Binary Black Holes
A GENERIC Approach
Ref Bari
Advisor: Prof. Brendan Keith


Binary Black Holes
A GENERIC Approach
- Proved equivalence between two parameterizations of Schwarzschild Metric
- Parameter Estimation for Schwarzschild Metric
- AI for Schwarzschild Metric (in Hamiltonian form)!

Binary Black Holes
A GENERIC Approach
- Proved equivalence between two parameterizations of Schwarzschild Metric
- Parameter Estimation for Schwarzschild Metric
- AI for Schwarzschild Metric (in Hamiltonian form)!

Binary Black Holes
A GENERIC Approach
- Proved equivalence between two parameterizations of Schwarzschild Metric
- Parameter Estimation for Schwarzschild Metric
- AI for Schwarzschild Metric (in Hamiltonian form)!

Binary Black Holes
A GENERIC Approach
- Proved equivalence between two parameterizations of Schwarzschild Metric
- Parameter Estimation for Schwarzschild Metric
- AI for Schwarzschild Metric (in Hamiltonian form)!

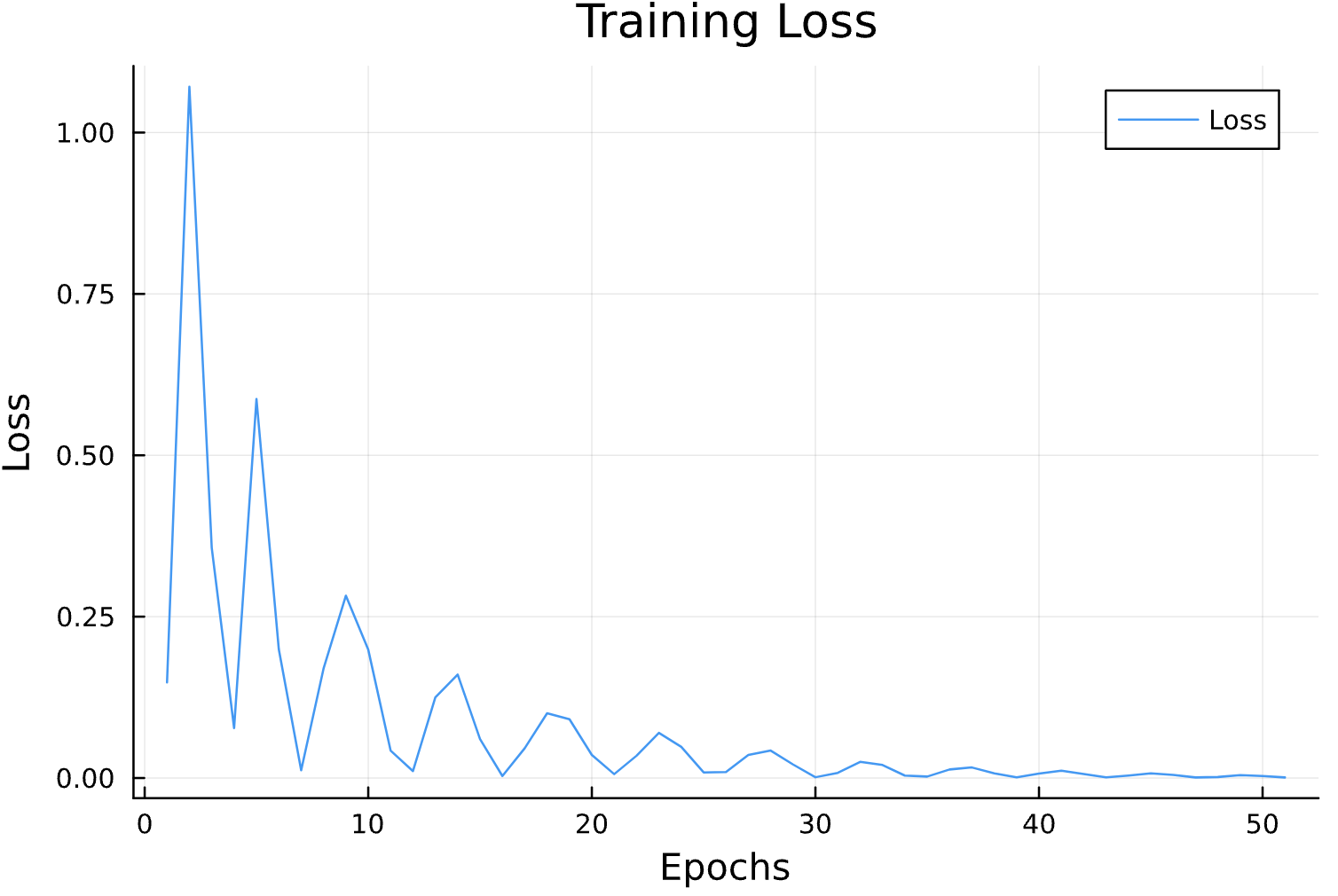
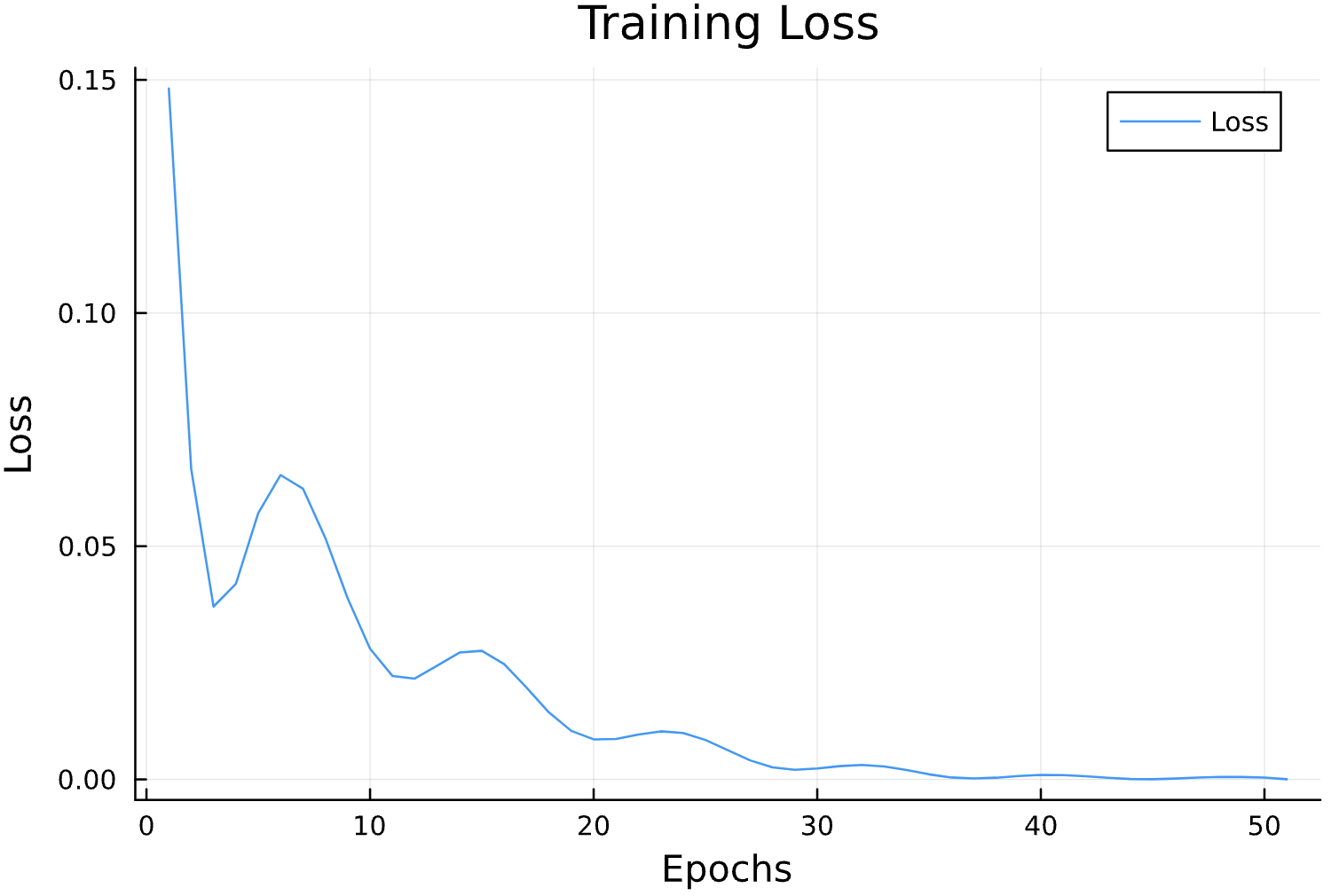
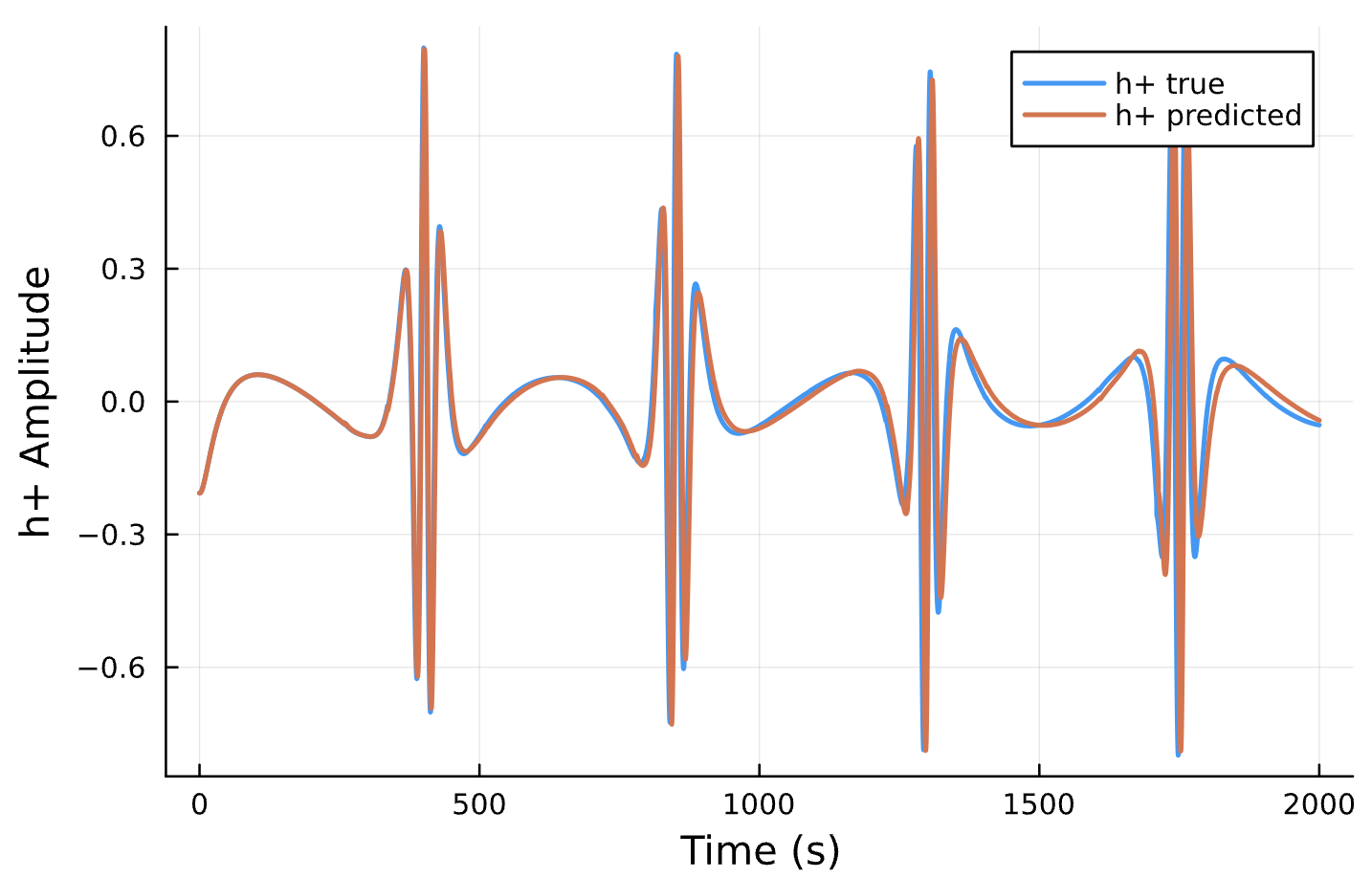
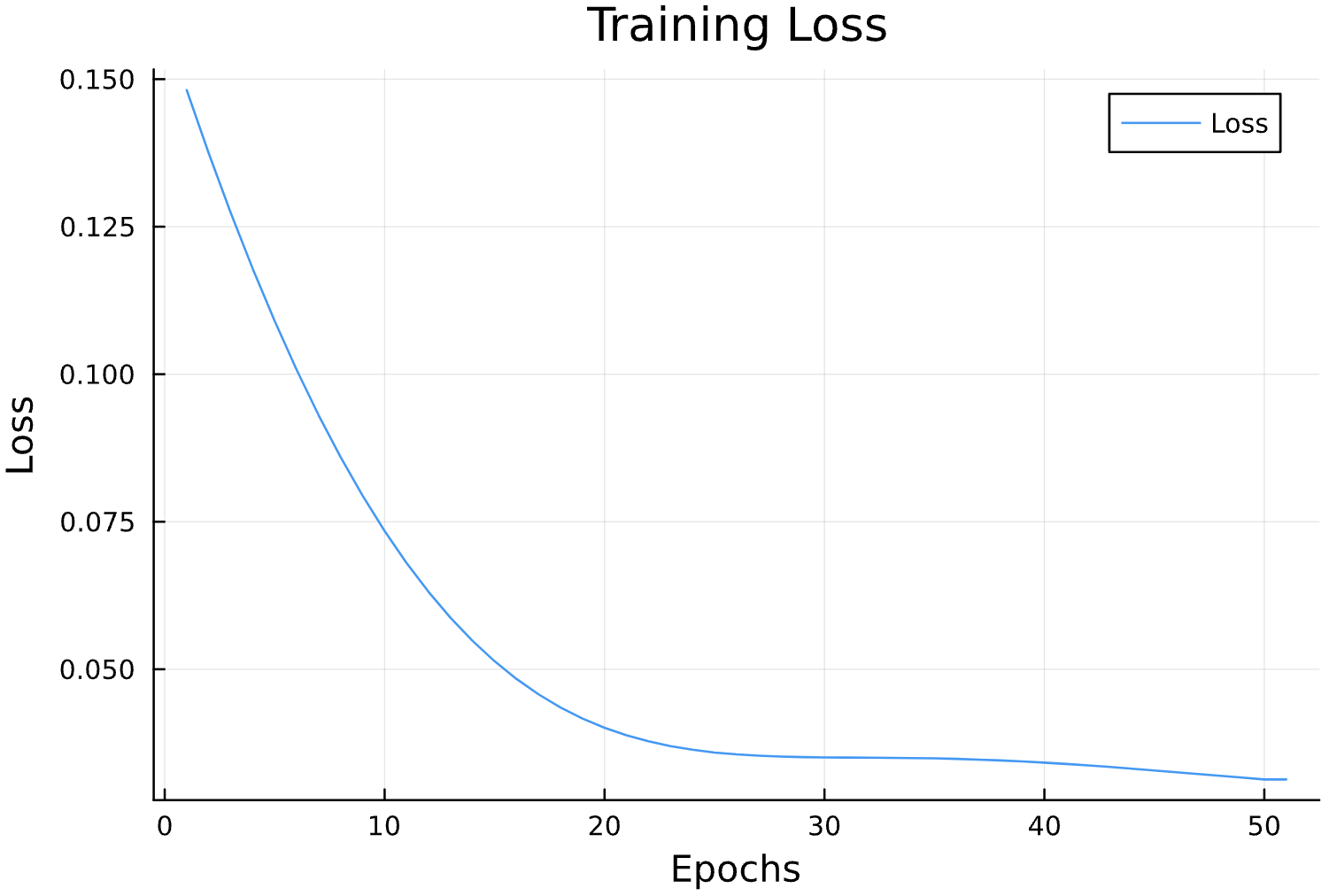
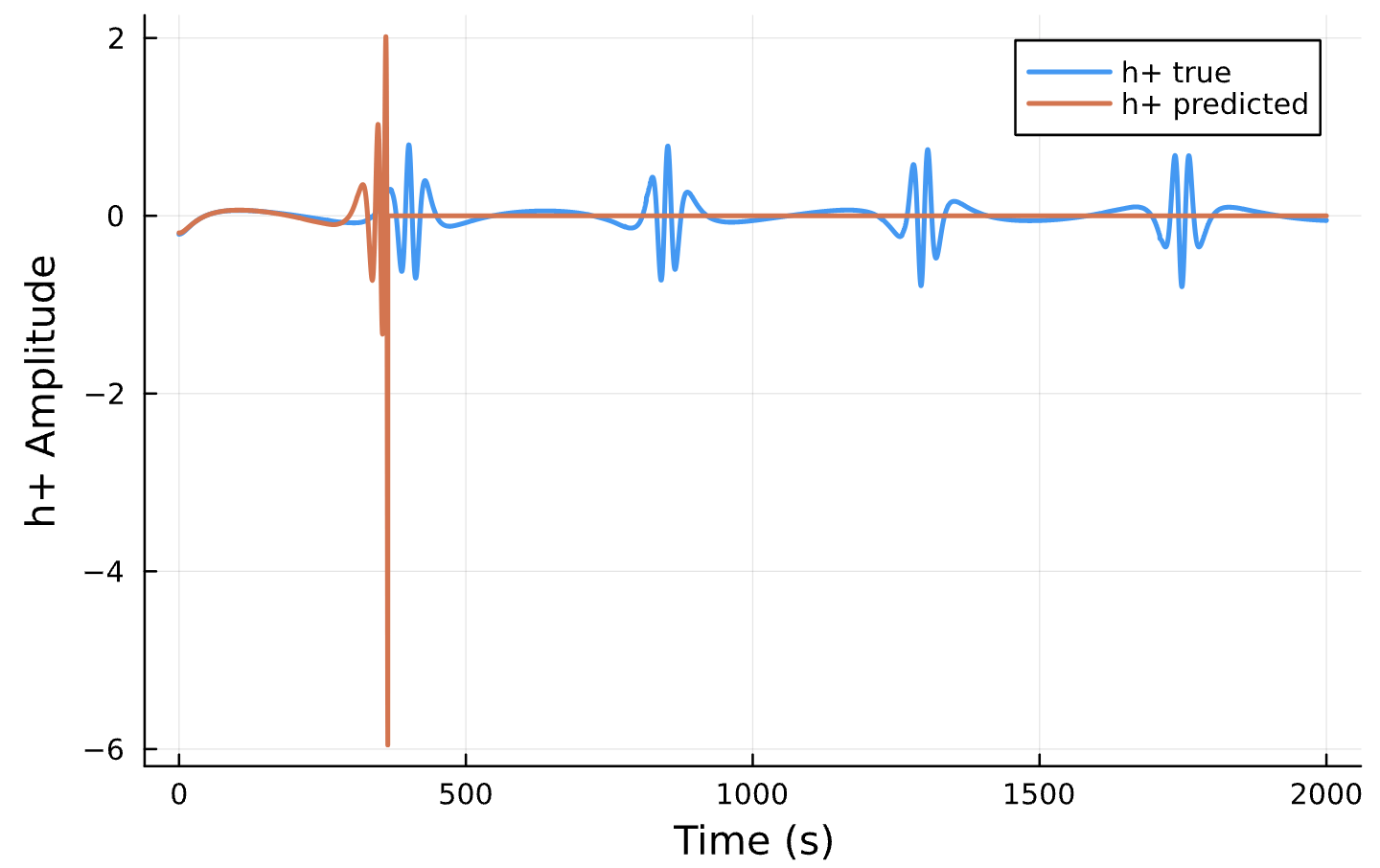
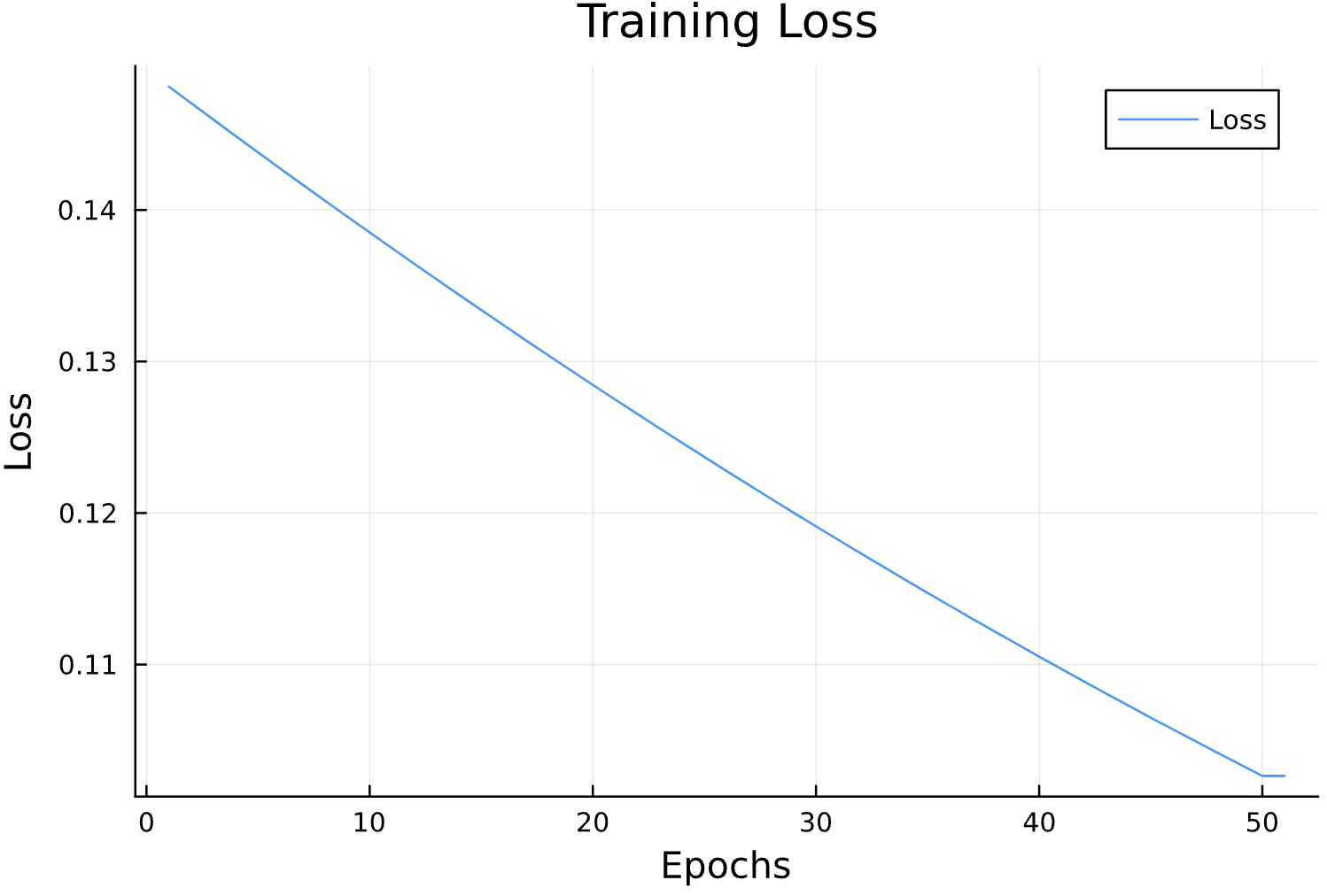
