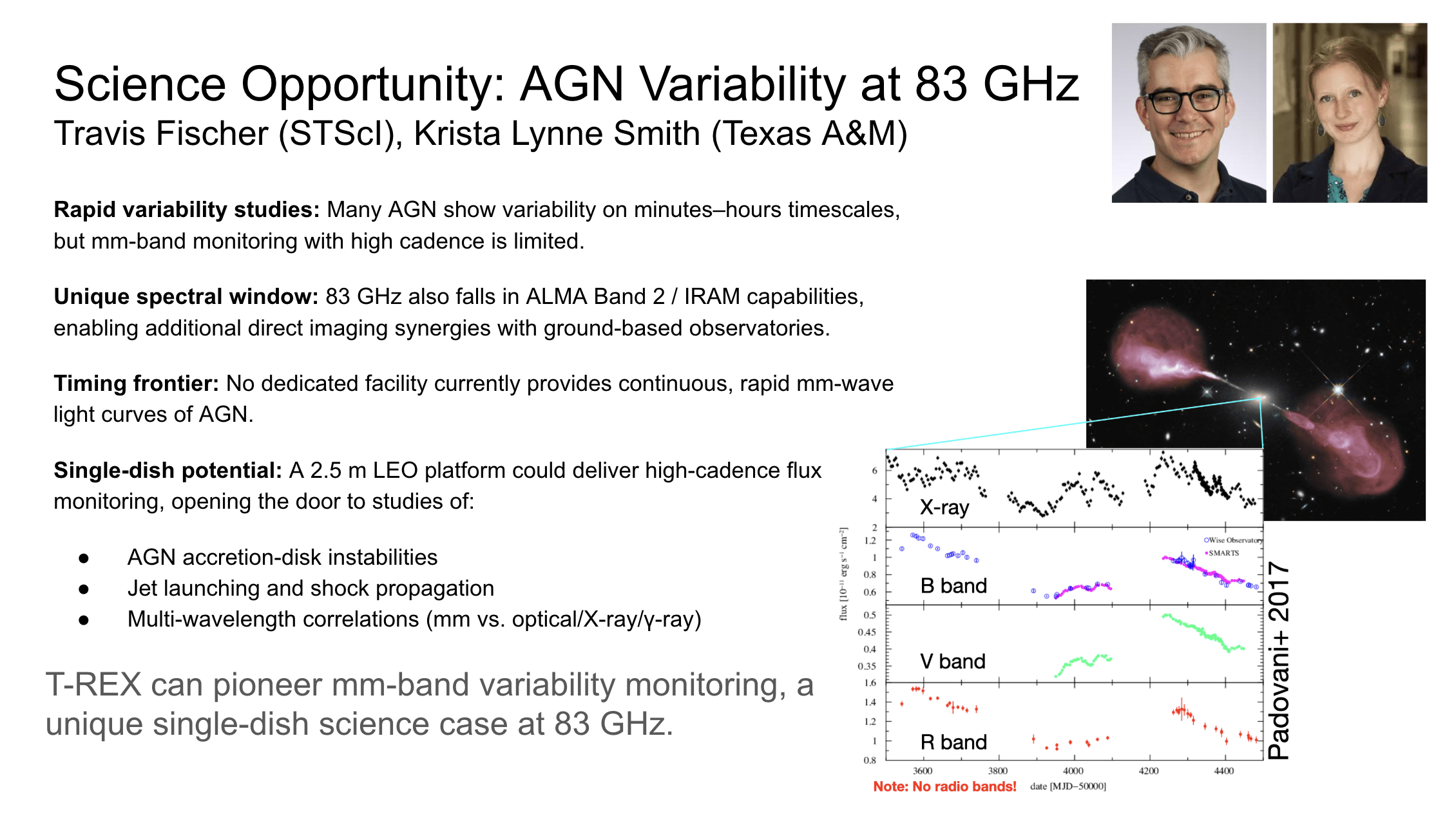
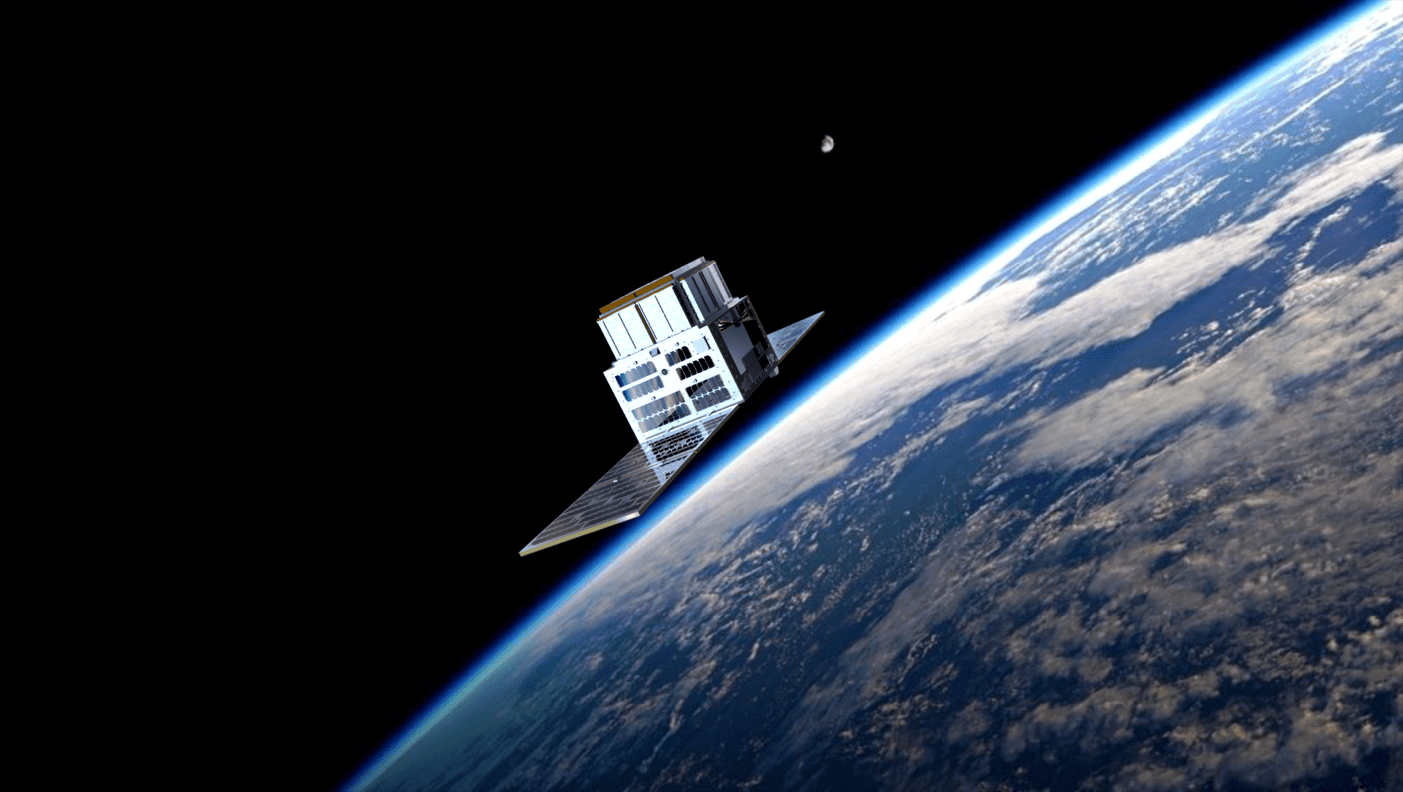
Time-Resolving Sgr A* from LEO



Ref Bari (Brown University)

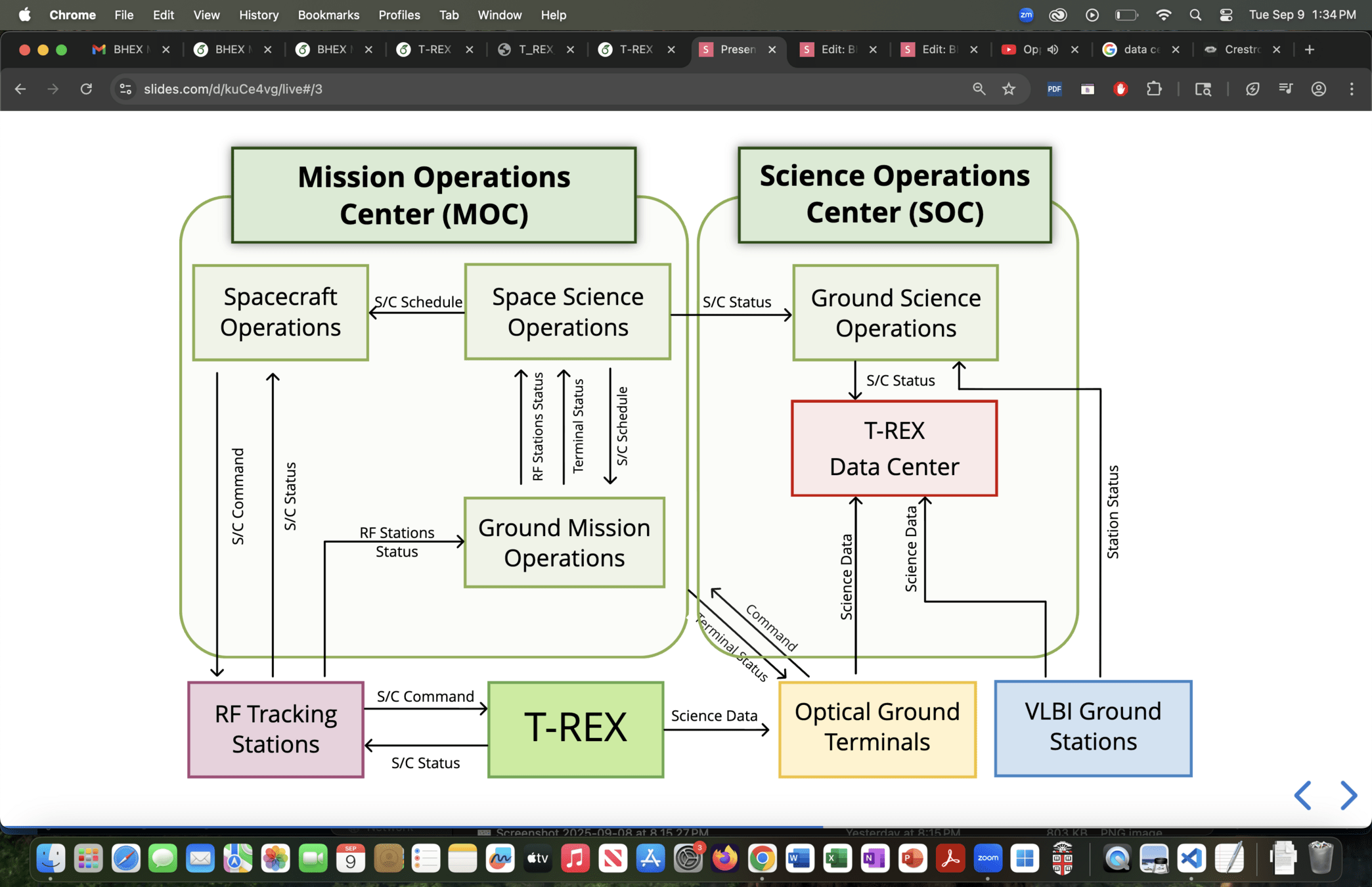
T-REX

T-REX


T-REX


T-REX


Optical Terminals
RF Tracking Stations


VLBI Ground Stations






T-REX Data Center








% Gain Error
NRMSE
0%
25%
50%
100%
0
1
0.5
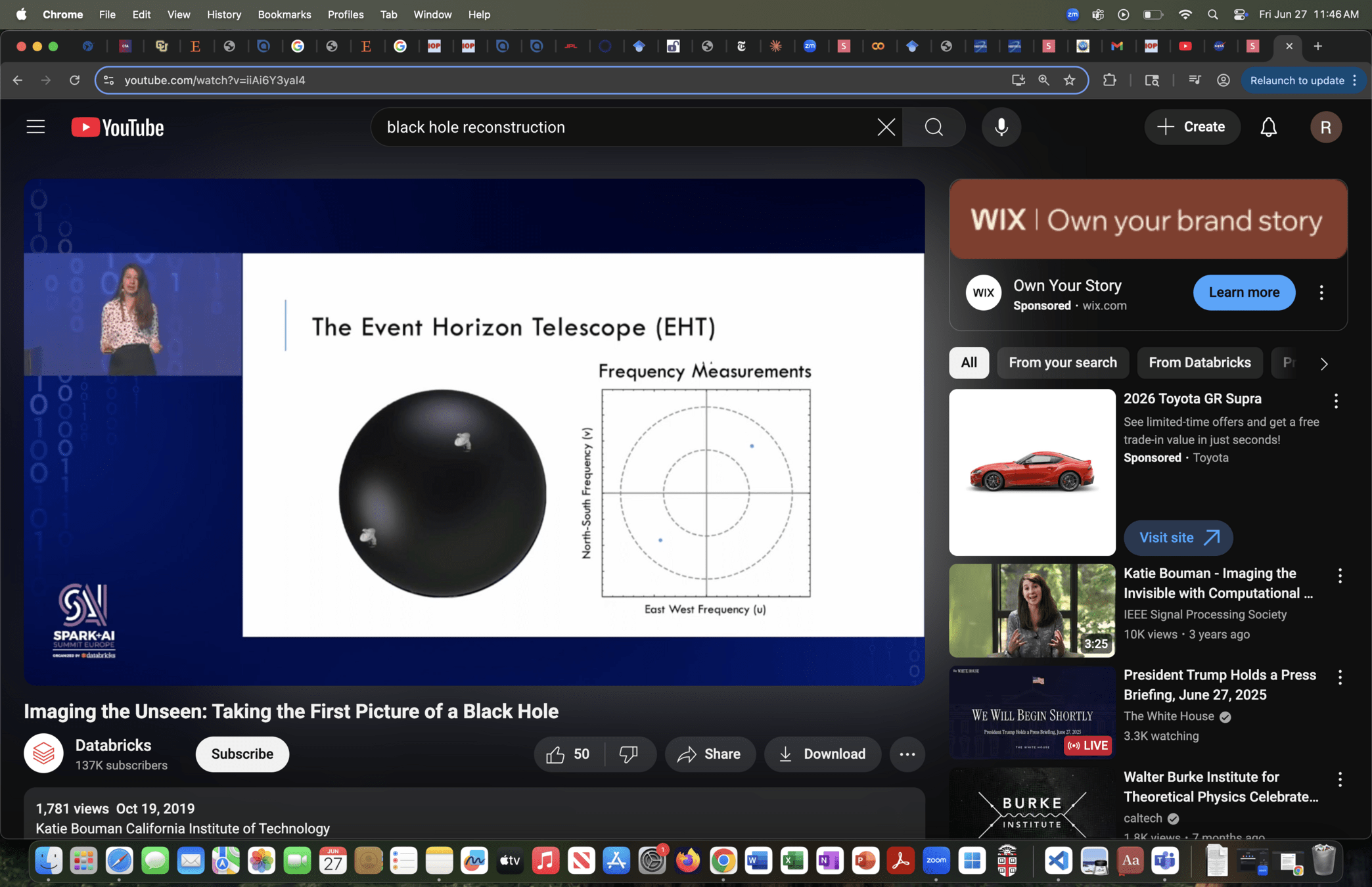
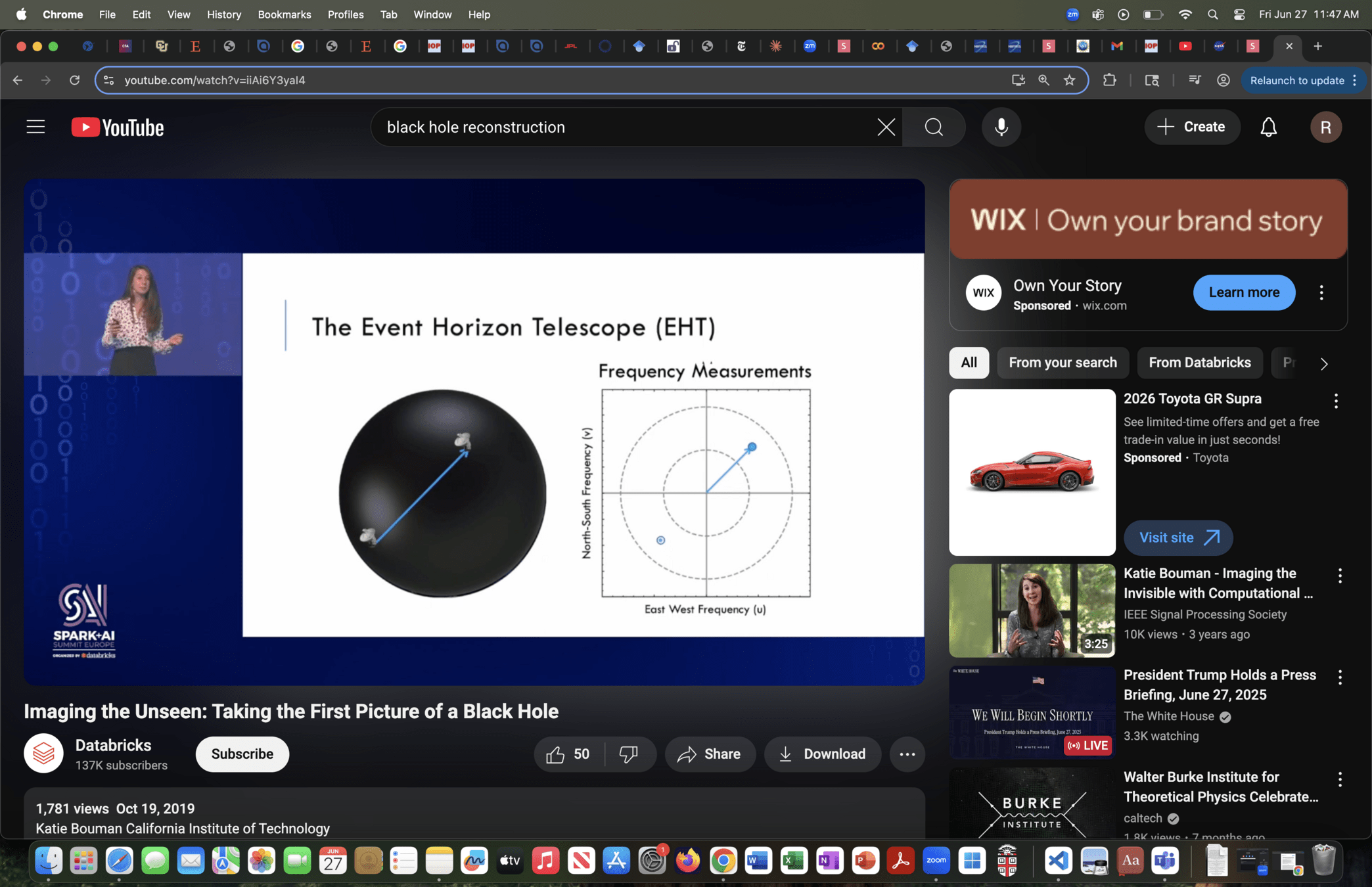
Bispectrum
Cl Amplitude + Cl Phase

