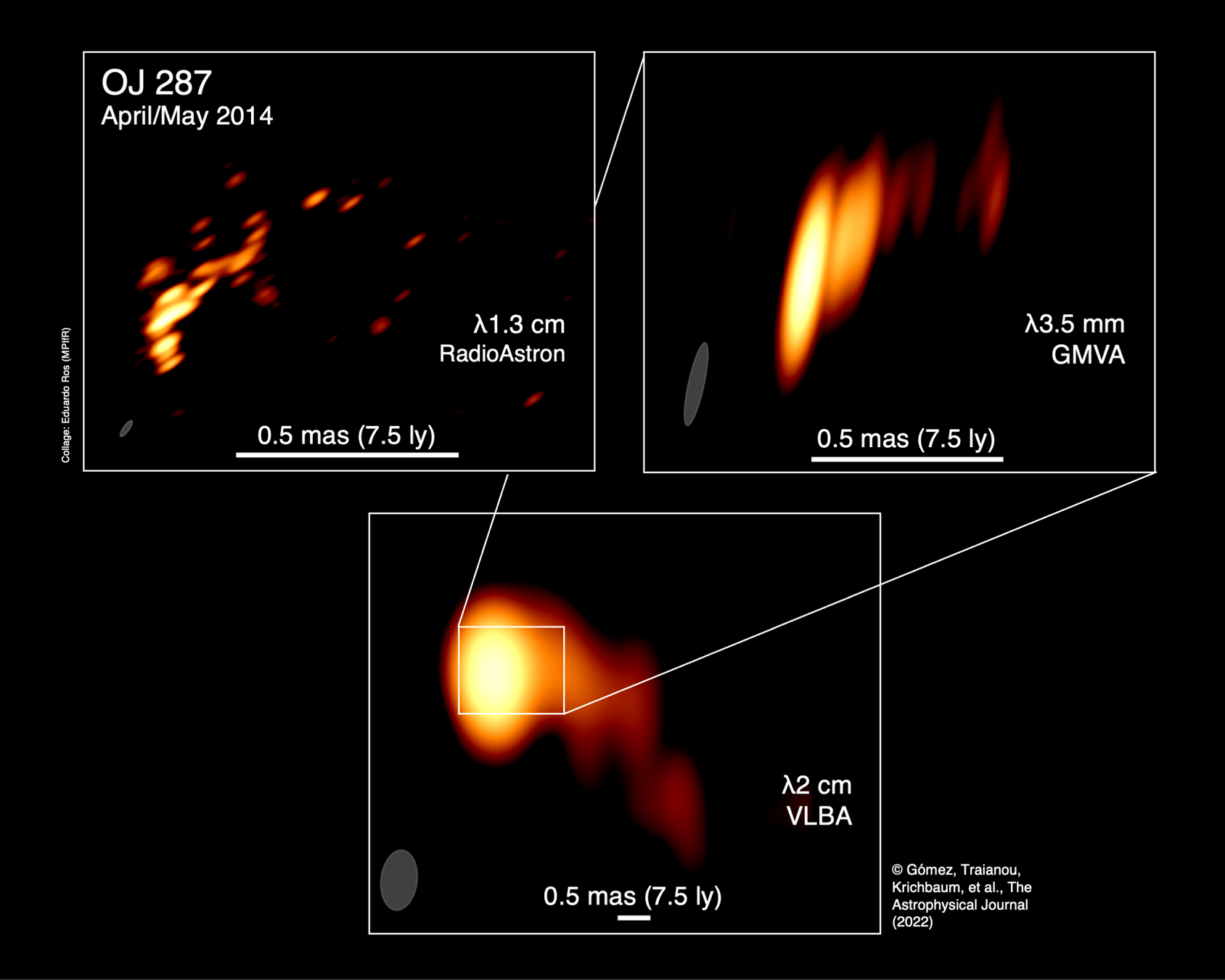
OJ 287

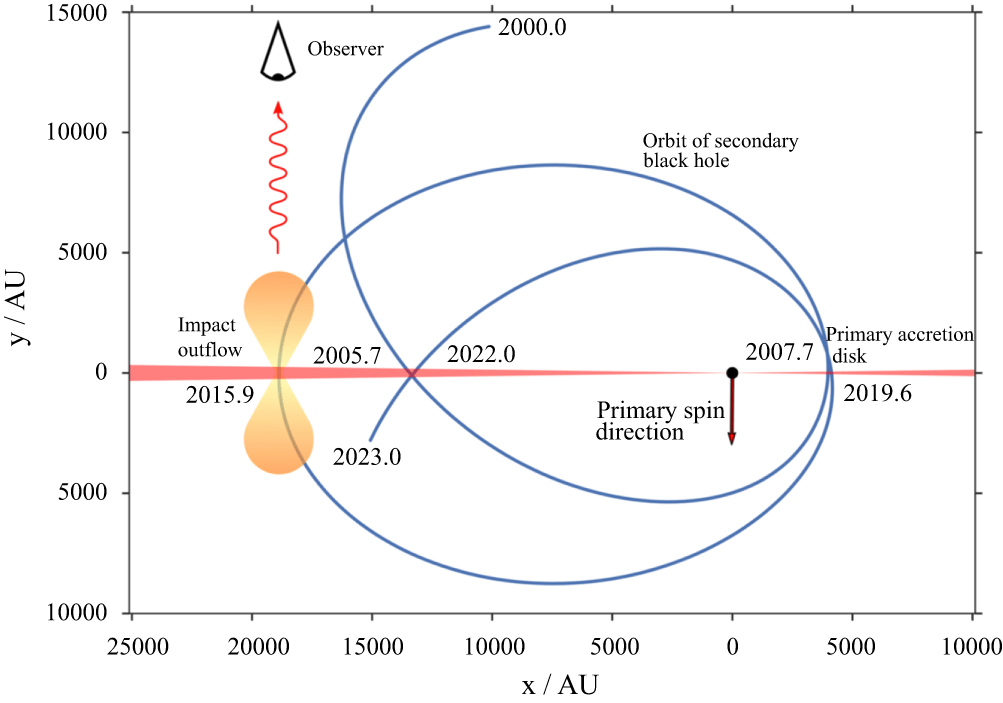
OJ 287

BHEX Mini

BHEX Mini

BHEX Mini

BHEX Mini

BHEX Mini

BHEX Mini


Partner Satellite to BHEX

Stand-alone Satellite

Pathfinder Mission
Supplement (u,v) coverage at 86 GHz
Enable parameter estimation of Sgr A*/M87
Achieve Space-Space VLBI
Supplement (u,v) coverage at 86 GHz
Enable parameter estimation of Sgr A*/M87
Achieve Space-Space VLBI
Survey of >25 AGN+BH Targets @86 GHz
Enable Population Modeling of SMBHs
Enable real-time imaging of dynamical accretion disk around Sgr A*
Enable multi-messenger gravitational astronomy w/ LIGO + LISA
Enable low-cost Space-Ground & Space-Space VLBI


BHEX Mini

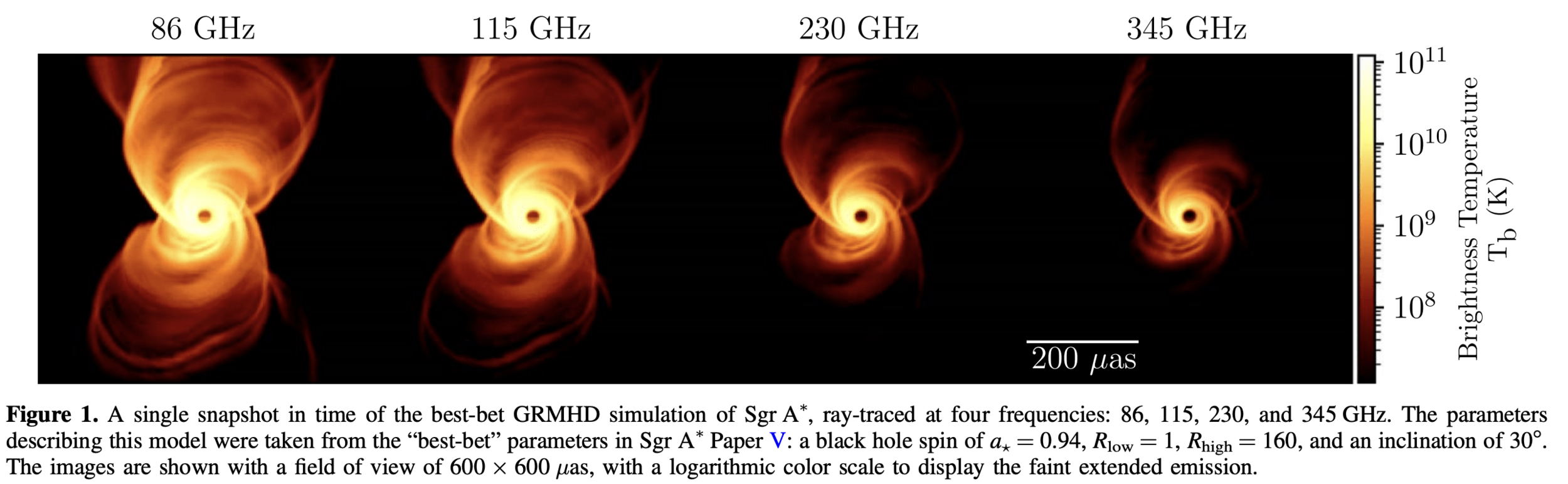
Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Rapid coverage of (u,v) plane
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO






BHEX Mini




BHEX Mini

Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Rapid coverage of (u,v) plane
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO