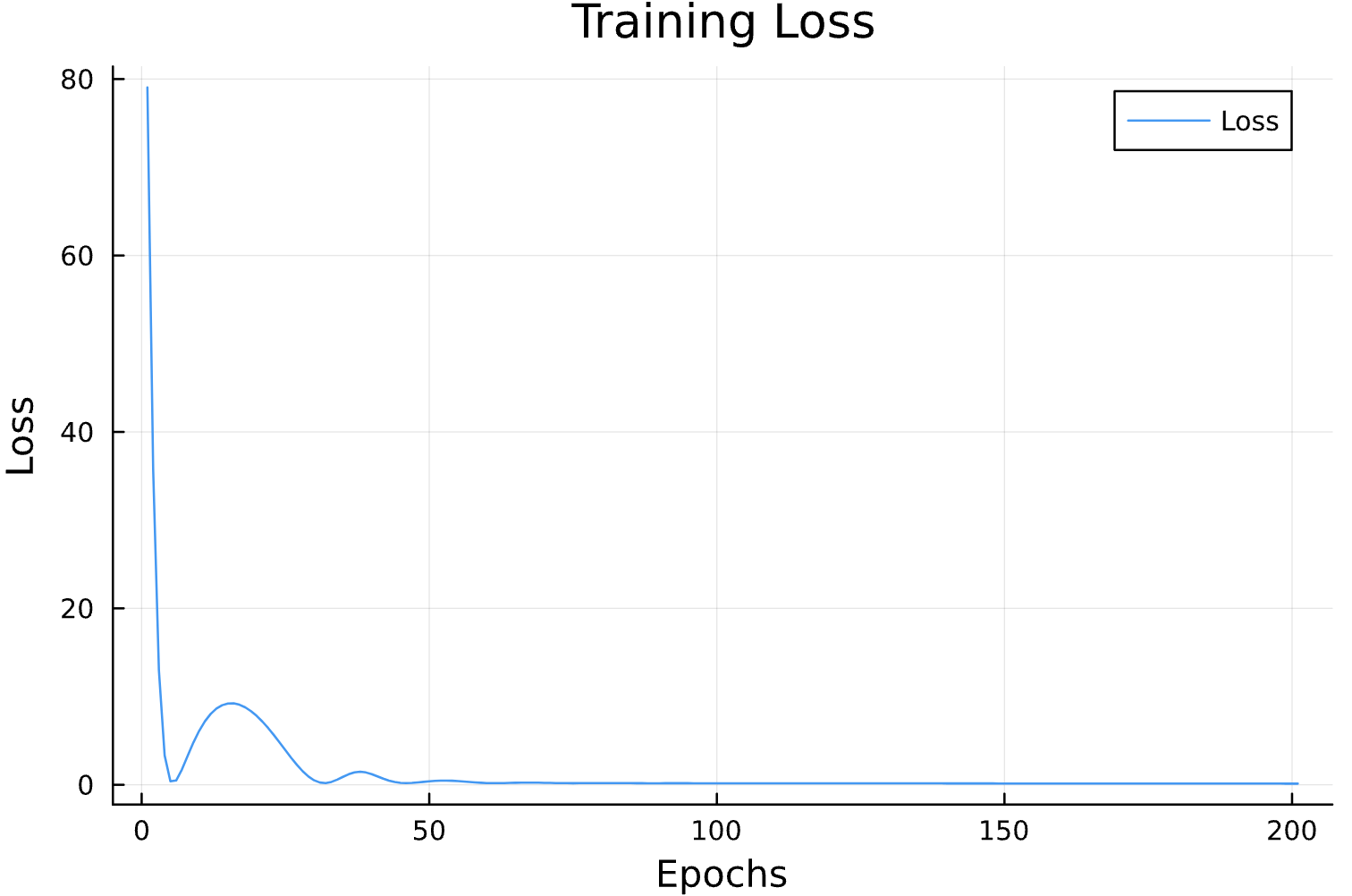
Parameter Estimation Results
Elliptical Orbits
Learning Rate
Circular Orbits
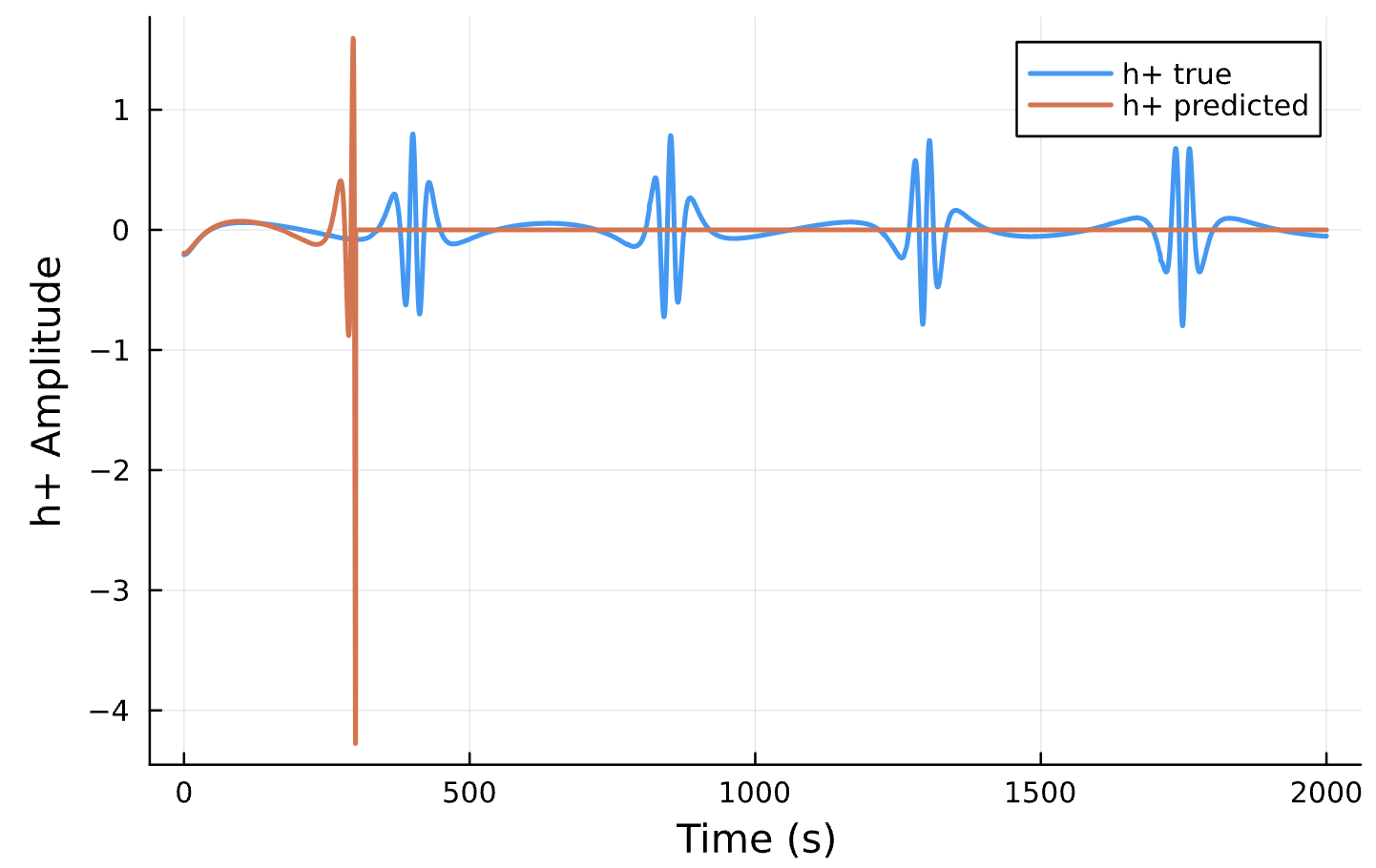
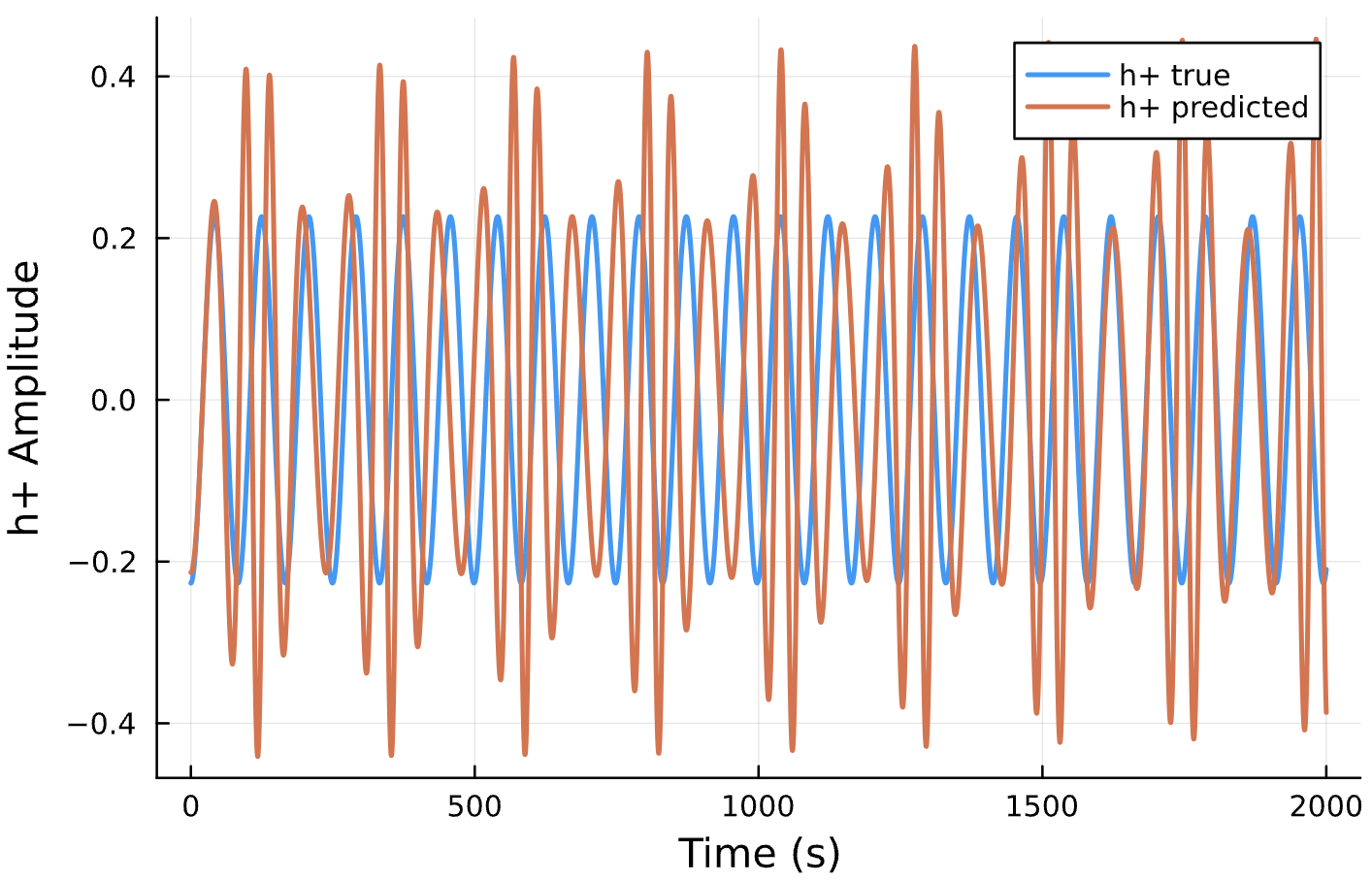
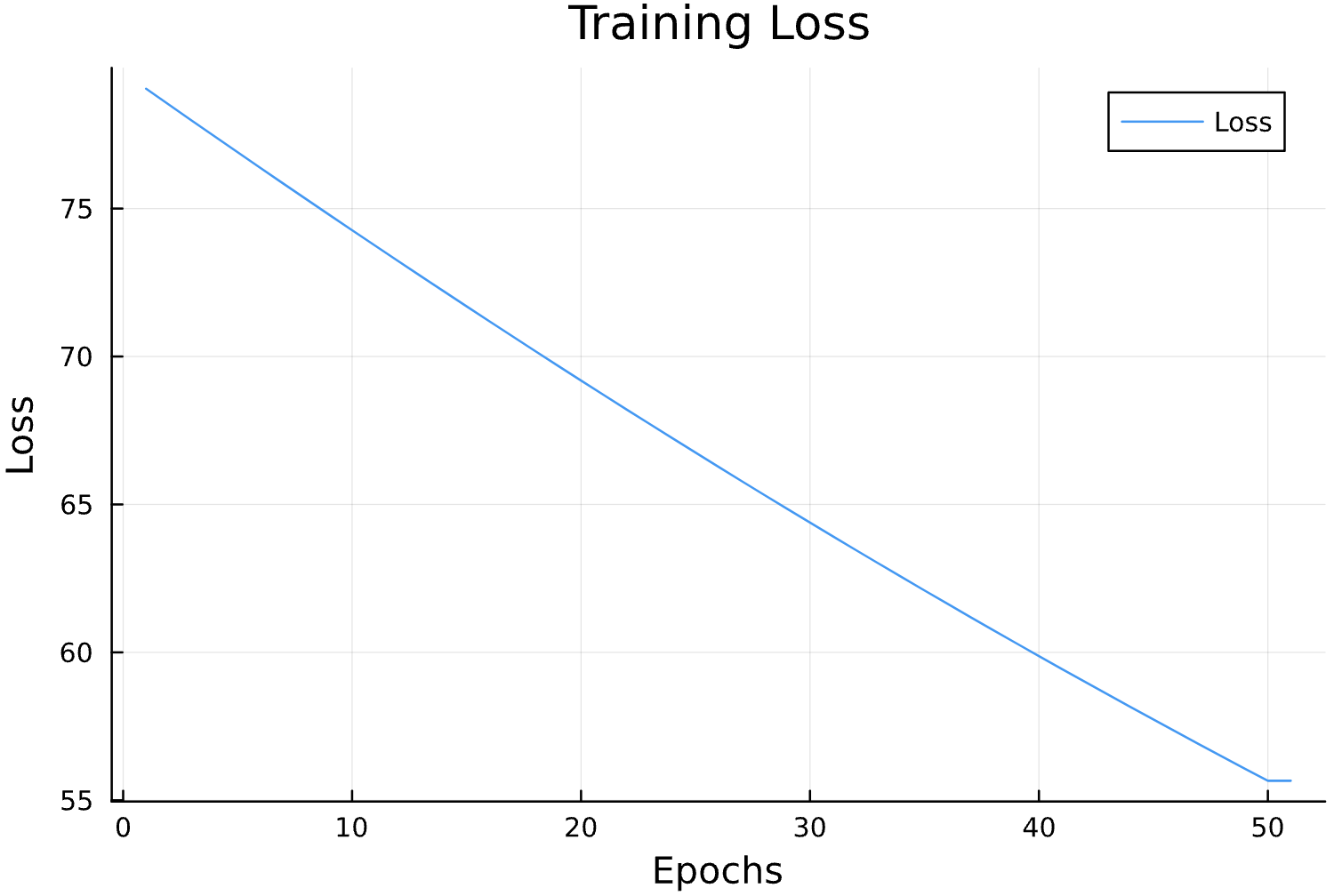
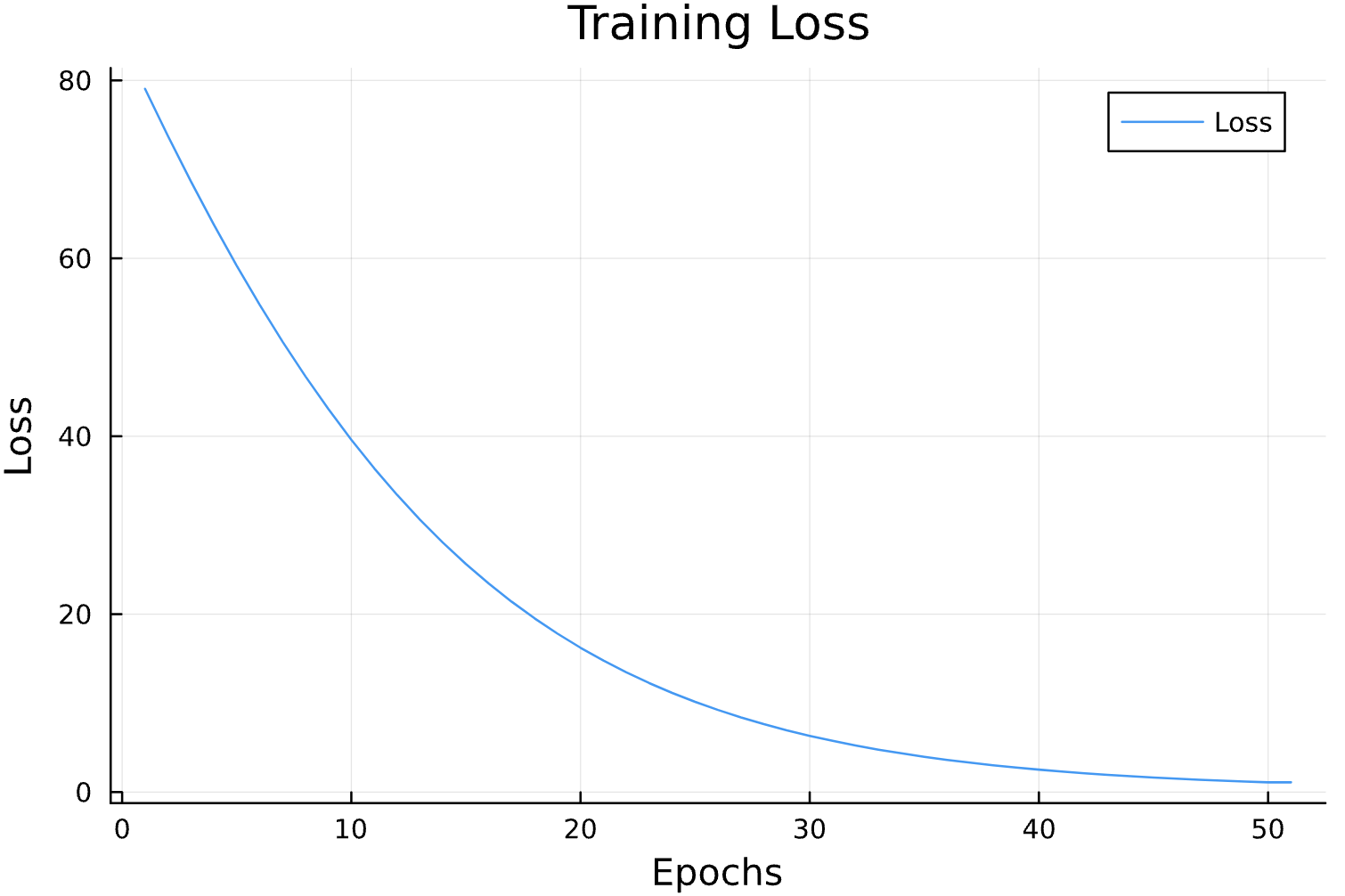
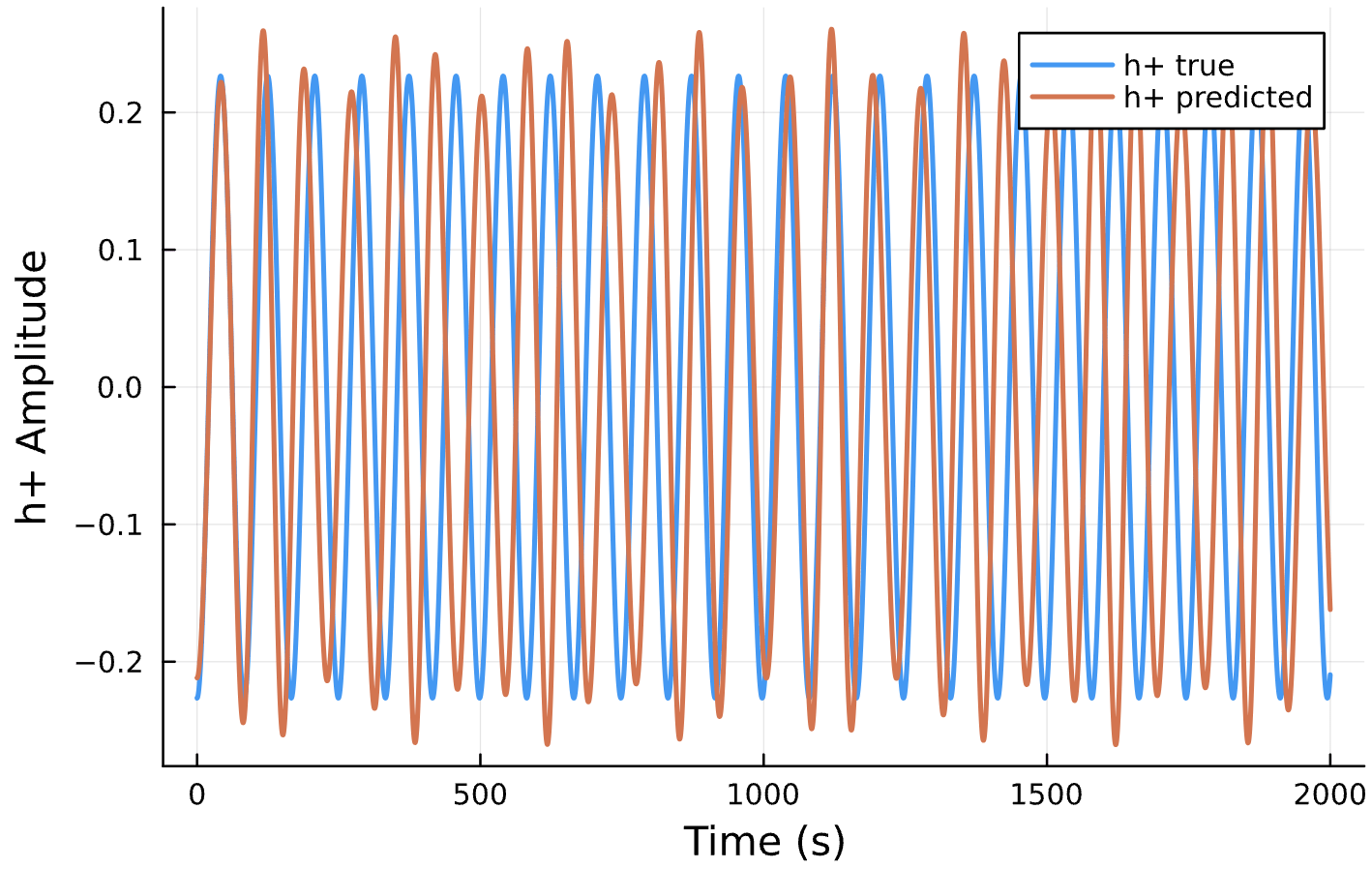
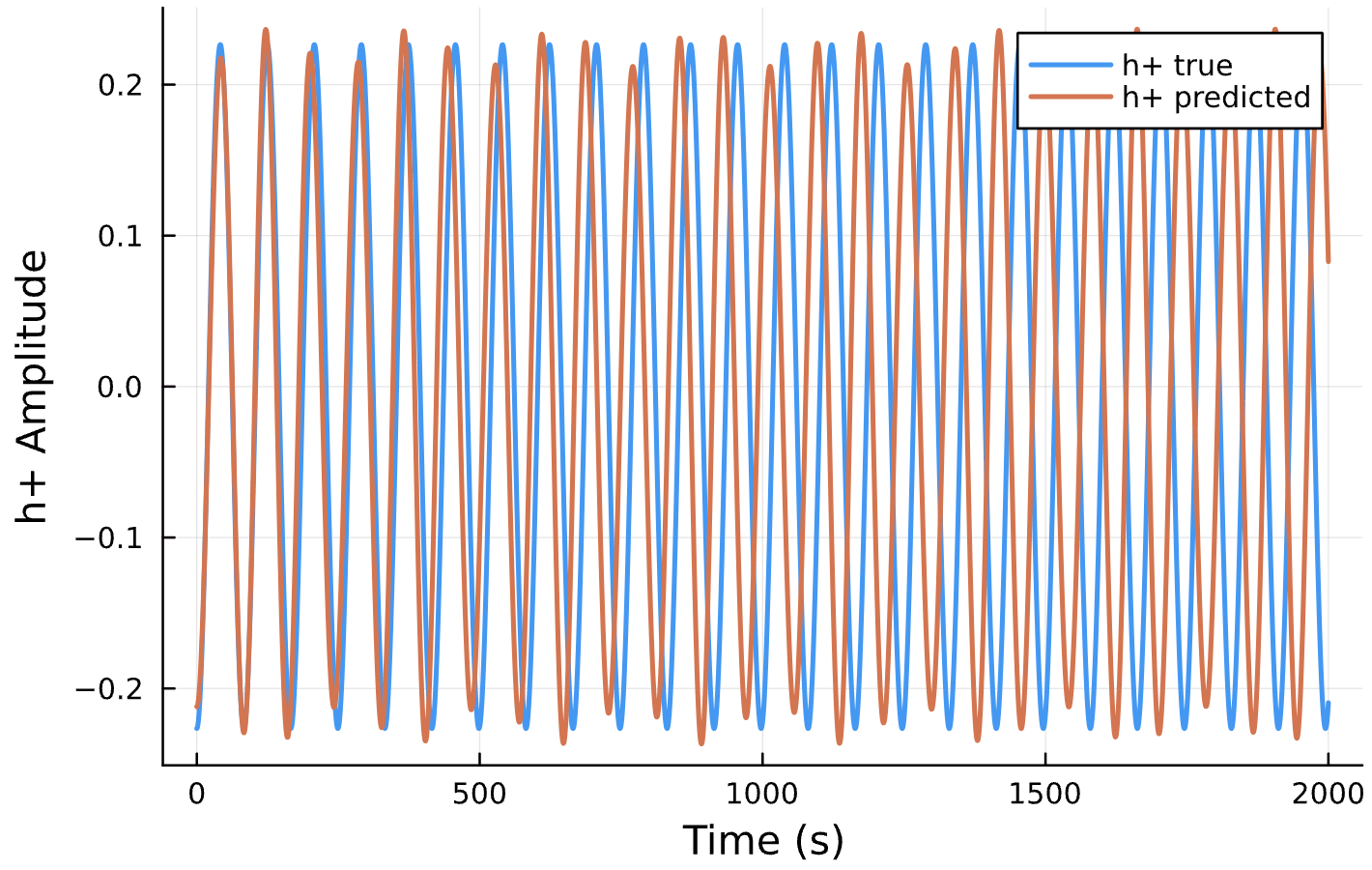
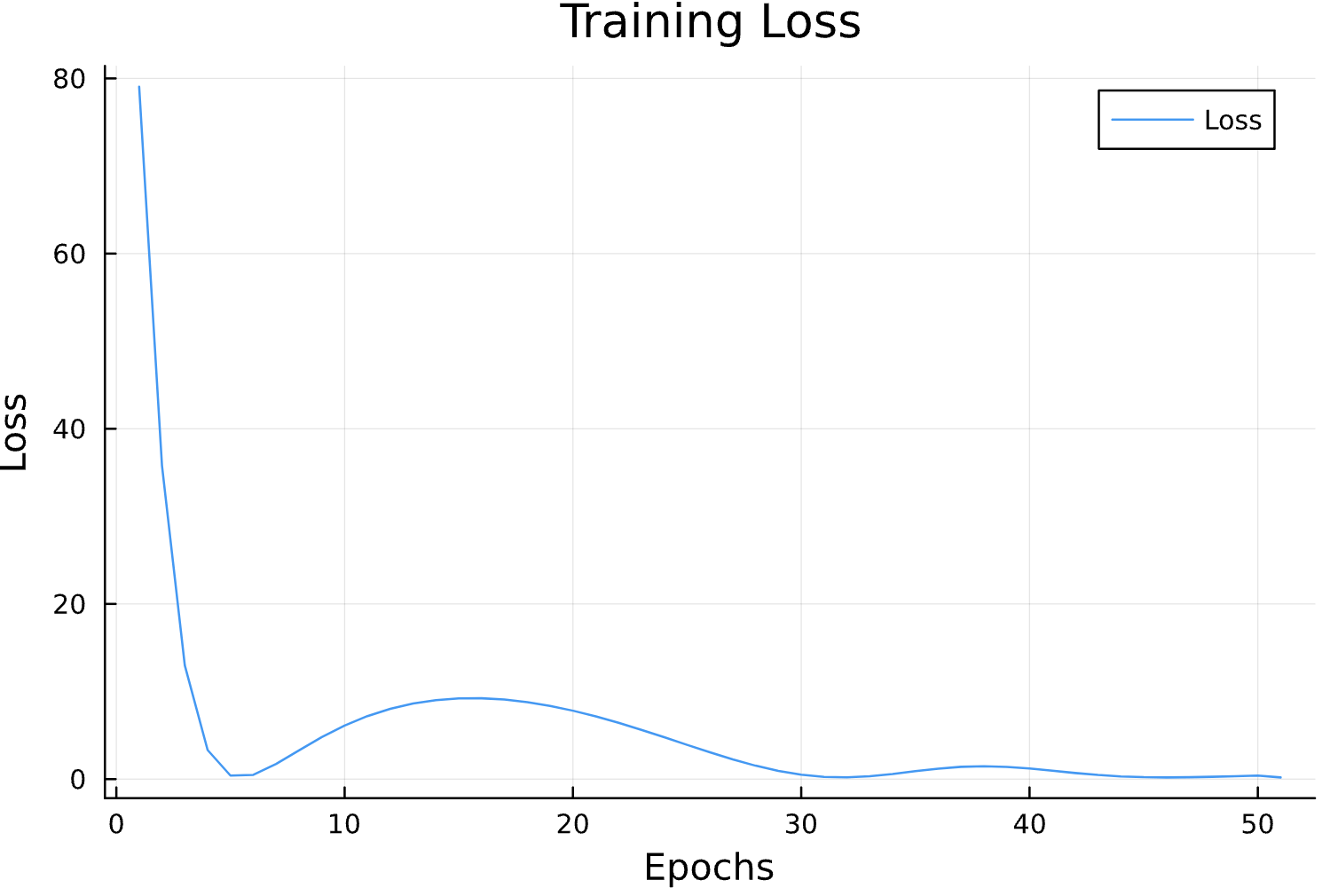
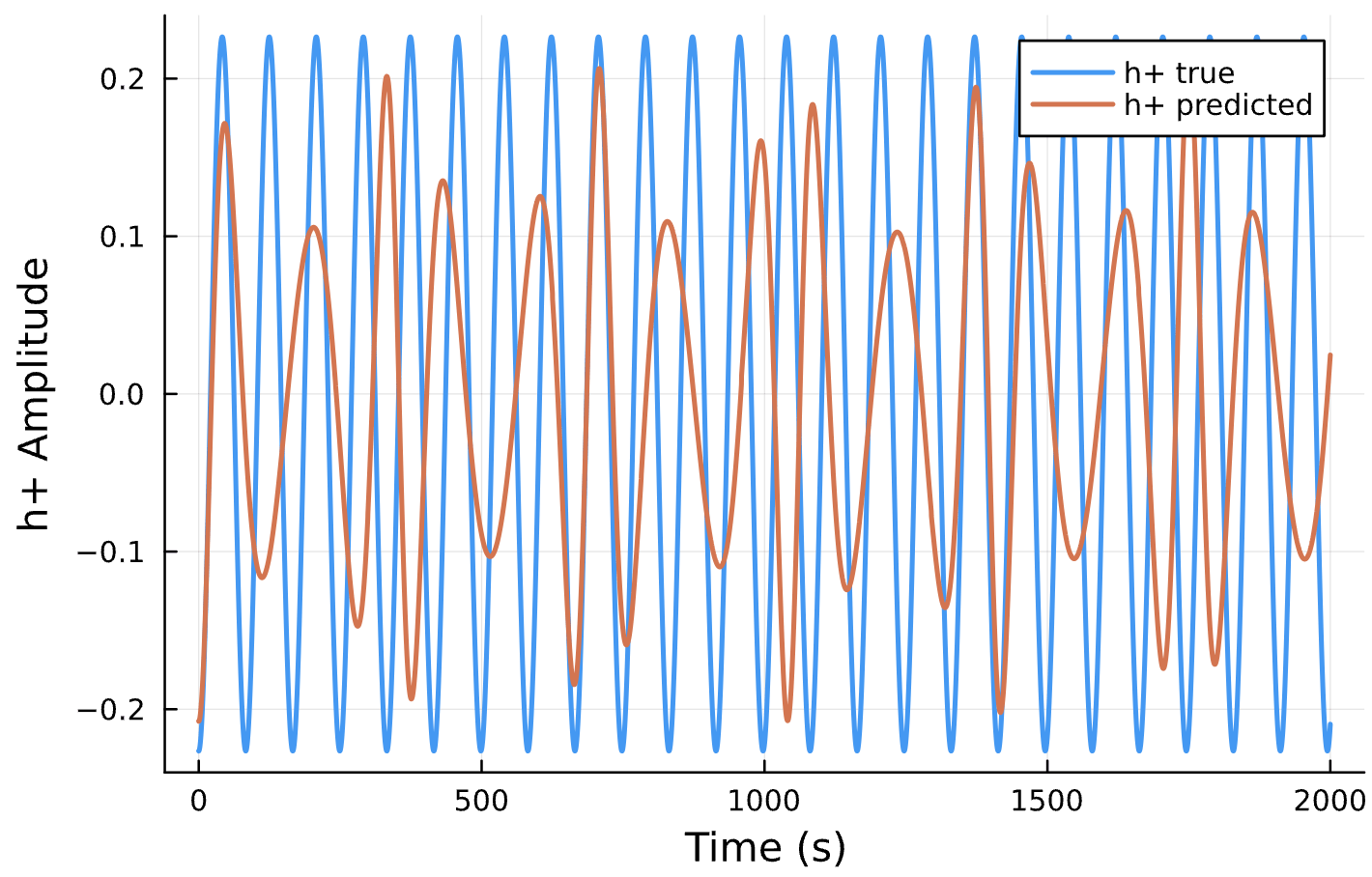
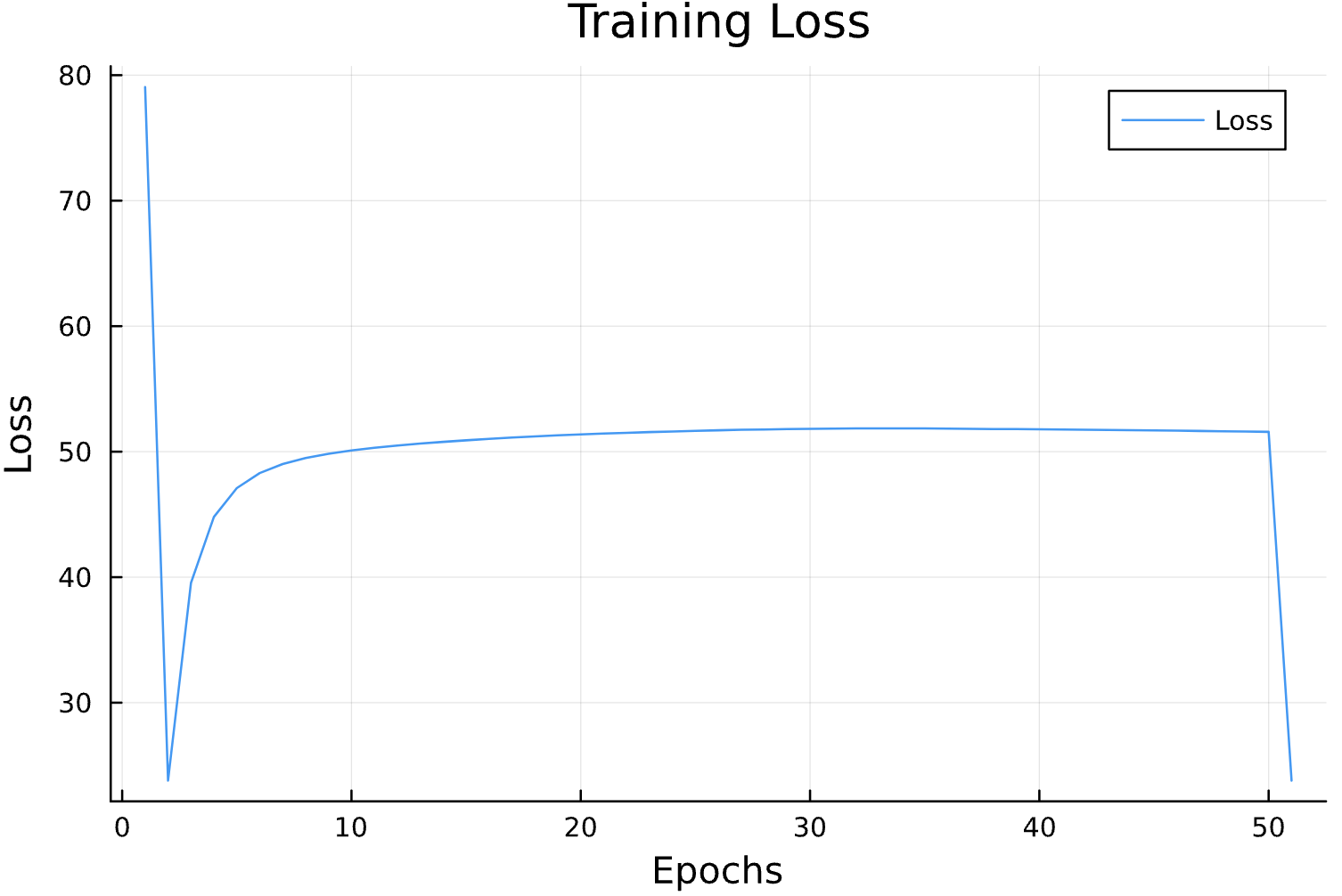
Parameter Estimation Results
Elliptical Orbits
Learning Rate
Circular Orbits
