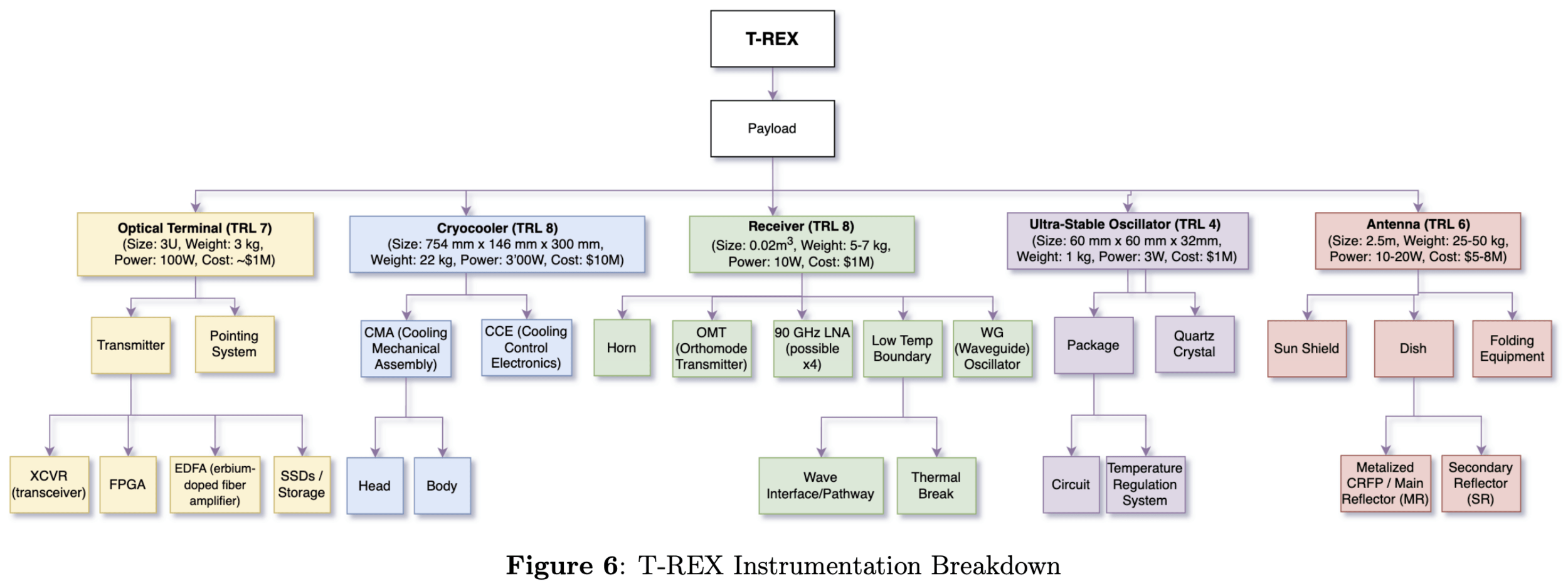
T-REX


SWaPC

Antenna
Cryocooler
Receiver
Oscillator
Backend
Downlink
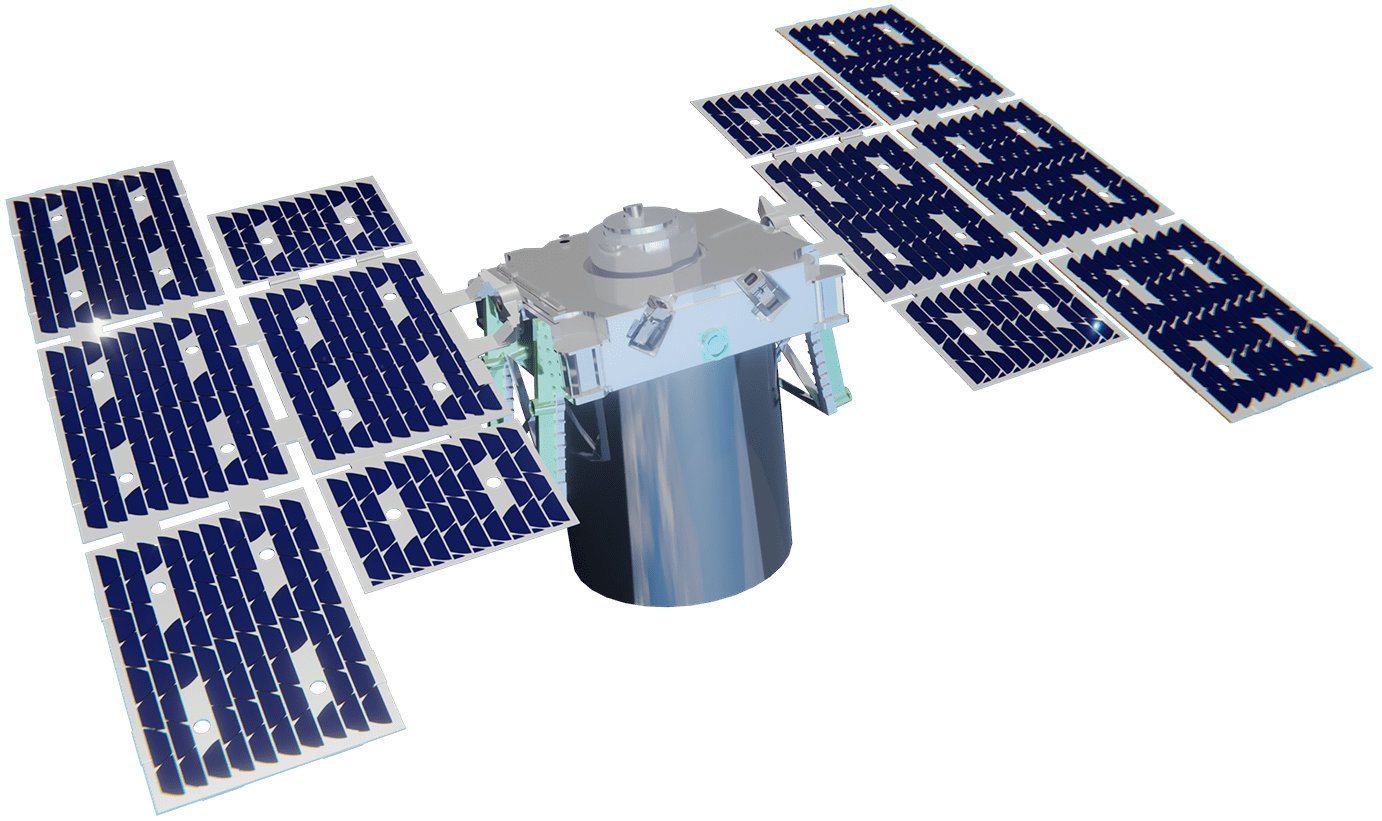
Satellite Bus


Cost
Weight
Power
Component

T-REX


T-REX

# LEO satellite altitudes [km] - triangular constellation
altitudes_km = [600.0, 620.0, 640.0]
sat_names = ["SAT1", "SAT2", "SAT3"]
# Common orbital elements
inc_deg = 85.0
ecc = 0.0
argp_deg = 0.0
# RAAN spacing: 120° apart for triangle
raan_base_deg = 110.0
raan_offsets = [0.0, 120.0, 240.0]
T-REX

# LEO satellite altitudes [km] - triangle
altitudes_km = [600.0, 620.0, 640.0]
sat_names = ["SAT1", "SAT2", "SAT3"]
# Common orbital elements
inc_deg = 85.0 # Inclination
ecc = 0.0 # Eccentricity
argp_deg = 0.0 # Arg of Perigee
# RAAN spacing: 120° apart for triangle
raan_base_deg = 110.0
raan_offsets = [0.0, 120.0, 240.0]
T-REX

# LEO satellite altitudes [km] - triangle
altitudes_km = [600.0, 620.0, 640.0]
sat_names = ["SAT1", "SAT2", "SAT3"]
# Common orbital elements
inc_deg = 85.0 # Inclination
ecc = 0.0 # Eccentricity
argp_deg = 0.0 # Arg of Perigee
# RAAN spacing: 120° apart for triangle
raan_base_deg = 110.0
raan_offsets = [0.0, 120.0, 240.0]
T-REX

# LEO satellite altitudes [km] - triangle
altitudes_km = [600.0, 620.0, 640.0]
sat_names = ["SAT1", "SAT2", "SAT3"]
# Common orbital elements
inc_deg = 85.0 # Inclination
ecc = 0.0 # Eccentricity
argp_deg = 0.0 # Arg of Perigee
# RAAN spacing: 120° apart for triangle
raan_base_deg = 110.0
raan_offsets = [0.0, 120.0, 240.0]
T-REX

# LEO satellite altitudes [km] - triangle
altitudes_km = [600.0, 620.0, 640.0]
sat_names = ["SAT1", "SAT2", "SAT3"]
# Common orbital elements
inc_deg = 85.0 # Inclination
ecc = 0.0 # Eccentricity
argp_deg = 0.0 # Arg of Perigee
# RAAN spacing: 120° apart for triangle
raan_base_deg = 110.0
raan_offsets = [0.0, 120.0, 240.0]
T-REX

# Sgr A* coordinates
ra_hr = 17 + 45/60 + 40.0383/3600 # 17h 45m 40.0383s
dec_deg = -(29 + 0/60 + 28.069/3600) # -29° 00' 28.069"
# Observation setup
rf = 230e9 # Reference frequency [Hz] (230 GHz)
bw = 4e9 # Bandwidth [Hz]
mjd = 58211 # Modified Julian Date (April 2018)
# Scheduling
tint = 10.0 # Integration time [s]
tadv = 60.0 # Cadence between samples [s]
tstart = 0.0 # Start time [hr UTC]
tstop = 24.0 # Stop time [hr UTC]
elevmin = 15.0 # Min ground elevation [deg]
T-REX

# Sgr A* coordinates
ra_hr = 17 + 45/60 + 40.0383/3600 # 17h 45m 40.0383s
dec_deg = -(29 + 0/60 + 28.069/3600) # -29° 00' 28.069"
# Observation setup
rf = 86e9 # Reference frequency [Hz]
bw = 8e9 # Bandwidth [Hz]
mjd = 26226 # Modified Julian Date

T-REX

# Scheduling
tint = 10.0 # Integration time [s]
tadv = 60.0 # Cadence between samples [s]
tstart = 0.0 # Start time [hr UTC]
tstop = 24.0 # Stop time [hr UTC]
elevmin = 15 # Minimum elevation for ground stations [deg]
T-REX

# Scheduling
tint = 10.0 # Integration time [s]
tadv = 60.0 # Cadence between samples [s]
tstart = 0.0 # Start time [hr UTC]
tstop = 24.0 # Stop time [hr UTC]
elevmin = 15 # Minimum elevation for ground stations [deg]
T-REX

# Scheduling
tint = 10.0 # Integration time [s]
tadv = 60.0 # Cadence between samples [s]
tstart = 0.0 # Start time [hr UTC]
tstop = 24.0 # Stop time [hr UTC]
elevmin = 15 # Minimum elevation for ground stations [deg]

T-REX


T-REX

# Generate observation with uv sampling (no visibilities yet)
obs0 = arr.obsdata(
ra_hr, dec_deg, rf, bw,
tint=tint, tadv=tadv, tstart=tstart, tstop=tstop,
mjd=mjd, timetype='UTC', polrep='stokes',
elevmin=elevmin, no_elevcut_space=True
)
T-REX

# Simple Gaussian source for debugging
total_flux = 2.0 # Total flux [Jy]
fwhm_uas = 60.0 # FWHM [μas]
fwhm_rad = fwhm_uas * eh.RADPERUAS # FWHM [rad]
T-REX

# Simple Ring source
total_flux = 2.0
fwhm_uas = 60.0
fwhm_rad = fwhm_uas * eh.RADPERUAS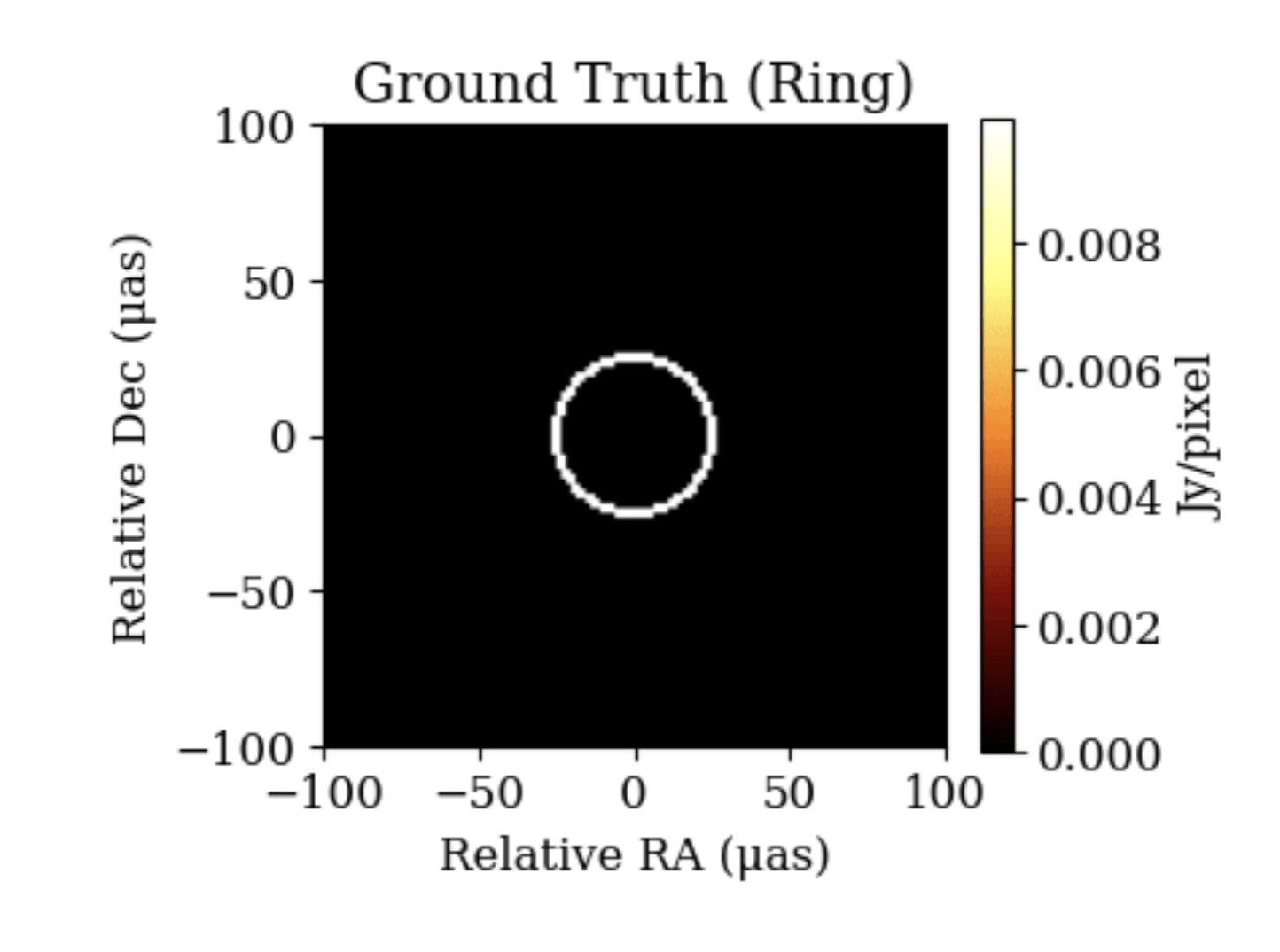

T-REX

# SEFDs (System Equivalent Flux Density)
alma_sefd = 100.0 # ALMA SEFD
sat_sefd = 60000.0 # Space antennas
# Initialize empty array
arr = eh.array.Array(np.array([], dtype=ehc.DTARR))
# Add ALMA
arr = arr.add_site("ALMA", coords=(ALMA_x, ALMA_y, ALMA_z), sefd=alma_sefd)
# Add T-REX
for i, params in enumerate(orbital_params):
# Phase the satellites in their orbits (spread by 1/3 of period)
perigee_offset_days = i * params['period_days'] / 3.0
arr = arr.add_satellite_elements(
params['name'],
perigee_mjd=mjd + tstart/24.0 + perigee_offset_days,
period_days=params['period_days'],
eccentricity=ecc,
inclination=inc_deg,
arg_perigee=argp_deg,
long_ascending=params['raan_deg'],
sefd=sat_sefd
)
ALMA

T-REX

# SEFDs (System Equivalent Flux Density)
alma_sefd = 100.0 # ALMA SEFD
sat_sefd = 60000.0 # Space antennas
# Initialize empty array
arr = eh.array.Array(np.array([], dtype=ehc.DTARR))
# Add ALMA
arr = arr.add_site("ALMA", coords=(ALMA_x, ALMA_y, ALMA_z), sefd=alma_sefd)
# Add T-REX
for i, params in enumerate(orbital_params):
# Phase the satellites in their orbits (spread by 1/3 of period)
perigee_offset_days = i * params['period_days'] / 3.0
arr = arr.add_satellite_elements(
params['name'],
perigee_mjd=mjd + tstart/24.0 + perigee_offset_days,
period_days=params['period_days'],
eccentricity=ecc,
inclination=inc_deg,
arg_perigee=argp_deg,
long_ascending=params['raan_deg'],
sefd=sat_sefd
)
ALMA

T-REX

# Generate observation with uv sampling (no visibilities yet)
obs0 = arr.obsdata(
ra_hr, dec_deg, rf, bw,
tint=tint, tadv=tadv, tstart=tstart, tstop=tstop,
mjd=mjd, timetype='UTC', polrep='stokes',
elevmin=elevmin, no_elevcut_space=True
)
T-REX