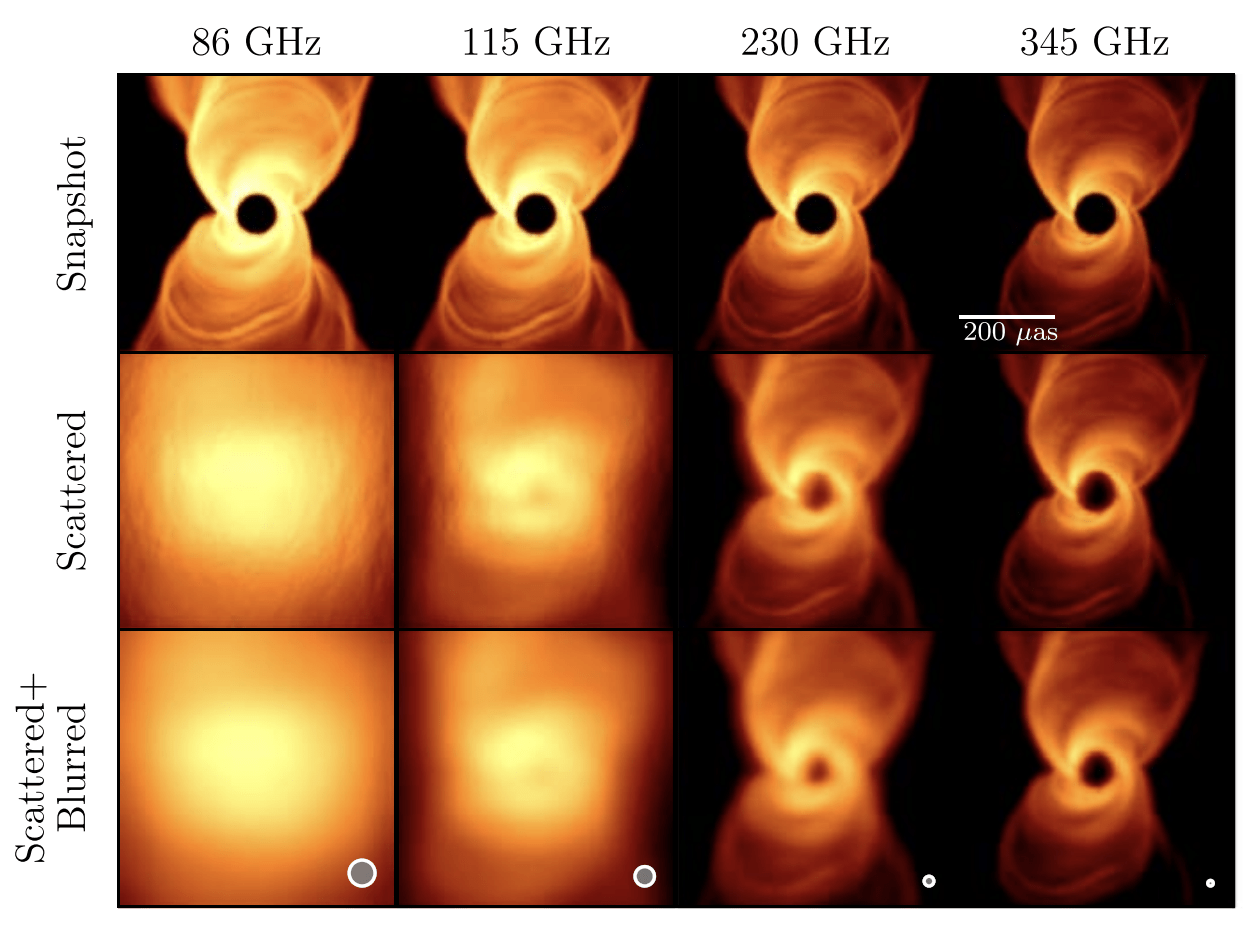
Prospects of Detecting a Jet in Sagittarius A* with VLBI (Chavez et. al., ApJ 2024)


BHEX Mini

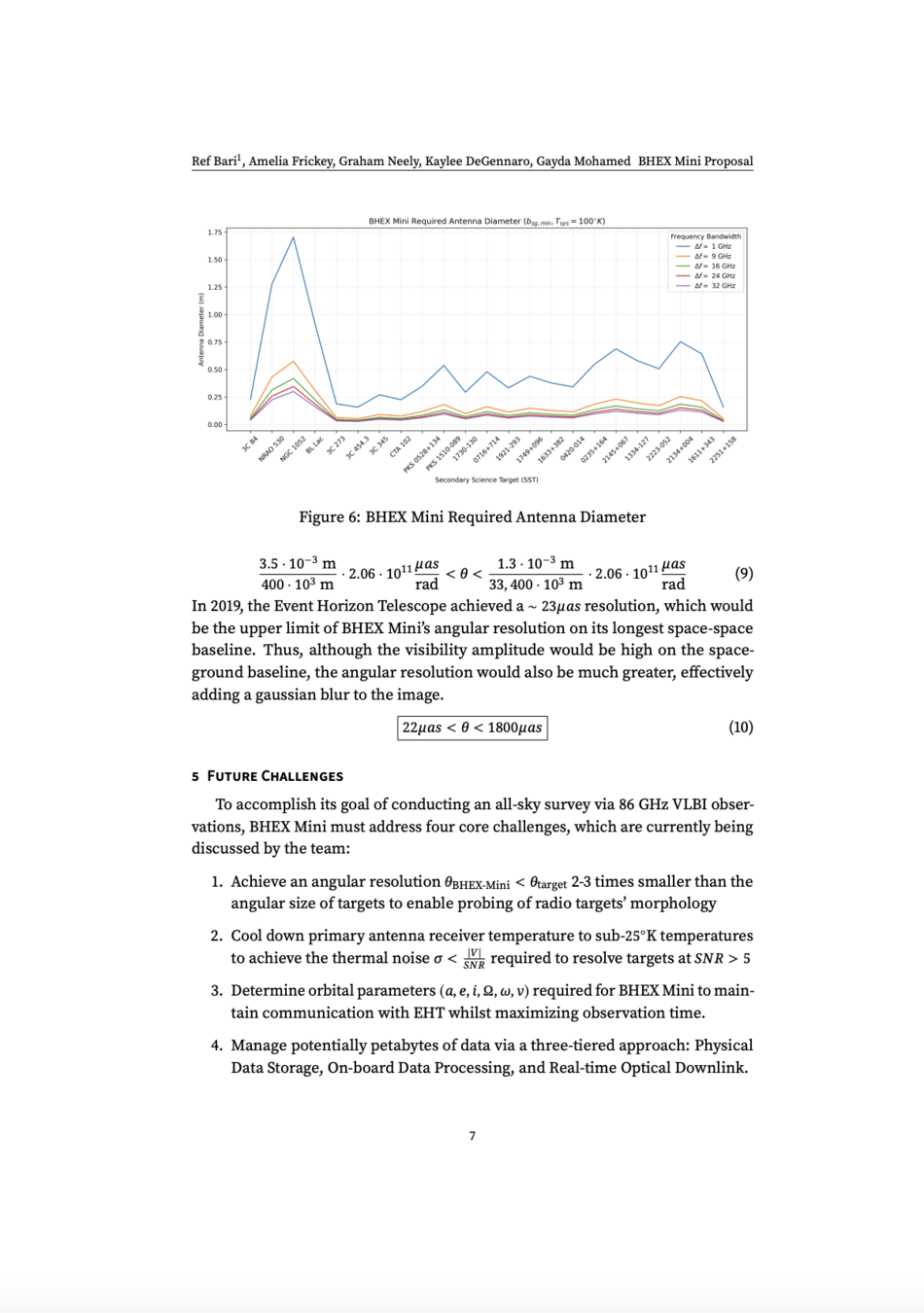
Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution:
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Rapid coverage of (u,v) plane
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO





- What kind of targets can we observe with this angular resolution?


BHEX Mini

Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution:
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Rapid coverage of (u,v) plane
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO





- What kind of targets can we observe with this angular resolution?




BHEX Mini

Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution:
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Rapid coverage of (u,v) plane
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO





- What kind of targets can we observe with this angular resolution?



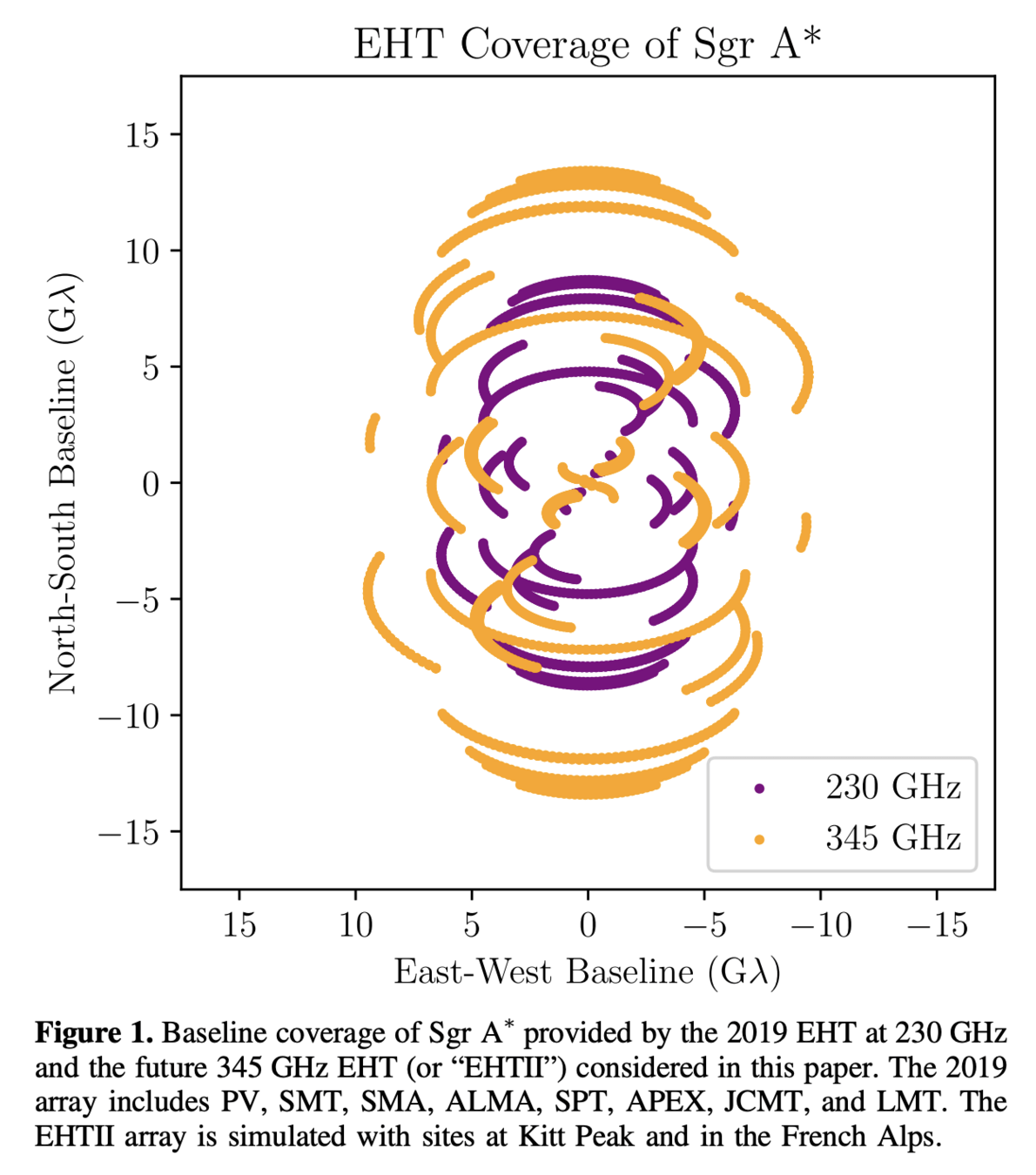
Metrics and Motivations for Earth–Space VLBI: Time-resolving Sgr A* with the Event Horizon Telescope (Palumbo et. al., ApJ 2019)

BHEX Mini

Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution:
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Rapid coverage of (u,v) plane
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO





- What kind of targets can we observe with this angular resolution?