Parameter Estimation Results
Elliptical Orbits
Learning Rate
Circular Orbits




Parameter Estimation Results
Circular Orbits
Epochs
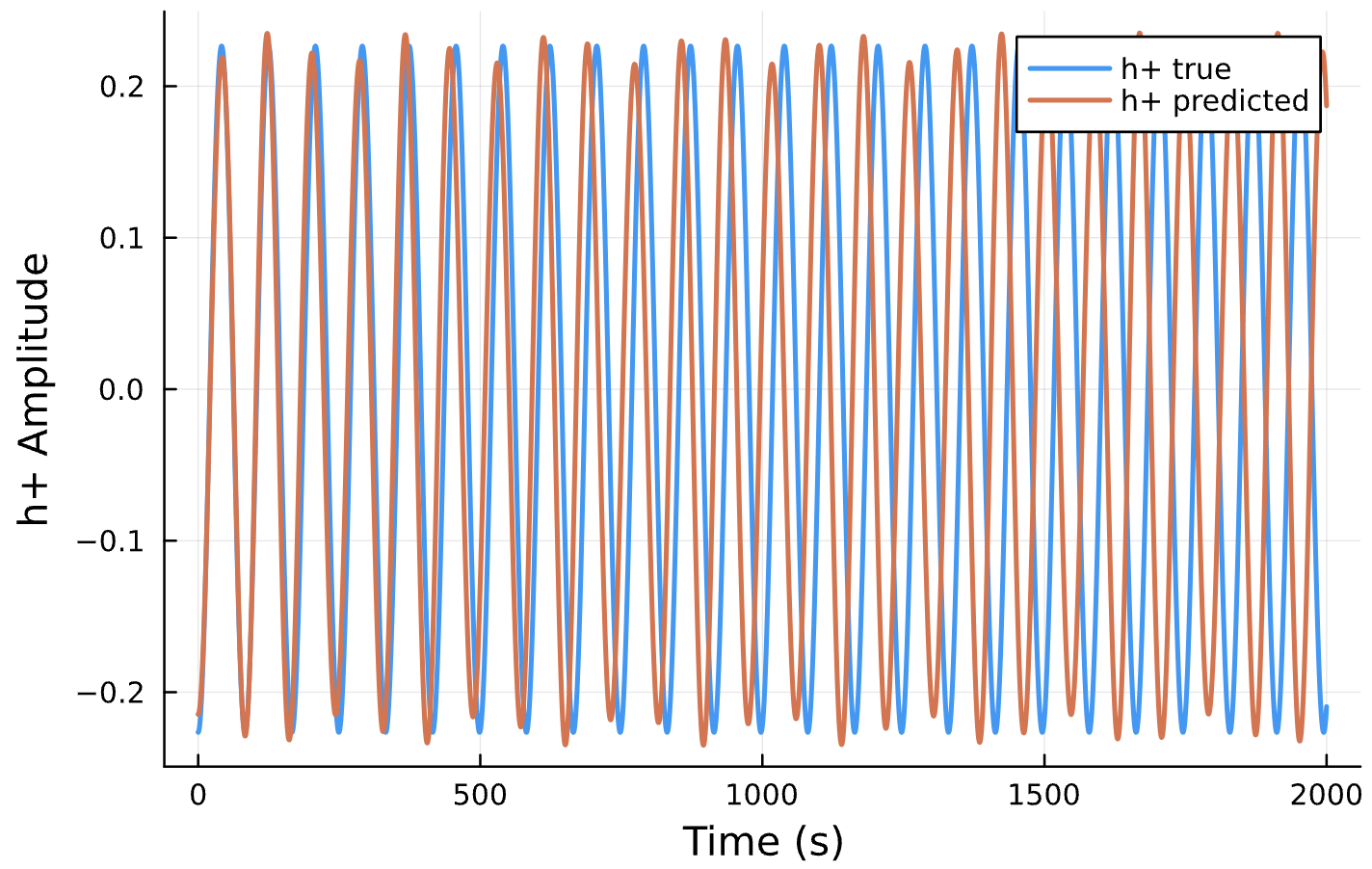
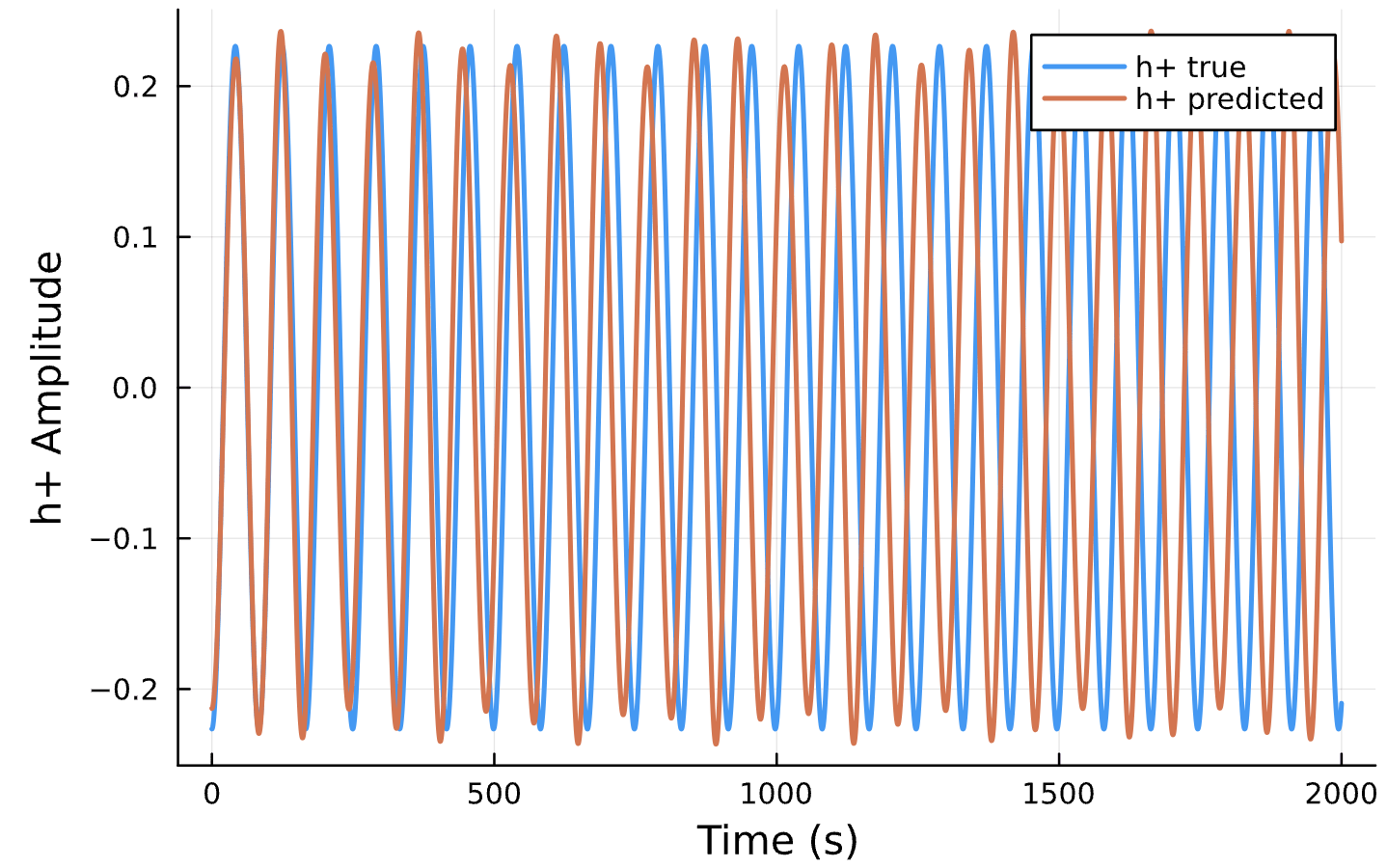
Generate Training Data
Define
Loss Function
Define
Callback
Optimize!
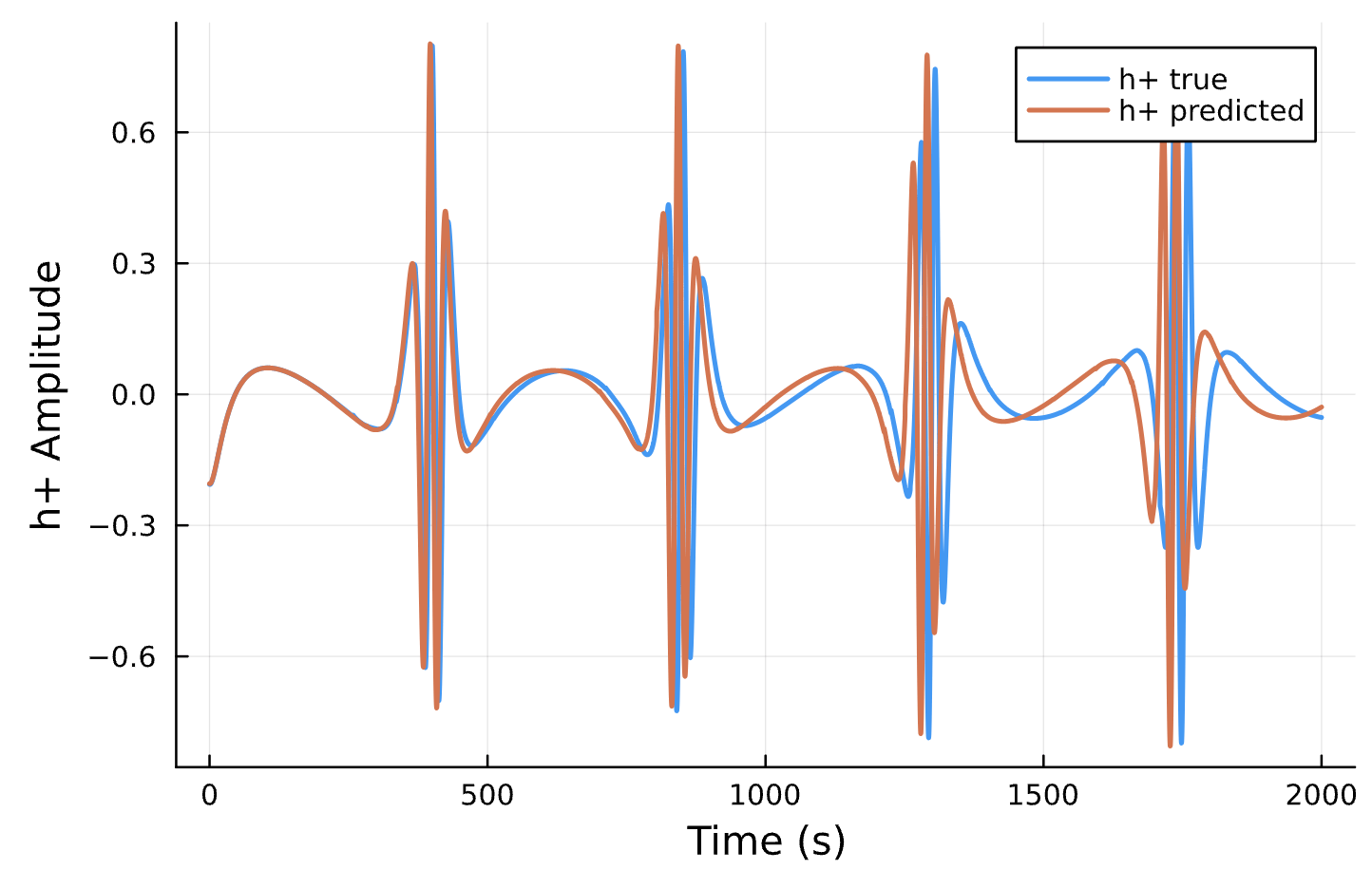
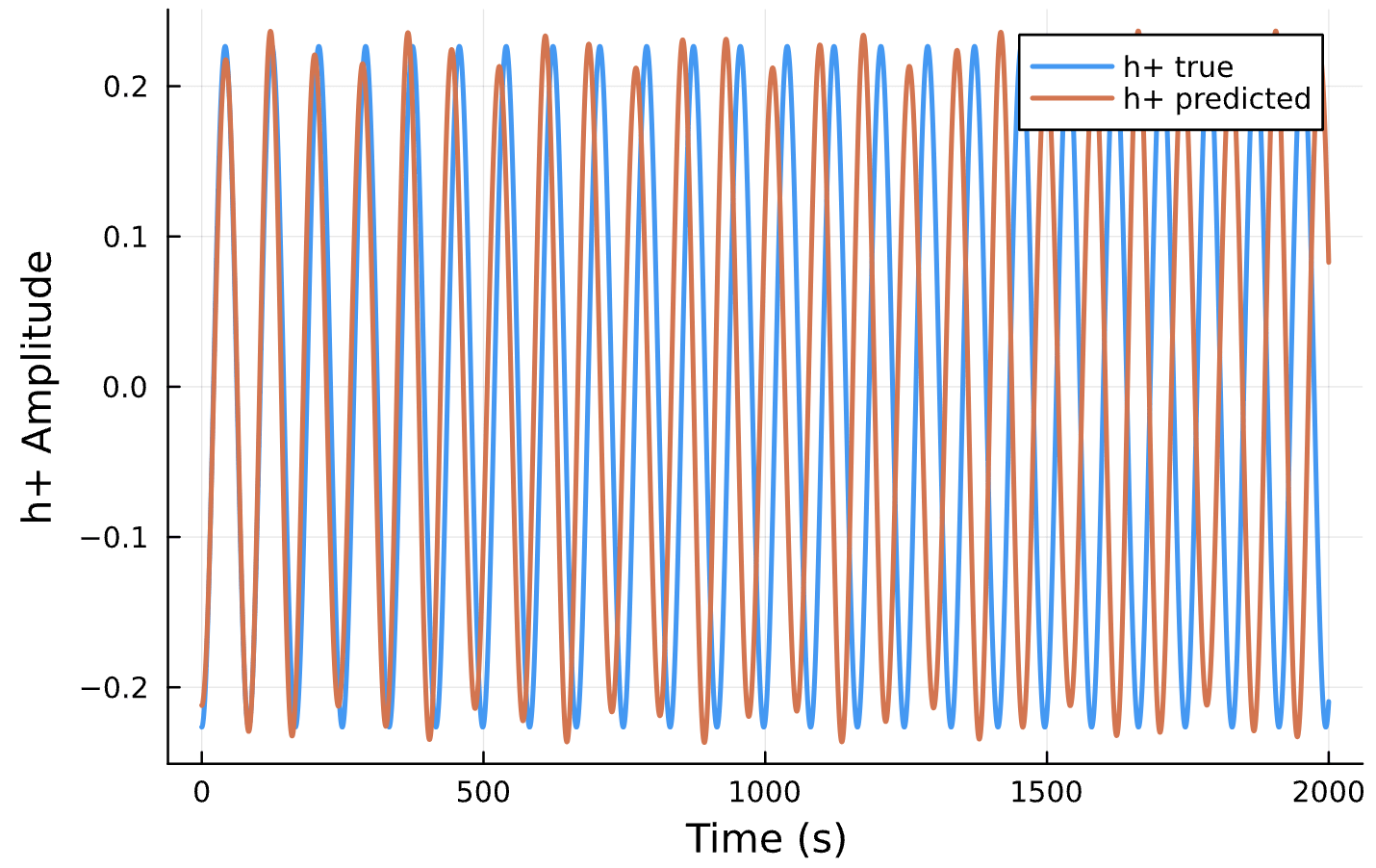
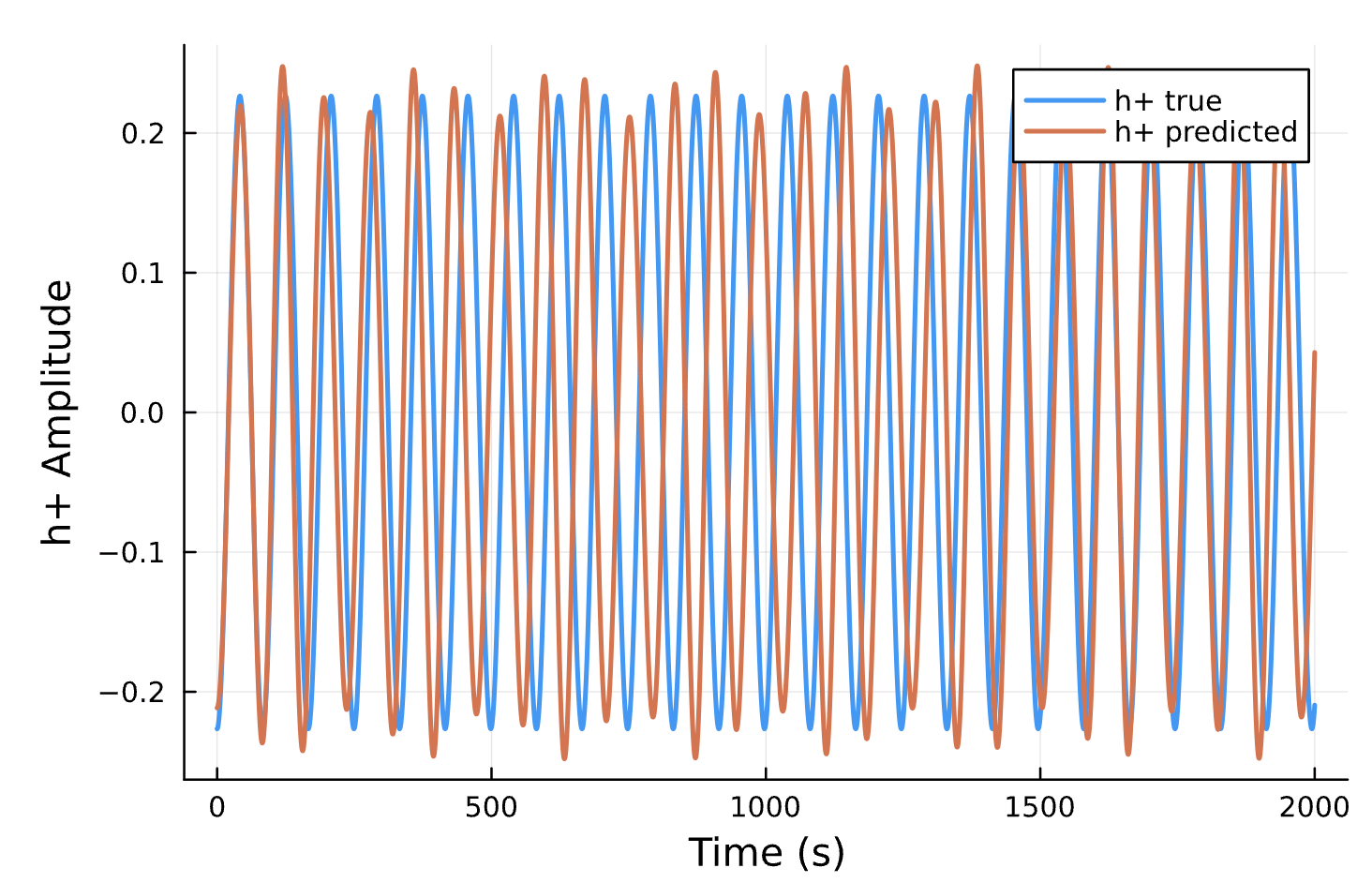
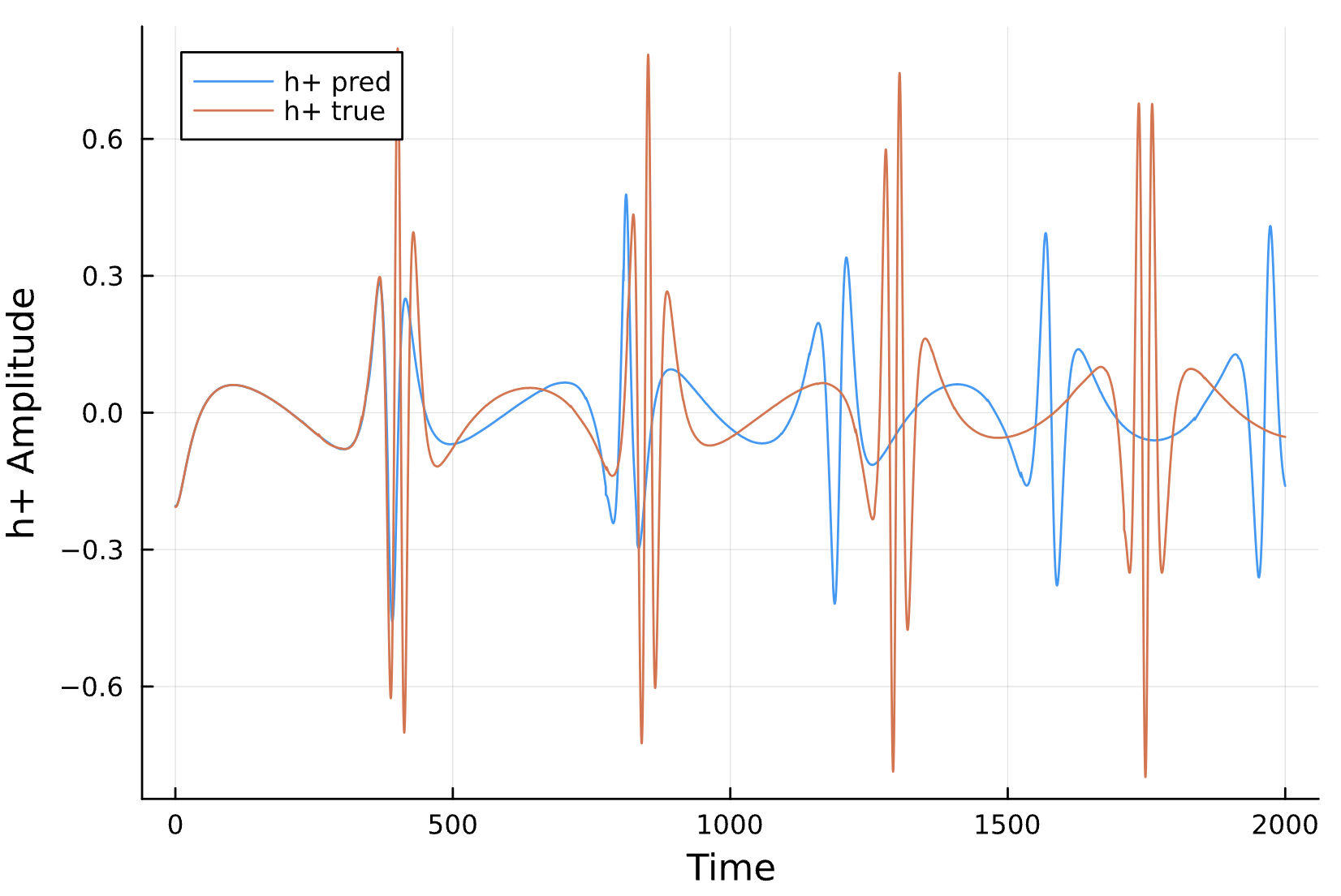
Compare Predicted & Truth
Declare Success
Parameter Estimation Pipeline
Generate Training Data
Define
Loss Function
Define
Callback
Optimize!
Compare Predicted & Truth
Declare Success
Parameter Estimation Pipeline
Generate Training Data
Define
Loss Function
Define
Callback
Optimize!
Compare Predicted & Truth
Declare Success
Parameter Estimation Pipeline
Exact Schwarzschild
Hamiltonian
Geodesic Equations of Motion
Integrate Equations to get Orbit
Convert Orbit to Waveform
Generate Training Data
Define
Loss Function
Define
Callback
Optimize!
Compare Predicted & Truth
Declare Success
Parameter Estimation Pipeline
Exact Schwarzschild Hamiltonian
Geodesic Equations of Motion
Integrate Equations to get Orbit
Convert Orbit to Waveform
Generate Training Data
Define
Loss Function
Define
Callback
Optimize!
Compare Predicted & Truth
Declare Success
Parameter Estimation Pipeline
Define Loss Function
Define
Loss Function
Define
Callback
Optimize!
Compare Predicted & Truth
Declare Success
Parameter Estimation Pipeline
function loss(pn)
newprob = remake(prob, p = pn)
sol = solve(newprob, Tsit5(), saveat=0.1)
predicted_waveform_plus = compute_waveform(0.1, sol, 1.0)[1]
predicted_waveform_cross = compute_waveform(0.1, sol, 1.0)[2]
# Compare only the overlapping portion
n_pred = length(predicted_waveform_plus)
n_train = length(h_plus_training)
n_compare = min(n_pred, n_train)
loss = sum(abs2, predicted_waveform_plus[1:n_compare] .- h_plus_training[1:n_compare])
loss += sum(abs2, predicted_waveform_cross[1:n_compare] .- h_cross_training[1:n_compare])
return loss
endDefine Loss Function
Define
Loss Function
Define
Callback
Optimize!
Compare Predicted & Truth
Declare Success
Parameter Estimation Pipeline
function loss(pn)
newprob = remake(prob, p = pn)
sol = solve(newprob, Tsit5(), saveat=0.1)
predicted_waveform_plus = compute_waveform(0.1, sol, 1.0)[1]
predicted_waveform_cross = compute_waveform(0.1, sol, 1.0)[2]
# Compare only the overlapping portion
n_pred = length(predicted_waveform_plus)
n_train = length(h_plus_training)
n_compare = min(n_pred, n_train)
loss = sum(abs2, predicted_waveform_plus[1:n_compare] .- h_plus_training[1:n_compare])
loss += sum(abs2, predicted_waveform_cross[1:n_compare] .- h_cross_training[1:n_compare])
return loss
endDefine Loss Function
Define
Loss Function
Define
Callback
Optimize!
Compare Predicted & Truth
Declare Success
Parameter Estimation Pipeline
function loss(pn)
newprob = remake(prob, p = pn)