T-REX

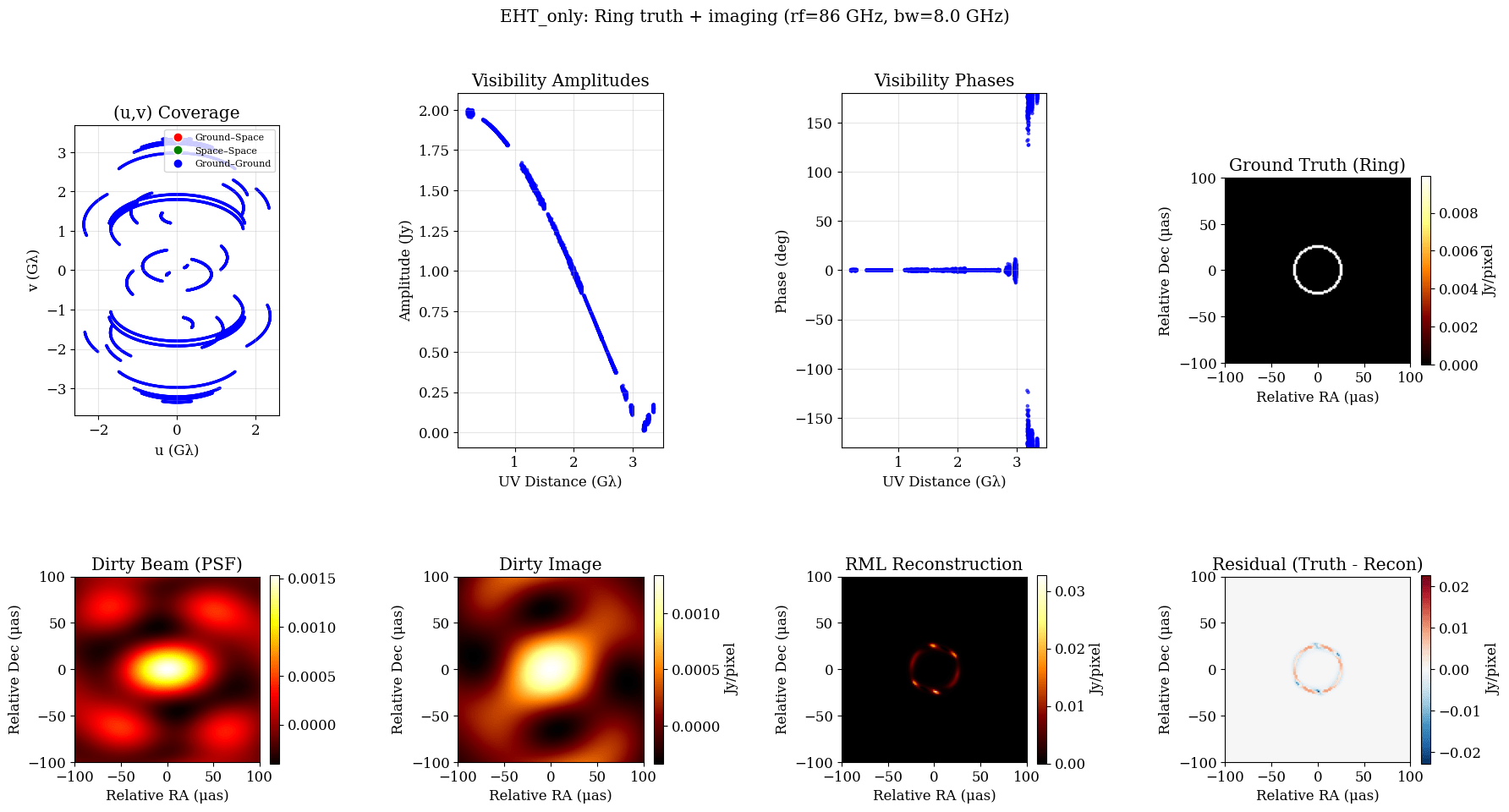

T-REX

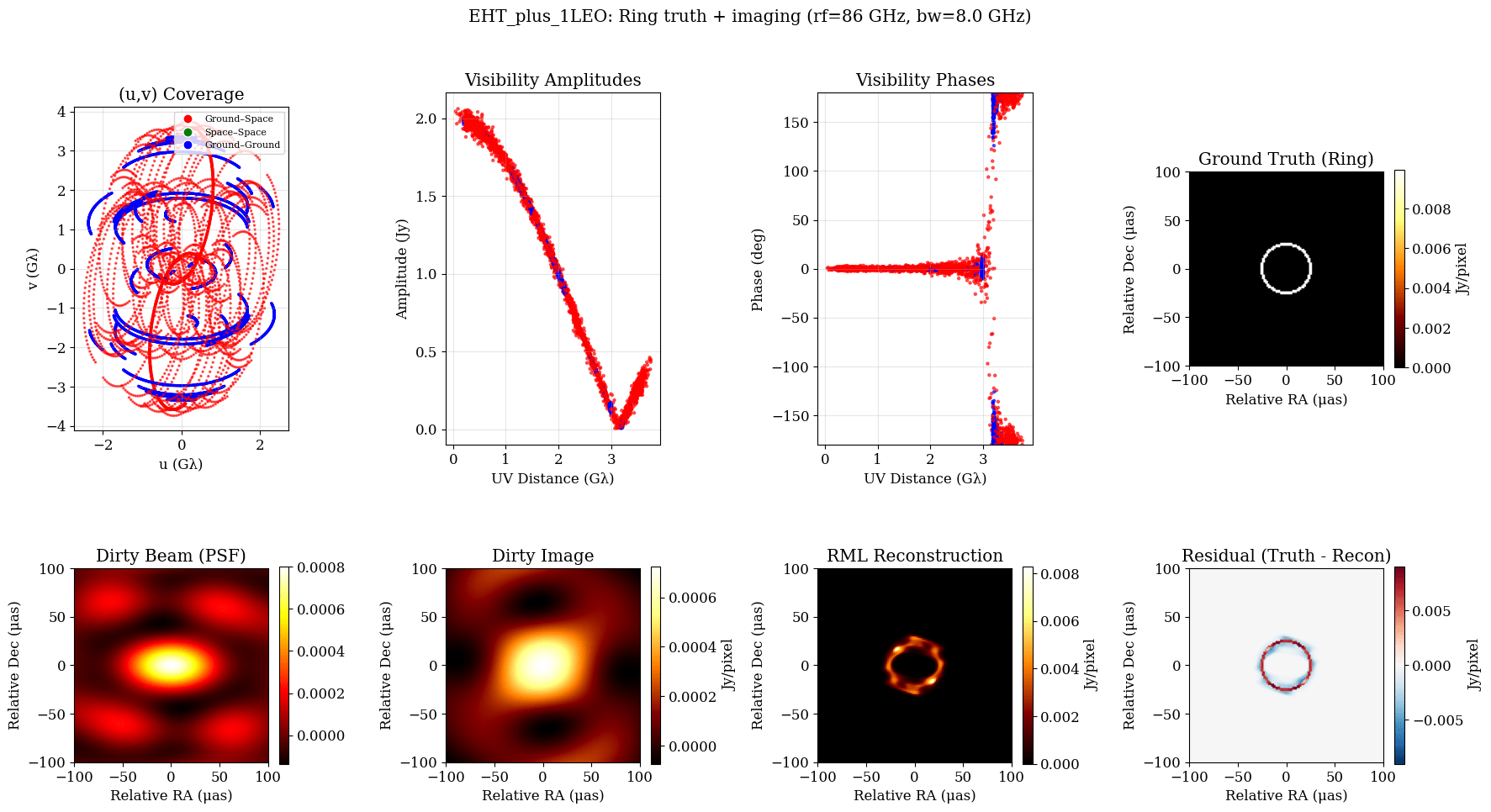

T-REX

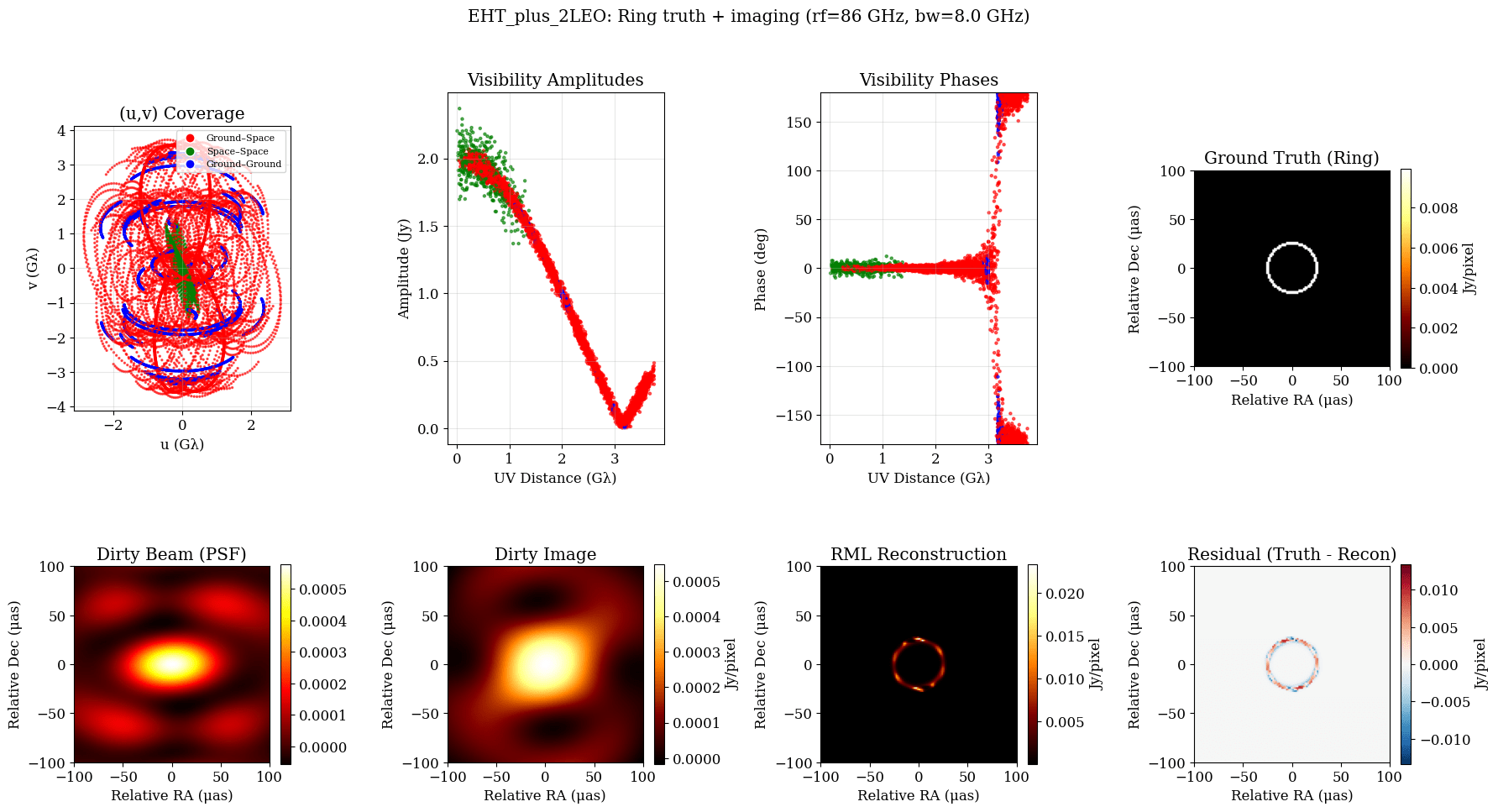
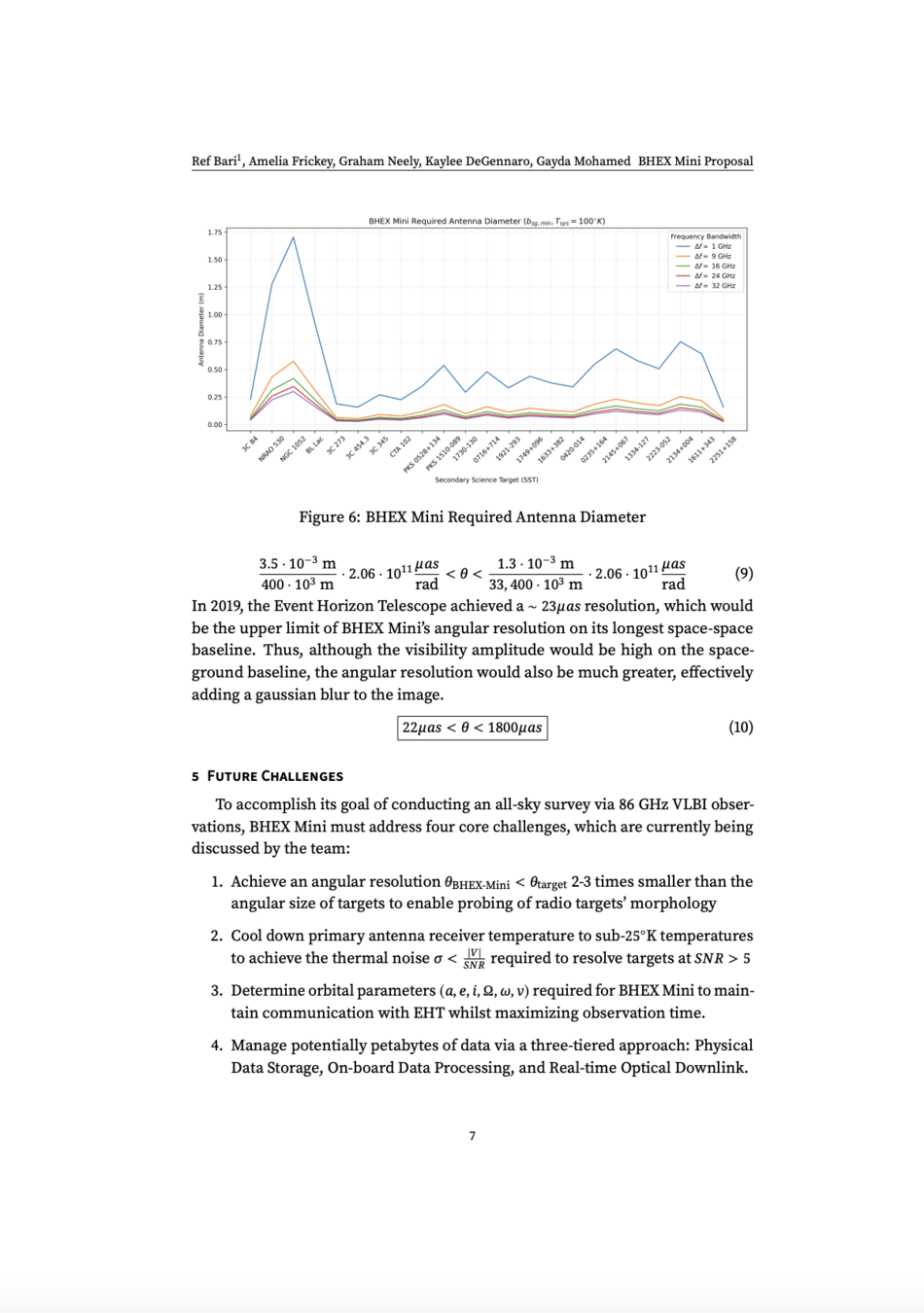
Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution:
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO






Satellite Bus Class
Bus Parameters
Bus Payload Capacity
T-REX Bus
Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution:
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO






T-REX Bus
SBC
- ESPA-Grande
- 4-point mount launch vehicle interface
- Compliant to SpaceX Rideshare
BP
- Energy Storage: 75 Ah
- Orbital lifetime: LEO (>5 yrs)
- Solar Array Power: 1876 W (50% sunlight for LEO ~ 1kW)
BPC
- Standard rideshare payload capability: 250 kg
- Pointing accuracy: 0.002 (1-sigma), 3 axes, 2 trackers
- 40.0" x 40.0" x 45.0" (objective)
- Slew rate: 3.1 deg/sec


T-REX

- Introduction
- Science Traceability Matrix
- Primary Science Objectives
- SWaPC Requirements
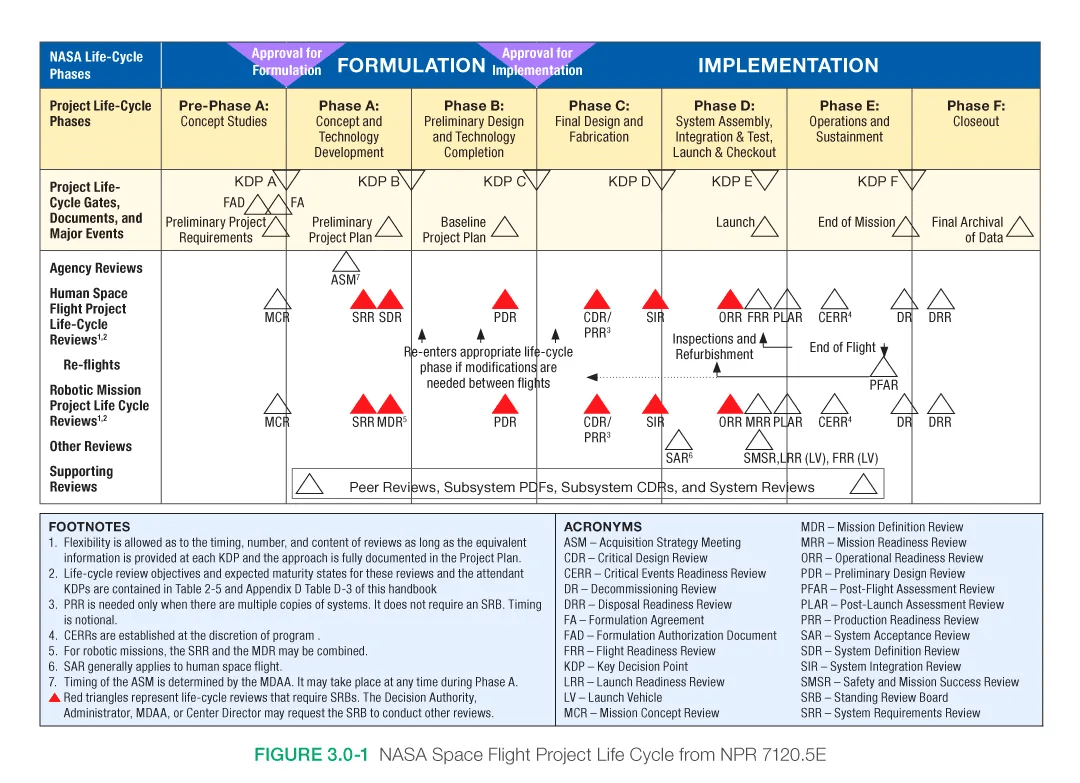
- NASA Mission Life Cycle
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- Critical Mission Parameters
- Preliminary Concept of Operations
- Expected Data Products
- Funding & Timeline

T-REX

- Introduction
- Science Traceability Matrix
- Primary Science Objectives
- SWaPC Requirements
- NASA Mission Life Cycle
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- Critical Mission Parameters
- Preliminary Concept of Operations
- Expected Data Products
- Funding & Timeline

T-REX

Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution:
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO






T-REX

Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution:
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO






- Introduction
- Science Traceability Matrix
- Primary Science Objectives
- SWaPC Requirements
- NASA Mission Life Cycle
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- Critical Mission Parameters
- Preliminary Concept of Operations
- Expected Data Products
- Funding & Timeline

T-REX

- Introduction
- Science Traceability Matrix
- Primary Science Objectives
- SWaPC Requirements
- NASA Mission Life Cycle
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- Critical Mission Parameters
- Preliminary Concept of Operations
- Expected Data Products
- Funding & Timeline

T-REX

Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution:
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO






T-REX

- Introduction
- Science Traceability Matrix
- Primary Science Objectives
- SWaPC Requirements
- NASA Mission Life Cycle
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- Critical Mission Parameters
- Preliminary Concept of Operations
- Expected Data Products
- Funding & Timeline

T-REX

- Introduction
- Science Traceability Matrix
- Primary Science Objectives
- SWaPC Requirements
- NASA Mission Life Cycle
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- Critical Mission Parameters
- Preliminary Concept of Operations
- Expected Data Products
- Funding & Timeline

T-REX

Mission Parameters

SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit

- Introduction
- Science Traceability Matrix
- Primary Science Objectives
- SWaPC Requirements
- NASA Mission Life Cycle
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- Critical Mission Parameters
- Preliminary Concept of Operations
- Expected Data Products
- Funding & Timeline

T-REX

- Introduction
- Science Traceability Matrix
- Primary Science Objectives
- SWaPC Requirements
- NASA Mission Life Cycle
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- Critical Mission Parameters
- Preliminary Concept of Operations
- Expected Data Products
- Funding & Timeline

T-REX

- Introduction
- Science Traceability Matrix
- Primary Science Objectives
- SWaPC Requirements
- NASA Mission Life Cycle
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- Critical Mission Parameters
- Preliminary Concept of Operations
- Expected Data Products
- Funding & Timeline

T-REX

- Introduction
- Science Traceability Matrix
- Primary Science Objectives
- SWaPC Requirements
- NASA Mission Life Cycle
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- Critical Mission Parameters
- Preliminary Concept of Operations
- Expected Data Products
- Funding & Timeline

T-REX

Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution:
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO






T-REX

T-REX


T-REX


T-REX

Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution:
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO




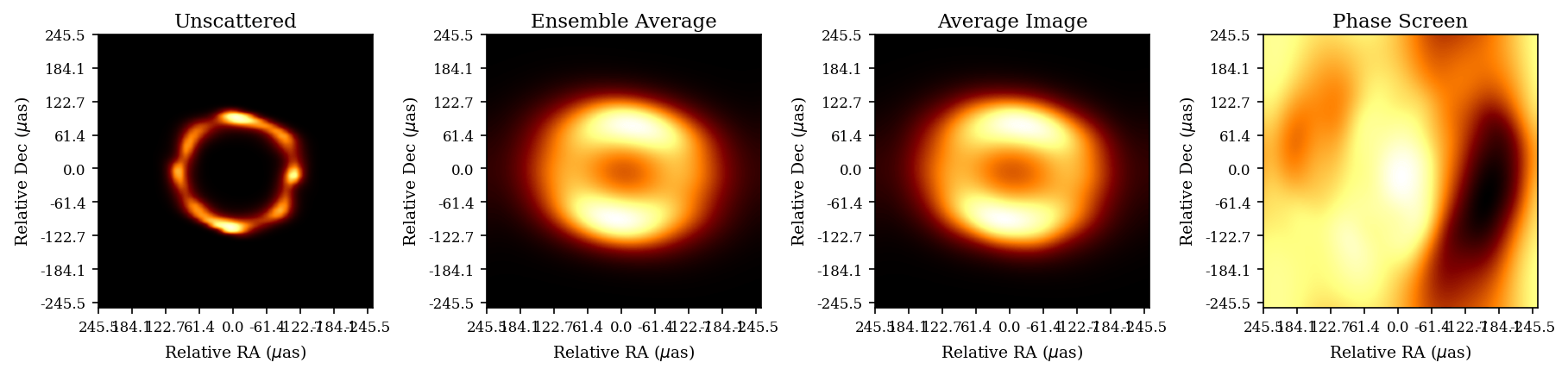


T-REX
Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution:
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO






T-REX
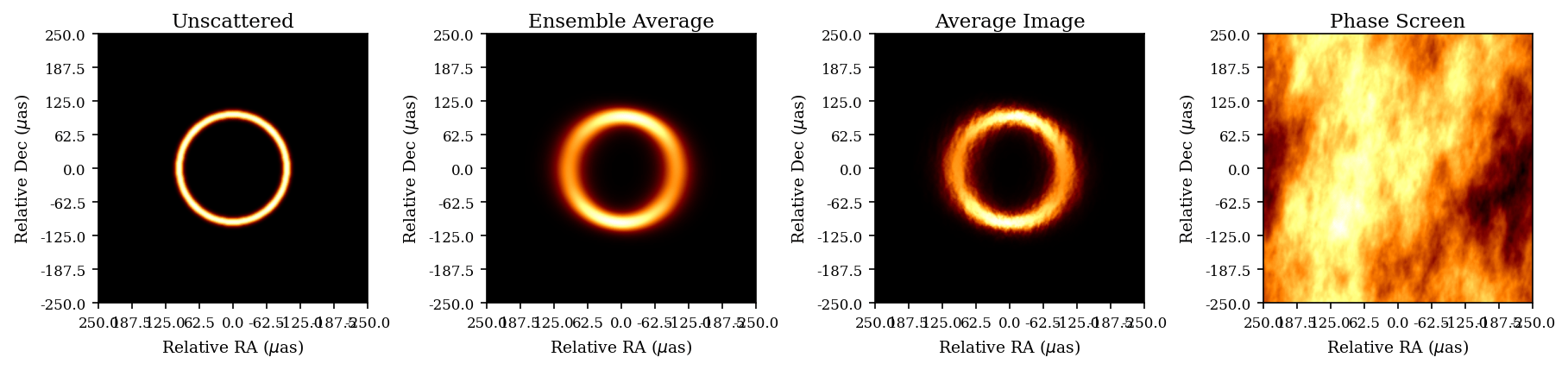
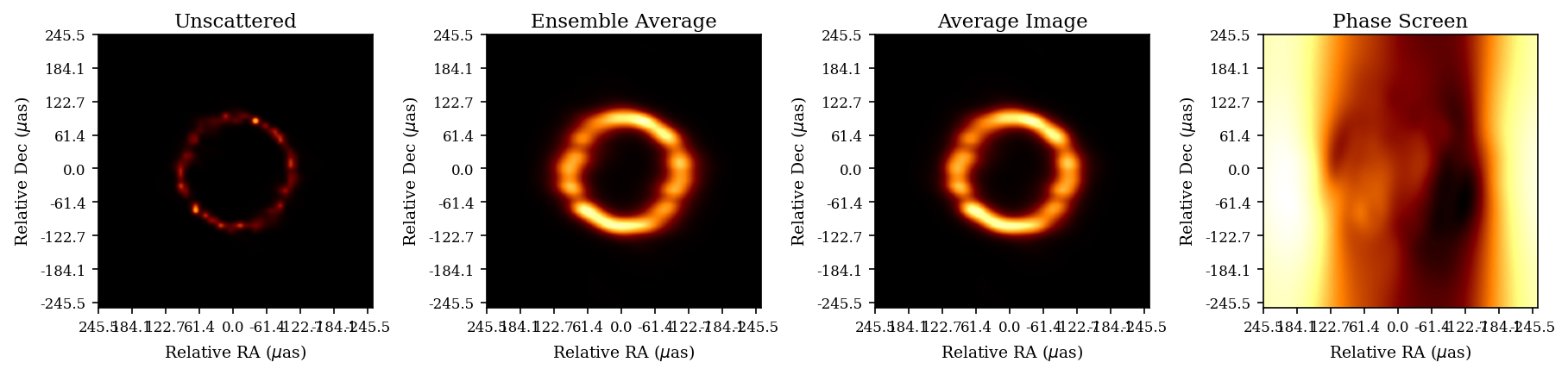
- Introduction
- Science Traceability Matrix
- Primary Science Objectives
- SWaPC Requirements
- NASA Mission Life Cycle
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- Critical Mission Parameters
- Preliminary Concept of Operations
- Expected Data Products
- Funding & Timeline

T-REX

- Introduction
- Science Traceability Matrix
- Primary Science Objectives
- SWaPC Requirements
- NASA Mission Life Cycle
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- Critical Mission Parameters
- Preliminary Concept of Operations
- Expected Data Products
- Funding & Timeline

T-REX

Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution:
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO






T-REX
Oct

-
NASA NIAC Phase I
- Submitted: July 15
- Decision: Sep 6
$175,000
$60,000

-
Brown DSI Grant
- Submitted: Oct 15
- Decision: Dec 10

-
AAS Splinter Meeting
- Submitted: Sep 25
- Decision: Oct 30

-
CSA FAST Grant
- Submitted: Oct 26
- Decision: Dec 15
>$400,000

- Introduction
- What is a black hole?
- How do you image a black hole?
- How do you record a black hole?
- T-REX Primary Science Objectives
- T-REX (u,v) Coverage
- T-REX Engineering Challenges
- T-REX SWaPC Requirements
- T-REX Concept of Operations
- T-REX Timeline & Funding Deadlines


T-REX


T-REX


T-REX
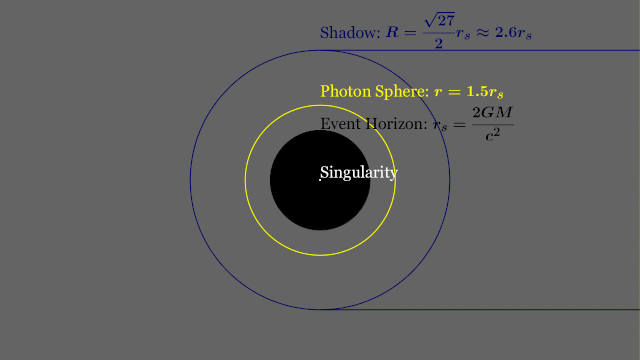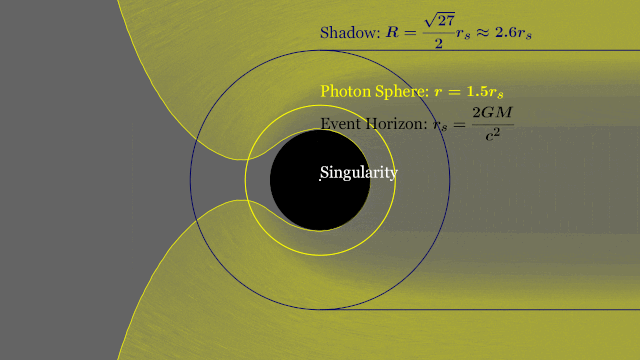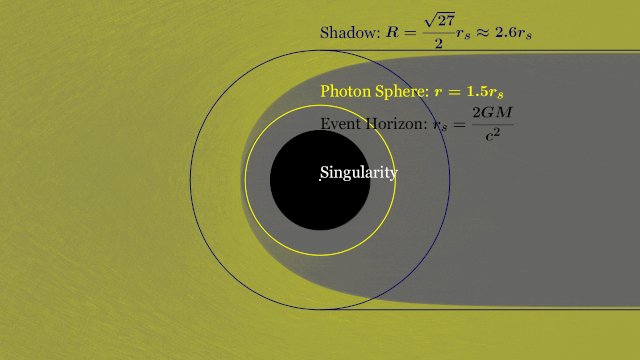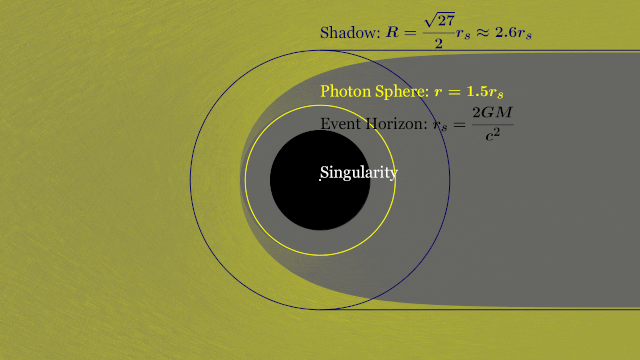
Event Horizon
Singularity


T-REX
Event Horizon
Singularity
Photon Sphere


T-REX
Event Horizon
Black Hole Shadow
Photon Ring


T-REX
Event Horizon
Black Hole Shadow
Photon Ring
Innermost Stable
Circular Orbit


T-REX
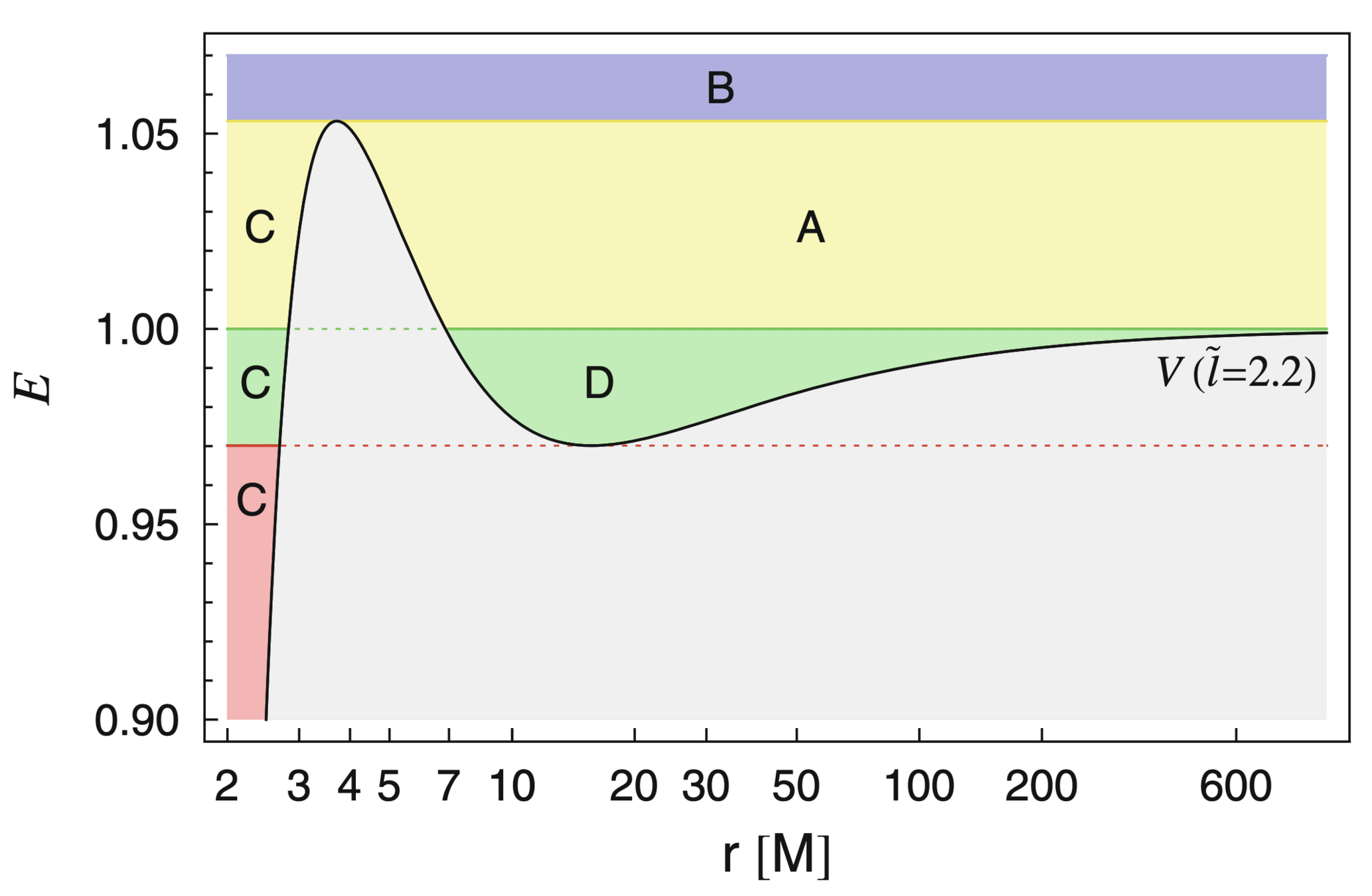
Event Horizon
Photon Ring
Shadow
ISCO


T-REX

Event Horizon
Photon Ring
Shadow
ISCO


T-REX

Event Horizon
Photon Ring
Shadow
ISCO
Photon Ring


T-REX

Event Horizon
Photon Ring
Shadow
ISCO
Photon Ring


T-REX

Event Horizon
Photon Ring
Shadow
ISCO
ISCO


T-REX


T-REX



T-REX



- Introduction
- What is a black hole?
- How do you image a black hole?
- How do you record a black hole?
- T-REX Primary Science Objectives
- T-REX (u,v) Coverage
- T-REX Engineering Challenges
- T-REX SWaPC Requirements
- T-REX Concept of Operations
- T-REX Timeline & Funding Deadlines


T-REX

M87



T-REX
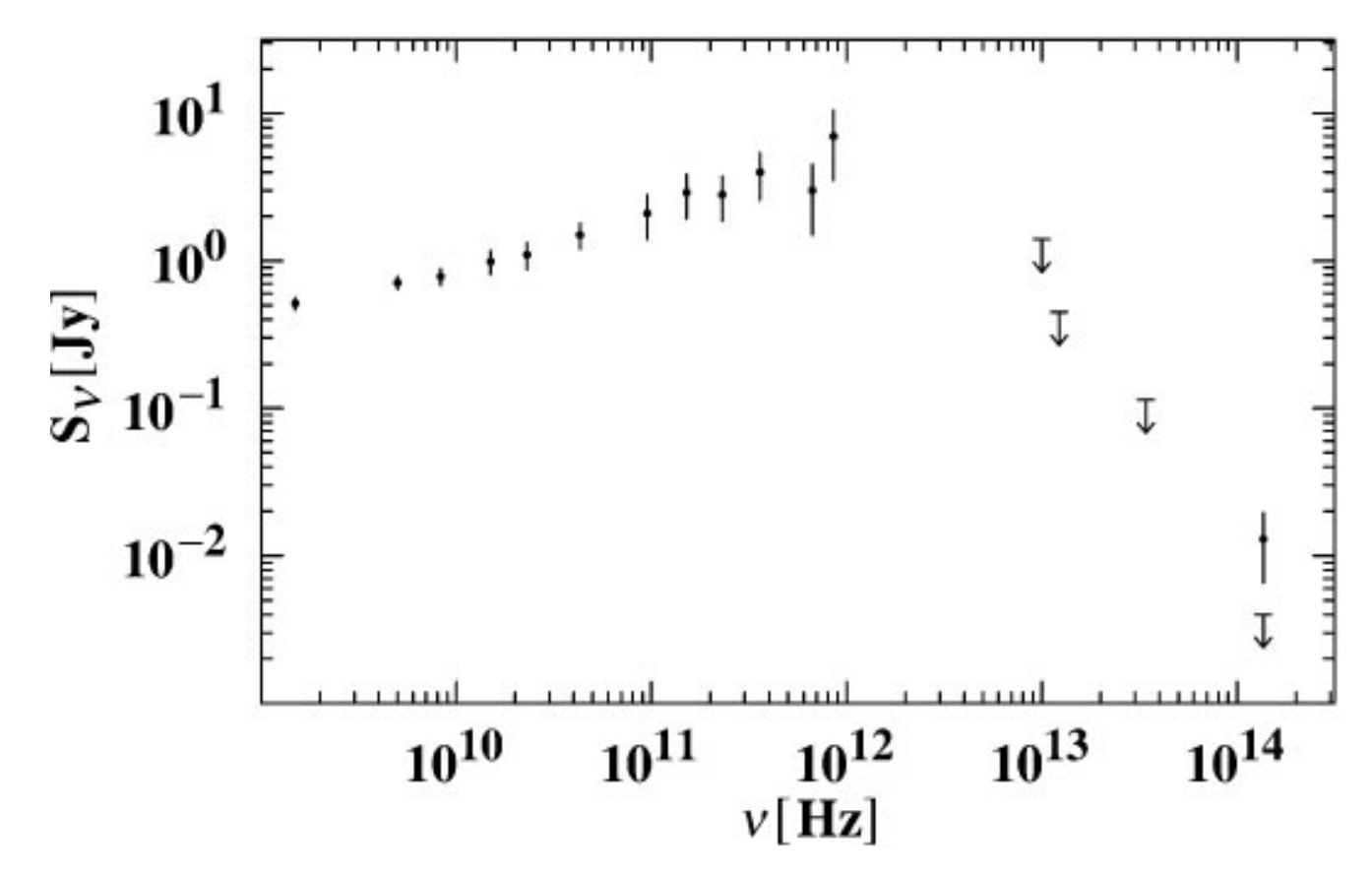
SED, Sgr A*
The Supermassive Black Hole at the Galactic Center (Melia & Falcke, 2001)
The Supermassive Black Hole at the Galactic Center (Melia & Falcke, 2001)



T-REX

Spectral Energy Distribution (Sgr A*)
The Supermassive Black Hole at the Galactic Center (Melia & Falcke, 2001)
The Supermassive Black Hole at the Galactic Center (Melia & Falcke, 2001)
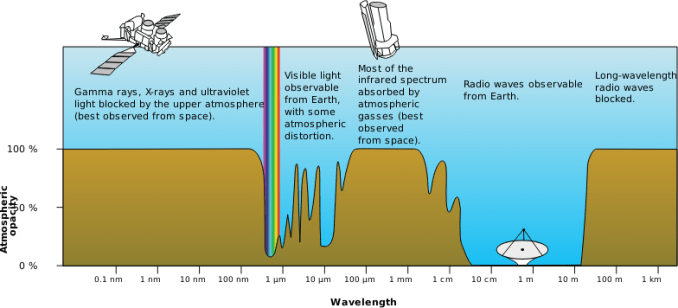

radio
infrared



T-REX


SED, Sgr A*
The Supermassive Black Hole at the Galactic Center (Melia & Falcke, 2001)
The Supermassive Black Hole at the Galactic Center (Melia & Falcke, 2001)



T-REX


SED, Sgr A*
The Supermassive Black Hole at the Galactic Center (Melia & Falcke, 2001)



T-REX


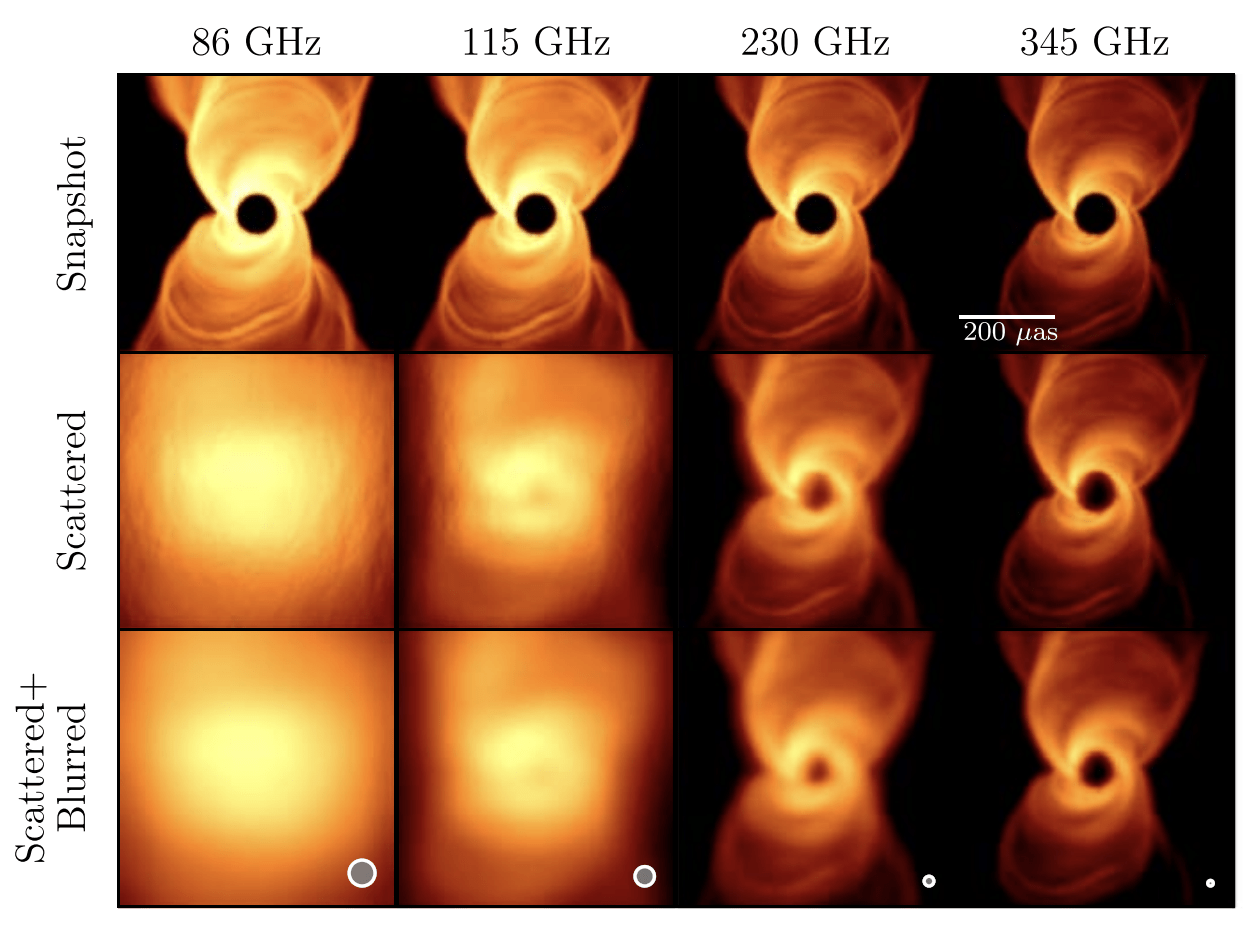




T-REX



T-REX


SED, Sgr A*
The Supermassive Black Hole at the Galactic Center (Melia & Falcke, 2001)