Metrics and Motivations for Earth–Space VLBI: Time-resolving Sgr A* with the Event Horizon Telescope (Palumbo et. al., ApJ 2019)

BHEX Mini

Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution:
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Rapid coverage of (u,v) plane



- What kind of targets can we observe with this angular resolution?
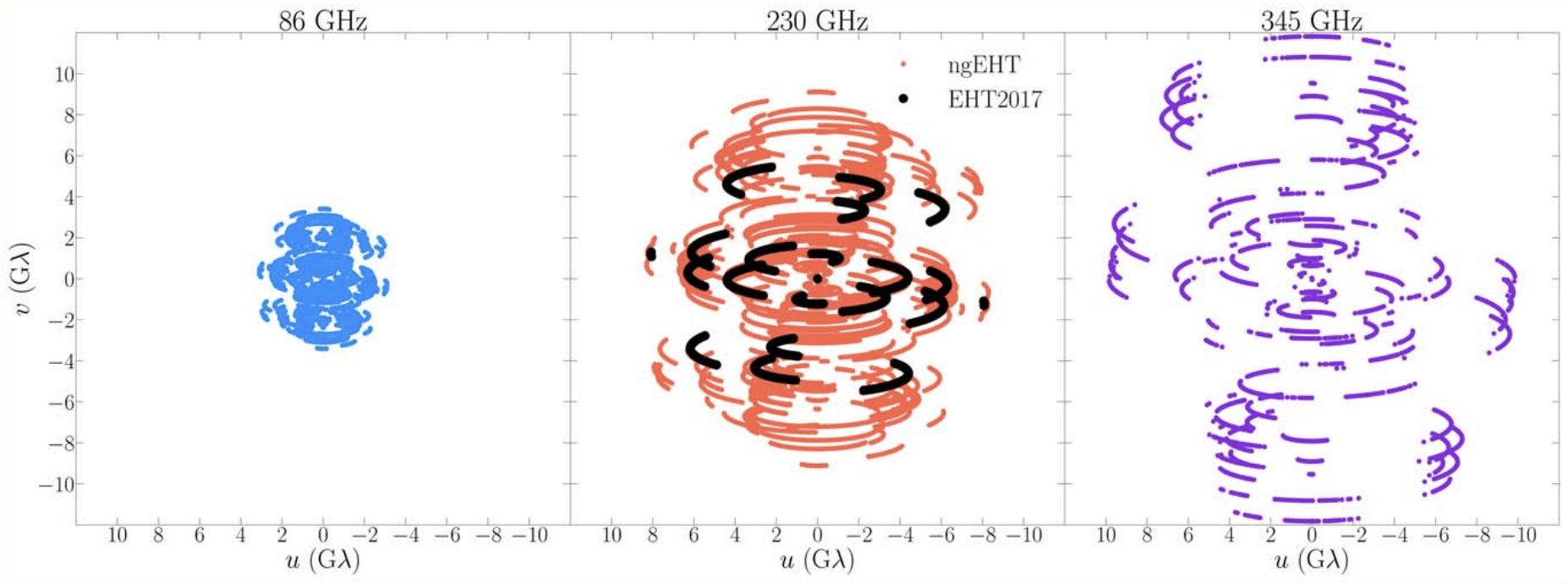
Multifrequency Black Hole Imaging for the Next-generation Event Horizon Telescope (Chael et. al., 2023, ApJ)




BHEX Mini

Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution:
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Rapid coverage of (u,v) plane
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO





- What is the integration time for BHEX Mini on the (u,v) plane?
- Could BHEX Mini possibly enable direct imaging of dynamic accretion disk around Sgr A*? (i.e., creating a movie of a black hole!)

BHEX Mini

Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Rapid coverage of (u,v) plane
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO






BHEX Mini

Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Rapid coverage of (u,v) plane
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO







Maximum data transmission rate (in bits per second); How fast can you send data from BHEX Mini to the earth?

BHEX Mini

Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Rapid coverage of (u,v) plane
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO







Power of Transmitted Signal: Strength of downlink signal in Watts (i.e., shouting louder to be heard further away!)

BHEX Mini

Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Rapid coverage of (u,v) plane
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO







Transmitter Gain: How well-focused your signal is when it leaves the satellite
(i.e., shouting into a megaphone instead of into the wind)

BHEX Mini

Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Rapid coverage of (u,v) plane
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO







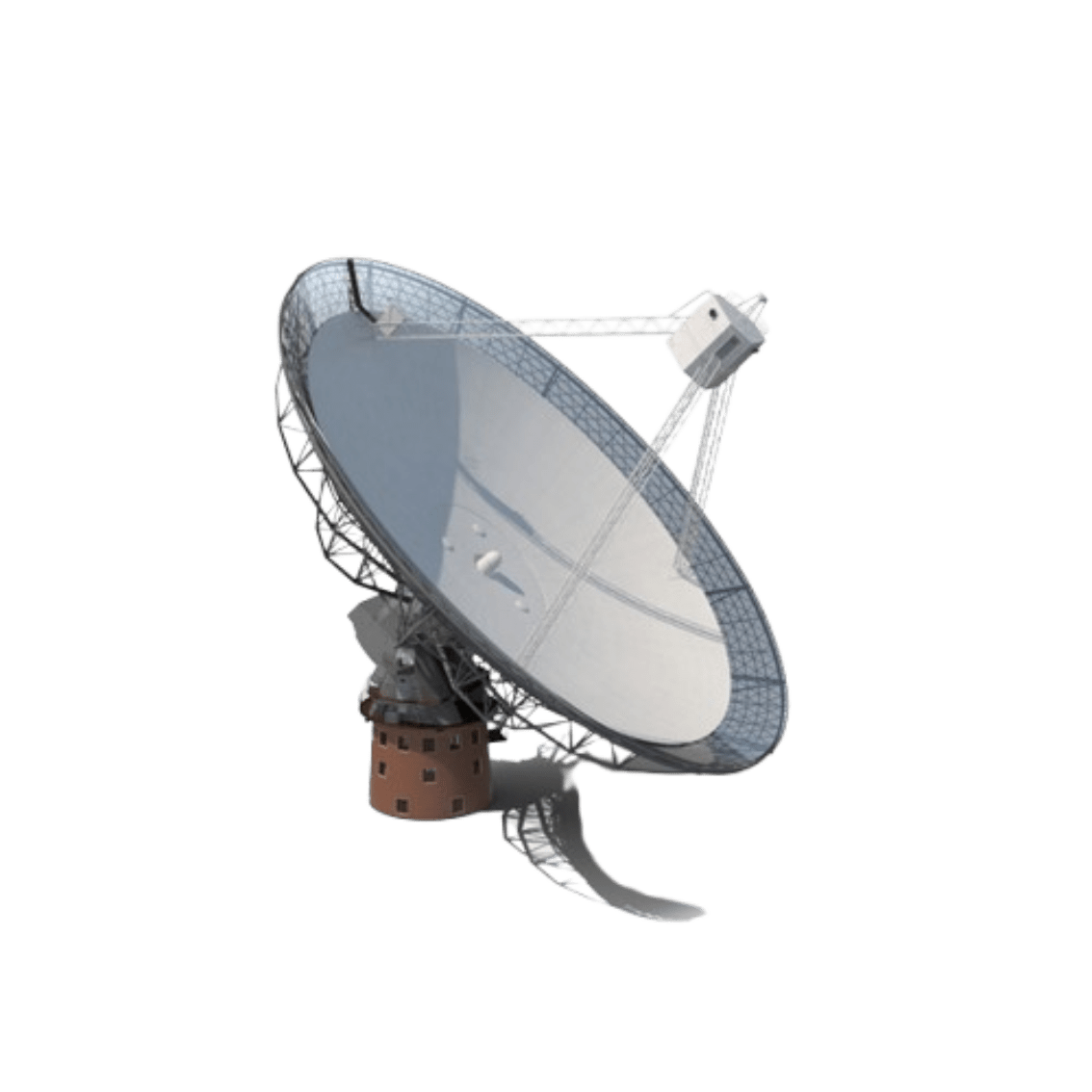
Receiver Gain: How effectively the ground station collects and concentrates the incoming signal (i.e., ALMA's big dish listening to our incoming signal)
Received Power: How strong is the signal once it hits the ground receiver? (after traveling through empty space)

BHEX Mini

Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Rapid coverage of (u,v) plane
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO







Receiver Gain: How effectively the ground station collects and concentrates the incoming signal (i.e., ALMA's big dish listening to our incoming signal)
Distance: How much distance did the signal travel through free space? (LEO vs. MEO!)

BHEX Mini

Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Rapid coverage of (u,v) plane
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO







Receiver Gain: How effectively the ground station collects and concentrates the incoming signal (i.e., ALMA's big dish listening to our incoming signal)
- Since BHEX Mini's laser downlink would suffer less signal loss from LEO than BHEX at MEO, can we transmit more data?
- Can this be leveraged to use 2-bit quantization instead of 1-bit quantization?

BHEX Mini
Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Rapid coverage of (u,v) plane
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO




Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Rapid coverage of (u,v) plane
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO





Decreased ISM scattering at LEO than MEO



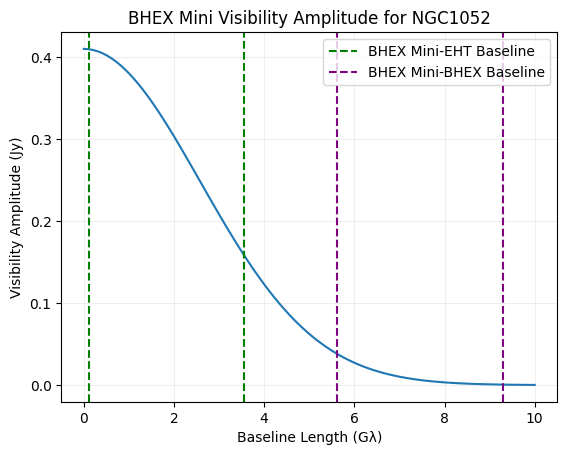
BHEX Mini
Decreased ISM scattering at LEO than MEO