sol = solve(newprob, Tsit5(), saveat=0.1)
predicted_waveform_plus = compute_waveform(0.1, sol, 1.0)[1]
predicted_waveform_cross = compute_waveform(0.1, sol, 1.0)[2]
# Compare only the overlapping portion
n_pred = length(predicted_waveform_plus)
n_train = length(h_plus_training)
n_compare = min(n_pred, n_train)
loss = sum(abs2, predicted_waveform_plus[1:n_compare] .- h_plus_training[1:n_compare])
loss += sum(abs2, predicted_waveform_cross[1:n_compare] .- h_cross_training[1:n_compare])
return loss
endDefine Loss Function
Define
Loss Function
Define
Callback
Optimize!
Compare Predicted & Truth
Declare Success
Parameter Estimation Pipeline
function loss(pn)
newprob = remake(prob, p = pn)
sol = solve(newprob, Tsit5(), saveat=0.1)
predicted_waveform_plus = compute_waveform(0.1, sol, 1.0)[1]
predicted_waveform_cross = compute_waveform(0.1, sol, 1.0)[2]
# Compare only the overlapping portion
n_pred = length(predicted_waveform_plus)
n_train = length(h_plus_training)
n_compare = min(n_pred, n_train)
loss = sum(abs2, predicted_waveform_plus[1:n_compare] .- h_plus_training[1:n_compare])
loss += sum(abs2, predicted_waveform_cross[1:n_compare] .- h_cross_training[1:n_compare])
return loss
endDefine Loss Function
Define
Loss Function
Define
Callback
Optimize!
Compare Predicted & Truth
Declare Success
Parameter Estimation Pipeline
function loss(pn)
newprob = remake(prob, p = pn)
sol = solve(newprob, Tsit5(), saveat=0.1)
predicted_waveform_plus = compute_waveform(0.1, sol, 1.0)[1]
predicted_waveform_cross = compute_waveform(0.1, sol, 1.0)[2]
# Compare only the overlapping portion
n_pred = length(predicted_waveform_plus)
n_train = length(h_plus_training)
n_compare = min(n_pred, n_train)
loss = sum(abs2, predicted_waveform_plus[1:n_compare] .- h_plus_training[1:n_compare])
loss += sum(abs2, predicted_waveform_cross[1:n_compare] .- h_cross_training[1:n_compare])
return loss
endGenerate Training Data
Define
Loss Function
Define
Callback
Optimize!
Compare Predicted & Truth
Declare Success
Parameter Estimation Pipeline
Define Callback Function
Define
Loss Function
Define
Callback
Optimize!
Compare Predicted & Truth
Declare Success
Parameter Estimation Pipeline
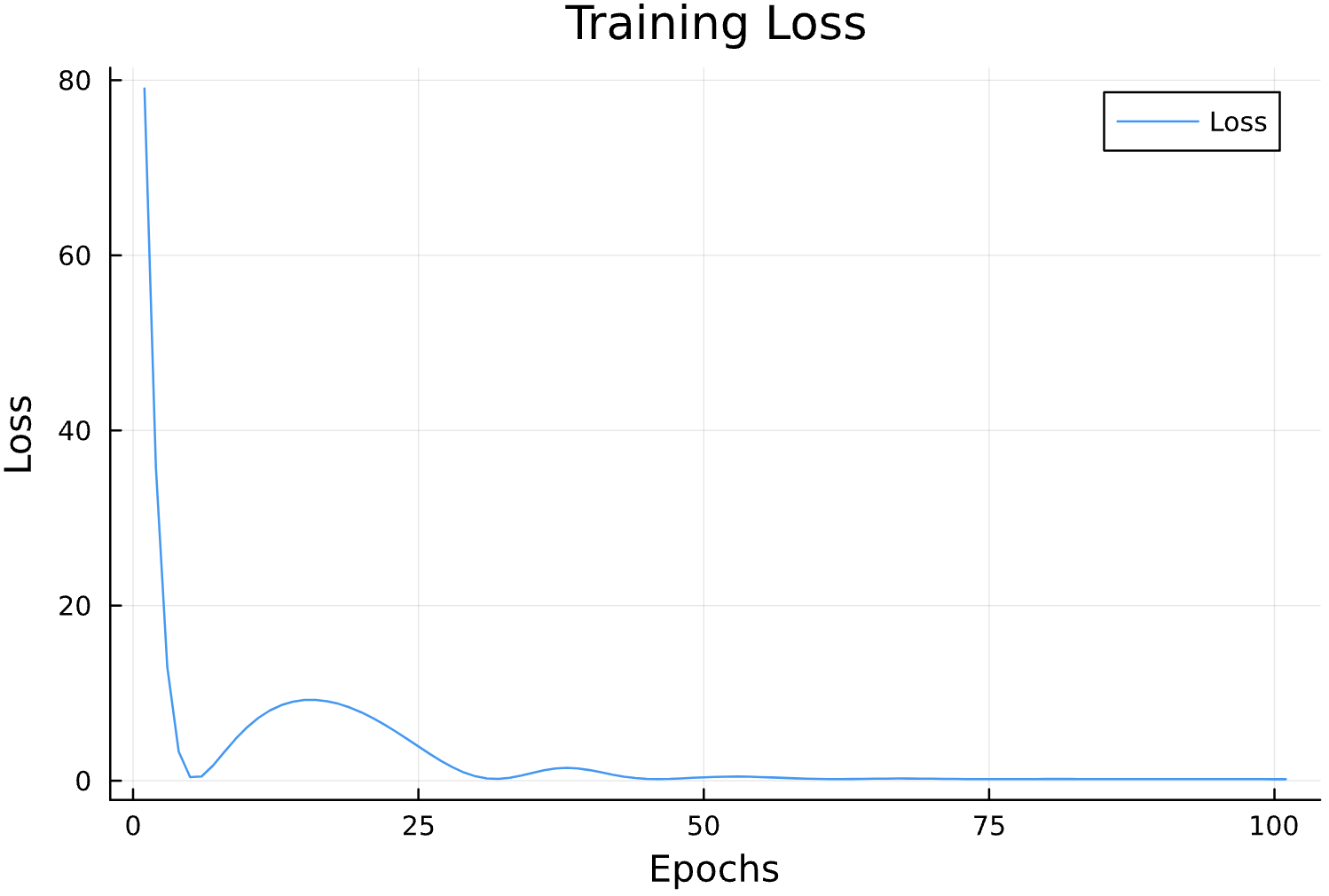
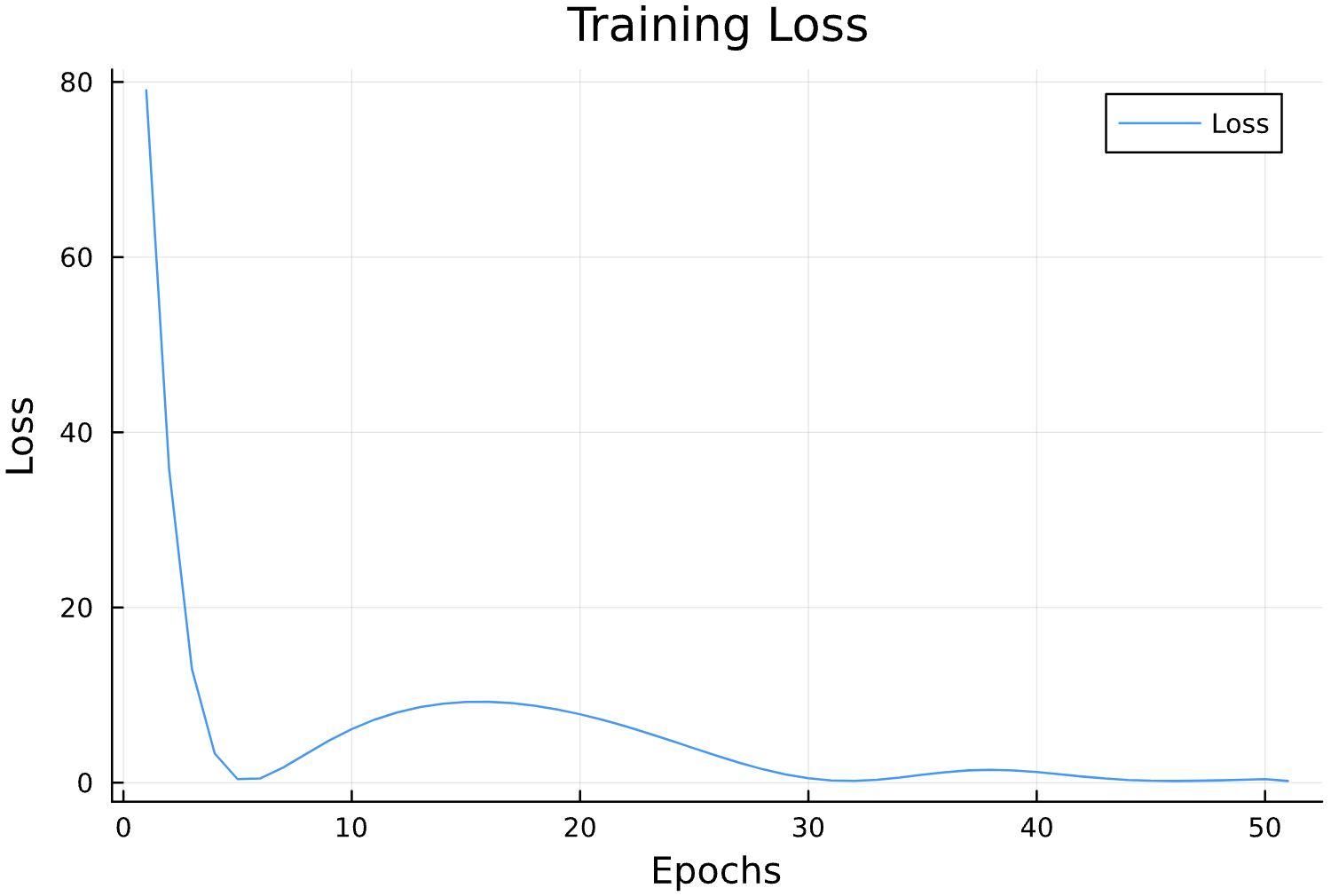
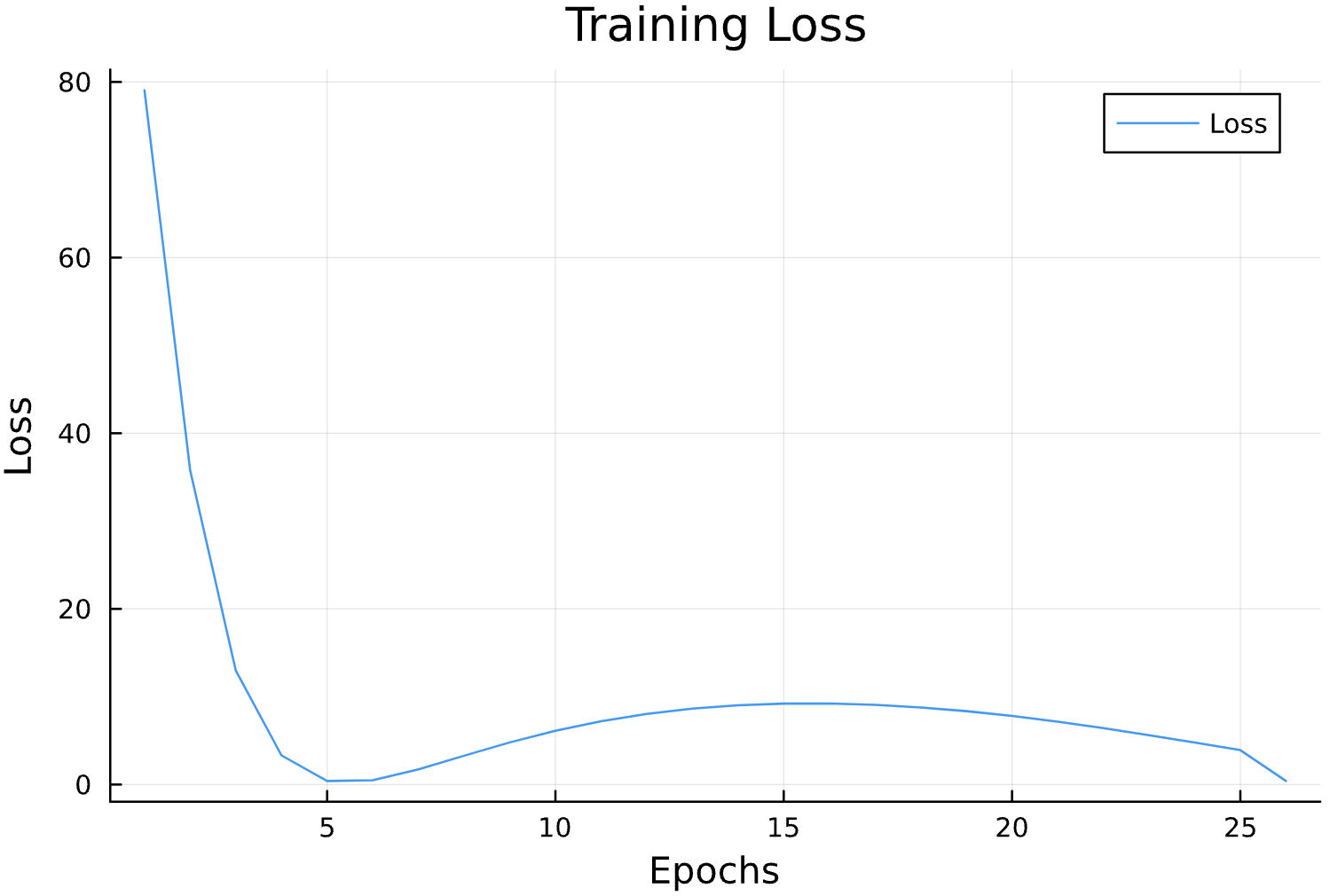
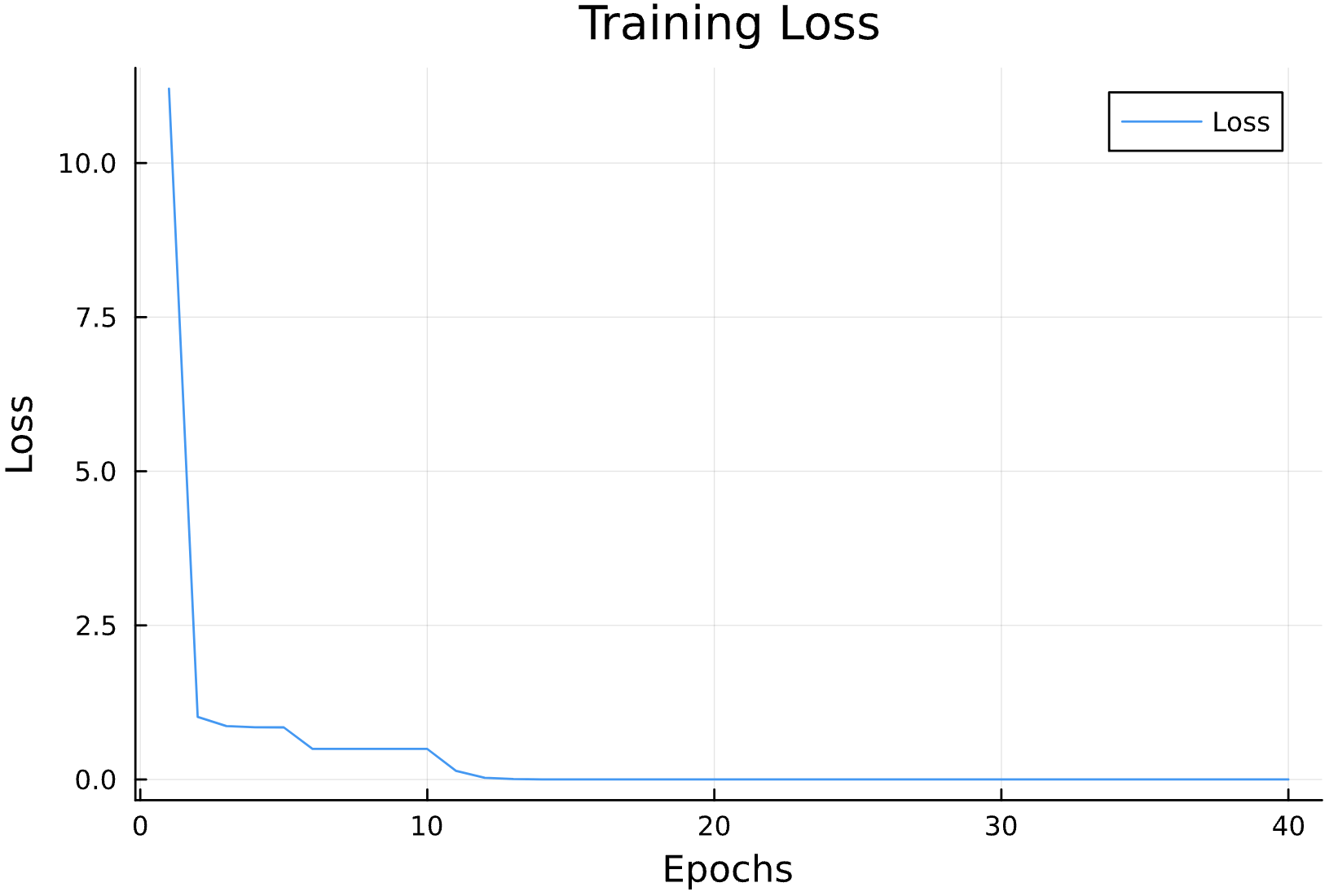
losses = []
function callback(pn, loss; dotrain = true)
if dotrain
push!(losses, loss);
@printf("Epoch: %d, Loss: %15.12f \n",length(losses),loss);
p = plot(losses, label = "Loss")
display(p)
else
prinln(l)
end
return false
endGenerate Training Data
Define
Loss Function
Define
Callback
Optimize!
Compare Predicted & Truth
Declare Success
Parameter Estimation Pipeline
Binary Black Holes
A GENERIC Approach
- Proved equivalence between two parameterizations of Schwarzschild Metric
- Parameter Estimation for Schwarzschild Metric
- AI for Schwarzschild Metric (in Hamiltonian form)!