T-REX


T-REX
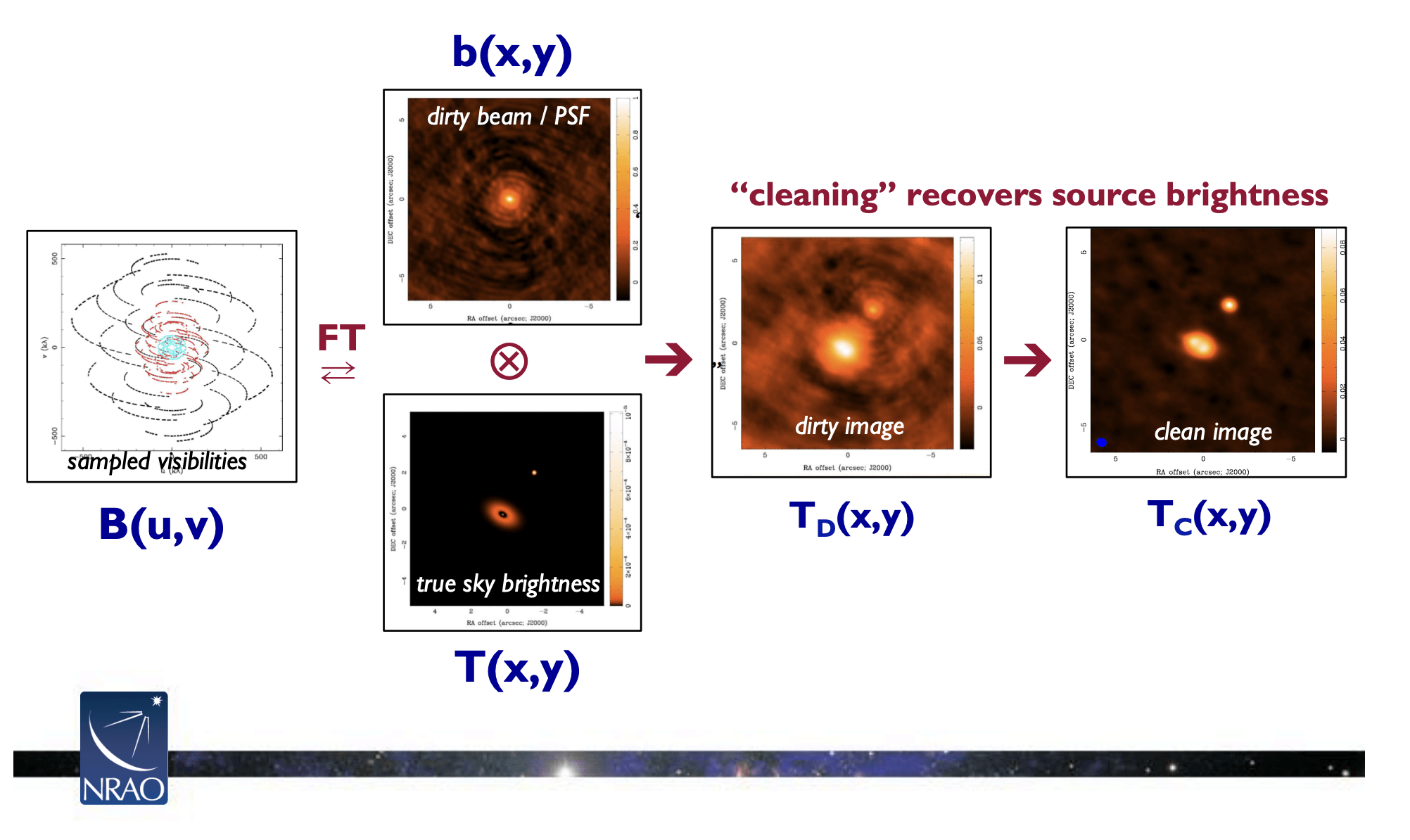
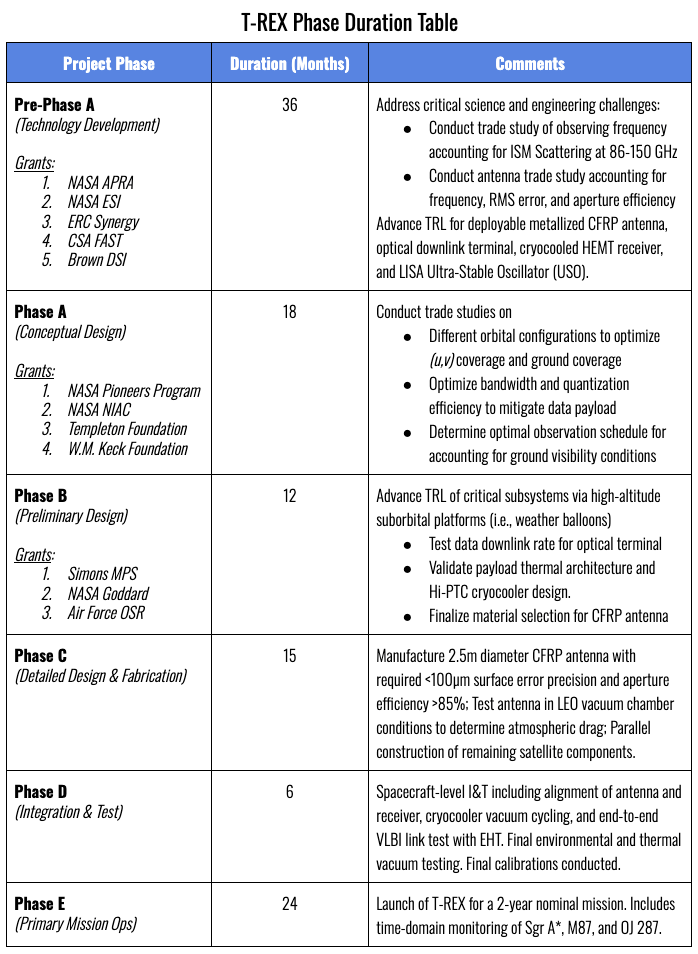
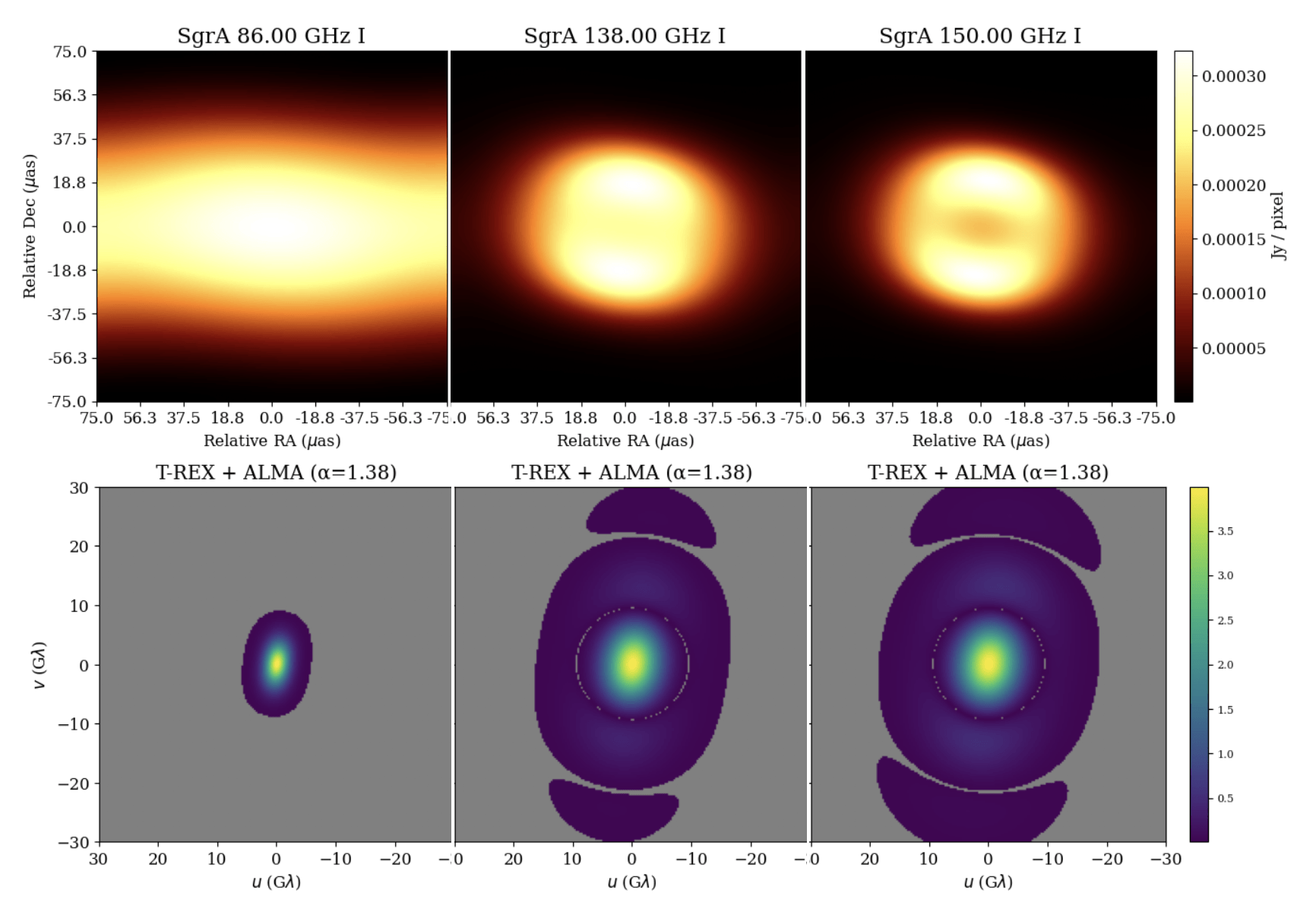
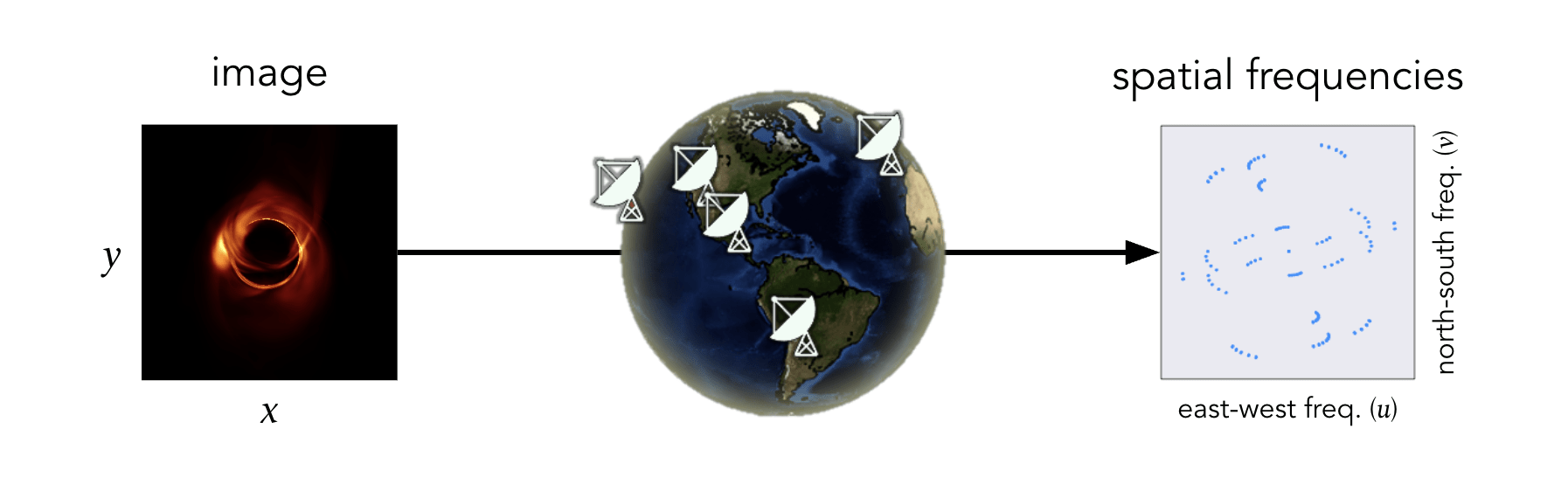
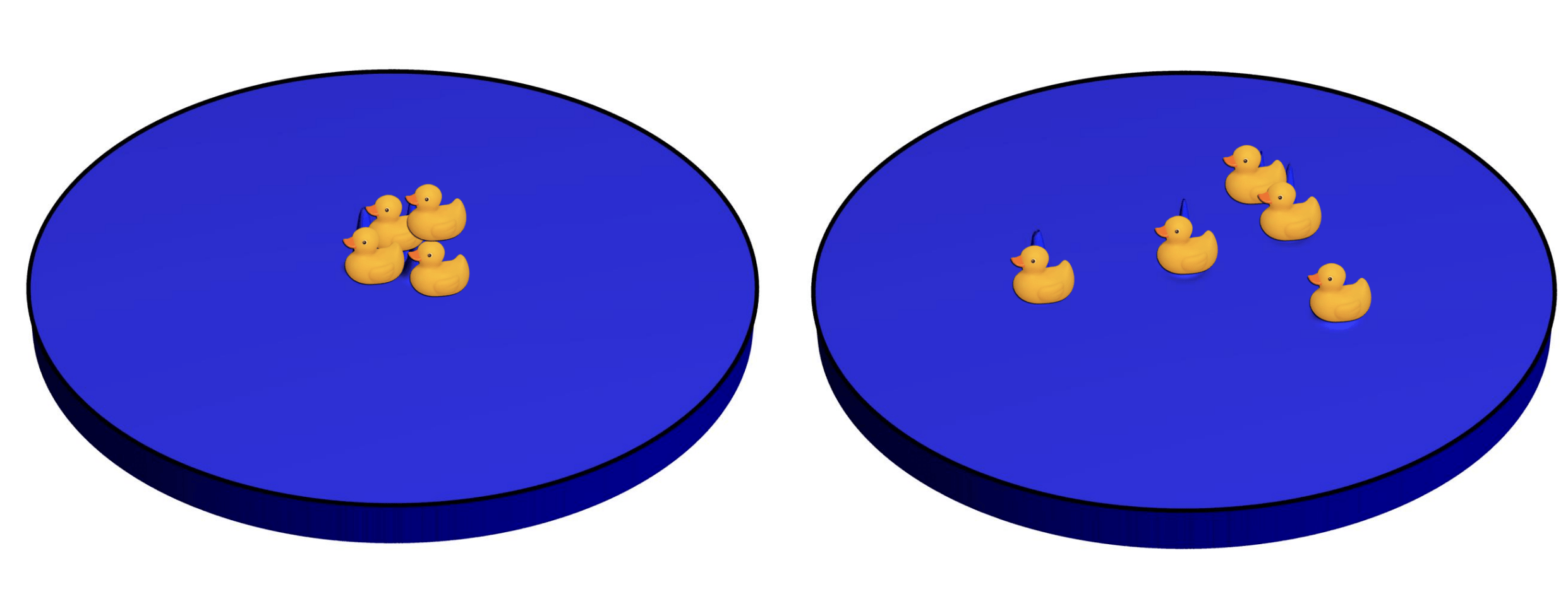
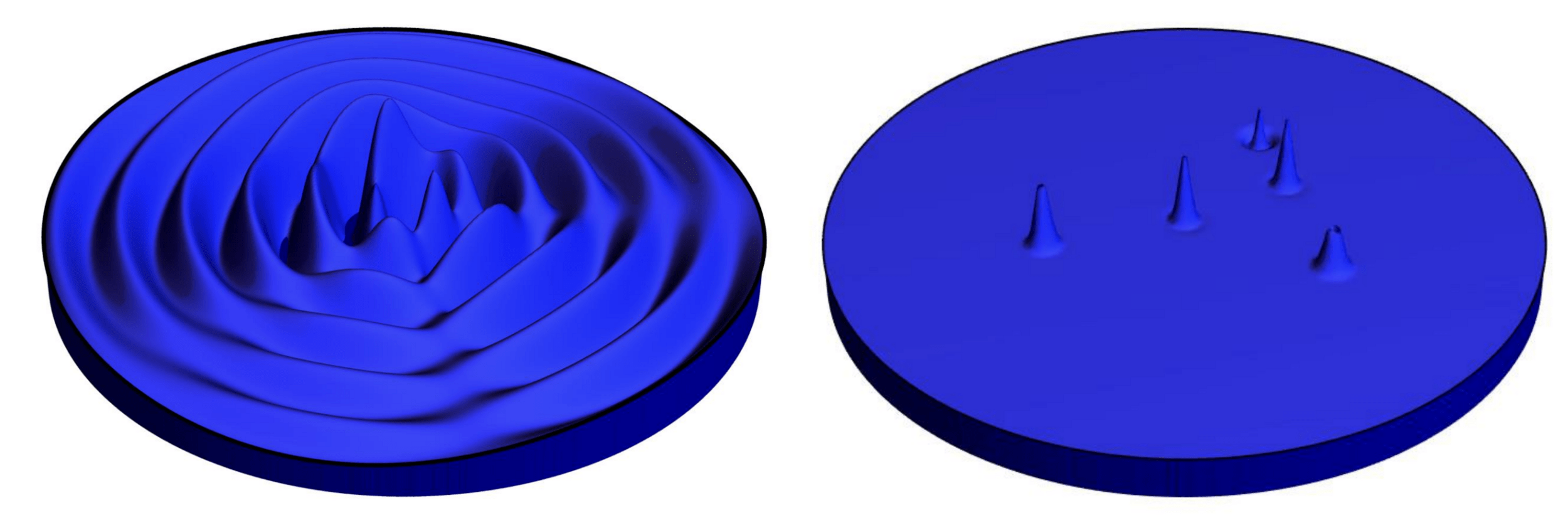
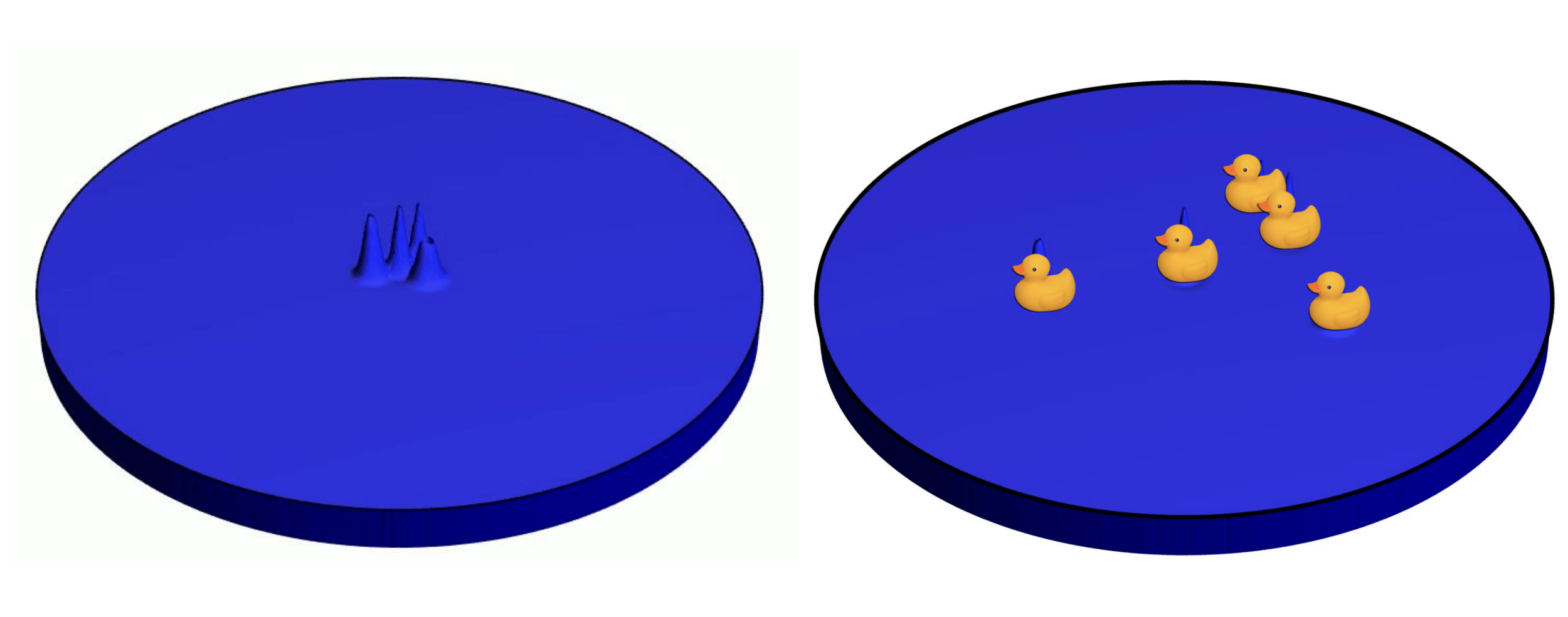
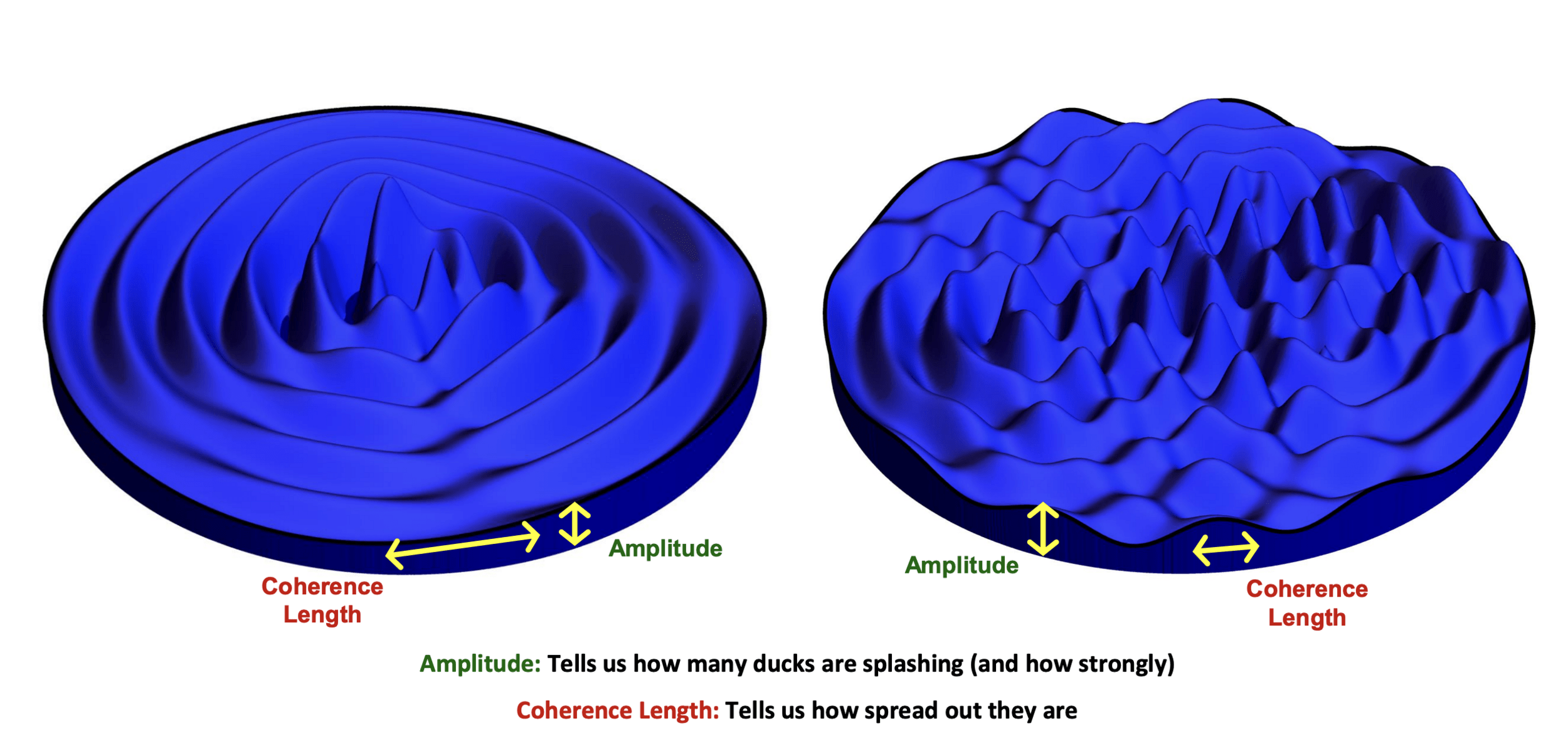
Knox et al., “Spatial coherence from ducks”, Physics Today, March 2010