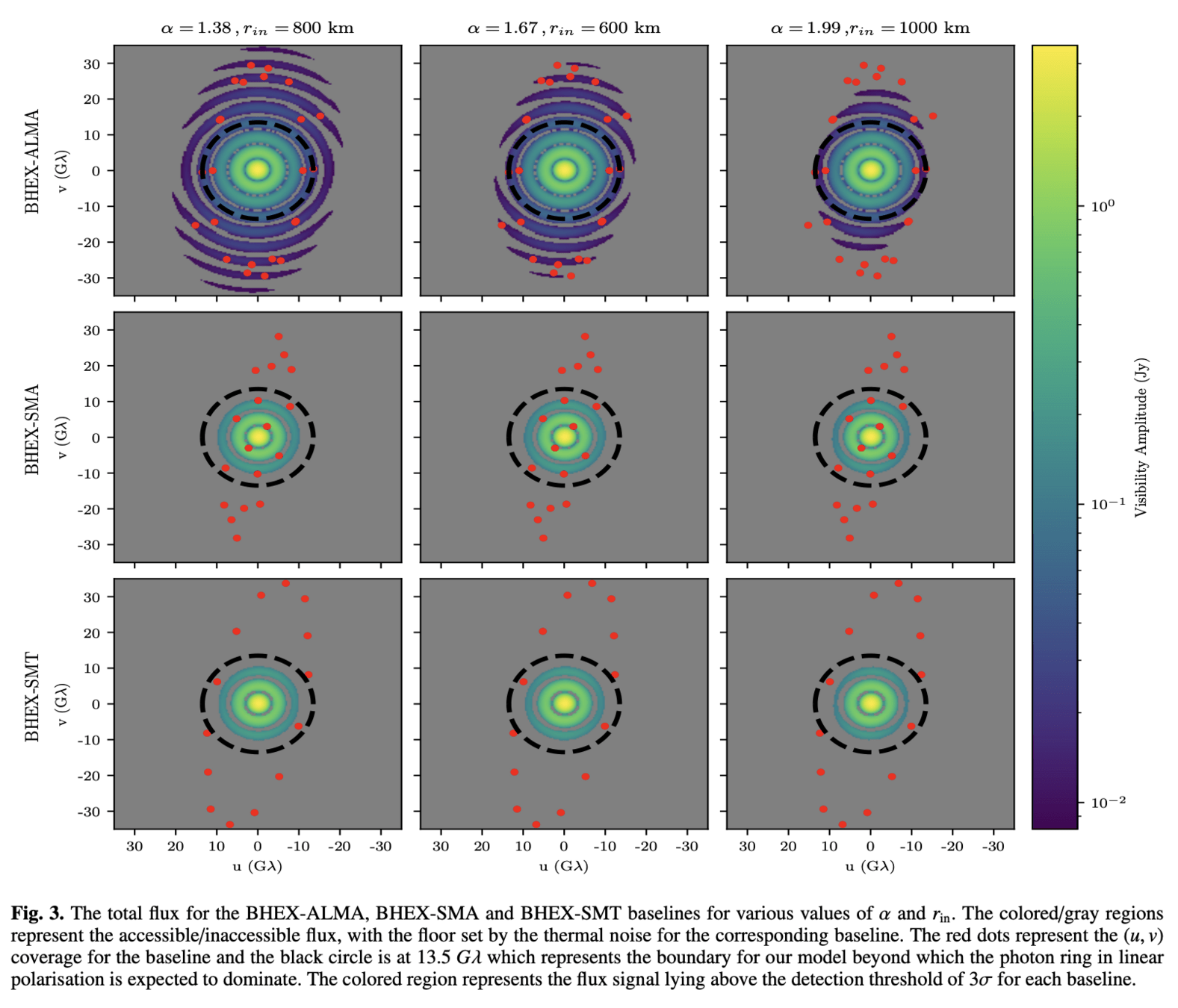
Orbit design for mitigating interstellar scattering effects in Earth-space VLBI observations of Sgr A* (Aditya Tamar, Ben Hudson, Daniel C.M. Palumbo, A&A, 2025)

BHEX Mini
Decreased ISM scattering at LEO than MEO


Intrinsic Gaussian Source

BHEX Mini
Decreased ISM scattering at LEO than MEO


ISM Scattering
- At MEO, BHEX is 20x the orbital altitude of BHEX Mini
- BHEX observes at a f=320 GHz, 4x higher than BHEX Mini

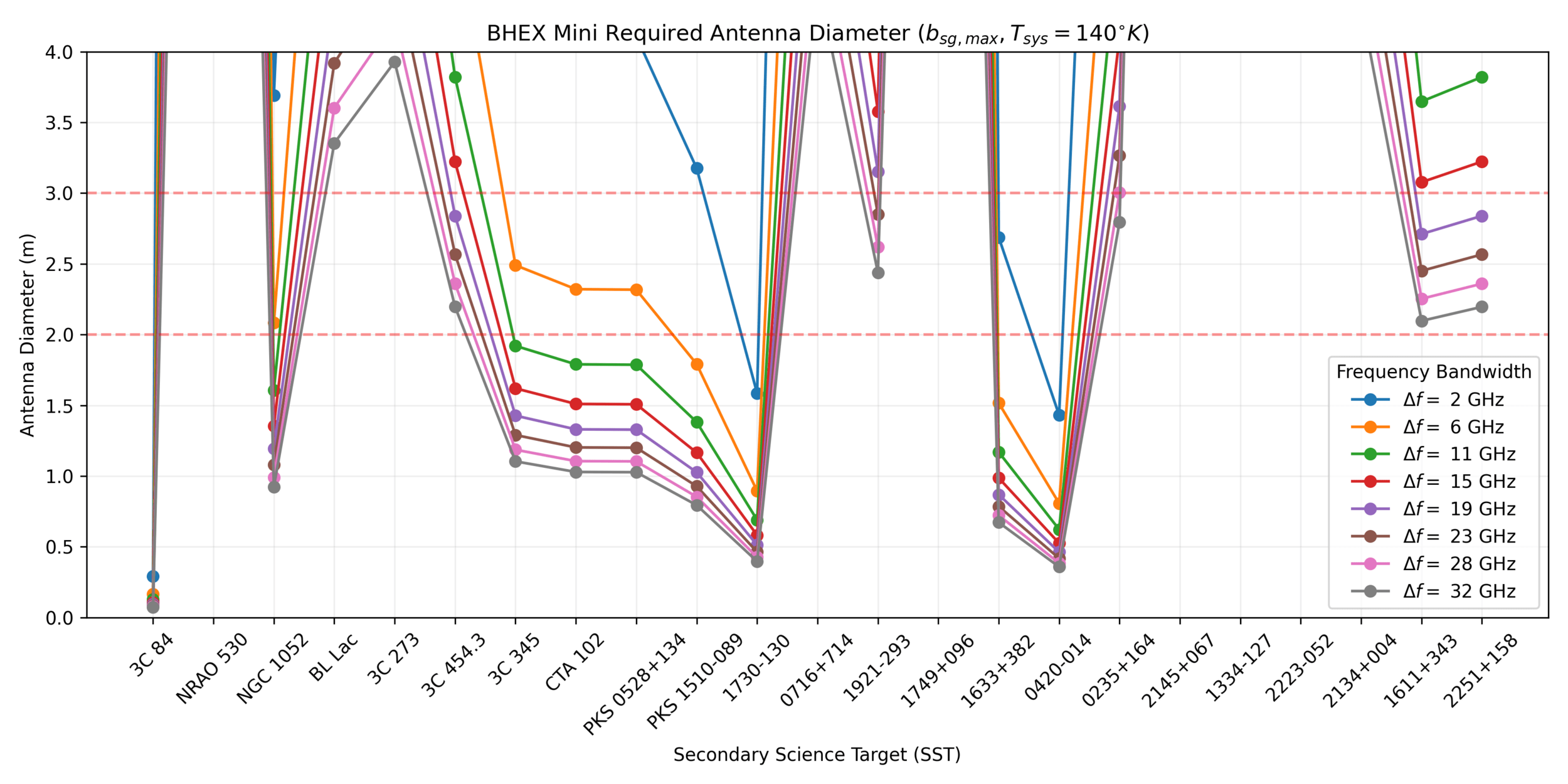
BHEX Mini
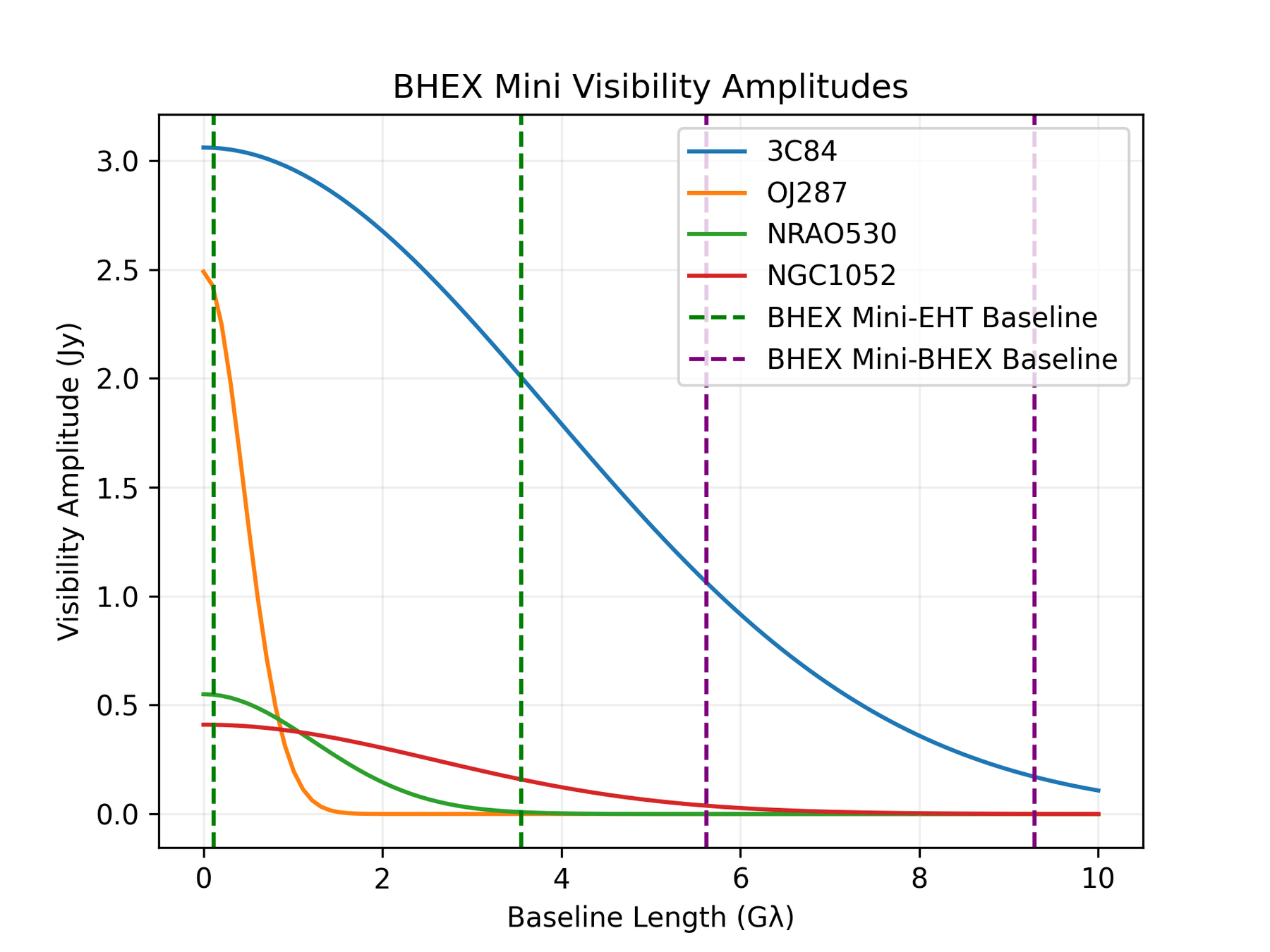
Decreased ISM scattering at LEO than MEO