Binary Black Holes
A GENERIC Approach
- Proved equivalence between two parameterizations of Schwarzschild Metric
- Parameter Estimation for Schwarzschild Metric
- AI for Schwarzschild Metric (in Hamiltonian form)!

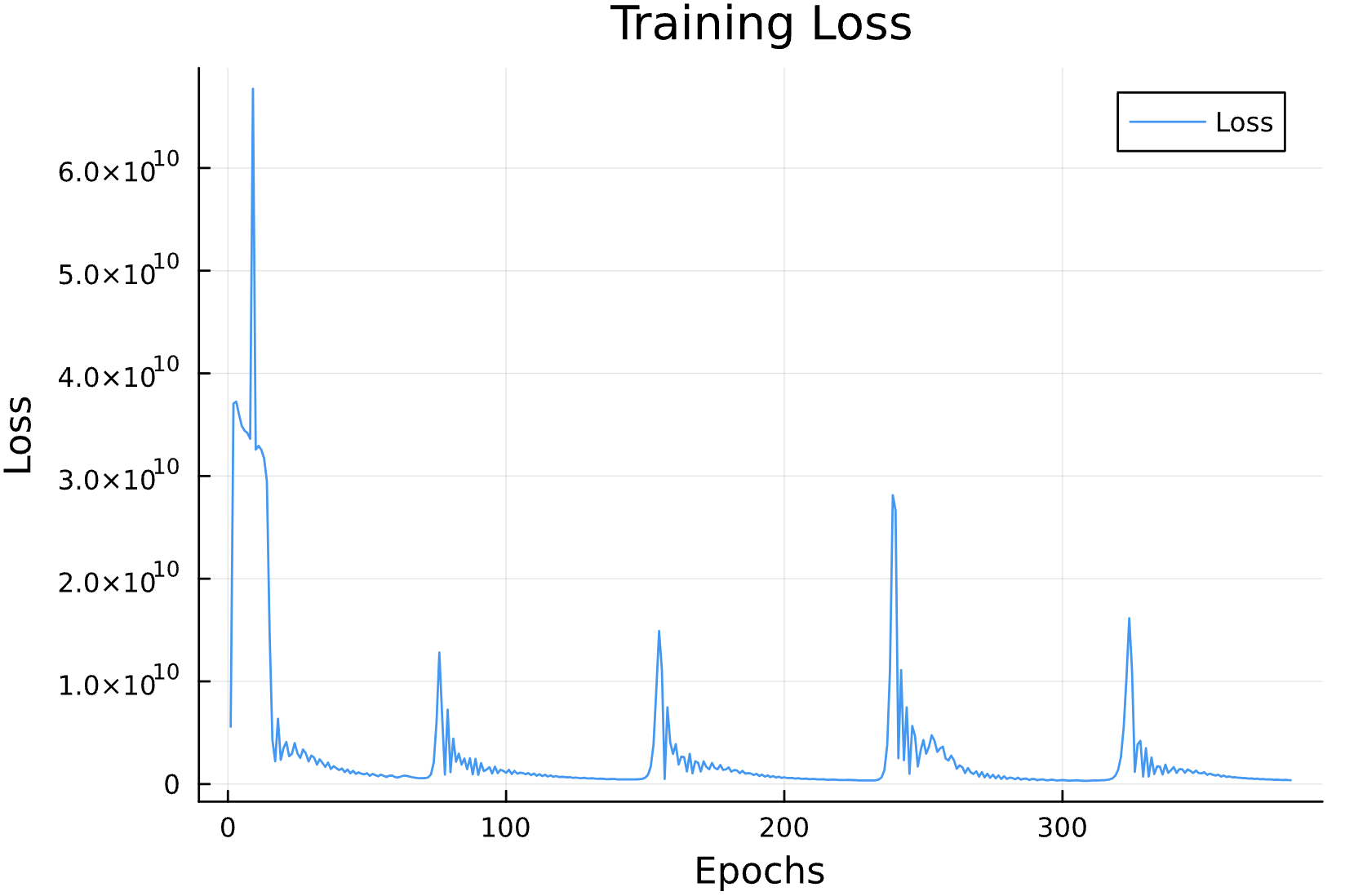
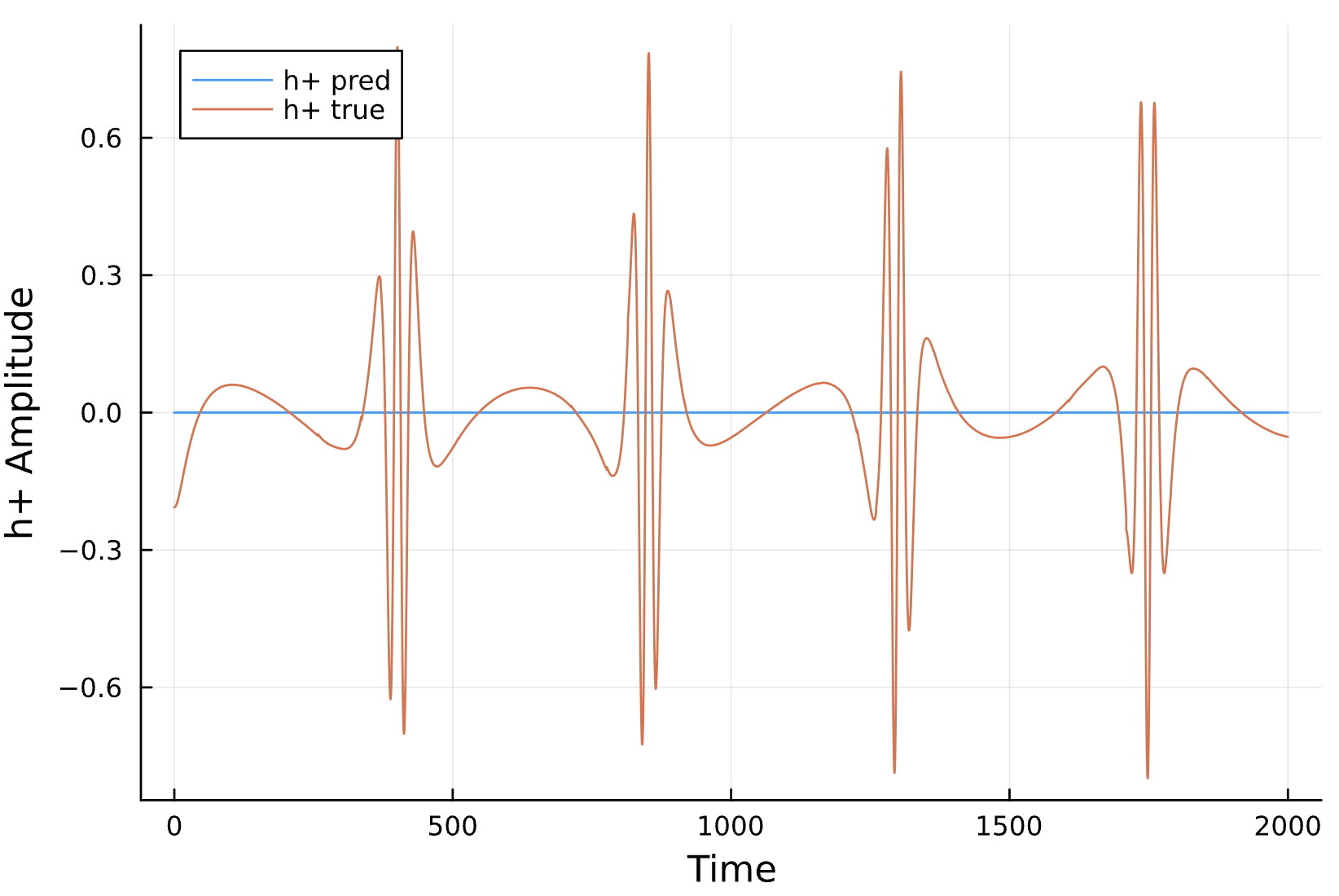
Predicted Hamiltonian
Equations of Motion
Predicted Waveform
Compare to True Waveform
Adjust Hamiltonian
Keep Training Network
Neural Network Pipeline
Predicted Hamiltonian
Equations of Motion
Predicted Waveform
Compare to True Waveform
Adjust Hamiltonian
Keep Training Network
Neural Network Pipeline
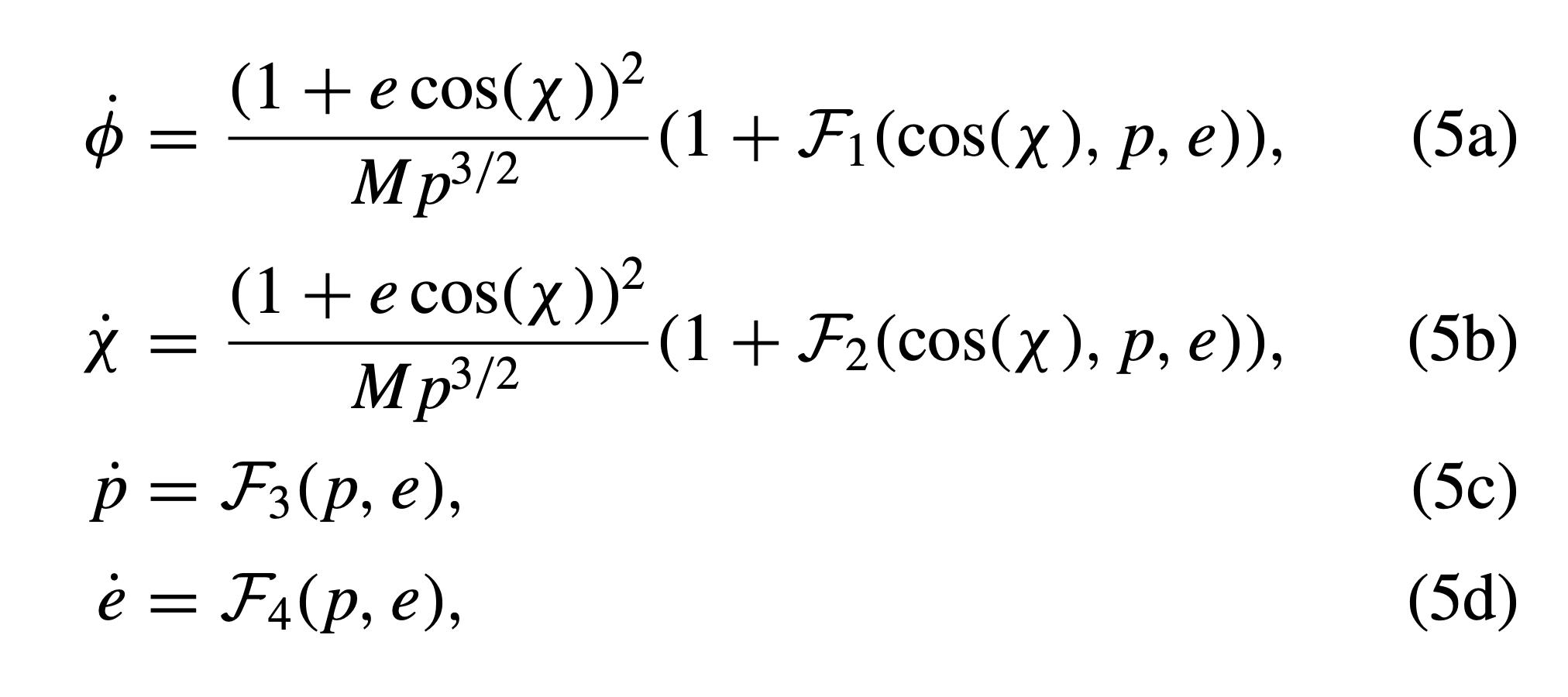
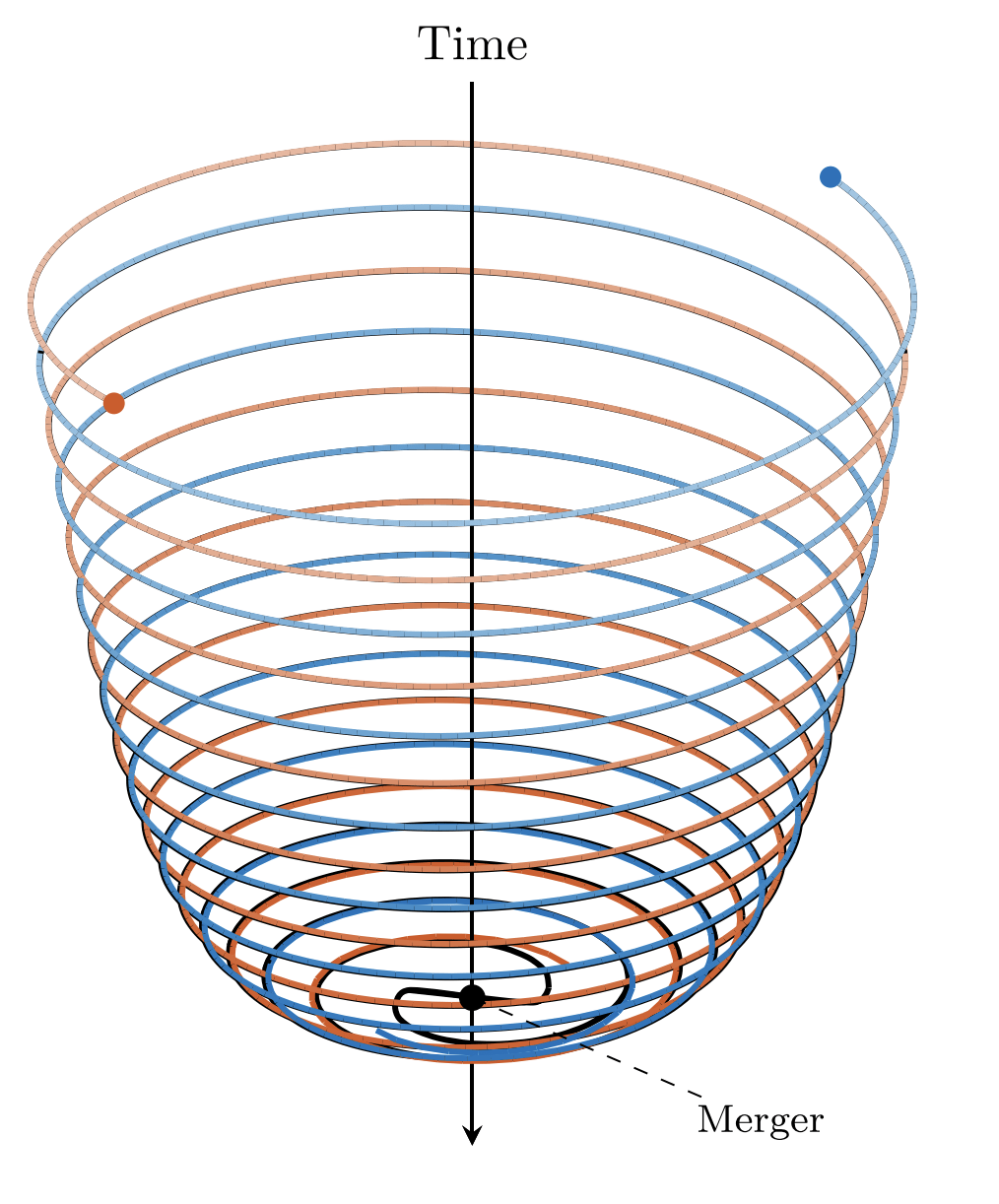
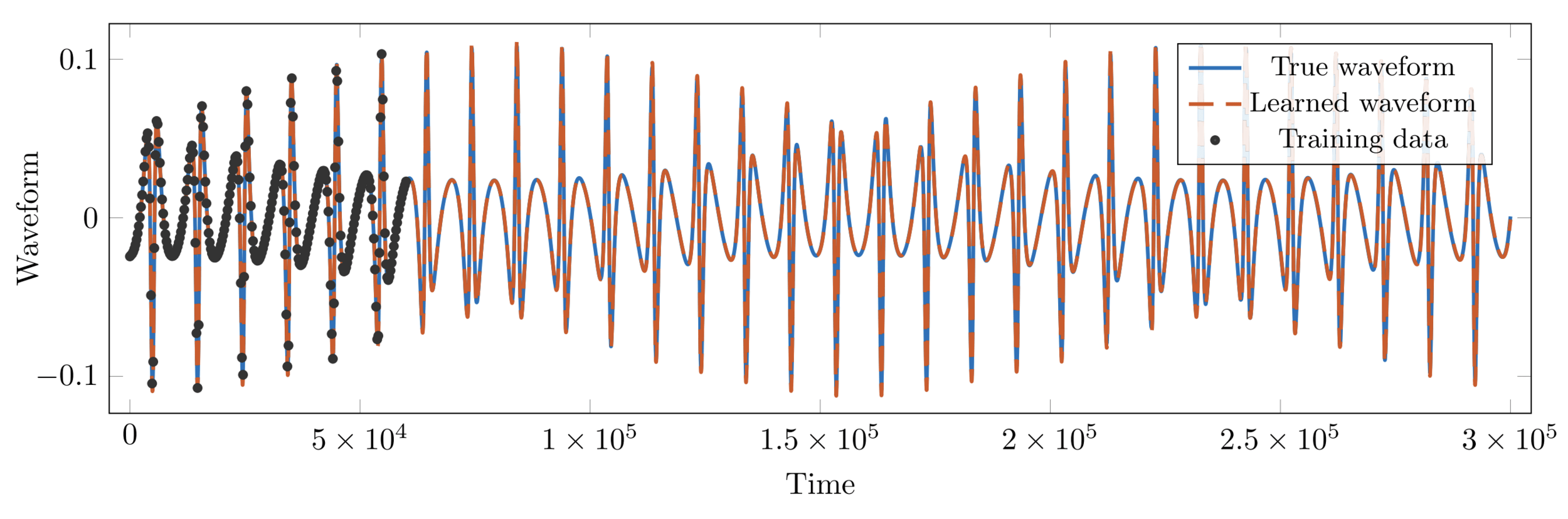
Learning orbital dynamics of binary black hole systems from gravitational wave measurements (B. Keith et. al., 2021)
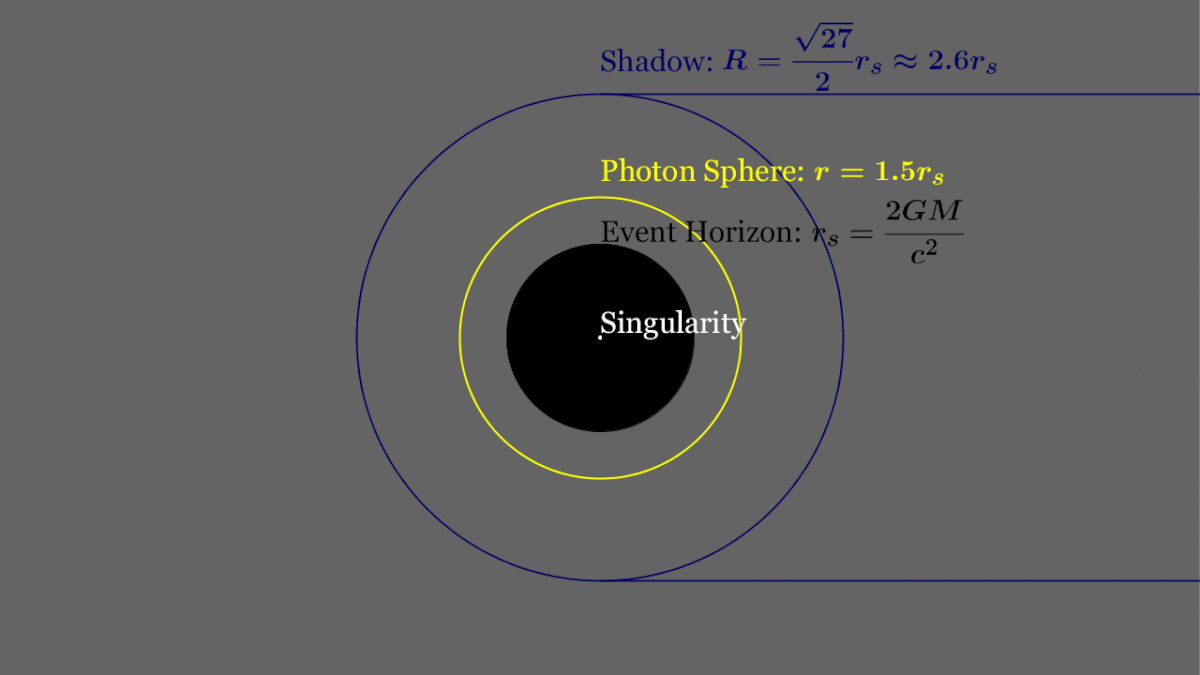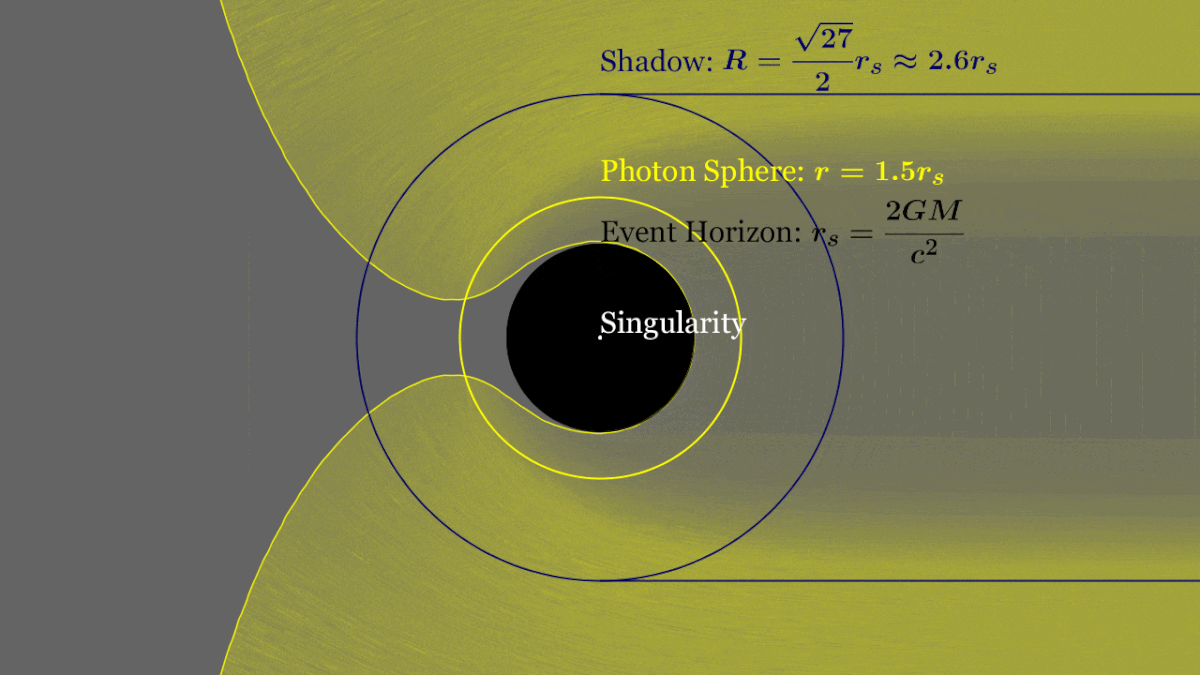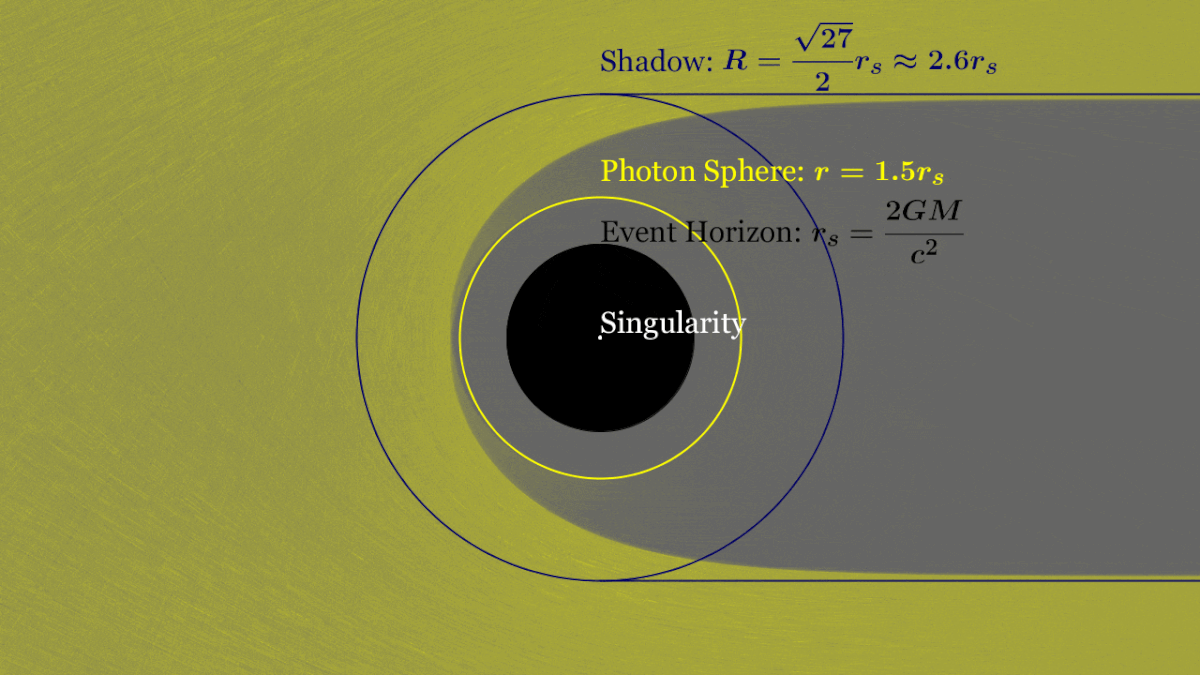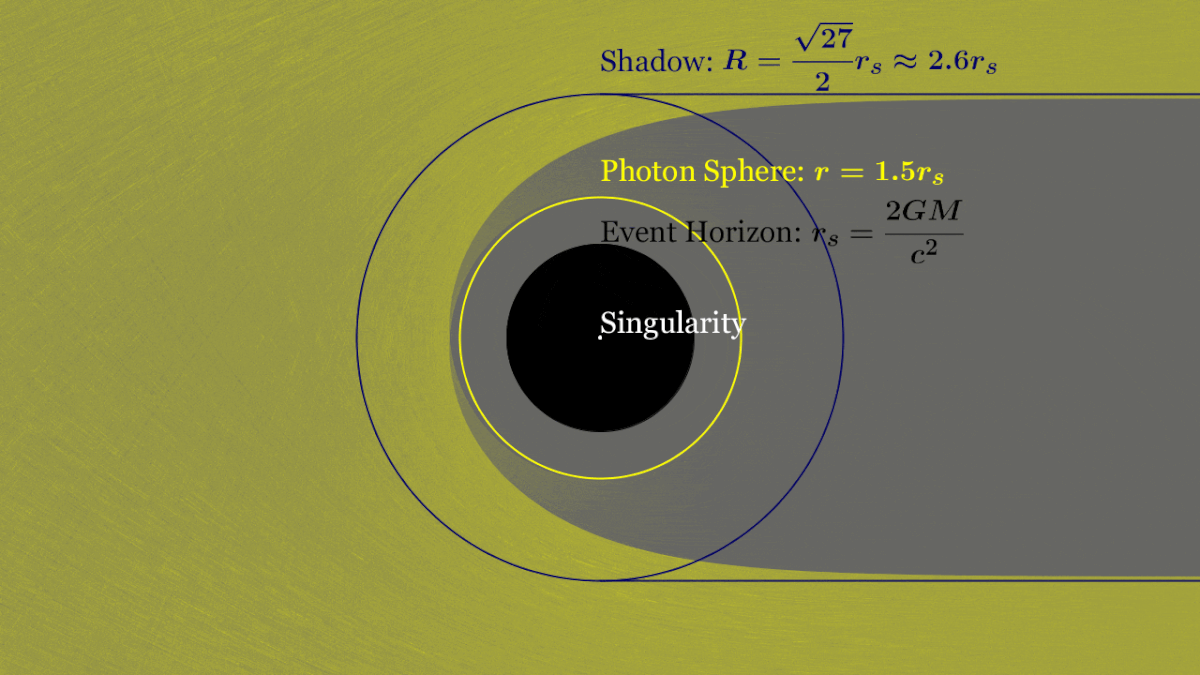
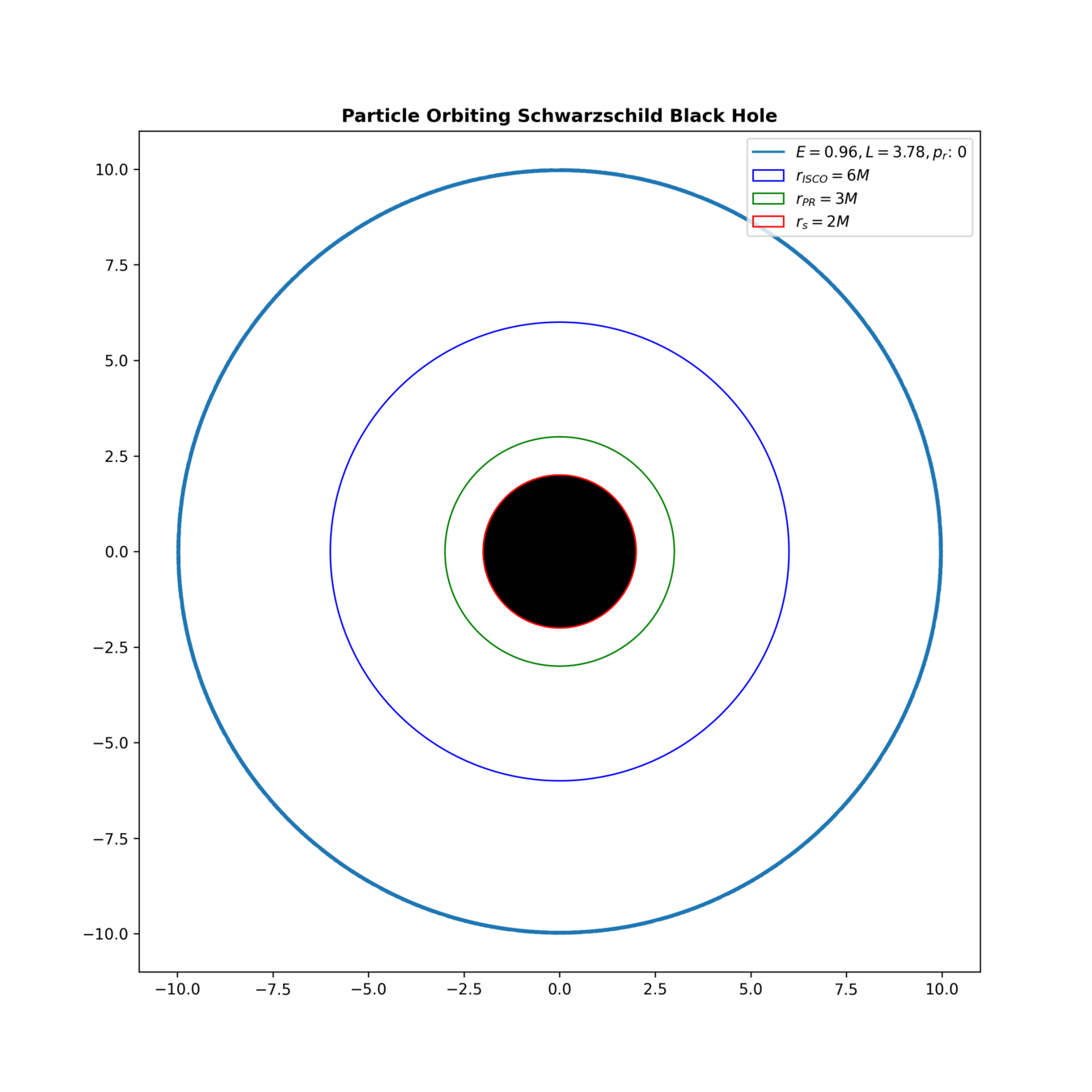
Anatomy of a Black Hole
Anatomy of a Black Hole
Schwarzschild Radius
Photon Ring
Innermost Stable Circular Orbit
Schwarzschild Radius
Photon Ring
Innermost Stable Circular Orbit
✅
✅
But we want this in terms of p and e ...
For a circular orbit ...
For a circular orbit:
For a circular orbit:
- Eccentric orbits require greater angular momentum!
- No particle with mass can orbit at the photon ring!
- Must reduce to Newtonian angular momentum for large r
Kinetic Energy
Fixed Constant Energy of Particle
Gravitational Potential created by Black Hole
radius is constant for a circular orbit!
For a circular orbit:
Why does this term keep showing up?
Ah ... it's a sign of the event horizon of the black hole!
The metric becomes singular at the event horizon of the black hole!
The metric becomes singular at the event horizon of the black hole!
The metric becomes singular at the event horizon of the black hole!
The metric becomes singular at the event horizon of the black hole!
The metric becomes singular at the event horizon of the black hole!
The metric becomes singular at the event horizon of the black hole!
The metric becomes singular at the event horizon of the black hole!
What if we had a circular orbit?
What if we had a circular orbit?
Time slows down dramatically near p=6! Why?
Time slows down dramatically near p=6! Why?
Time stops at the event horizon!
Binary Black Holes