T-REX


T-REX


T-REX





T-REX








T-REX






T-REX




T-REX





T-REX





T-REX




T-REX






T-REX


T-REX


T-REX
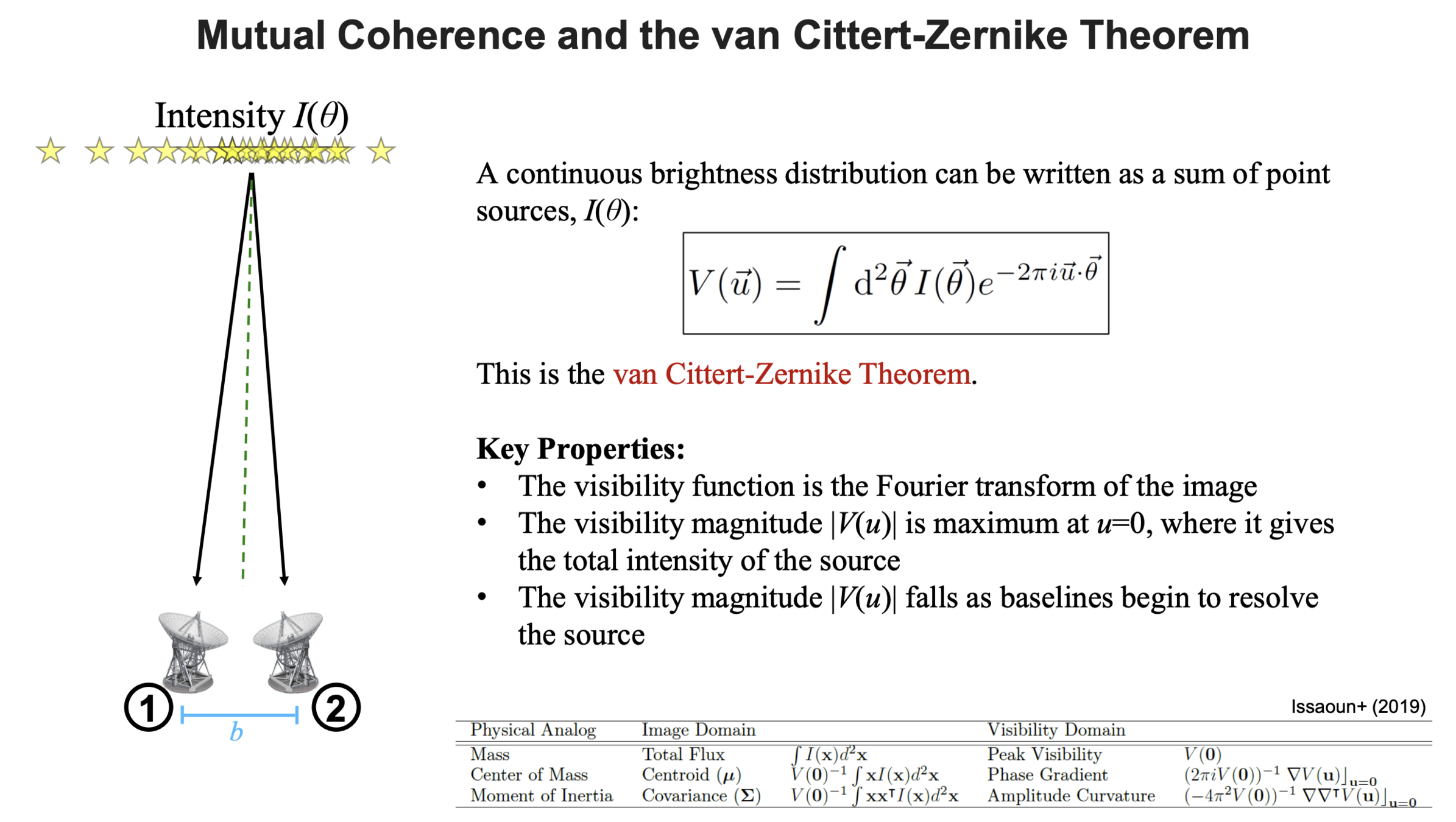



T-REX



T-REX


T-REX


T-REX


T-REX


T-REX


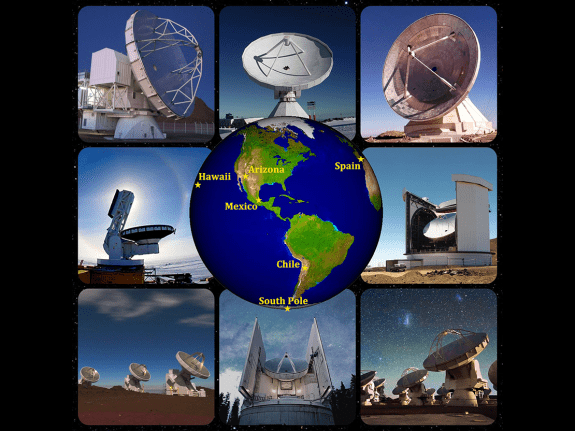
EHT

(2019)
Event Horizon Telescope (EHT)


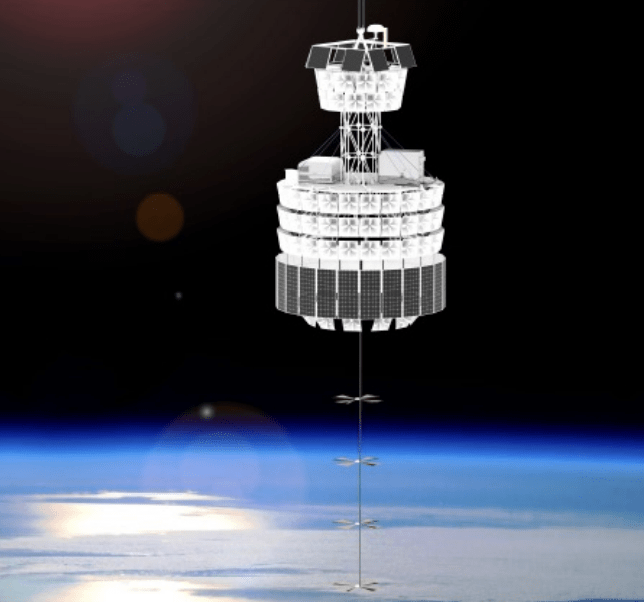
BHEX
(2031)
Black Hole Explorer Satellite (BHEX) Mission



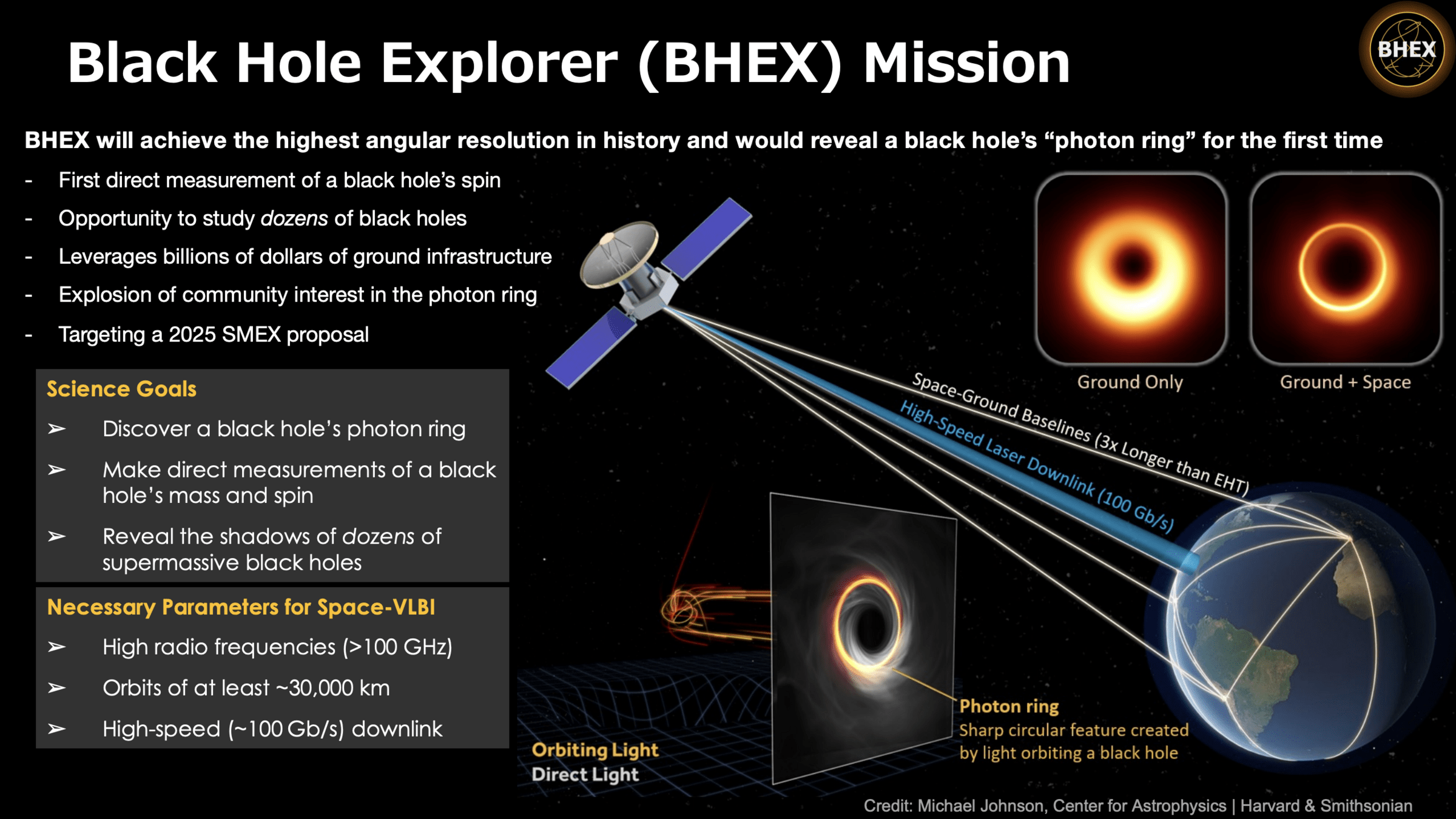

BHEX

- Introduction
- What is a black hole?
- How do you image a black hole?
- How do you record a black hole?
- T-REX Primary Science Objectives
- T-REX (u,v) Coverage
- T-REX Engineering Challenges
- T-REX SWaPC Requirements
- T-REX Concept of Operations
- T-REX Timeline & Funding Deadlines


T-REX

Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution:
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO





T-REX

Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution:
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Rapid coverage of (u,v) plane
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO





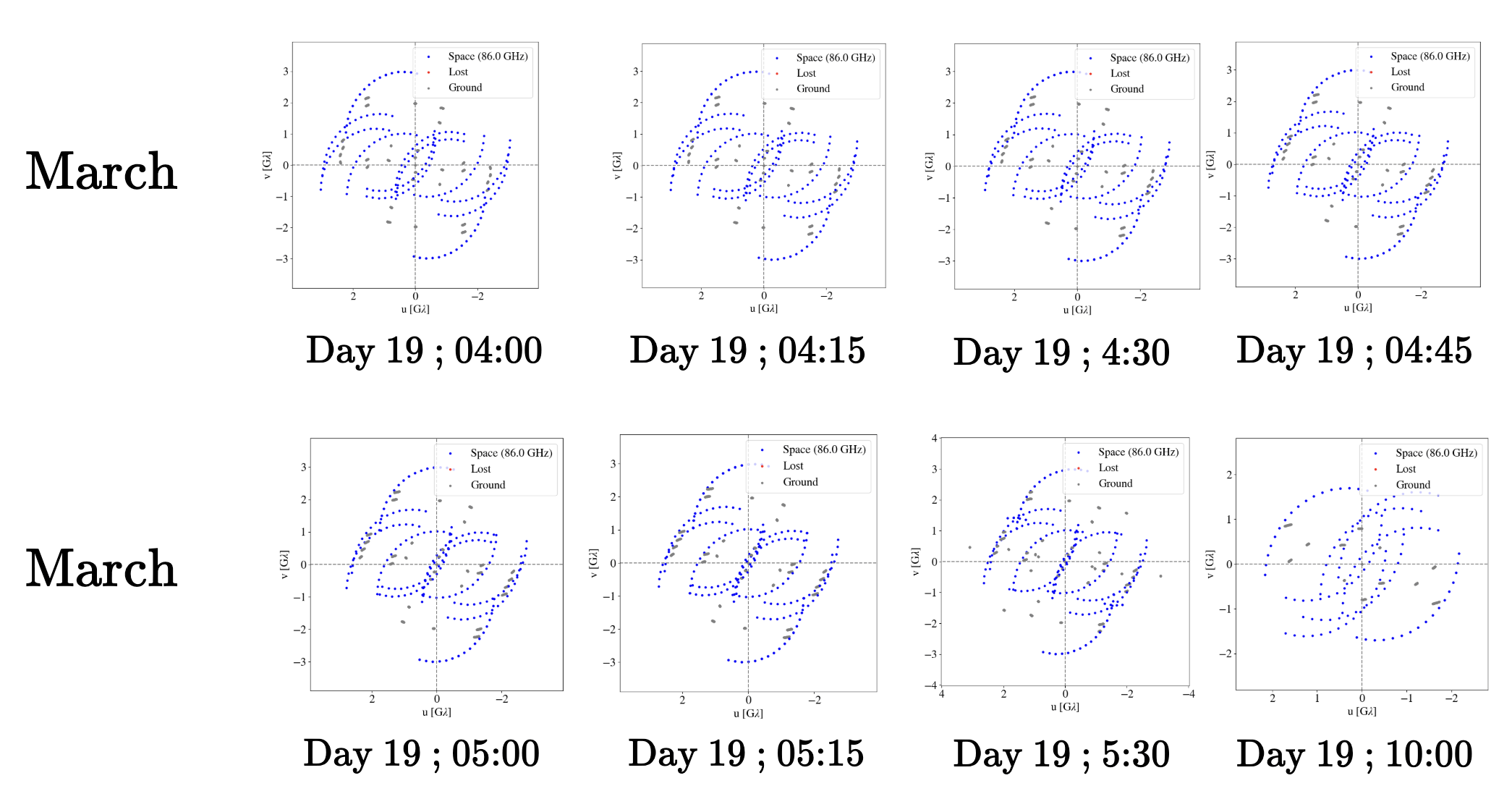
- Time-scale of Sgr A* accretion disk: 4<T<30 minutes (0<J<1)
- Time-scale of LEO Orbit: 90 minutes, with 22-minute (u,v) coverage

T-REX

Sub-milli arcsecond angular resolution:
Dual short and long baseline lengths
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO





T-REX
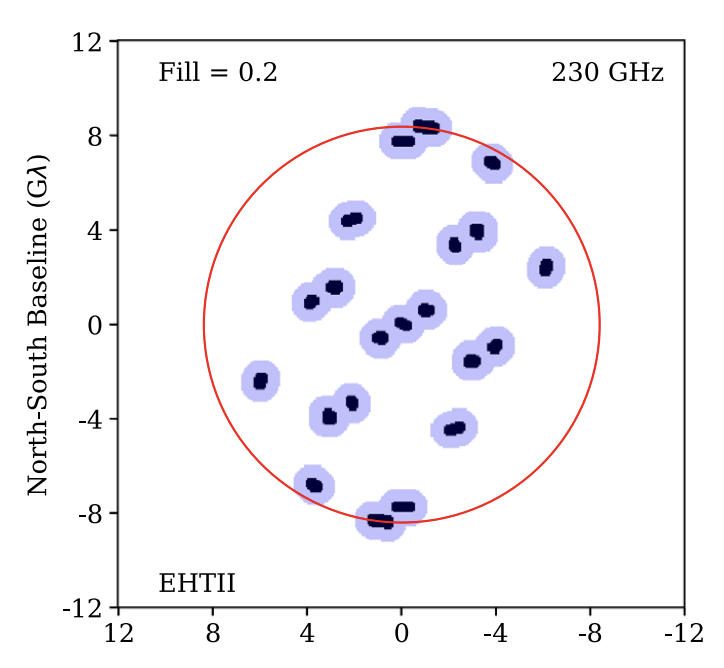
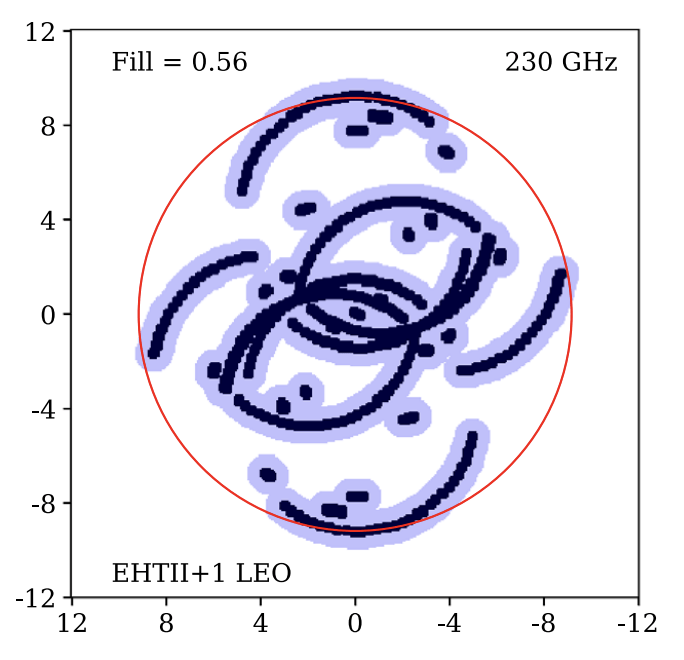

