Binary Black Holes
A GENERIC Approach
Ref Bari
Advisor: Prof. Brendan Keith


Binary Black Holes

Binary Black Holes

Binary Black Holes


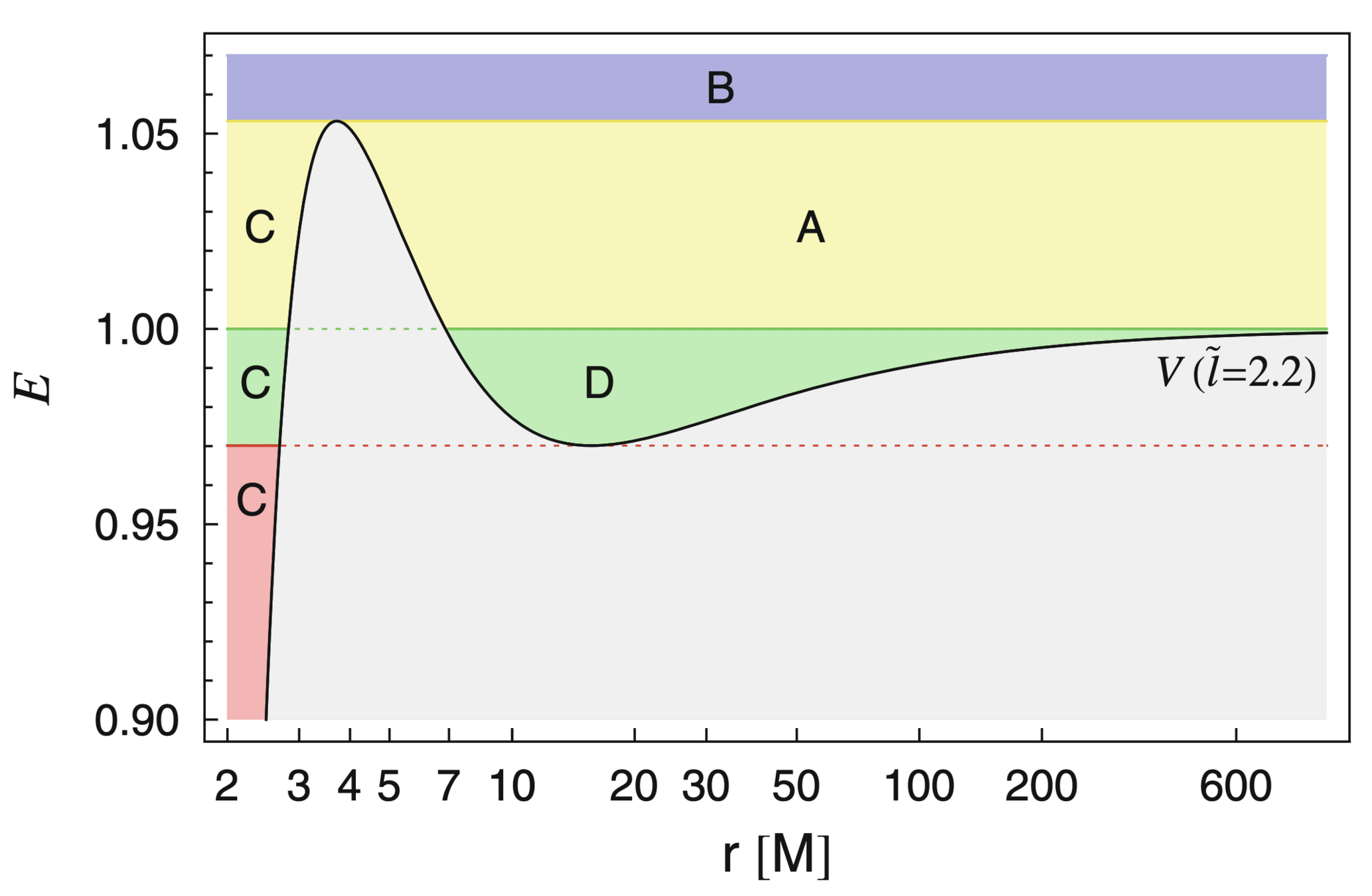
Analytical time-like geodesics in Schwarzschild space-time (Kostic, Gen. Rel. Grav., 2012)


Analytical time-like geodesics in Schwarzschild space-time (Kostic, Gen. Rel. Grav., 2012)
Stable Circular Orbit