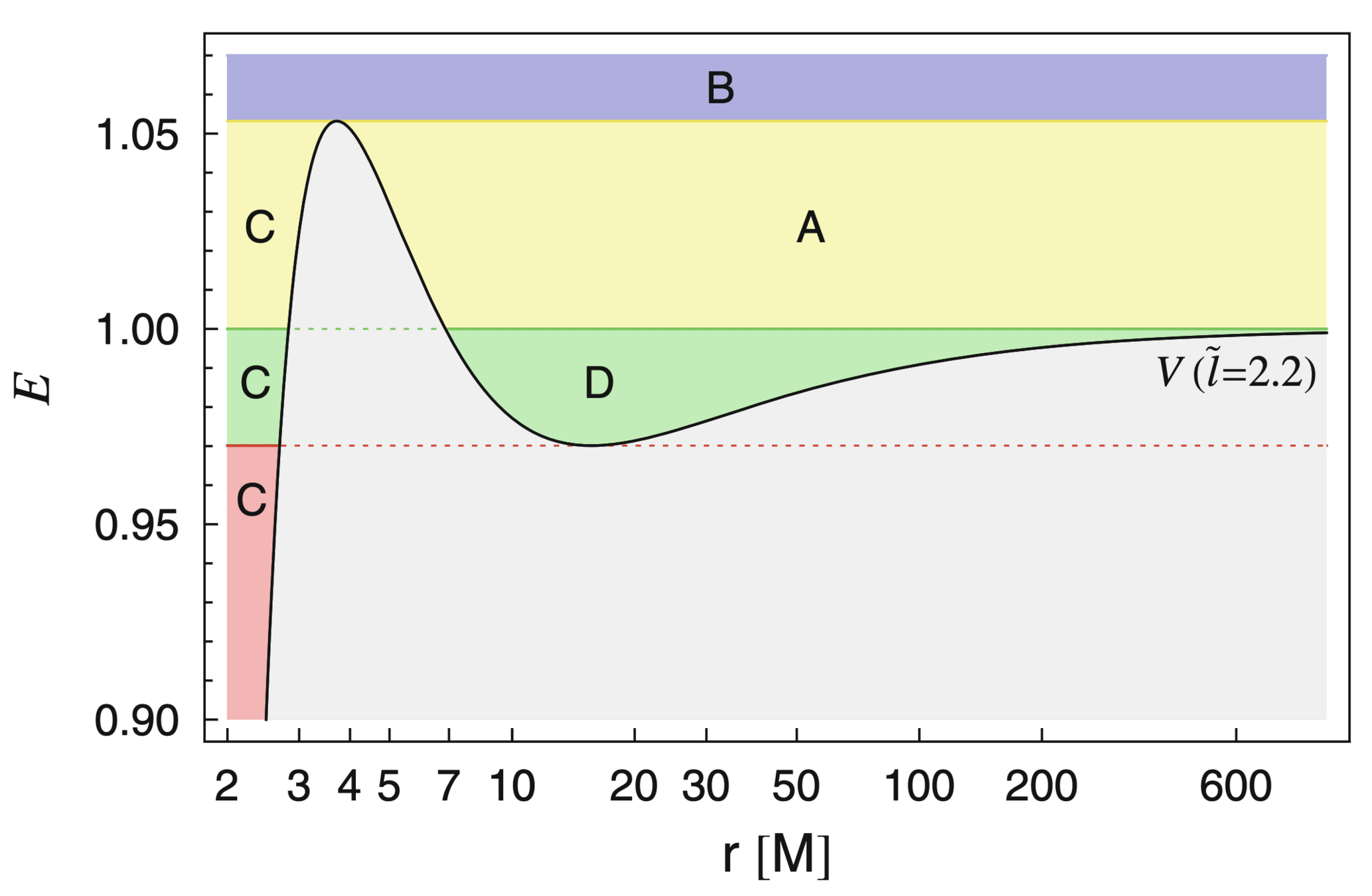
Analytical time-like geodesics in Schwarzschild space-time (Kostic, Gen. Rel. Grav., 2012)


Analytical time-like geodesics in Schwarzschild space-time (Kostic, Gen. Rel. Grav., 2012)
Stable Circular Orbit


Analytical time-like geodesics in Schwarzschild space-time (Kostic, Gen. Rel. Grav., 2012)
Elliptical Orbit


Analytical time-like geodesics in Schwarzschild space-time (Kostic, Gen. Rel. Grav., 2012)
Hyperbolic Orbit


Analytical time-like geodesics in Schwarzschild space-time (Kostic, Gen. Rel. Grav., 2012)
Unstable Circular Orbit


Analytical time-like geodesics in Schwarzschild space-time (Kostic, Gen. Rel. Grav., 2012)
Plunge Orbit

Circular
Elliptical
Hyperbolic
Plunge

Elliptical
Hyperbolic
Plunge
Circle

Elliptical
Hyperbolic
Plunge
Circle

Elliptical
Hyperbolic
Plunge
Circle

Hyperbolic
Plunge
Circle
Ellipse

Circle
Ellipse
Ellipse
Unbound

Circle
Ellipse
Ellipse
Constraints:
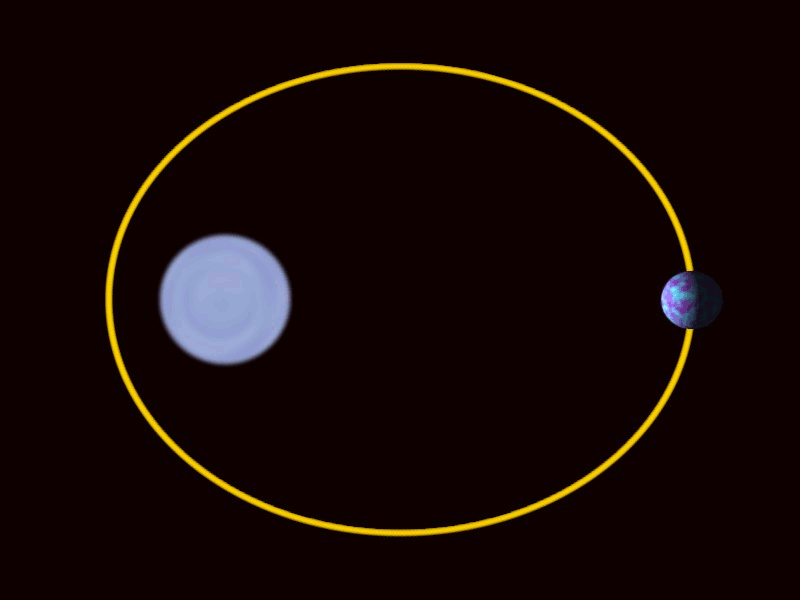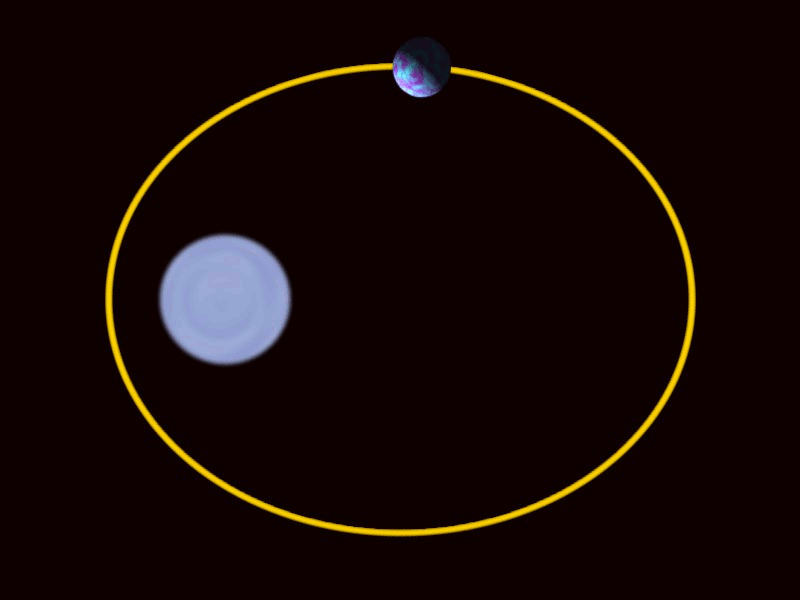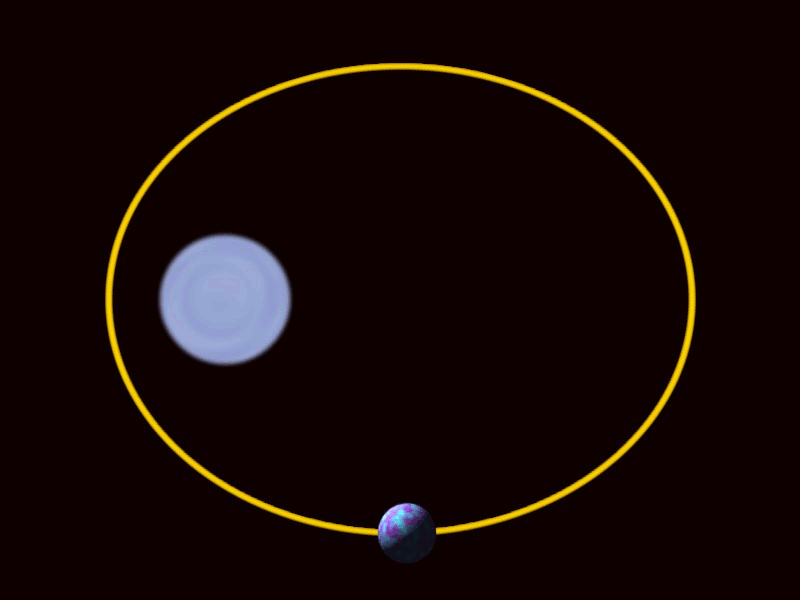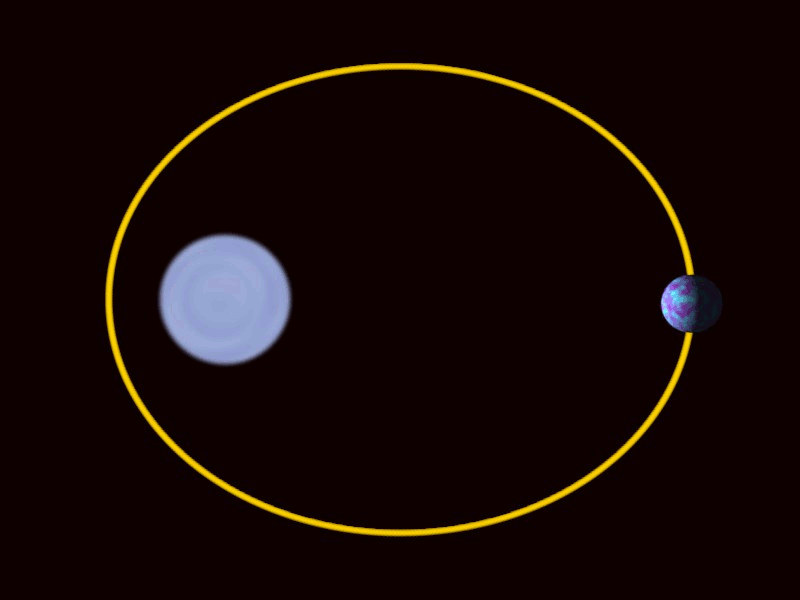
Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
-
Examples of GENERIC
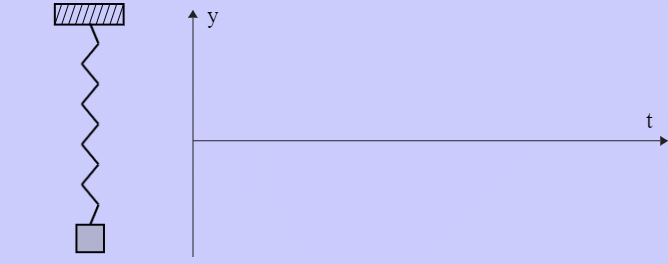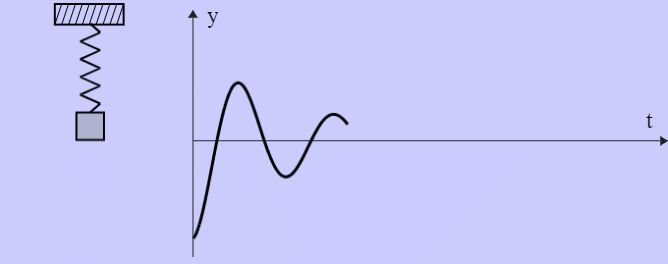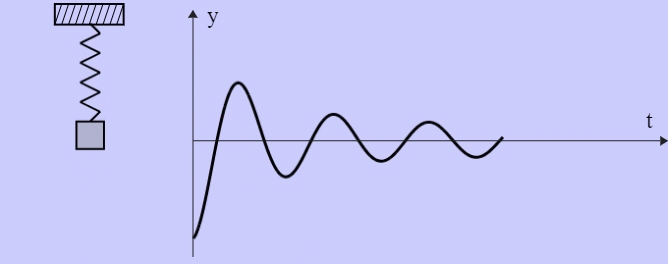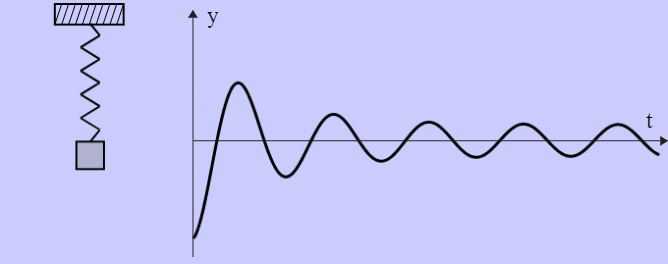
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
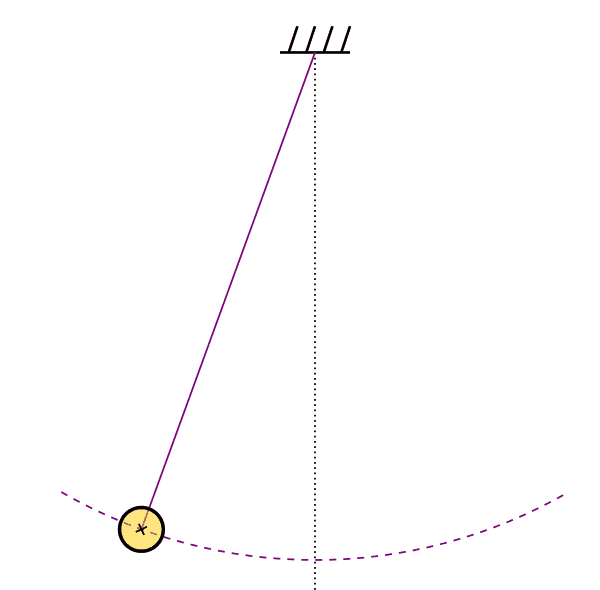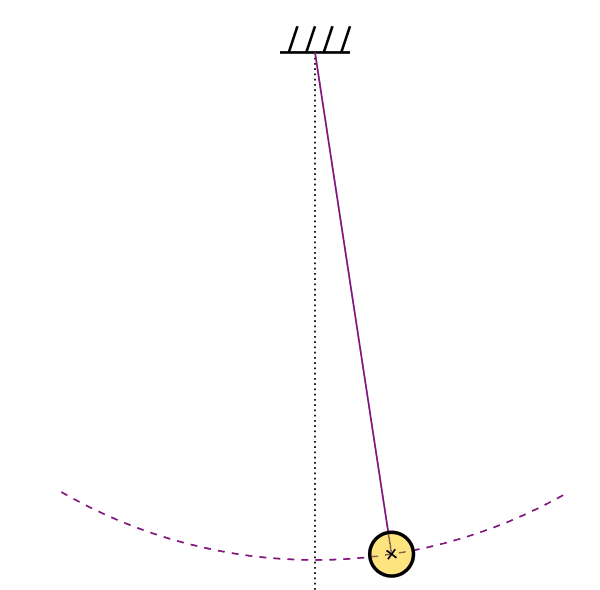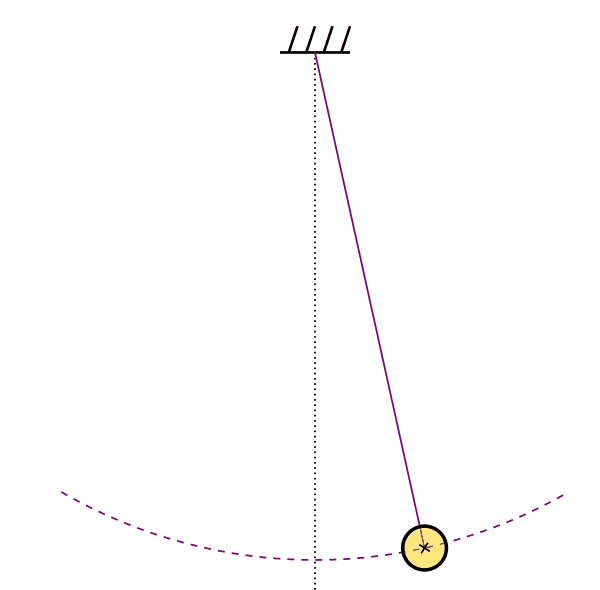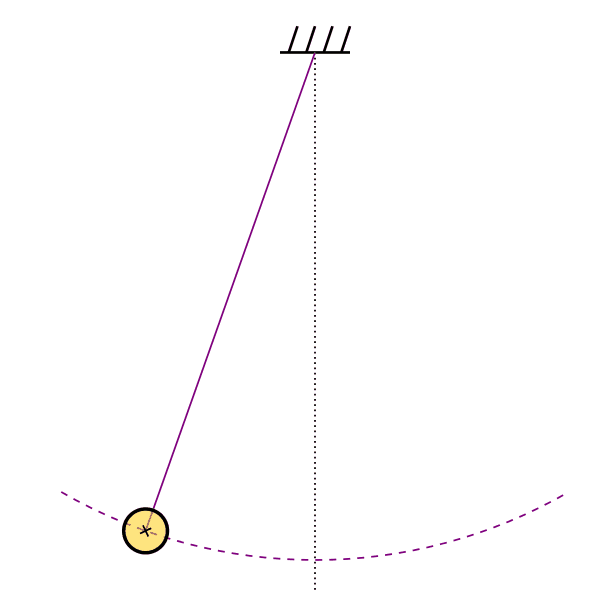
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