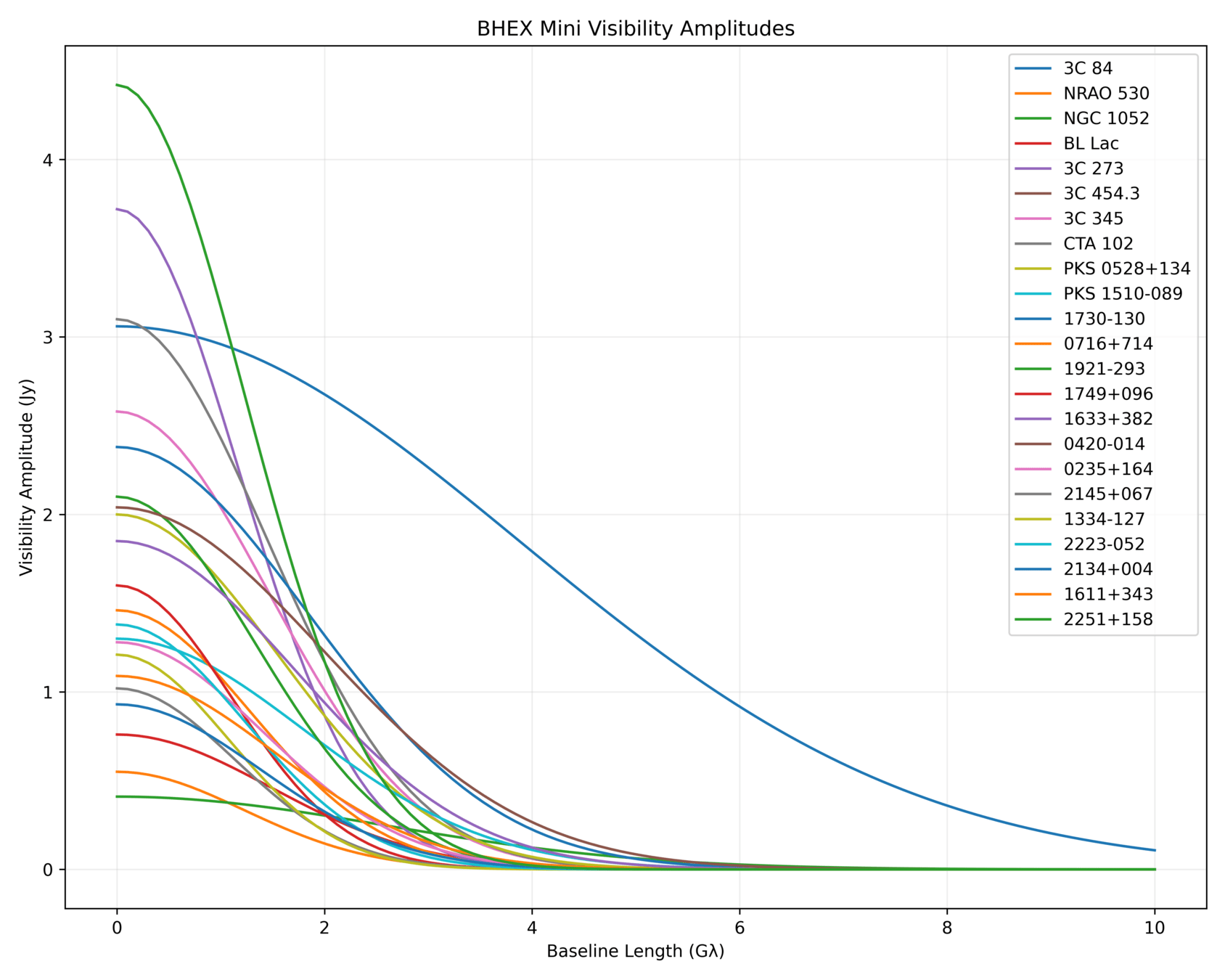
BHEX Mini Visibility Amplitude Advantage
Regardless of Source Flux Density!