Analytical time-like geodesics in Schwarzschild space-time (Kostic, Gen. Rel. Grav., 2012)
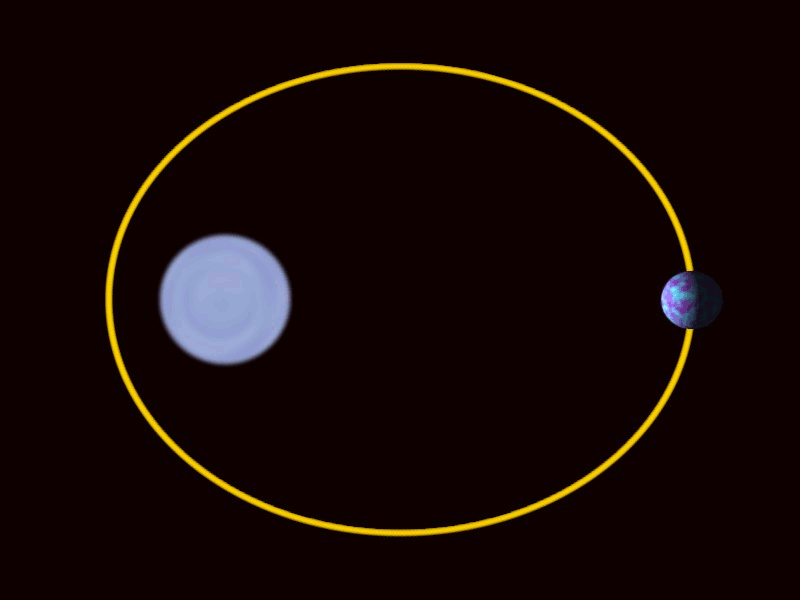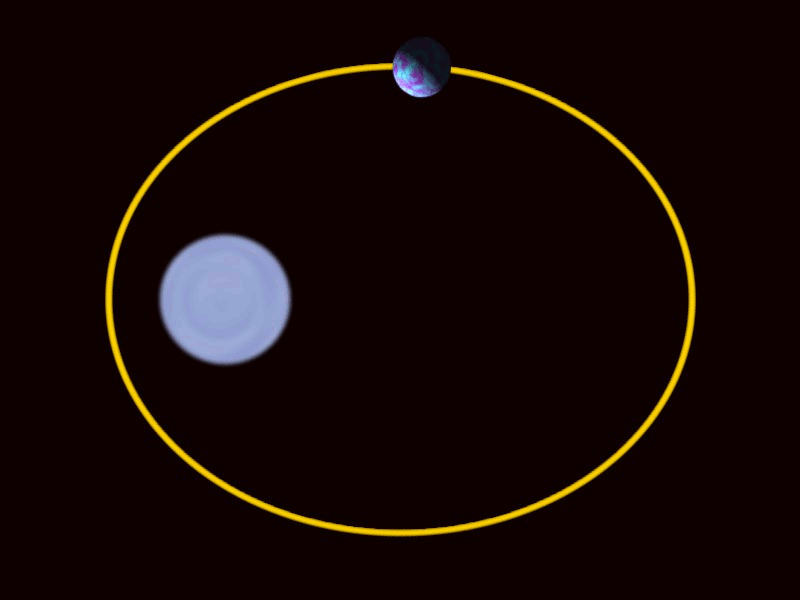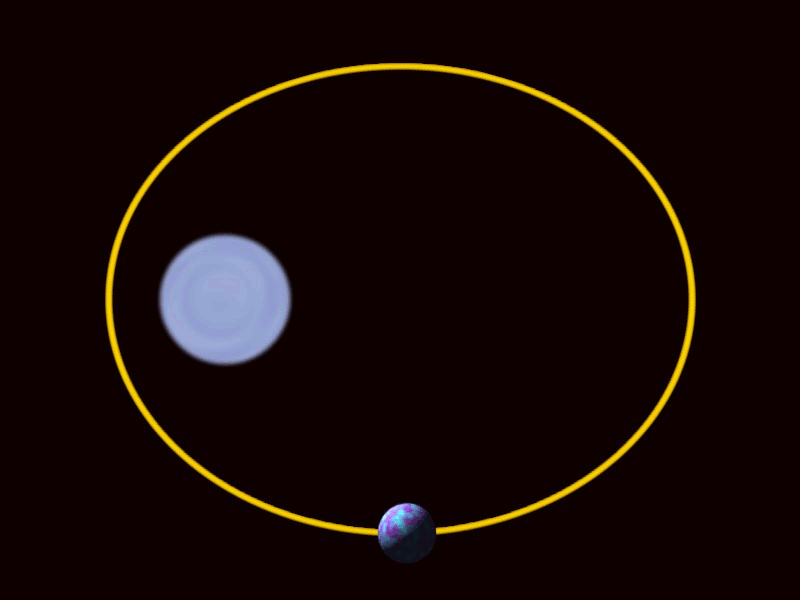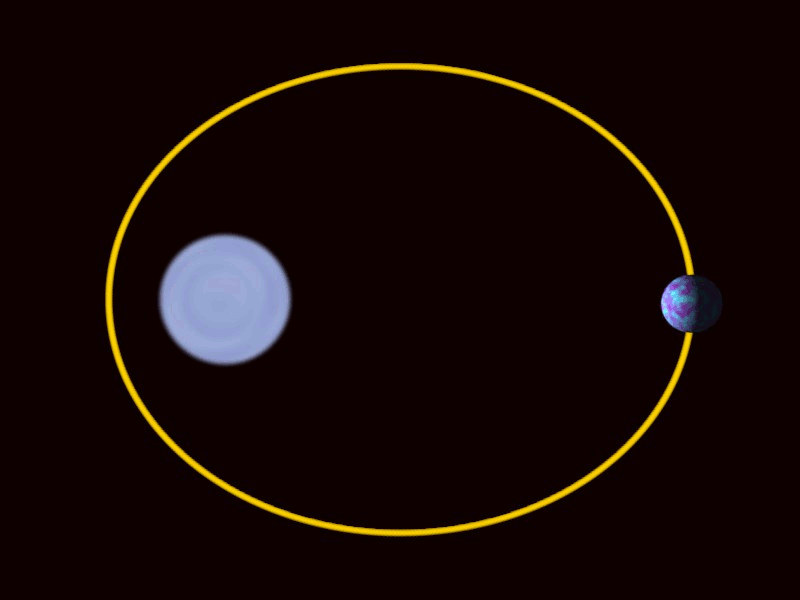
Elliptical Orbit


Analytical time-like geodesics in Schwarzschild space-time (Kostic, Gen. Rel. Grav., 2012)
Hyperbolic Orbit


Analytical time-like geodesics in Schwarzschild space-time (Kostic, Gen. Rel. Grav., 2012)
Unstable Circular Orbit


Analytical time-like geodesics in Schwarzschild space-time (Kostic, Gen. Rel. Grav., 2012)
Plunge Orbit

Circular
Elliptical
Hyperbolic
Plunge

Elliptical
Hyperbolic
Plunge
Circle

Elliptical
Hyperbolic
Plunge
Circle

Elliptical
Hyperbolic
Plunge
Circle

Hyperbolic
Plunge
Circle
Ellipse

Circle
Ellipse
Ellipse
Unbound

Circle
Ellipse
Ellipse
Constraints:
Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
-
Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