- Introduction
- What is a black hole?
- How do you image a black hole?
- How do you record a black hole?
- T-REX Primary Science Objectives
- T-REX (u,v) Coverage
- T-REX Engineering Challenges
- T-REX SWaPC Requirements
- T-REX Concept of Operations
- T-REX Timeline & Funding Deadlines


T-REX


T-REX

Capture Time-Resolved Videos of M87 & Sgr A*

Time-Resolve Binary Black Hole Systems

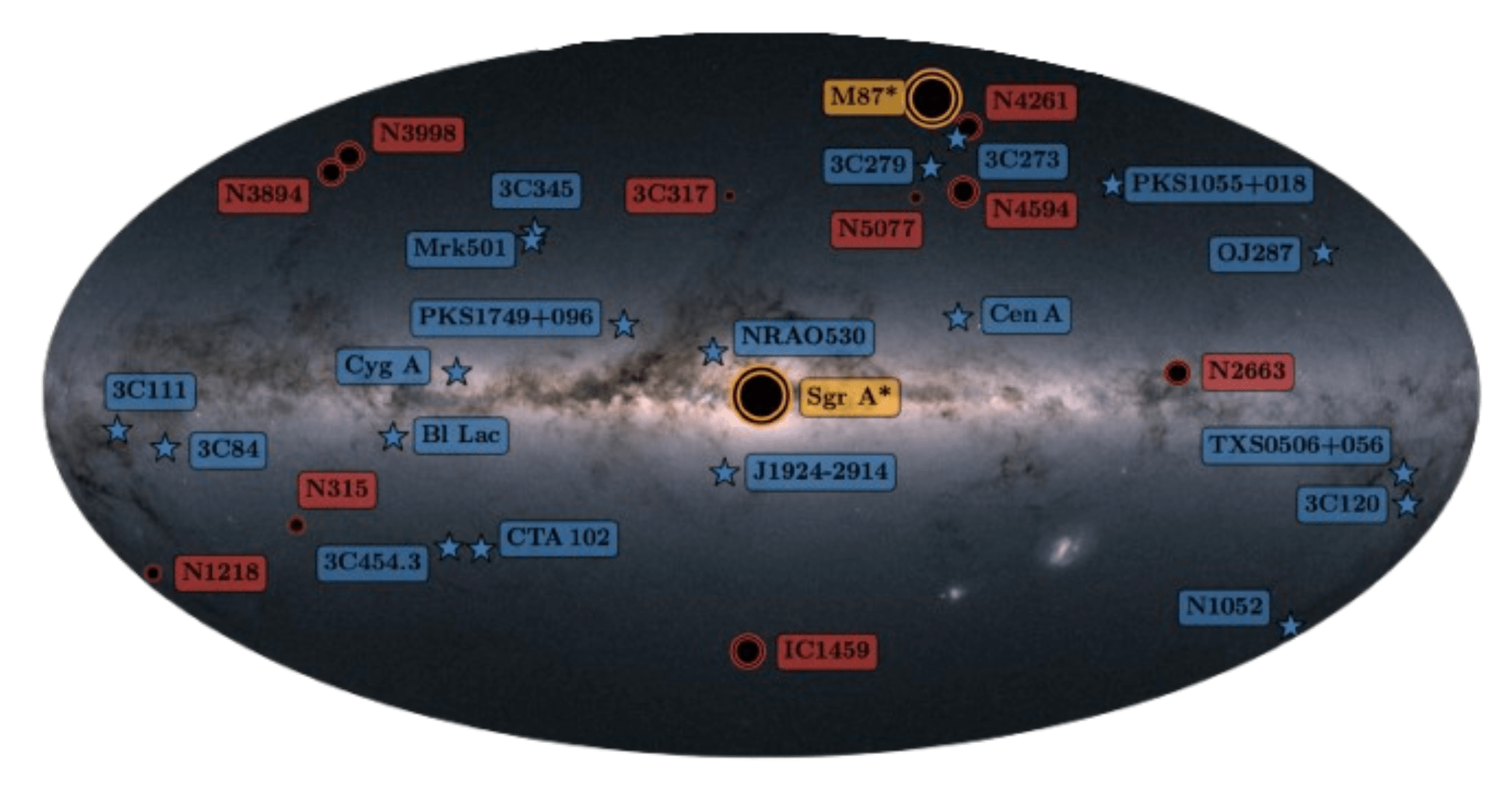
Conduct VLBI Survey of AGN targets at 86 GHz



T-REX

Capture Time-Resolved Videos of M87 & Sgr A*

Time-Resolve Binary Black Hole Systems

Conduct VLBI Survey of AGN targets at 86 GHz


T-REX

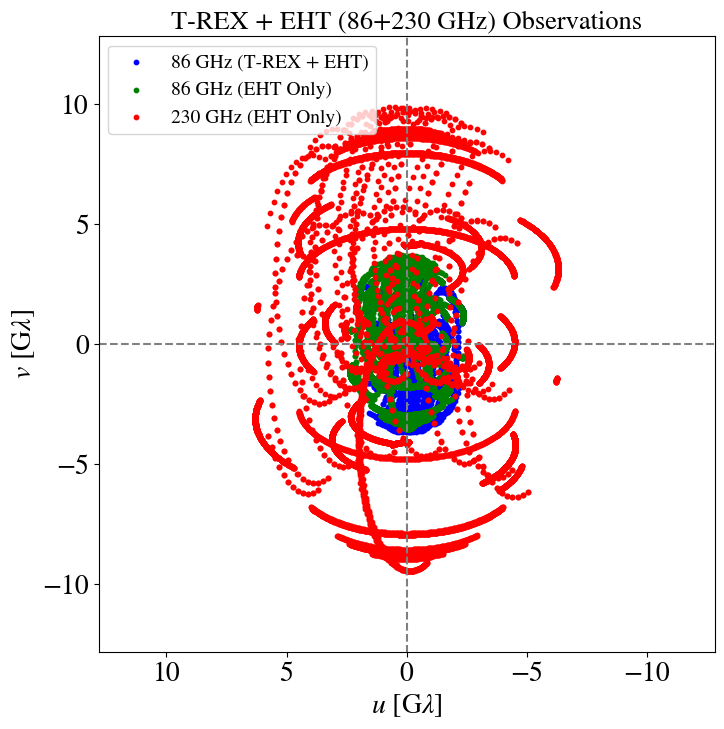
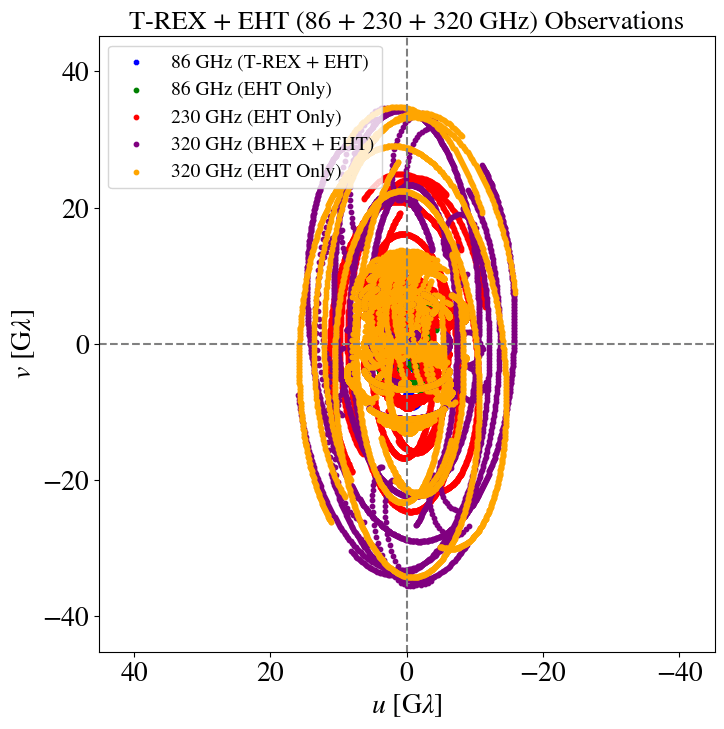
Supplement (u,v) coverage at 86 GHz
Enable parameter estimation of Sgr A*/M87


Capture Time-Resolved Videos of M87 & Sgr A*
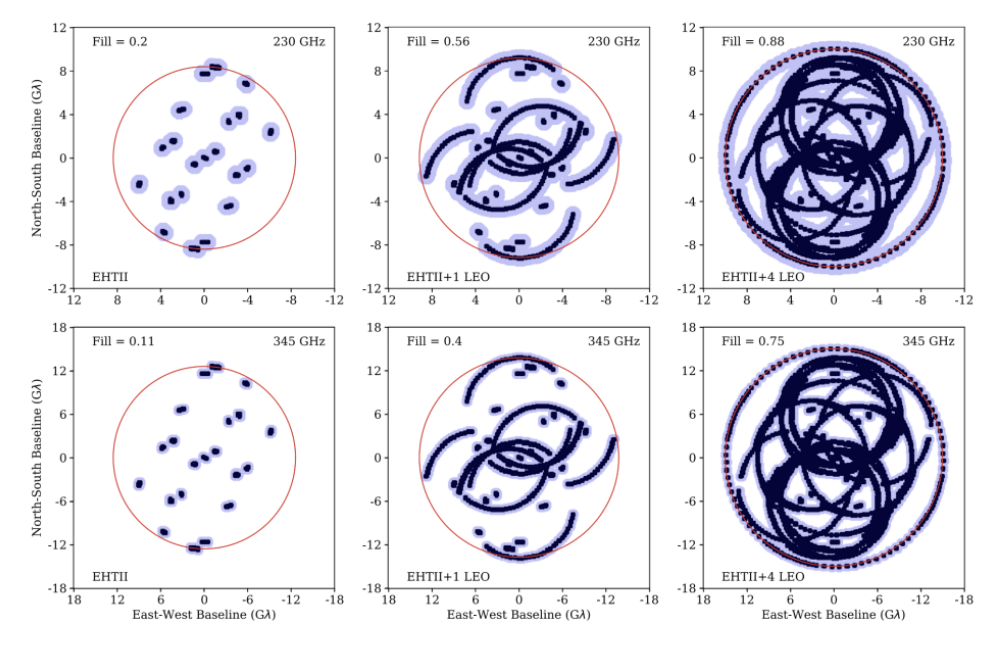


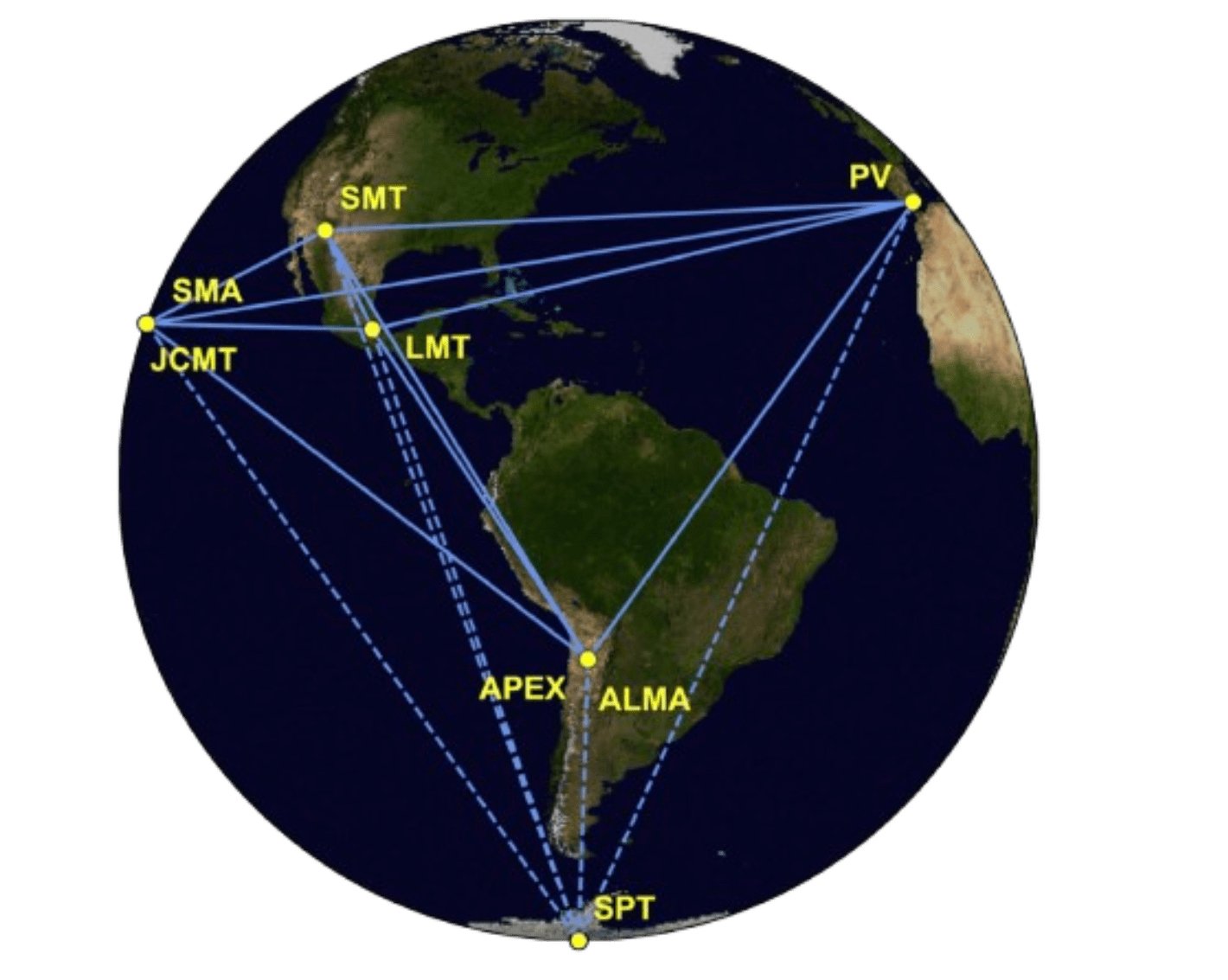
"Metrics and Motivations for Earth–Space VLBI: Time-resolving Sgr A* with the Event Horizon Telescope" Palumbo et. al. ApJ 2019

T-REX


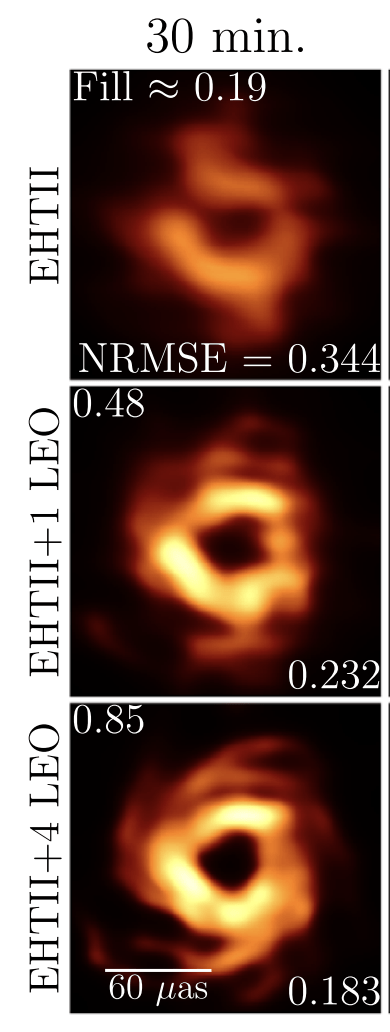
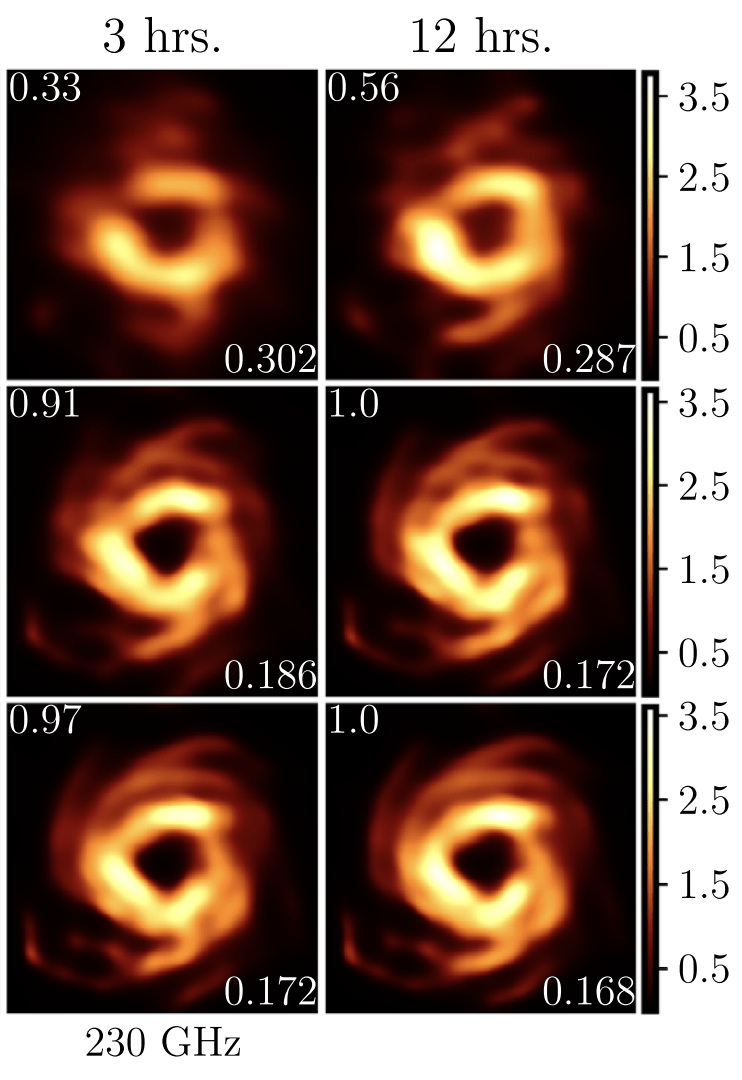
T-REX
"Metrics and Motivations for Earth–Space VLBI: Time-resolving Sgr A* with the Event Horizon Telescope" Palumbo et. al. ApJ 2019




T-REX
"Metrics and Motivations for Earth–Space VLBI: Time-resolving Sgr A* with the Event Horizon Telescope" Palumbo et. al. ApJ 2019