BHEX Mini

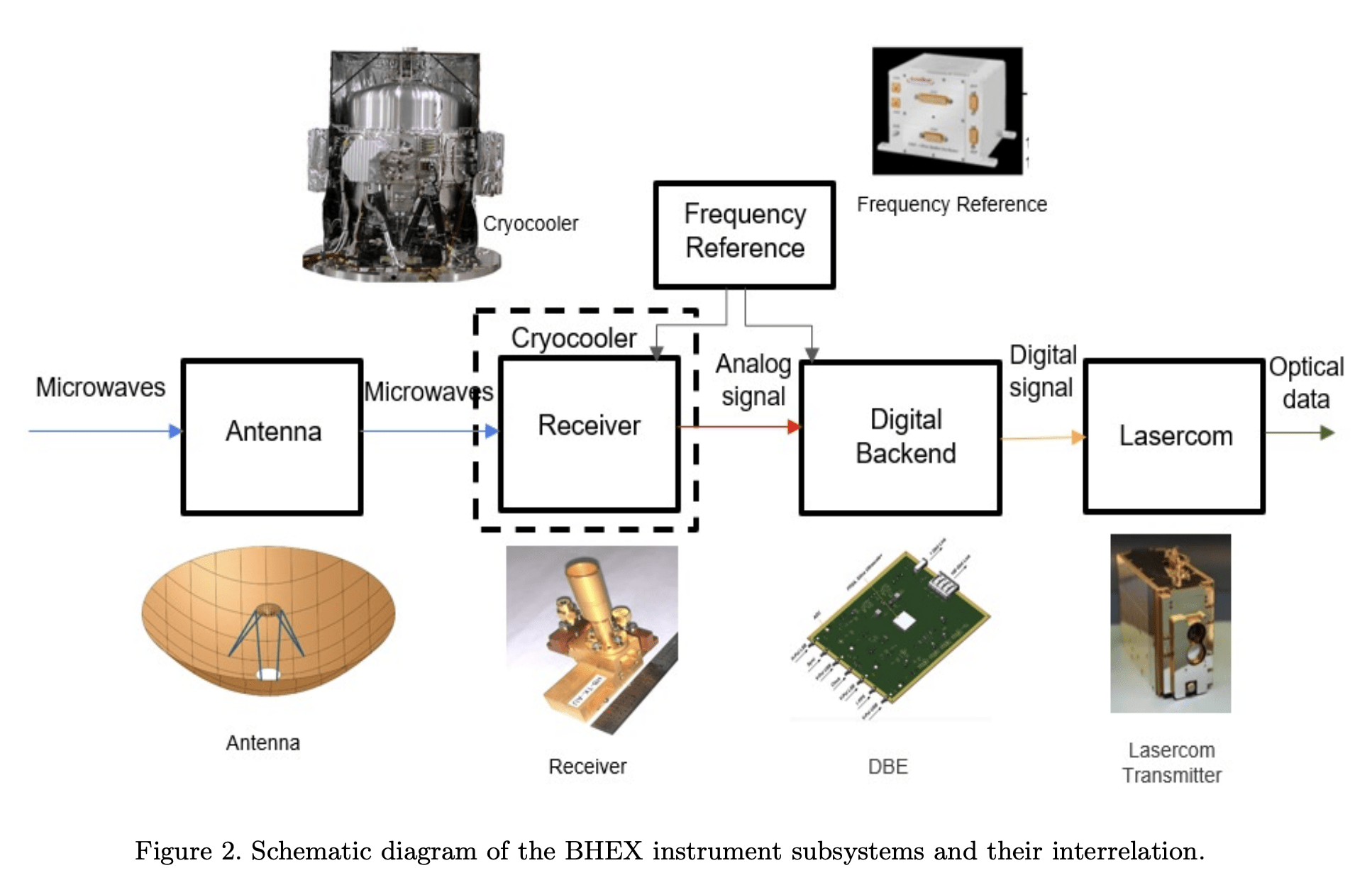

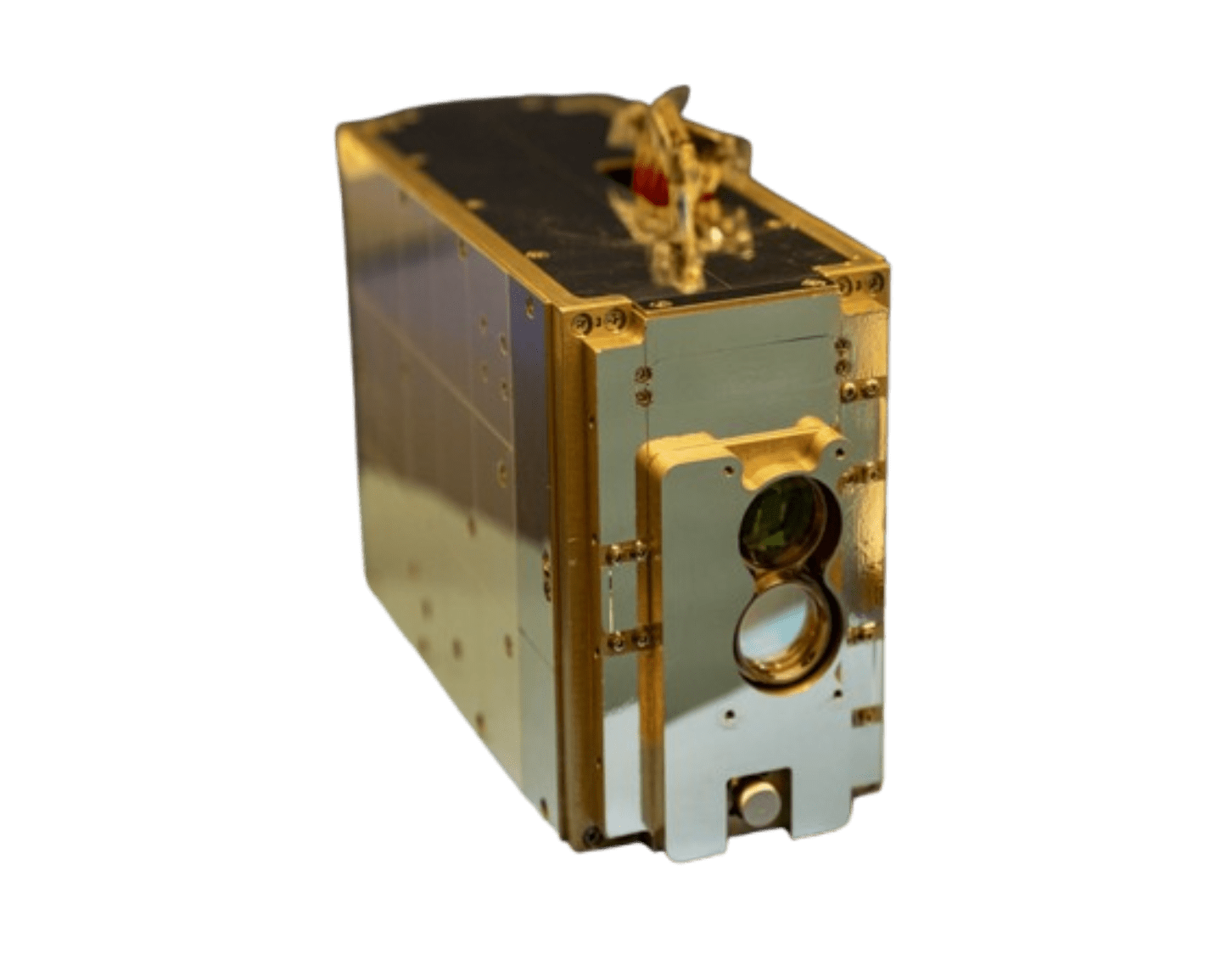




BHEX Mini


BHEX Mini









Antenna

BHEX Mini









Receiver

BHEX Mini









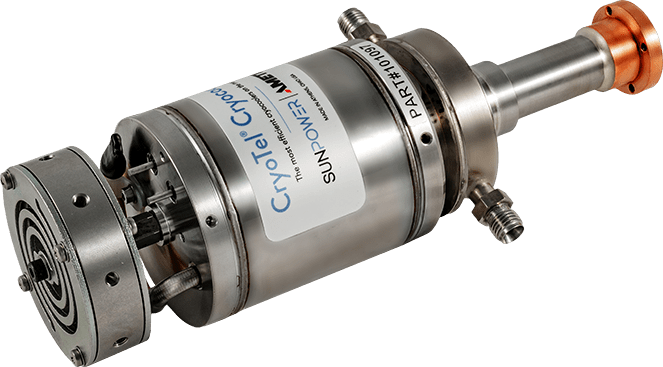
Cryocooler

BHEX Mini









Cryocooler

HiPTC Heat Intercepted Pulse Tube Cooler
- Cost: $10 Million
- Mass: 22kg
-
Cooling power
- 400 mW at 15K
- 5.2 W at 100K
- Electric power: 300 W

BHEX Mini









Solar Panels

BHEX Mini



Ultra-Stable Oscillator
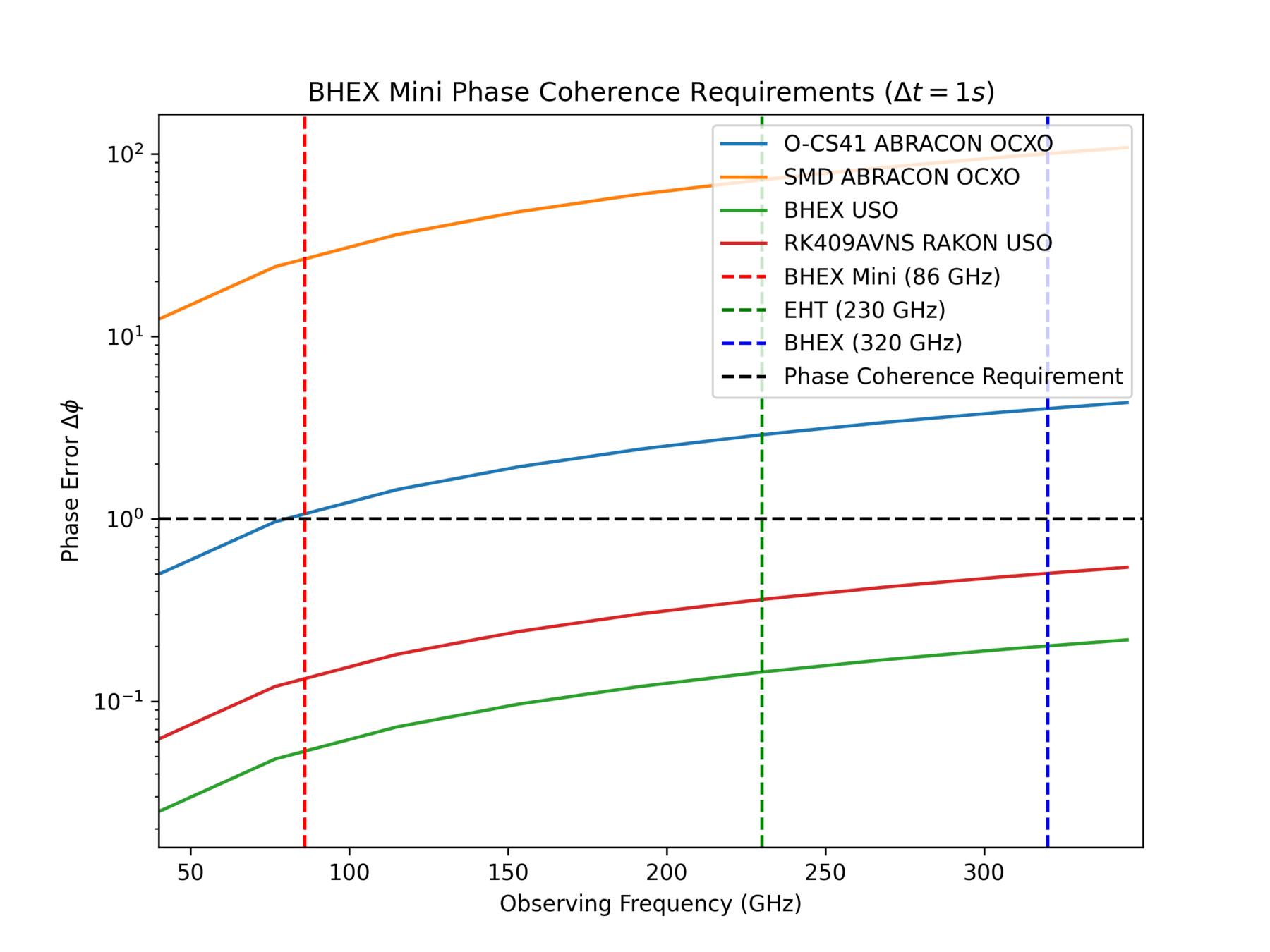
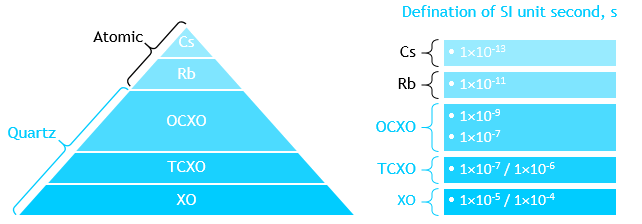