Mission Statement

Mission Statement

Mission Statement

Mission Statement



Mission Statement



Mission Statement

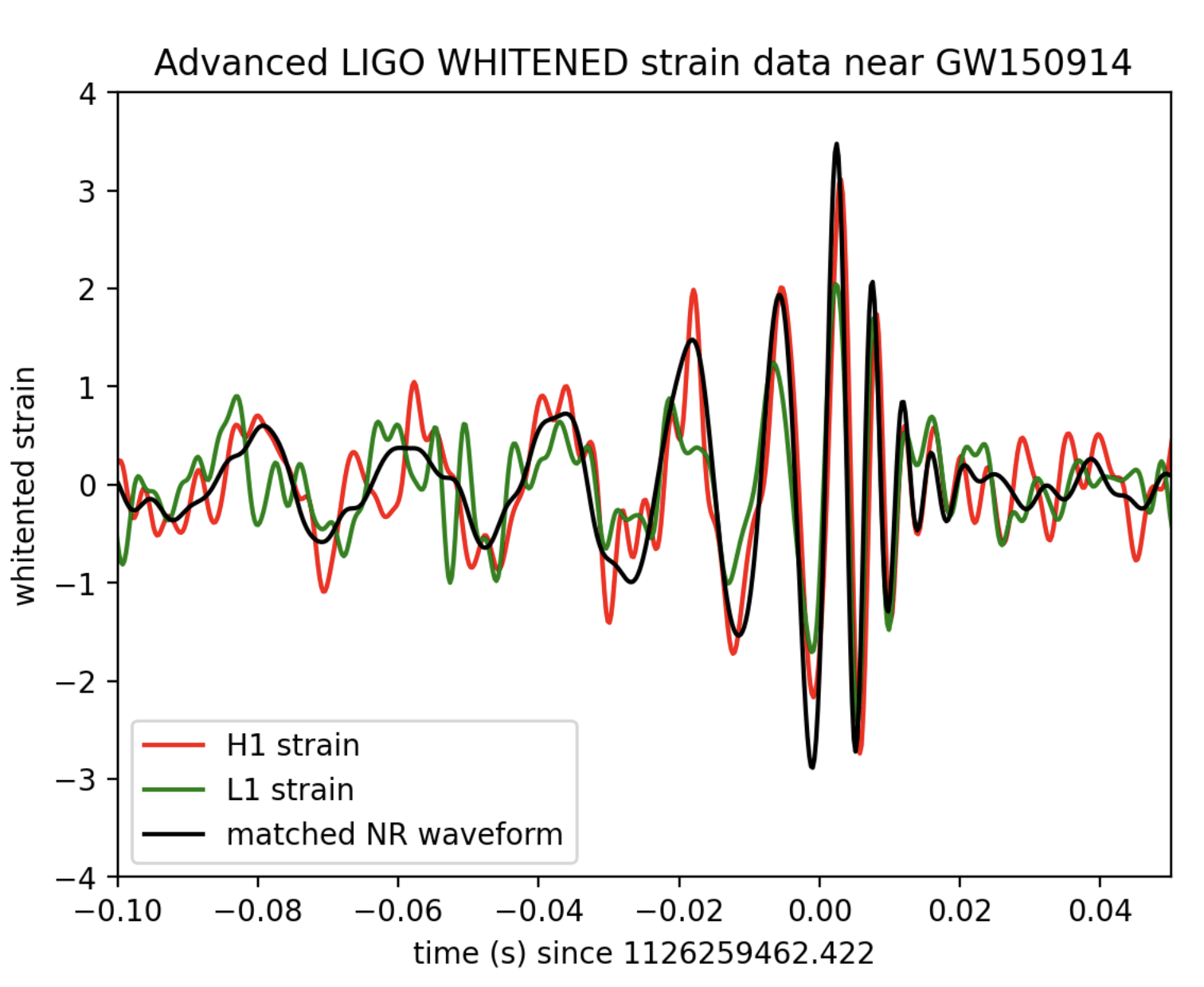
Mission Statement

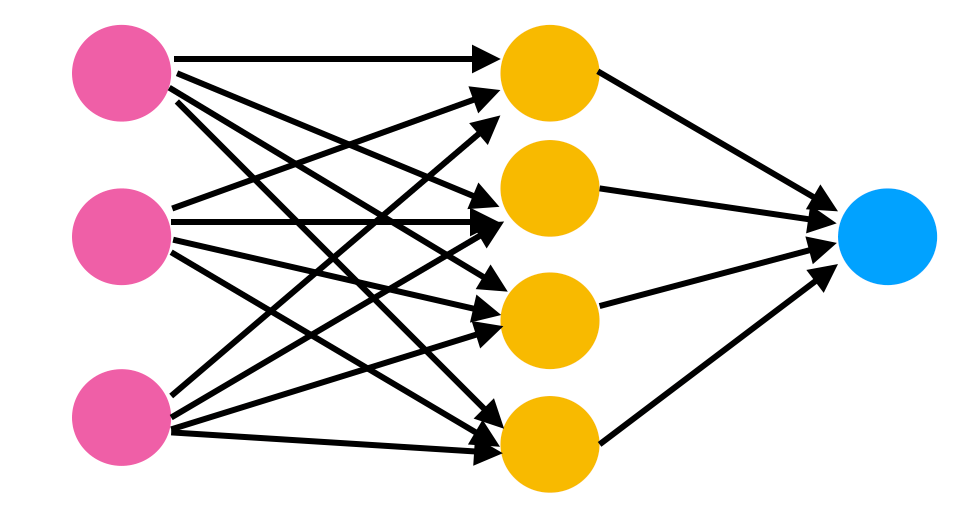
Mission Statement


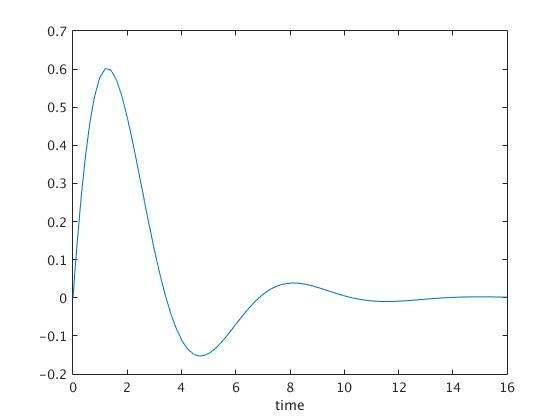
Mission Statement



Mission Statement



Mission Statement


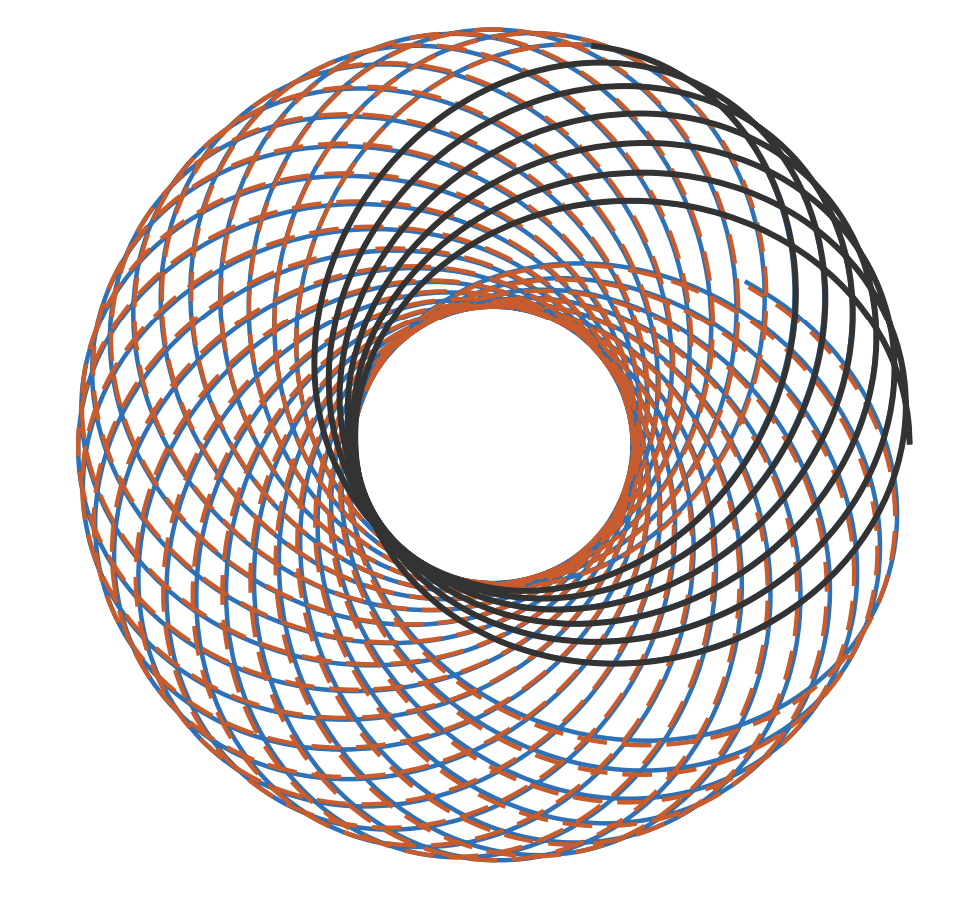
Mission Statement




Mission Statement




Mission Statement


Mission Statement

Mission Statement

Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
-
Examples of GENERIC
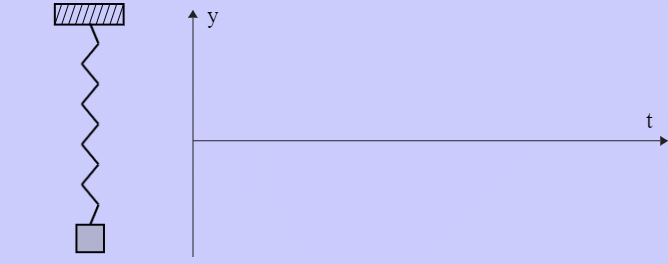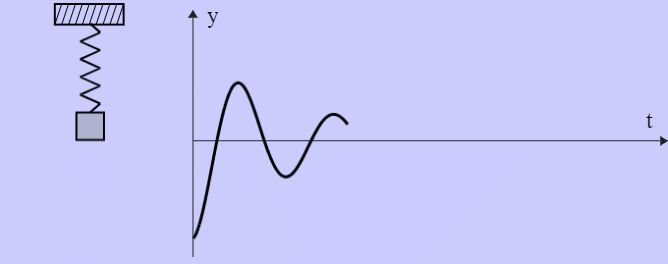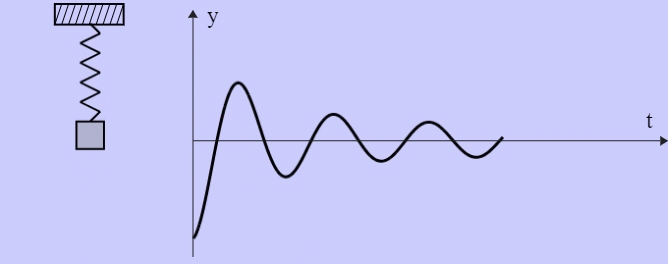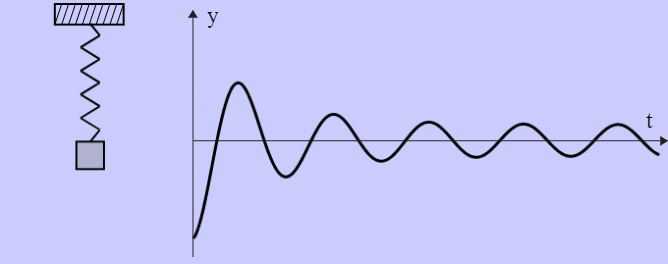
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
-
Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

Introduction to GENERIC

G
E
N
E
R
I
C
Introduction to GENERIC

G
E
N
E
R
I
C
eneral
quation for
on
quilibrium
eversible
rreversible
oupling


Introduction to GENERIC

Introduction to GENERIC

"reversible"
"irreversible"
Introduction to GENERIC

"reversible"
"irreversible"
Introduction to GENERIC

"reversible"
"irreversible"
Introduction to GENERIC

Equilibrium
Inequilibrium
Introduction to GENERIC

Equilibrium
Inequilibrium
Introduction to GENERIC

Equilibrium
Inequilibrium
Conservative Dynamics
Introduction to GENERIC

Equilibrium
Inequilibrium
Dissipative Dynamics
Introduction to GENERIC

Equilibrium
Inequilibrium
Introduction to GENERIC

Equilibrium
Inequilibrium
Introduction to GENERIC

Equilibrium
Inequilibrium
Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
-
Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
- Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

Examples of GENERIC




Examples of GENERIC


State Variables
State Variables
Examples of GENERIC


State Variables
Energy
Energy
Examples of GENERIC


State Variables
Energy
Energy
Entropy
Energy
Energy
Entropy
Examples of GENERIC


State Variables
Energy
Energy
Entropy
Entropy
Examples of GENERIC


Examples of GENERIC


Examples of GENERIC


Examples of GENERIC


Examples of GENERIC


Examples of GENERIC


Examples of GENERIC




Examples of GENERIC




Examples of GENERIC




Examples of GENERIC







Examples of GENERIC




Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
- Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
-
Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