Mission Statement

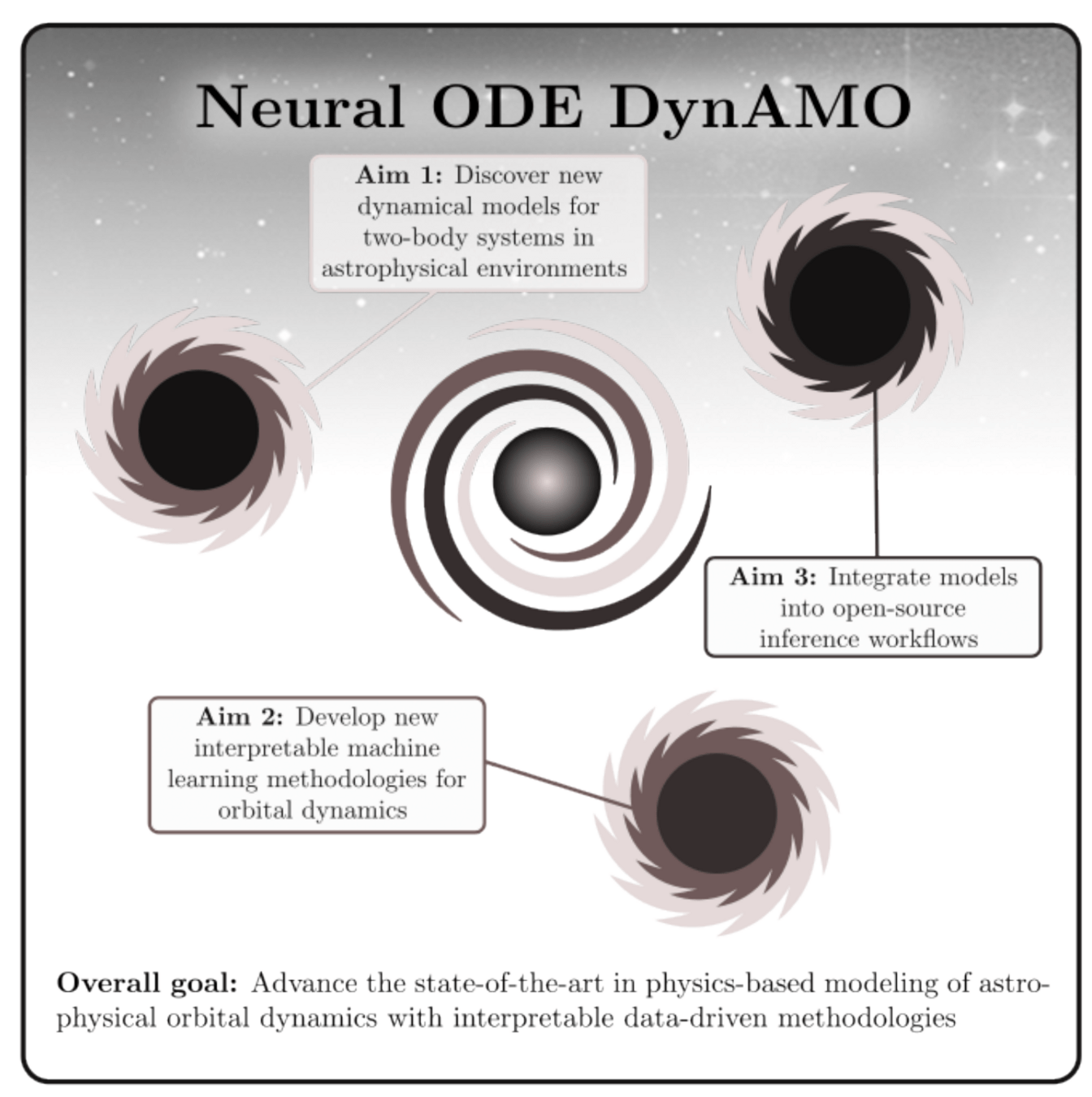
Mission Statement

Mission Statement

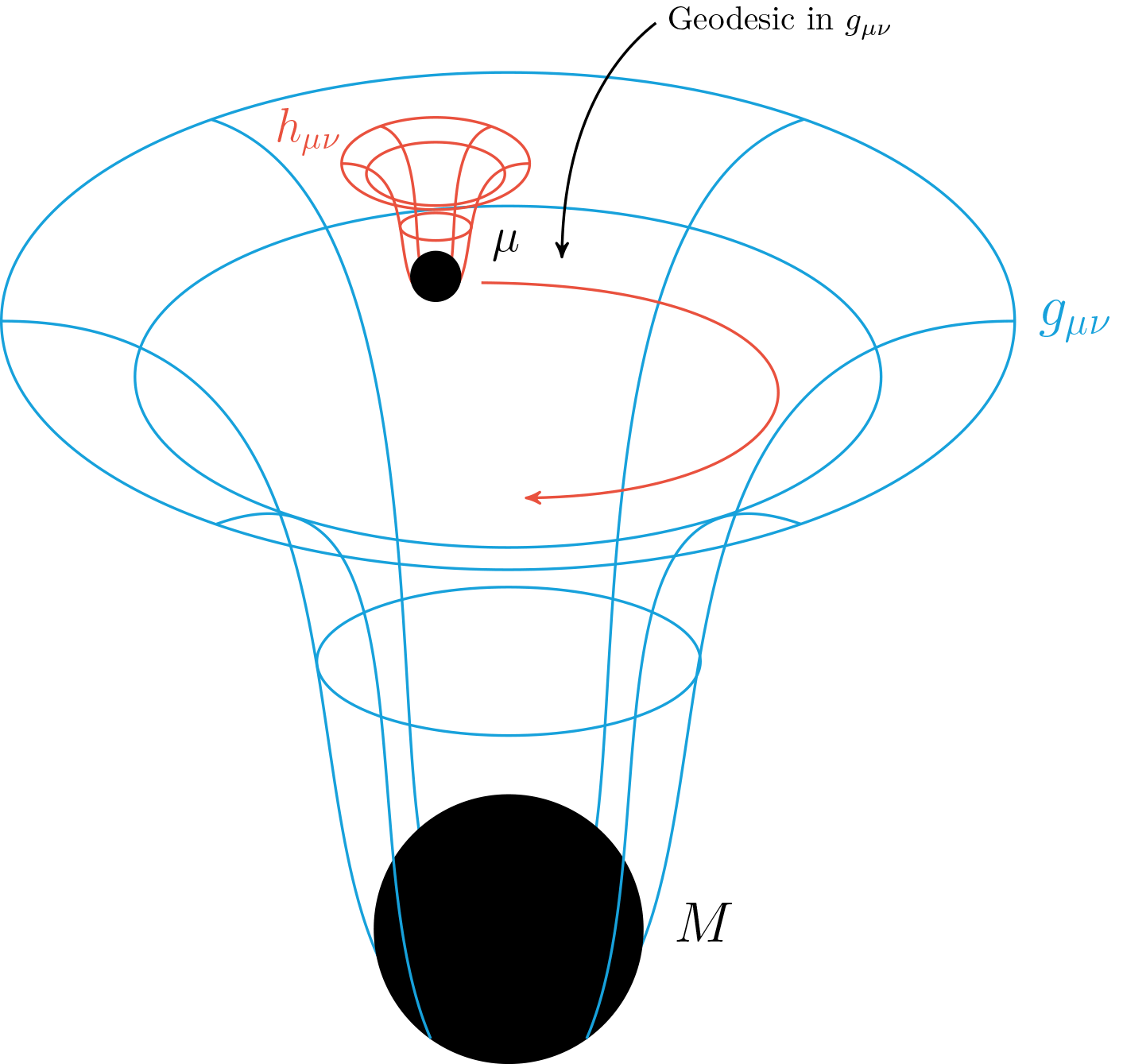
Mission Statement



Mission Statement



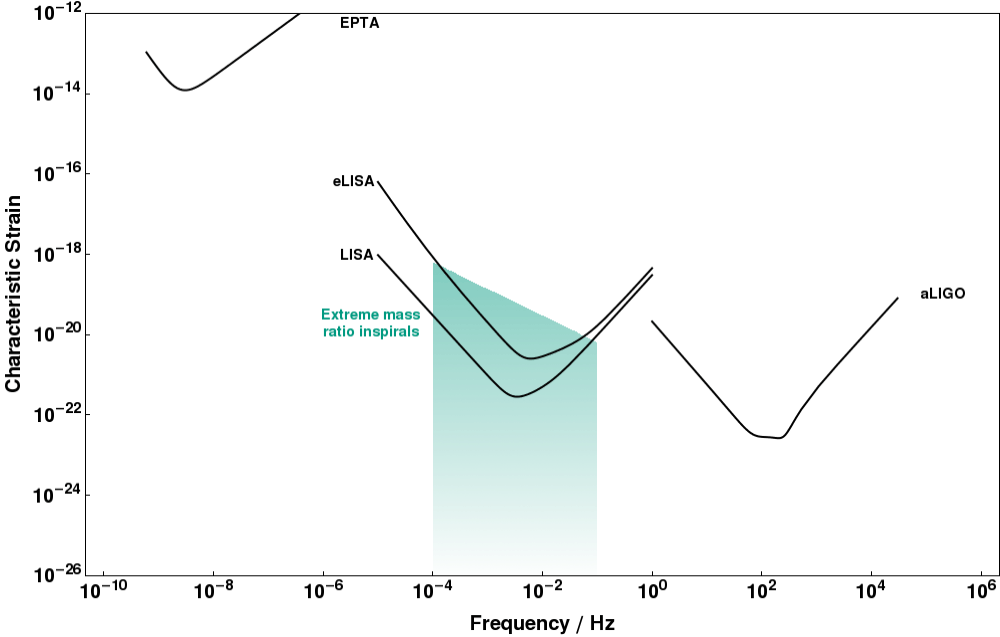
Mission Statement

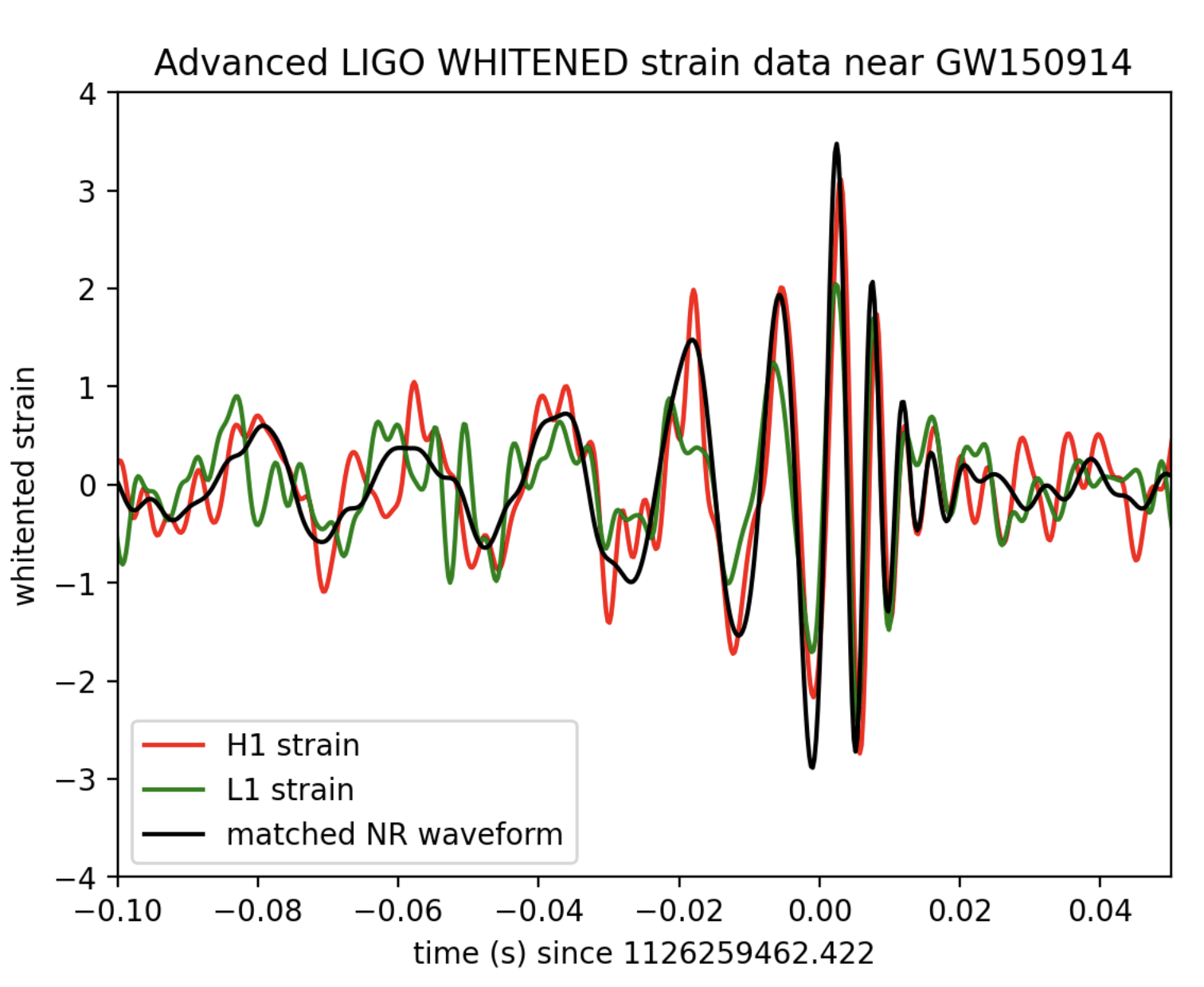
Mission Statement

Mission Statement


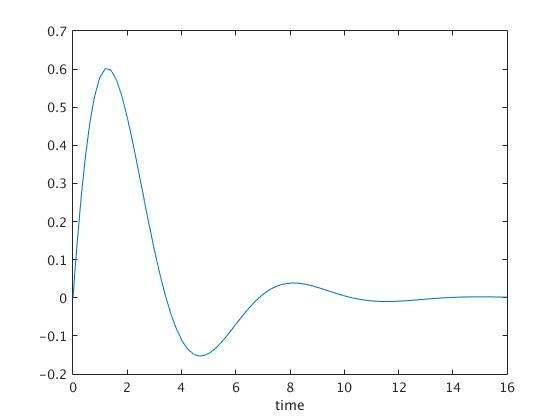
Mission Statement



Mission Statement



Mission Statement


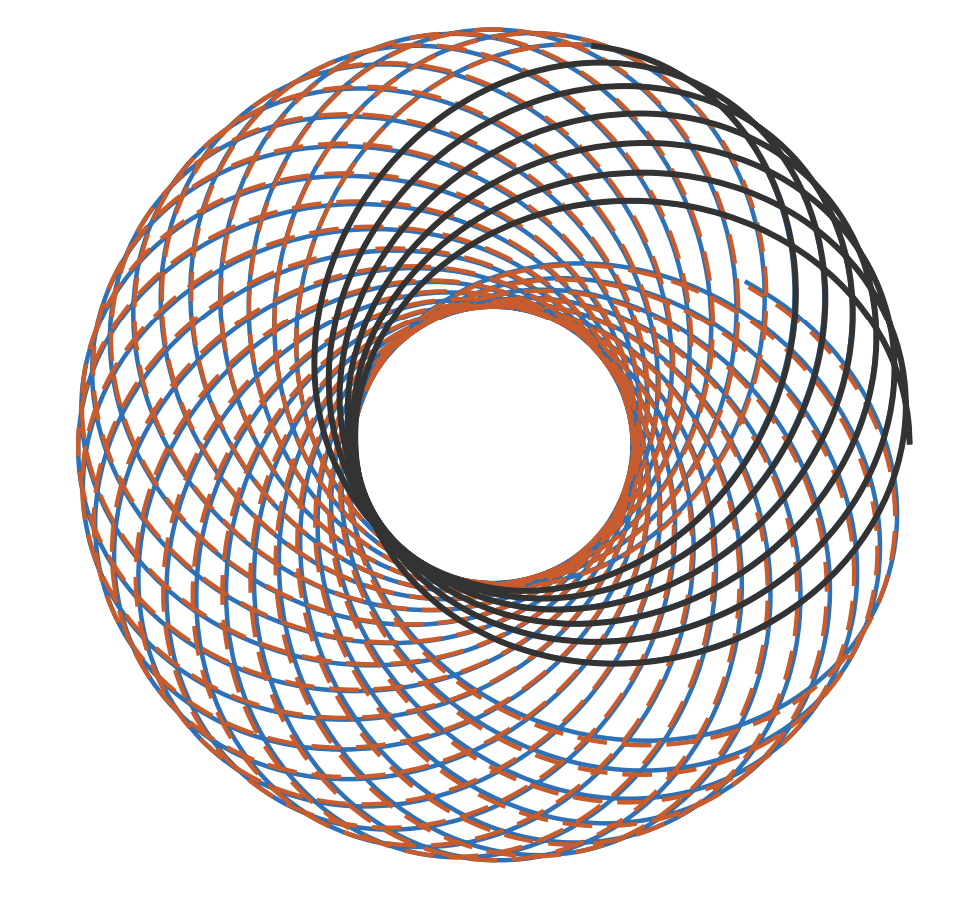
Mission Statement




Mission Statement




Mission Statement


Mission Statement

Mission Statement

Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
-
Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
-
Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

Introduction to GENERIC

G
E
N
E
R
I
C
Introduction to GENERIC

G
E
N
E
R
I
C
eneral
quation for
on
quilibrium
eversible
rreversible
oupling


Introduction to GENERIC

Introduction to GENERIC

"reversible"
"irreversible"
Introduction to GENERIC

"reversible"
"irreversible"
Introduction to GENERIC

"reversible"
"irreversible"
Introduction to GENERIC

Equilibrium
Inequilibrium
Introduction to GENERIC

Equilibrium
Inequilibrium
Introduction to GENERIC

Equilibrium
Inequilibrium
Conservative Dynamics
Introduction to GENERIC

Equilibrium
Inequilibrium
Dissipative Dynamics
Introduction to GENERIC

Equilibrium
Inequilibrium
Introduction to GENERIC

Equilibrium
Inequilibrium
Introduction to GENERIC

Equilibrium
Inequilibrium
Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
-
Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
- Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

Examples of GENERIC




Examples of GENERIC


State Variables
State Variables
Examples of GENERIC


State Variables
Energy
Energy
Examples of GENERIC


State Variables
Energy
Energy
Entropy
Energy
Energy
Entropy
Examples of GENERIC


State Variables
Energy
Energy
Entropy
Entropy
Examples of GENERIC


Examples of GENERIC


Examples of GENERIC


Examples of GENERIC


Examples of GENERIC


Examples of GENERIC


Examples of GENERIC




Examples of GENERIC




Examples of GENERIC




Examples of GENERIC







Examples of GENERIC




Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
- Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
-
Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)

GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)

GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)

GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)

GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)

GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)


GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)



GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)



GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)




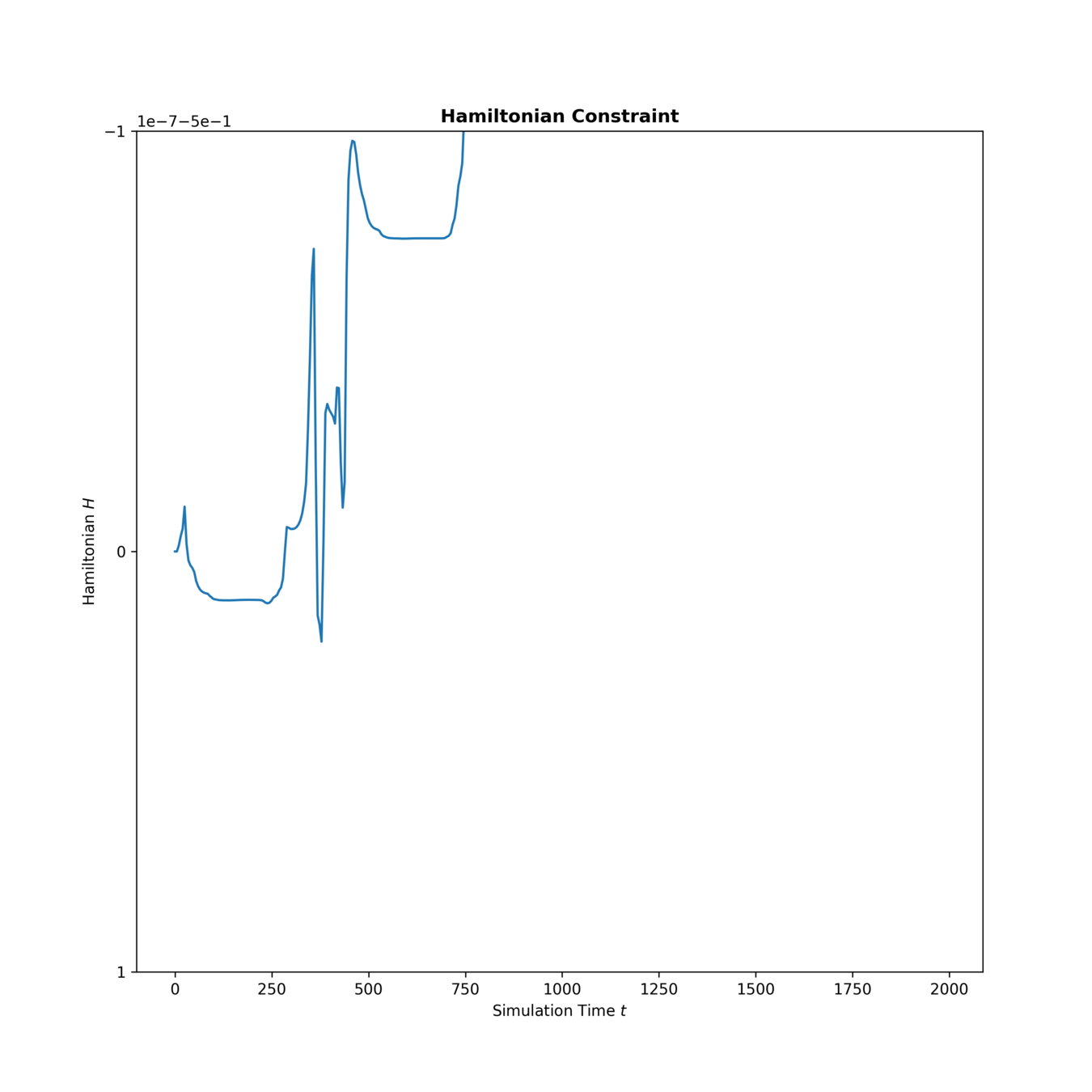
GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)





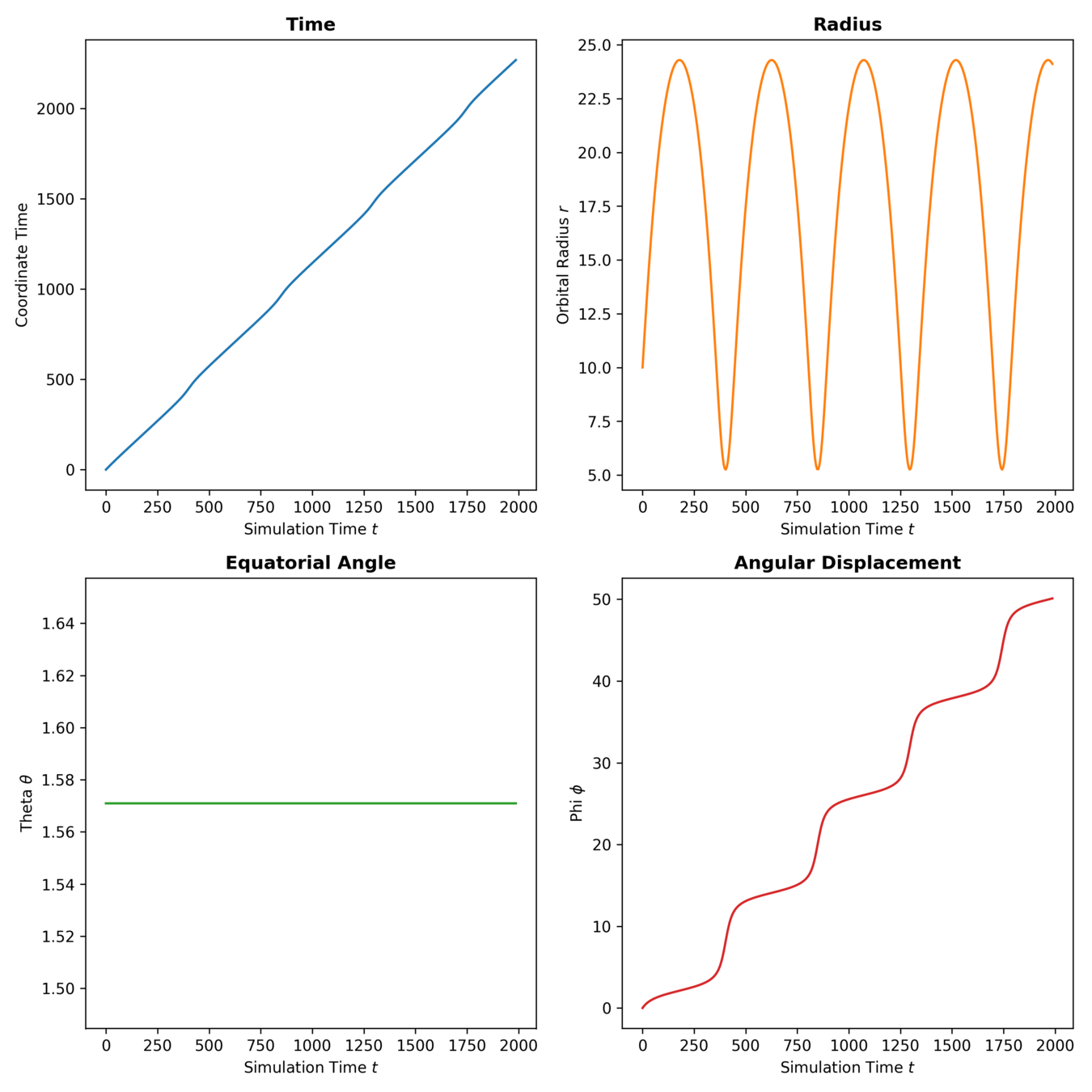
GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)





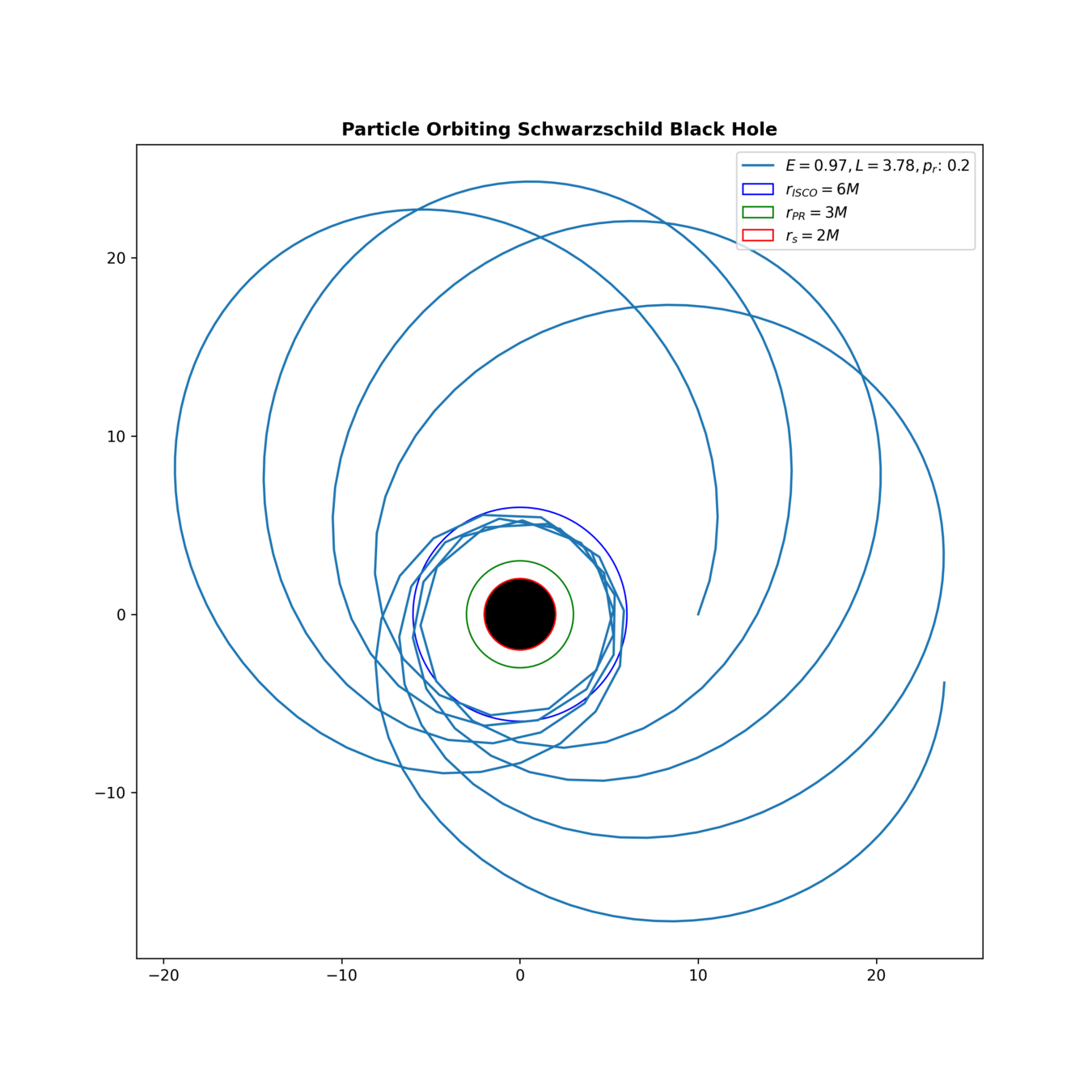

GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)







GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)







Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
-
Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
-
Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)