BHEX Mini



Ultra-Stable Oscillator
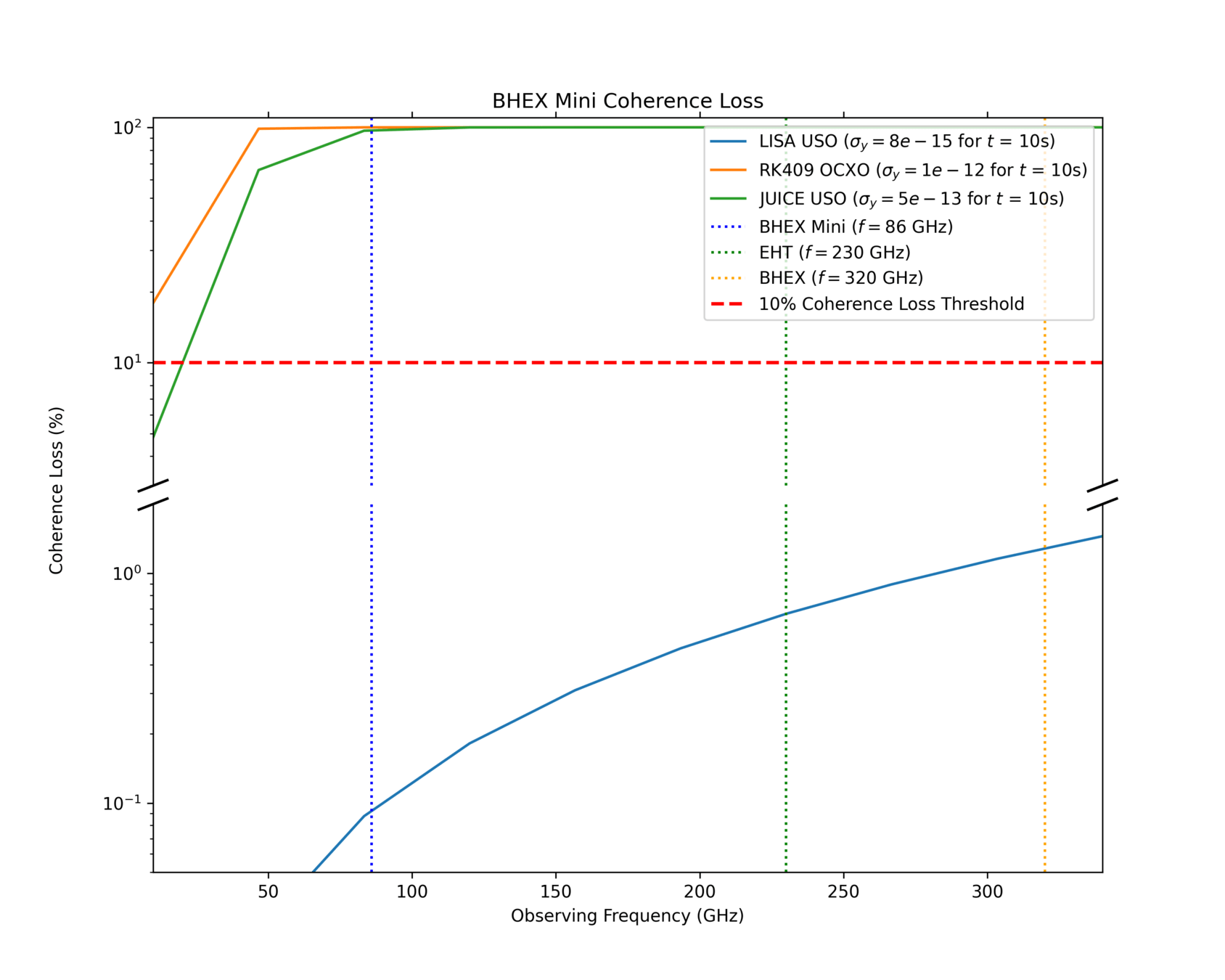
Phase Error

BHEX Mini



Ultra-Stable Oscillator


BHEX Mini



Ultra-Stable Oscillator
Allan Deviation
ABRACON SMD OCXO


BHEX Mini









Digital Backend

BHEX Mini



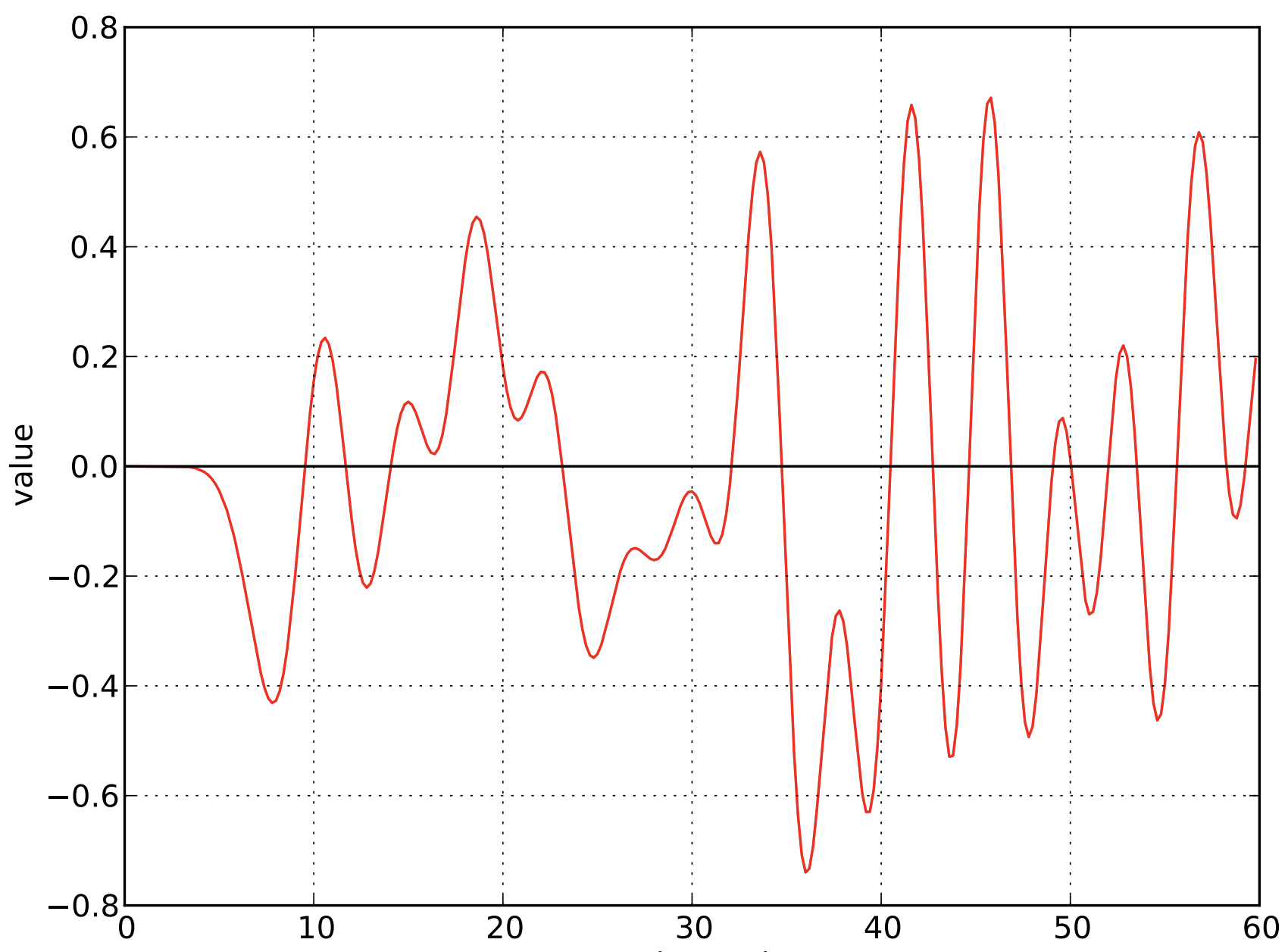
Original Analog Radio Signal

BHEX Mini



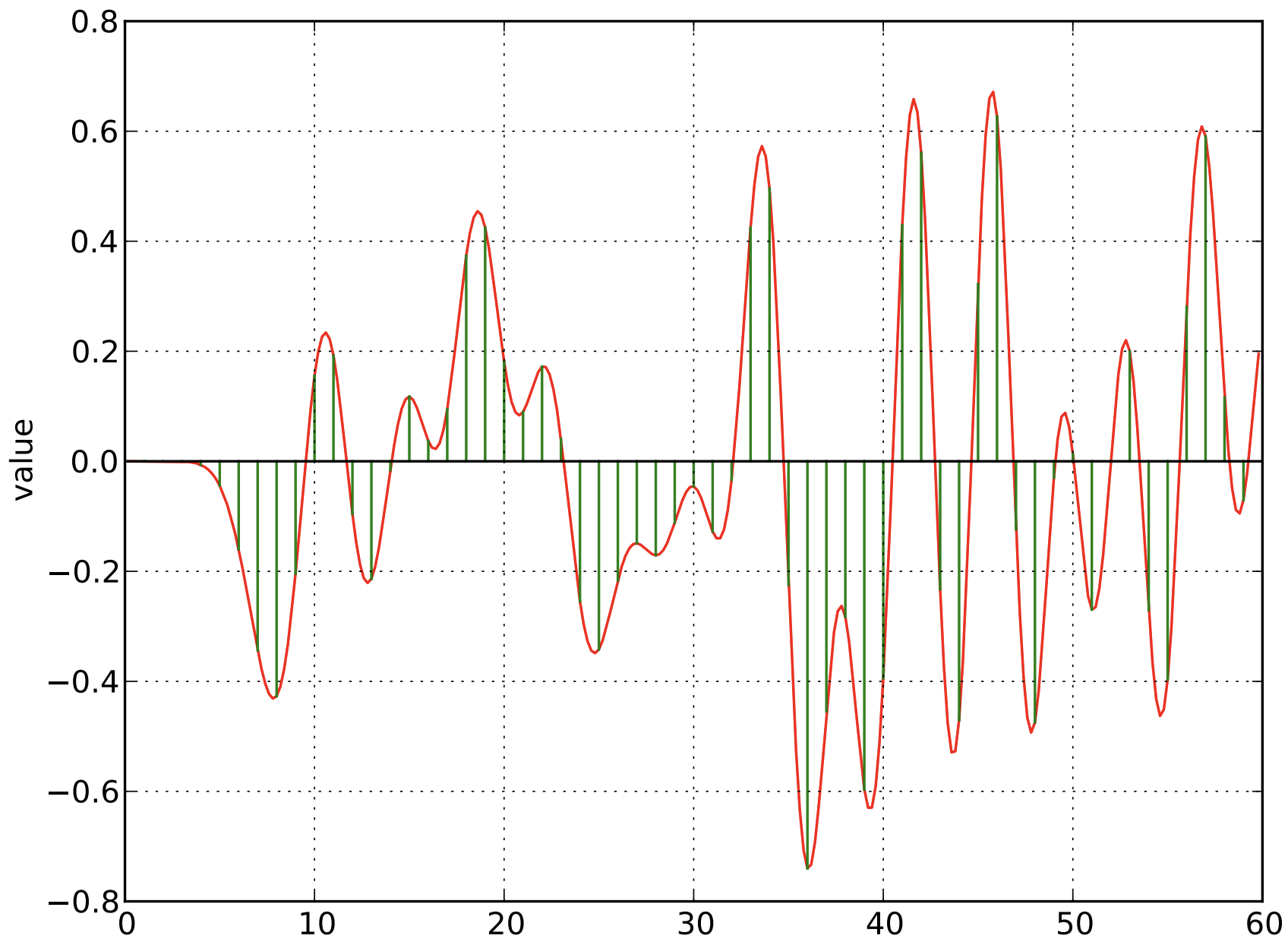
Sample the Signal every Unit Interval
Nyquist-Shannon Sampling Theorem

BHEX Mini



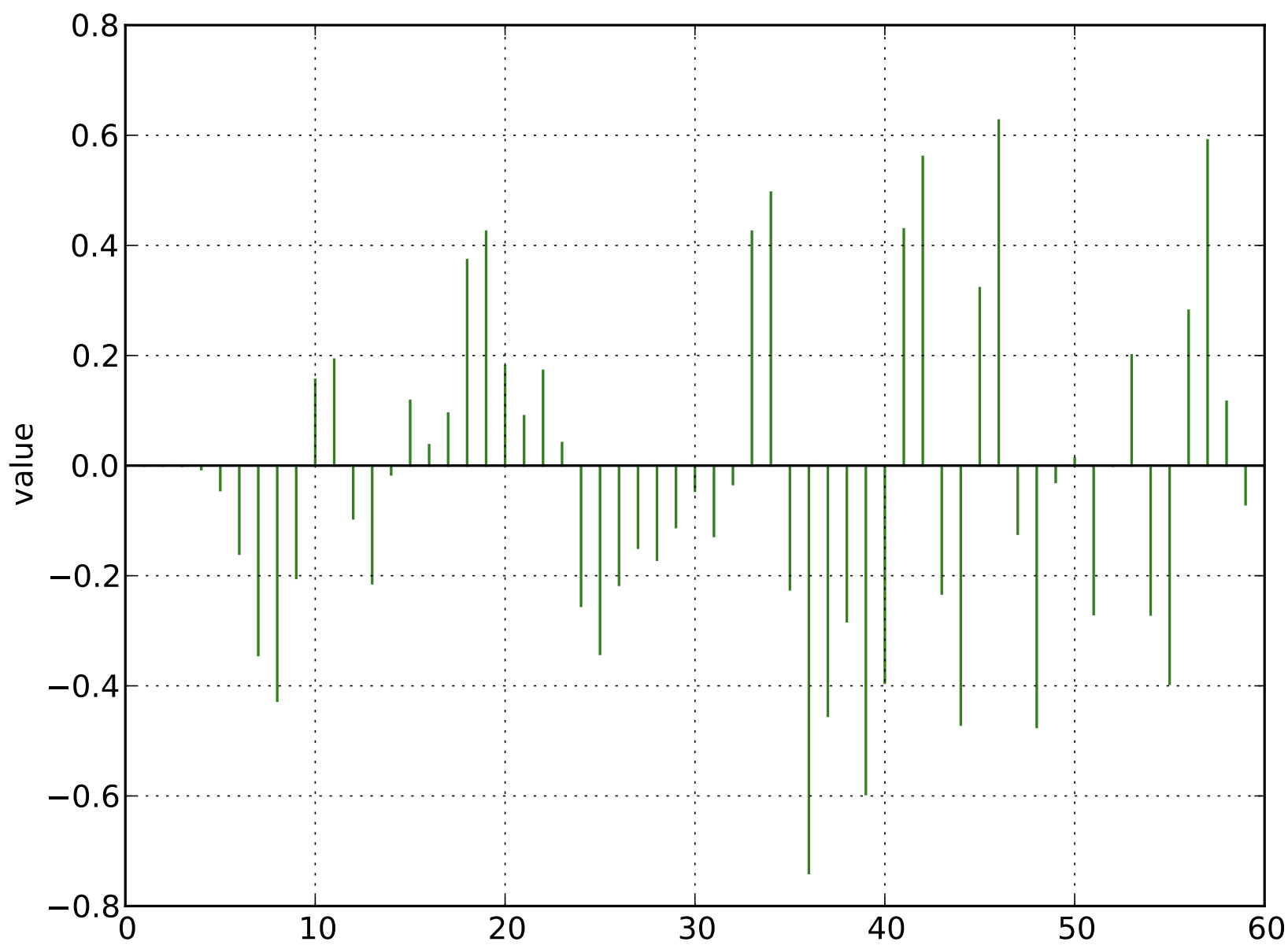
Retain only the samples and record the sign of the voltage for each sample