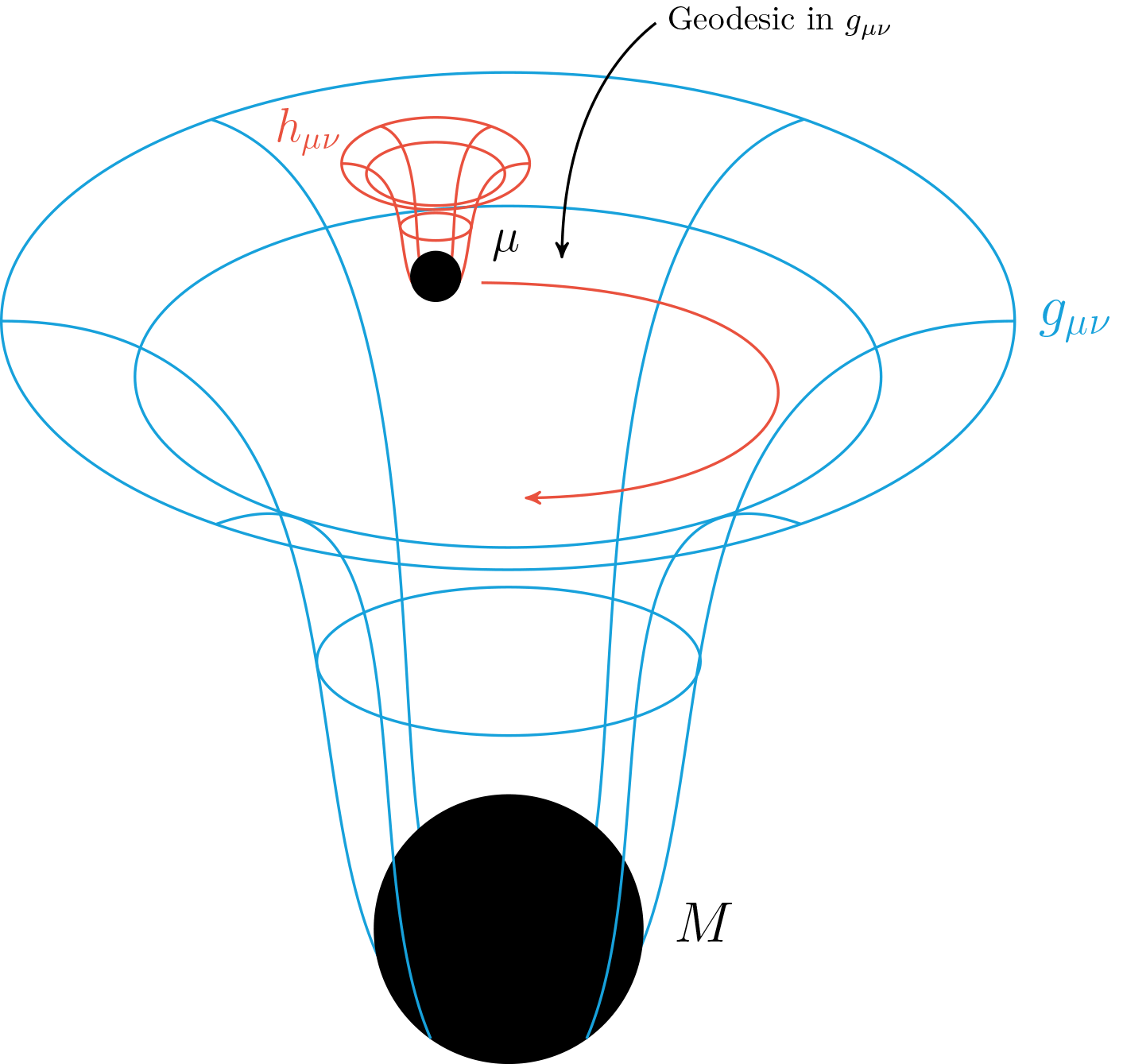
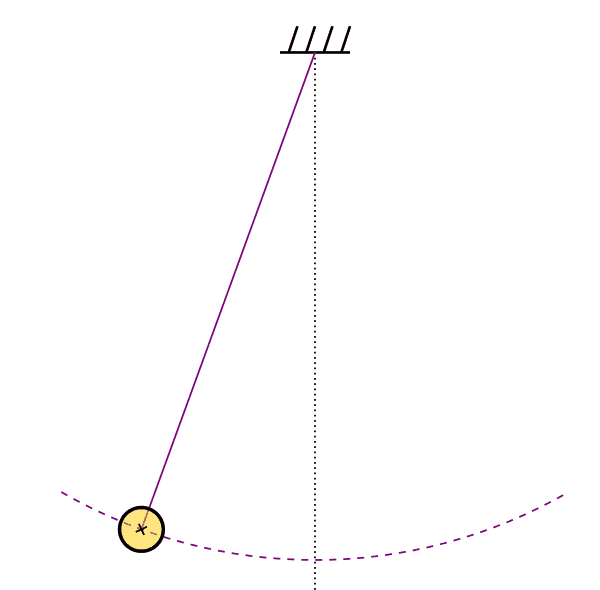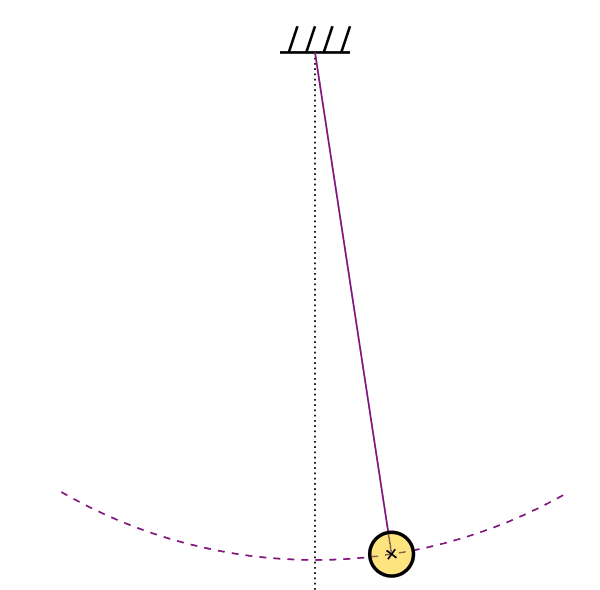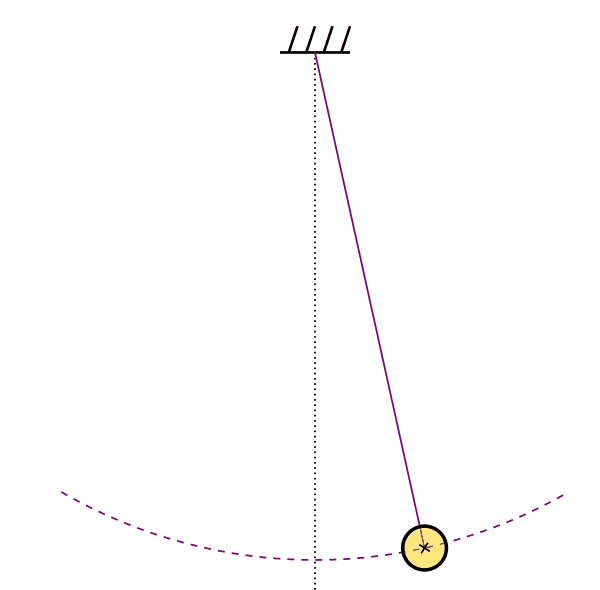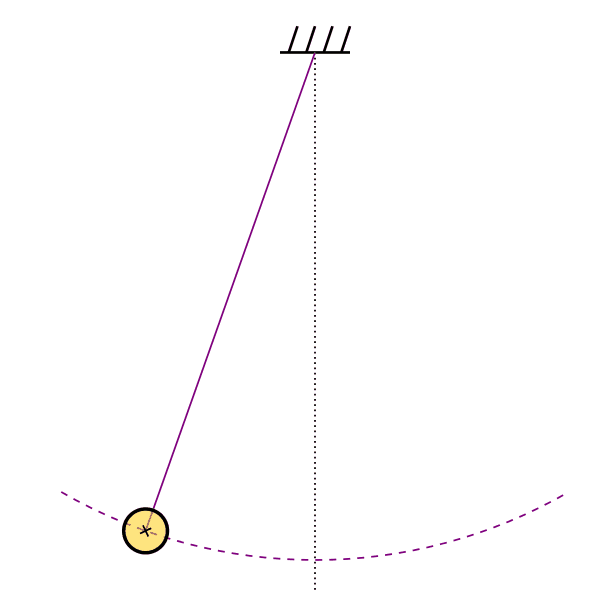
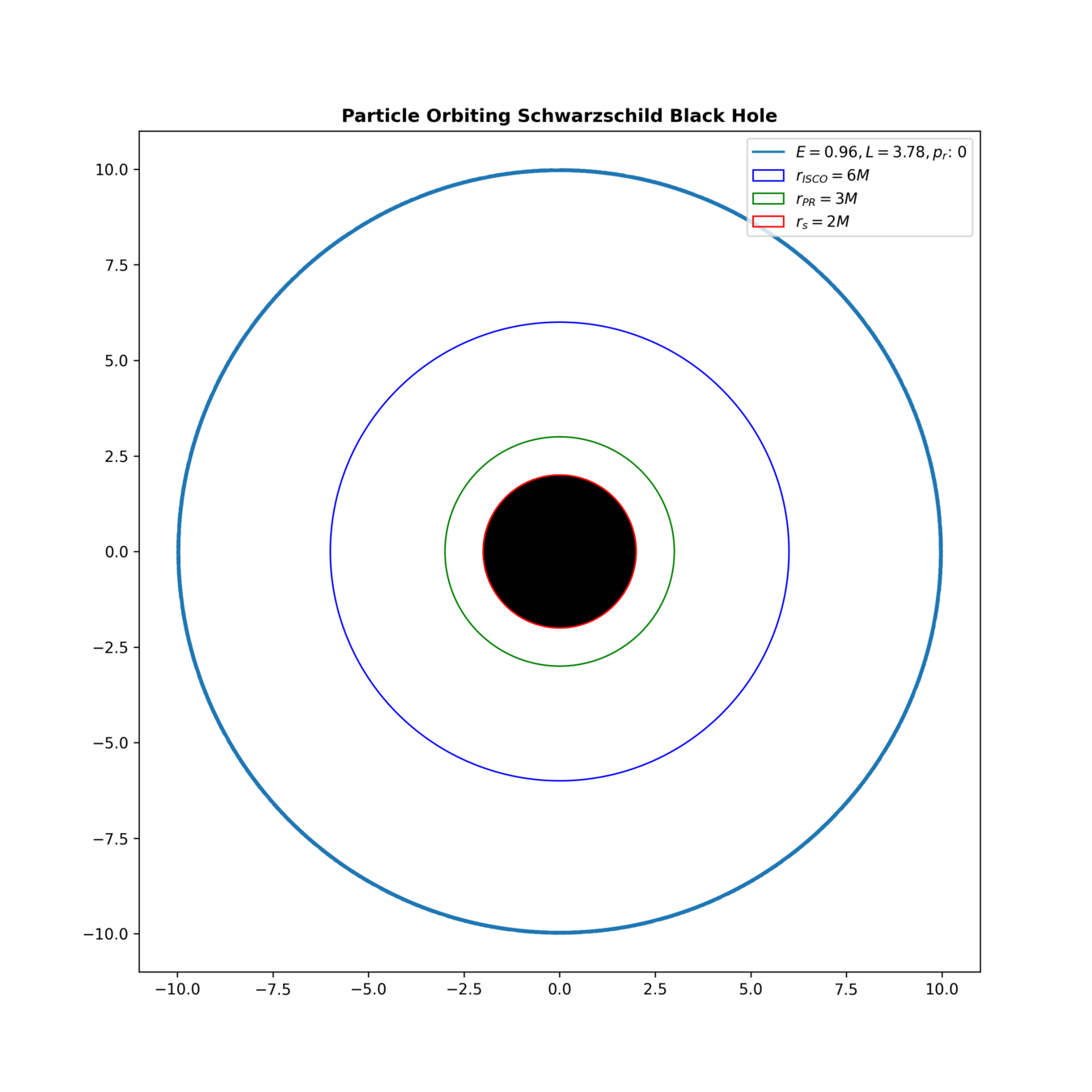