BHEX Mini



Reconstruct the original signal
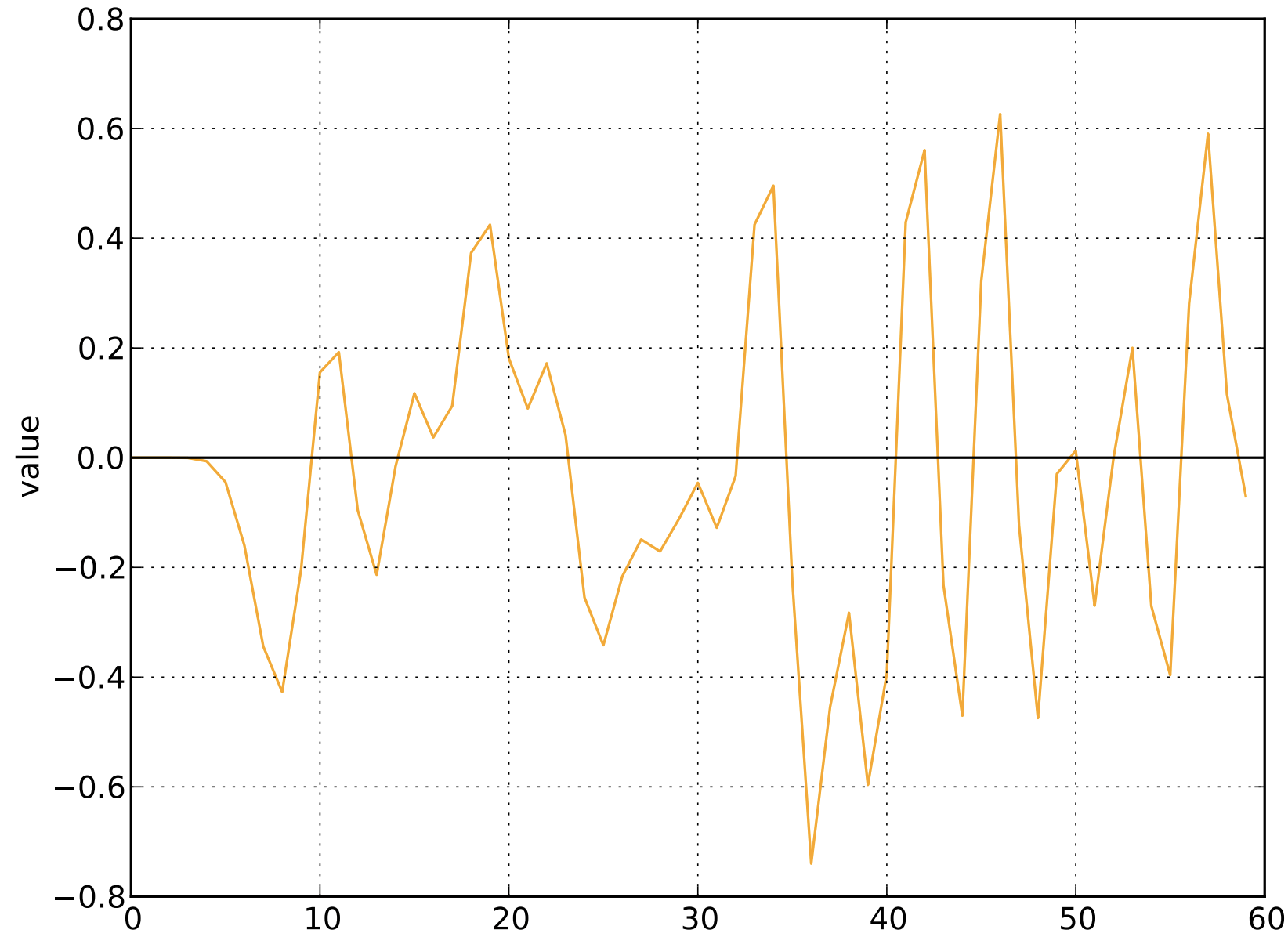

BHEX Mini




BHEX Mini



Quantization Efficiency: how much of the analog SNR is retained after digitization

BHEX Mini


SNR: Signal to Noise Ratio

BHEX Mini


Data Generation Rate: In Bits per Second

BHEX Mini

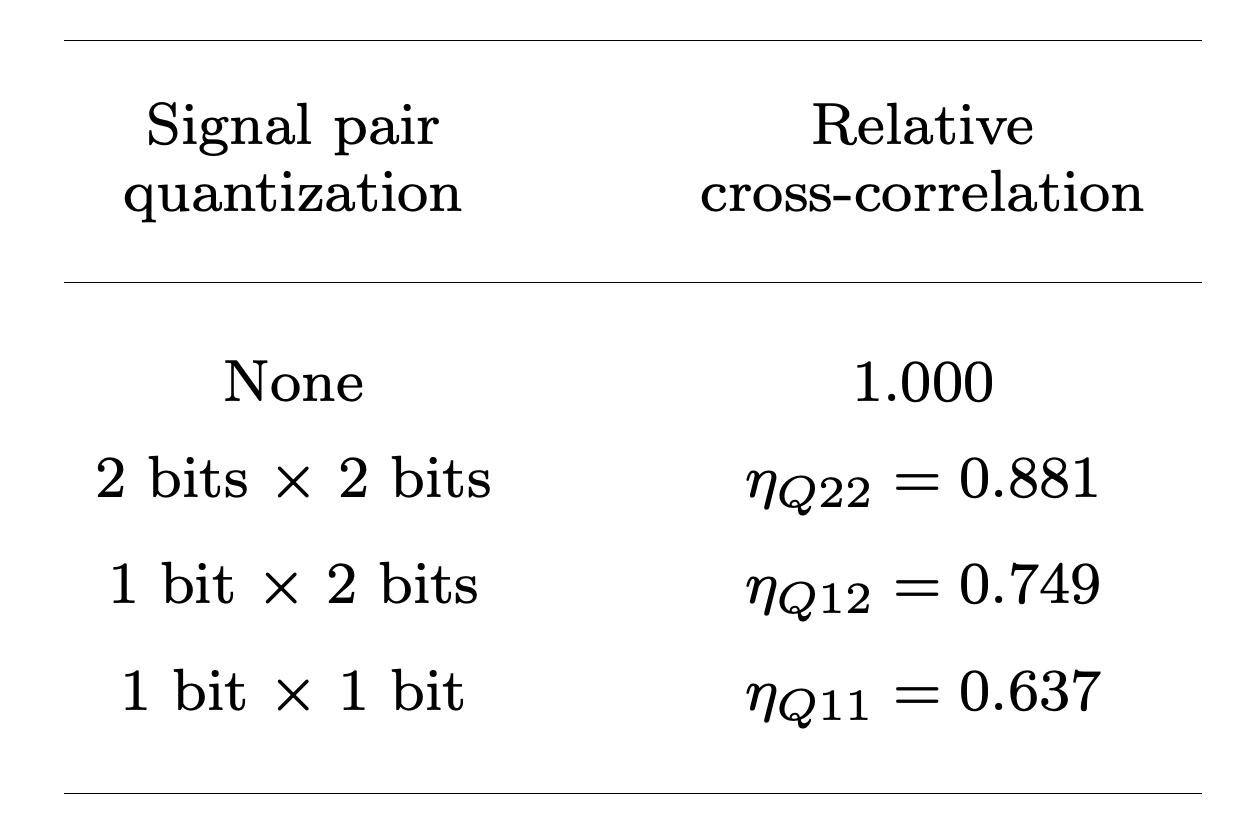
Cross-Correlation


🕒 Prospective Timeline

June
July
August
September

🕒 Prospective Timeline

June
July
August
September
- NASA NIAC 2025 Phase I Step I
- SpaceCom Conference 2026
- Brown Nelson + Hazeltine Grants
-
Antenna Focus
- Nacer Chahat
- Emmanuel Decrossas

🕒 Prospective Timeline

June
July
August
September


- NSF Foundational Research in Robotics Grant (FRR)
- Fall Walls Foundation Selections
- NASA NIAC 2025 Phase I Step I
- SpaceCom Conference 2026
- Brown Nelson + Hazeltine Grants
-
Antenna Focus
- Nacer Chahat
- Emmanuel Decrossas
-
Cryocooler Focus
- SunPower
- Blue Marble

🕒 Prospective Timeline

June
July
Aug
September


- NSF Foundational Research in Robotics Grant (FRR)
- Fall Walls Foundation Selections
- Brown University Co-Lab
- NASA NIAC Phase I Round I Step B Selections Announced
-
Solar Panel Focus
- DCubed Inc.
- DHV Tech
- NASA NIAC 2025 Phase I Step I
- SpaceCom Conference 2026
- Brown Nelson + Hazeltine Grants
-
Antenna Focus
- Nacer Chahat
- Emmanuel Decrossas
-
Cryocooler Focus
- SunPower
- Blue Marble

🕒 Prospective Timeline

June
July
Aug
Sep

-
Cryocooler Focus
- SunPower
- Blue Marble

- NSF Foundational Research in Robotics Grant (FRR)
- Fall Walls Foundation Selections

- Brown University Co-Lab
- NASA NIAC Phase I Round I Step B Selections Announced
-
Solar Panel Focus
- DCubed Inc.
- DHV Tech
- NSF Advanced Technologies and Instrumentation for the Astronomical Sciences (ATI)
-
Data Downlink Focus
- MIT Lincoln Labs
- ALICE/CLICK Teams
- NASA NIAC 2025 Phase I Step I
- SpaceCom Conference 2026
- Brown Nelson + Hazeltine Grants
-
Antenna Focus
- Nacer Chahat
- Emmanuel Decrossas

💰Funding Oppurtunities


June
$3,000
💰Funding Oppurtunities


July

$175,000
$3,000
$175,000
💰Funding Oppurtunities


Sep


$175,000
$3,000
$250,000
💰Funding Oppurtunities




Oct


$175,000
$3,000
$250,000
💰Funding Oppurtunities