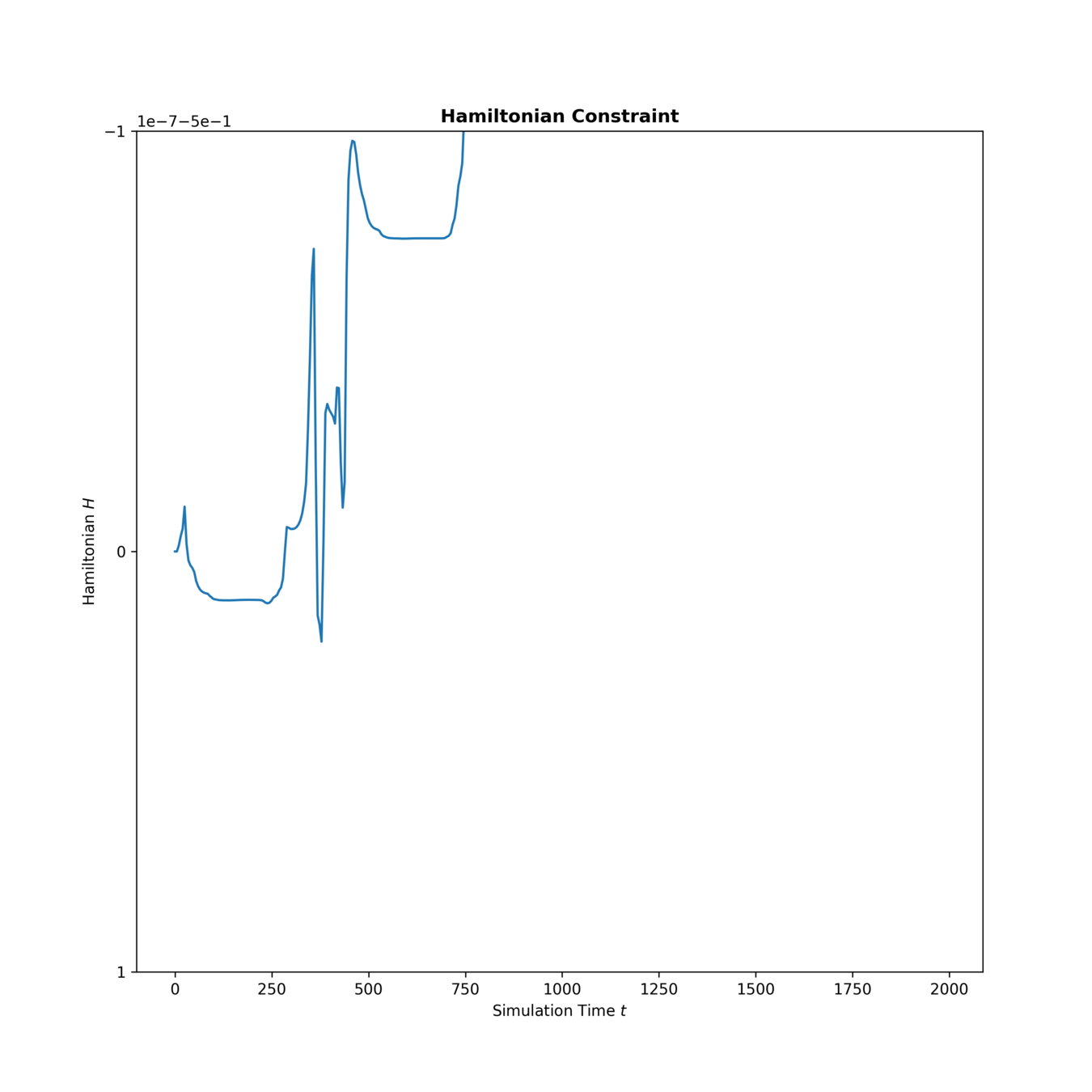
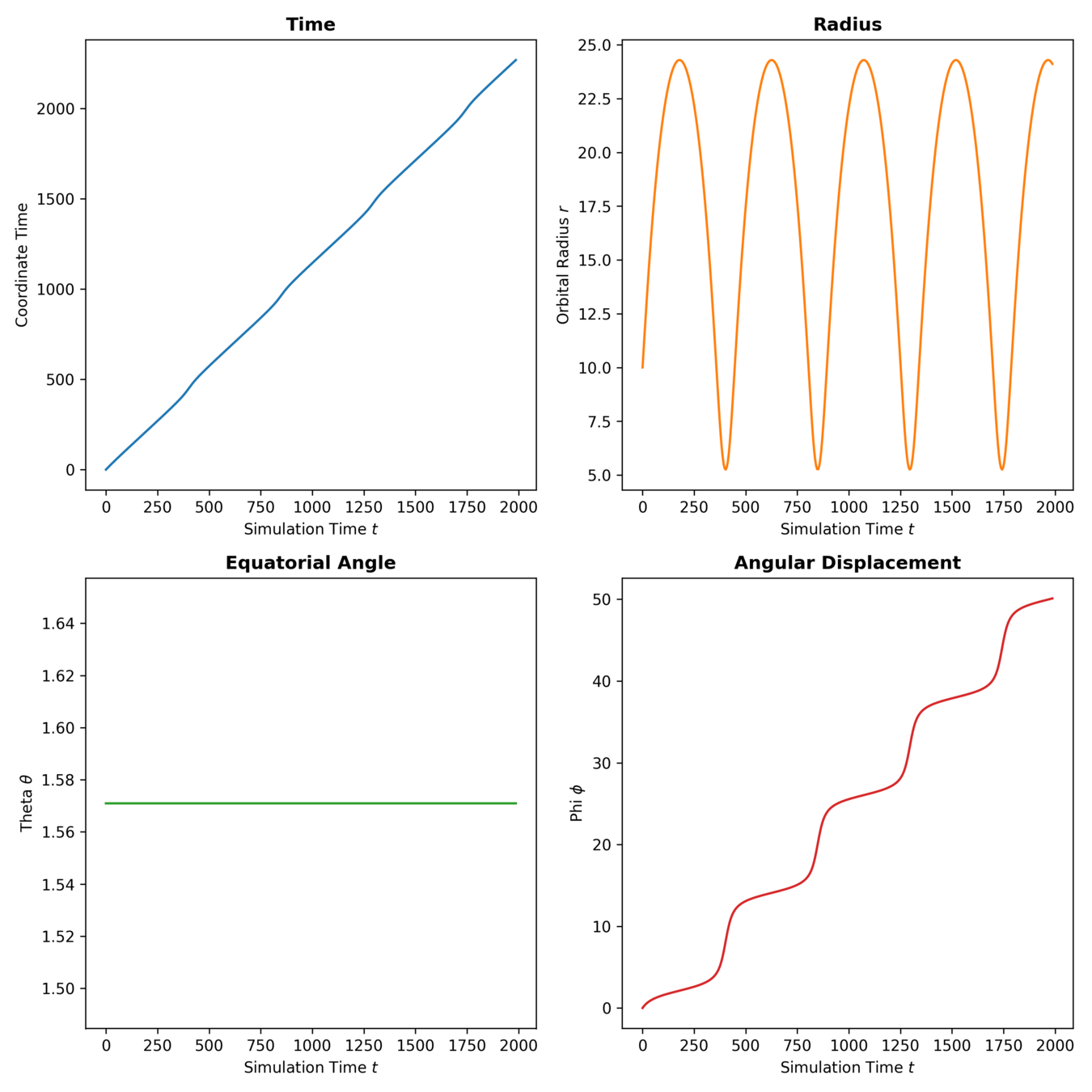
GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)

GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)

GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)

GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)

GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)

GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)


GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)



GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)



GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)




GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)





GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)





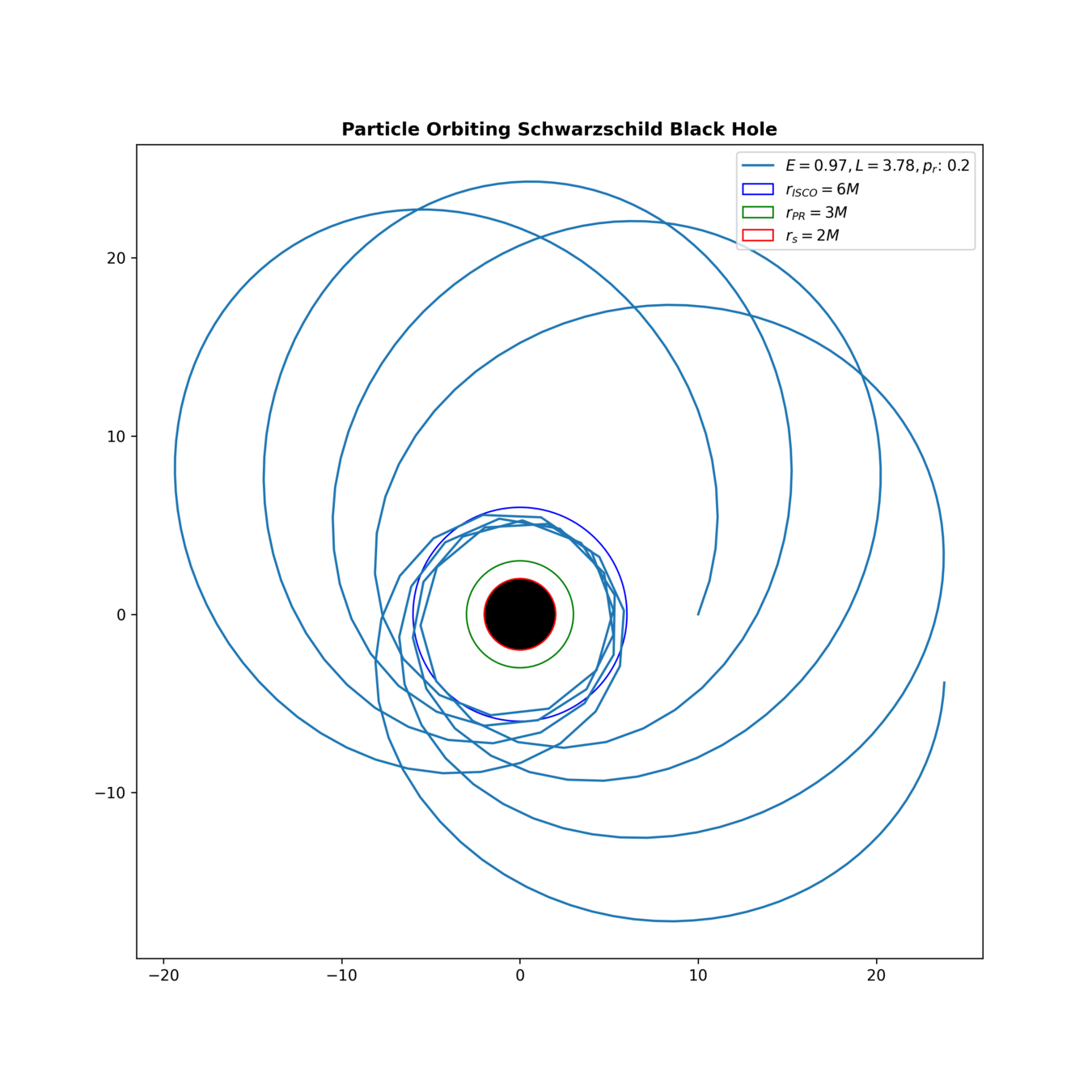

GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)







GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)







Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
-
Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
-
Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

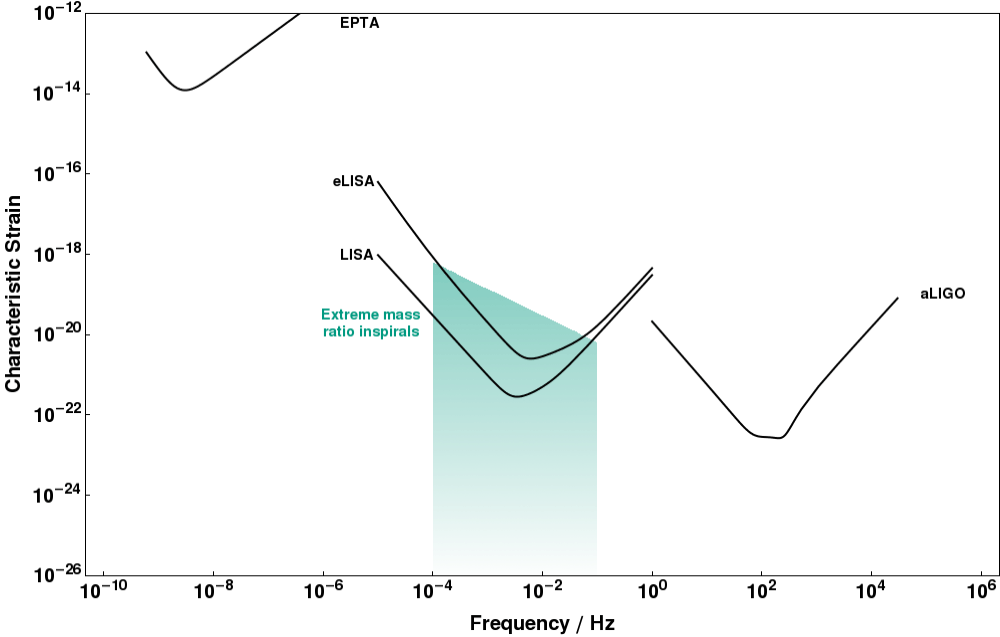
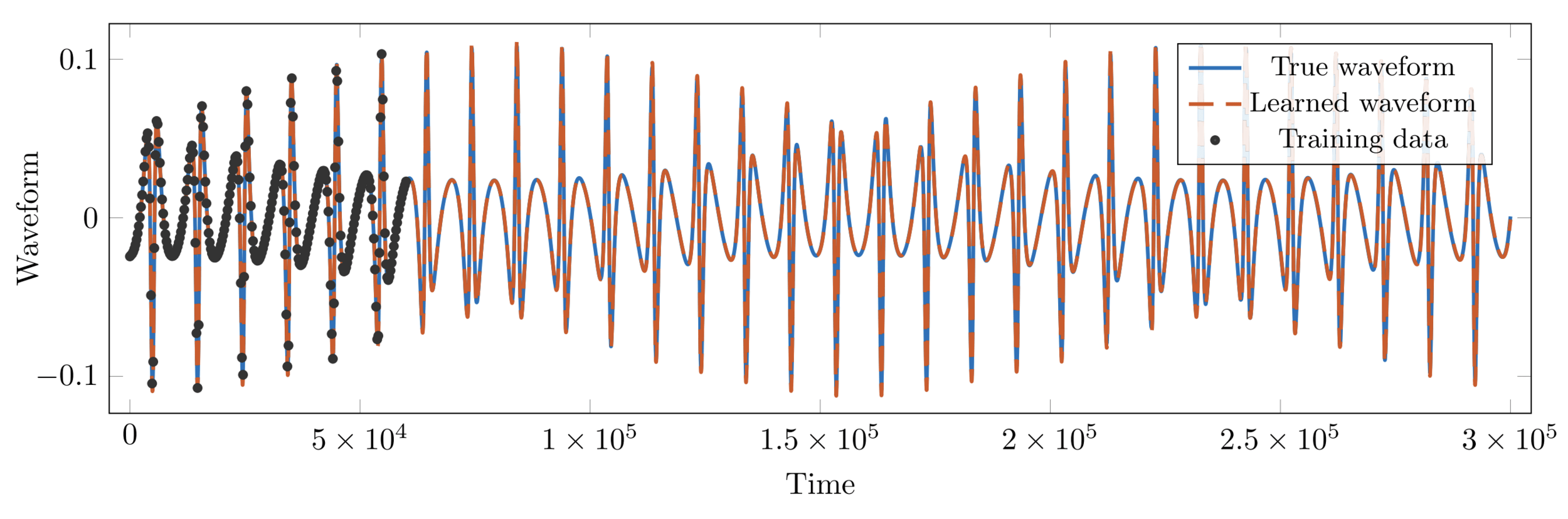
GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)