T-REX


T-REX
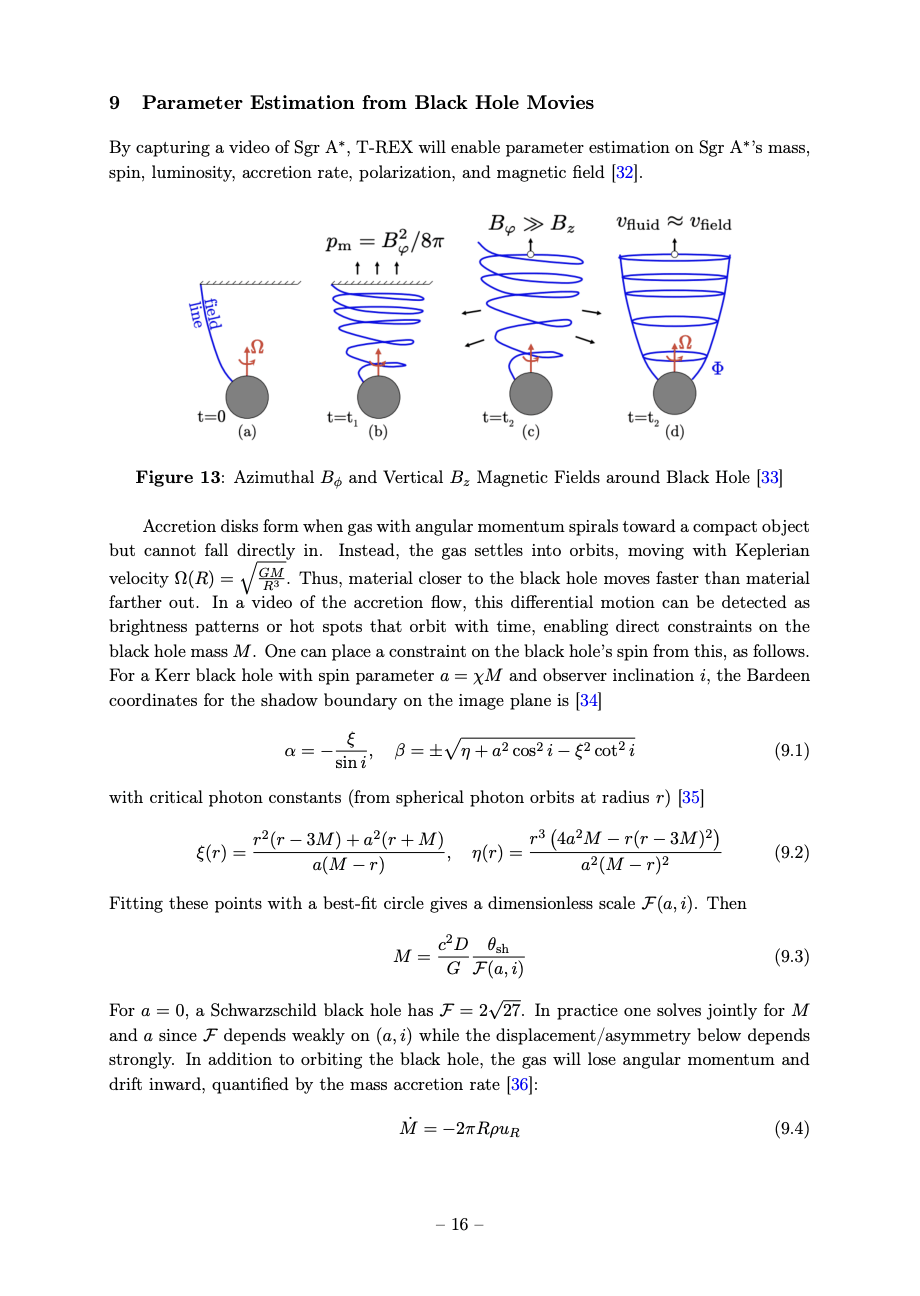
$$\alpha=-\frac{\xi}{\sin i}, \quad \beta= \pm \sqrt{\eta+a^2 \cos ^2 i-\xi^2 \cot ^2 i}$$
$$M=\frac{c^2 D}{G} \frac{\theta_{sh}}{\mathcal{F}(a, i)}$$
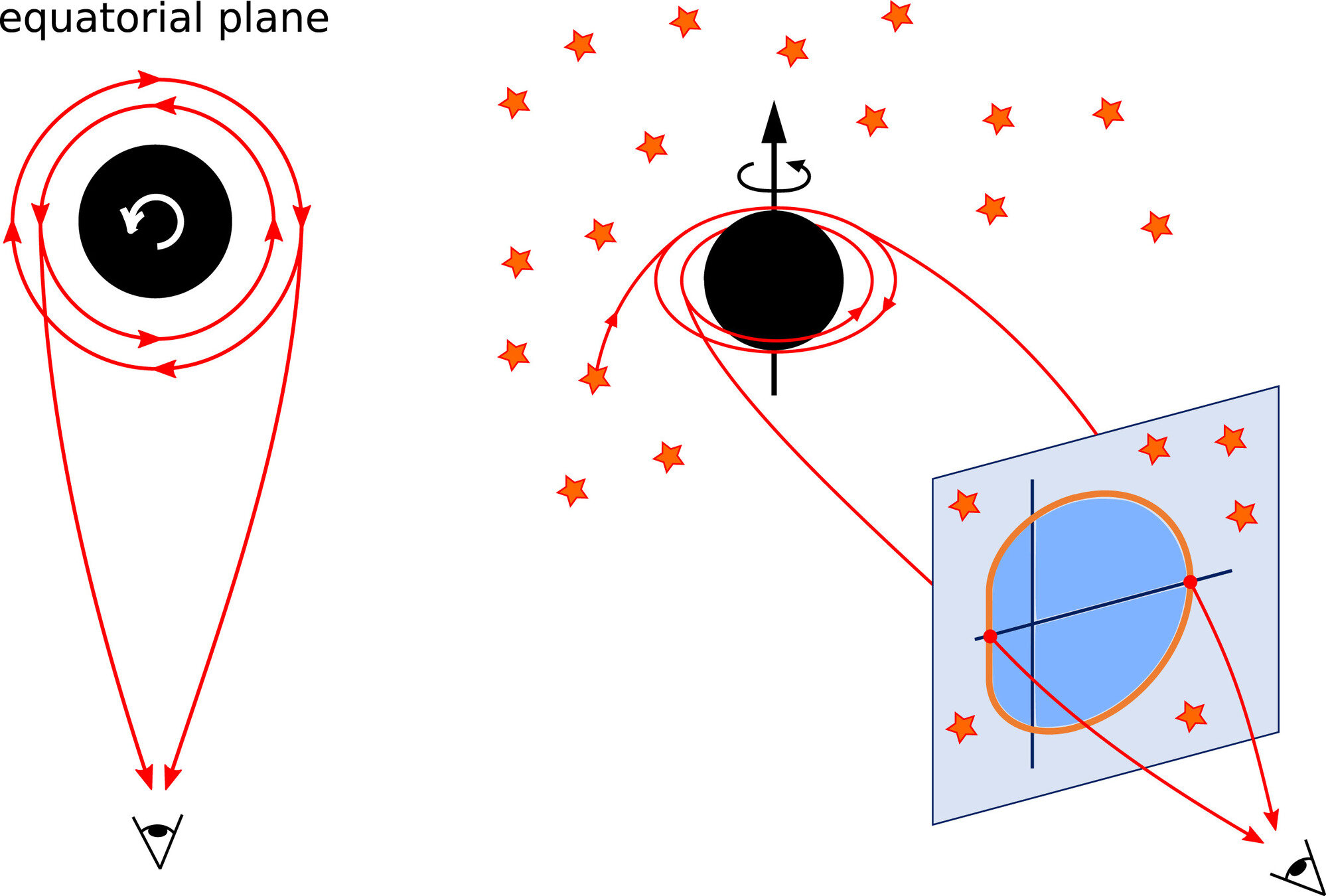


T-REX
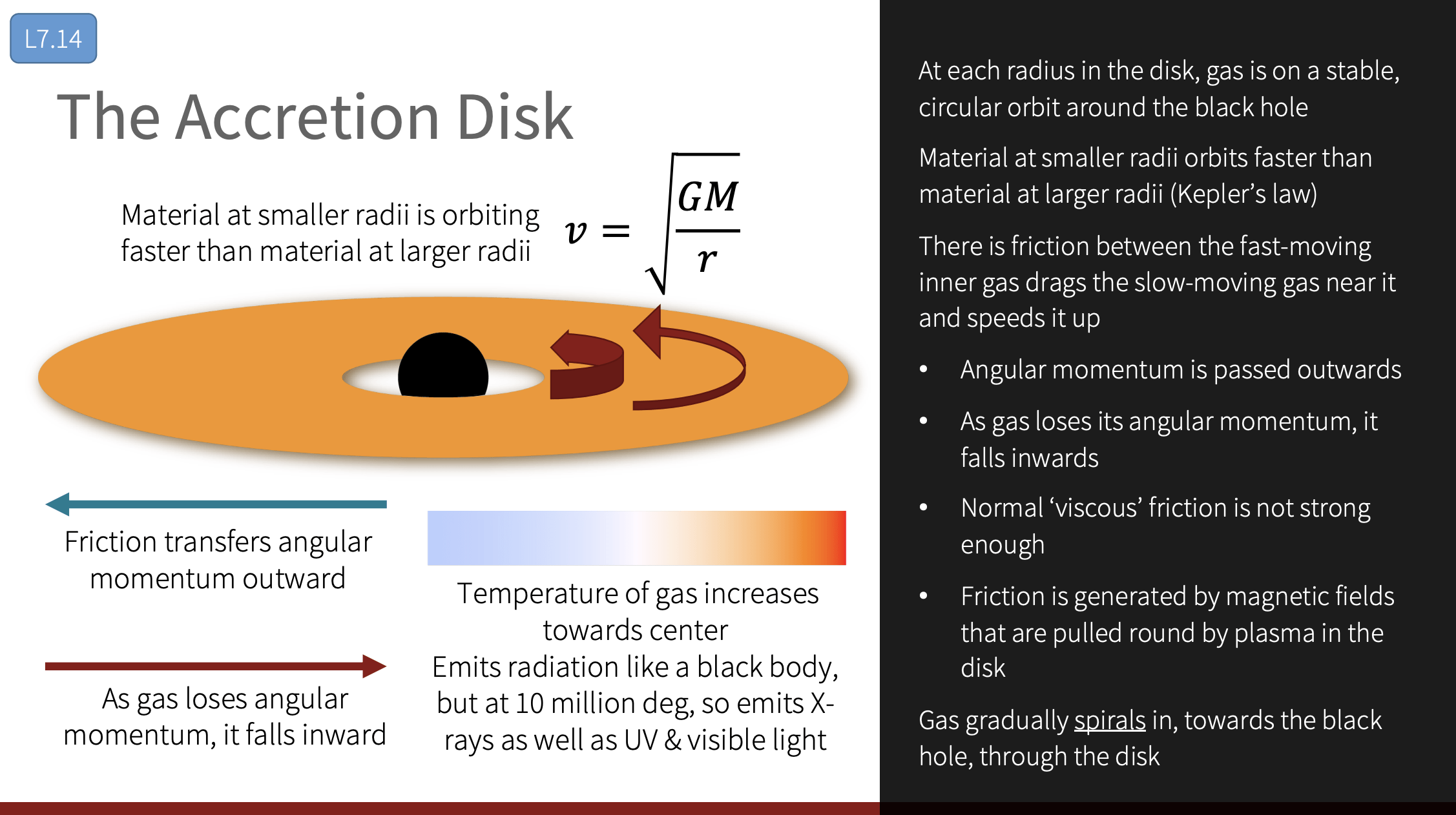

T-REX

Supplement (u,v) coverage at 86 GHz
Enable parameter estimation of Sgr A*/M87
Achieve Space-Space VLBI


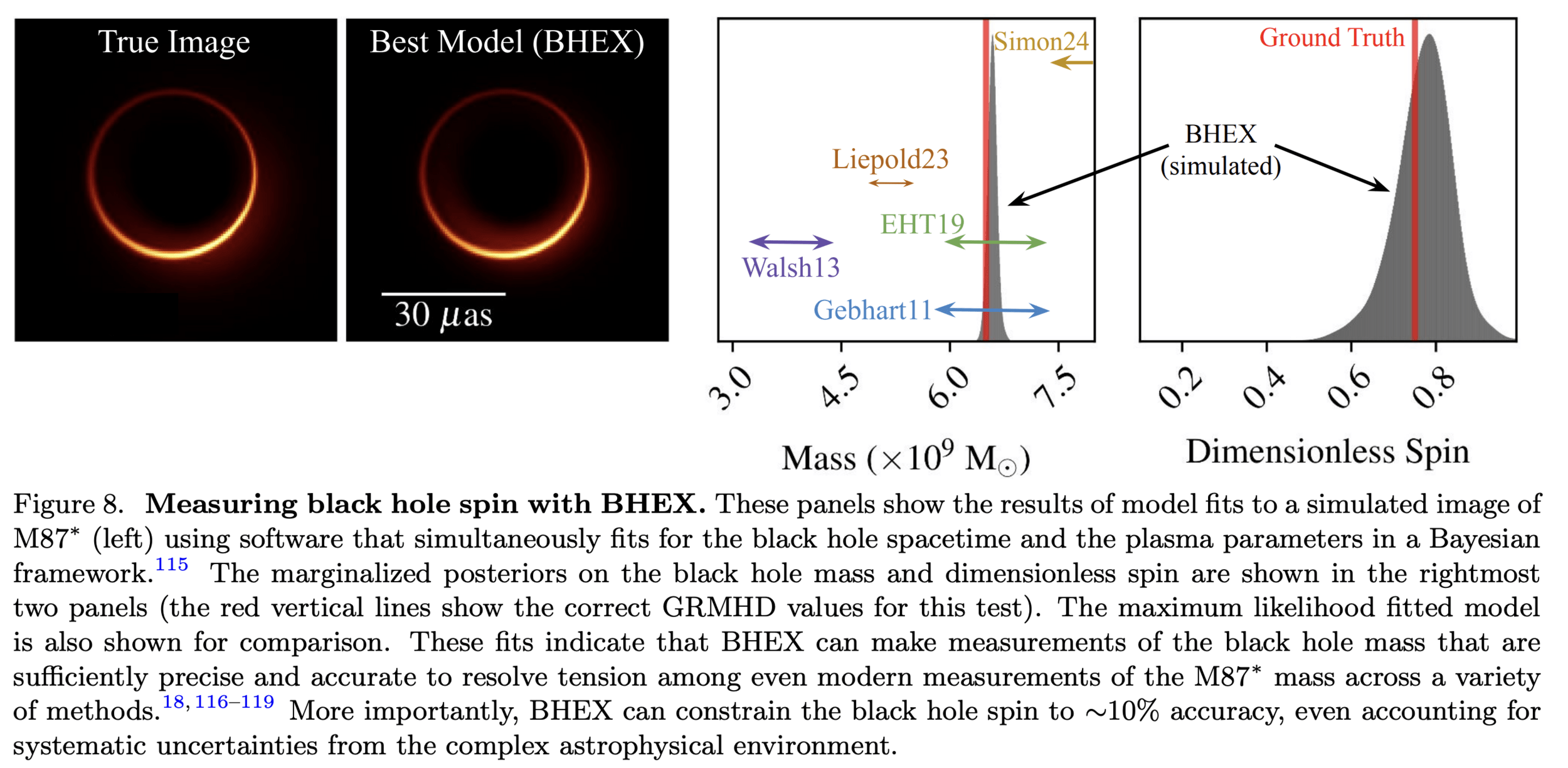
Videos of M87 & Sgr A*
"The Black Hole Explorer: Motivation and Vision" Johnson et. al. arXiv 2024


T-REX

Capture Time-Resolved Videos of M87 & Sgr A*

Time-Resolve Binary Black Hole Systems

Conduct VLBI Survey of AGN targets at 86 GHz



T-REX

Time-Resolve Binary Black Hole Systems
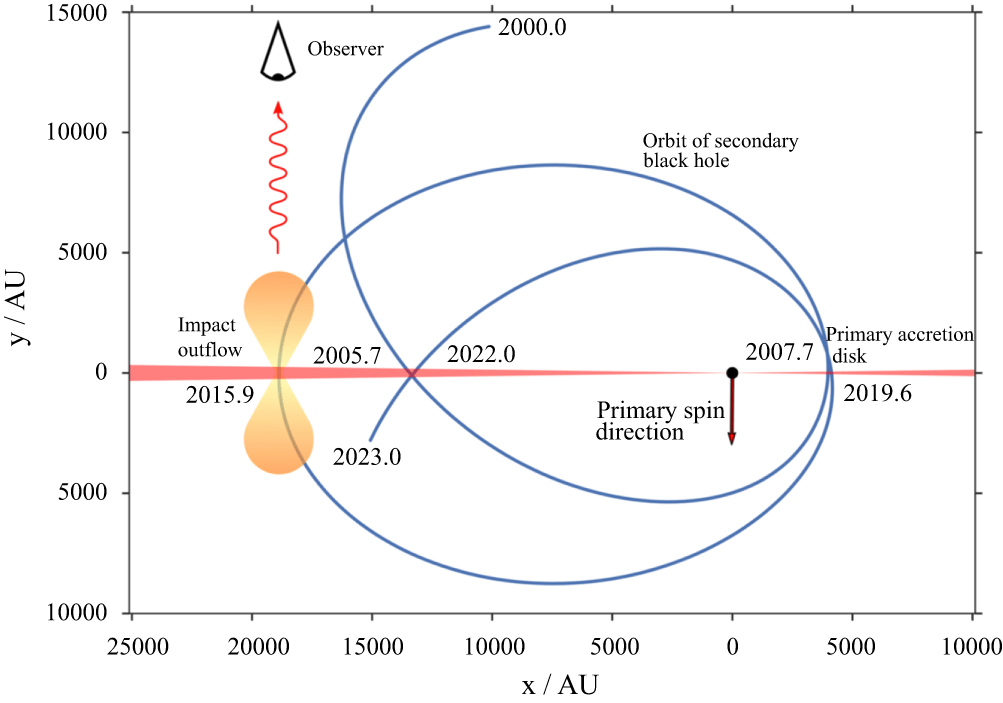


T-REX

Time-Resolve Binary Black Hole Systems


T-REX

Time-Resolve Binary Black Hole Systems


T-REX

Capture Time-Resolved Videos of M87 & Sgr A*

Time-Resolve Binary Black Hole Systems

Conduct VLBI Survey of AGN targets at 86 GHz



T-REX

Conduct VLBI Survey of AGN targets at 86 GHz

"The Black Hole Explorer: Motivation and Vision" Johnson et. al. arXiv 2024


T-REX

- Introduction
- What is a black hole?
- How do you image a black hole?
- How do you record a black hole?
- T-REX Primary Science Objectives
- T-REX (u,v) Coverage
- T-REX Engineering Challenges
- T-REX SWaPC Requirements
- T-REX Concept of Operations
- T-REX Timeline & Funding Deadlines


T-REX








"Metrics and Motivations for Earth–Space VLBI: Time-resolving Sgr A* with the Event Horizon Telescope" Palumbo et. al. ApJ 2019











T-REX


M87


Sgr A*
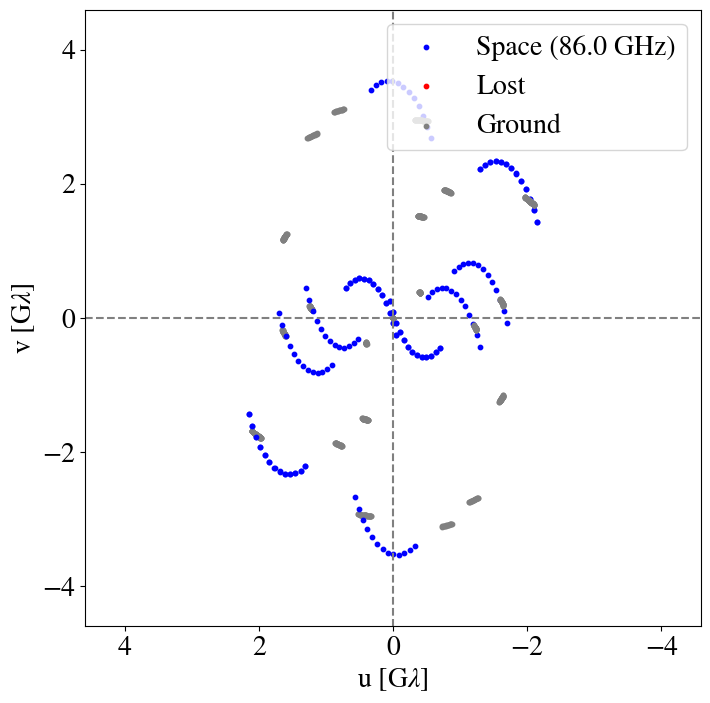
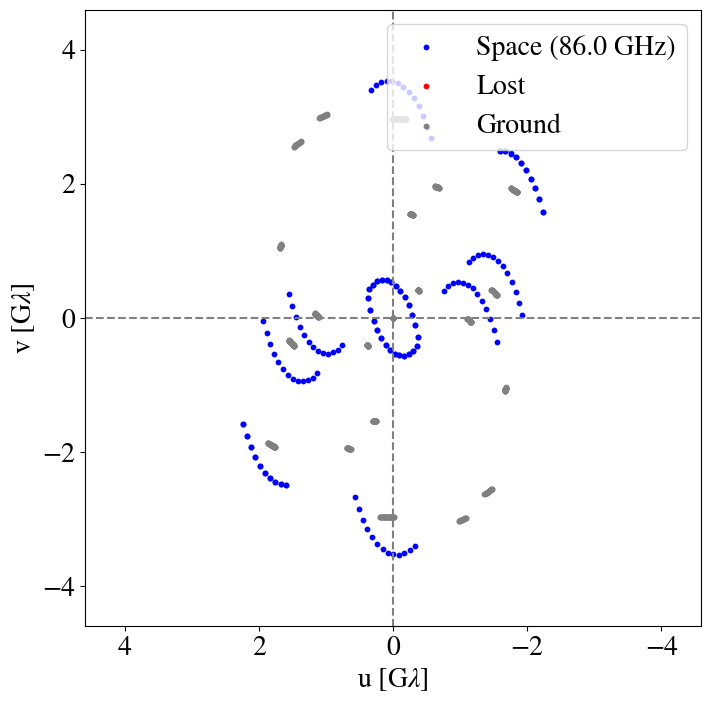
10:15
11:00
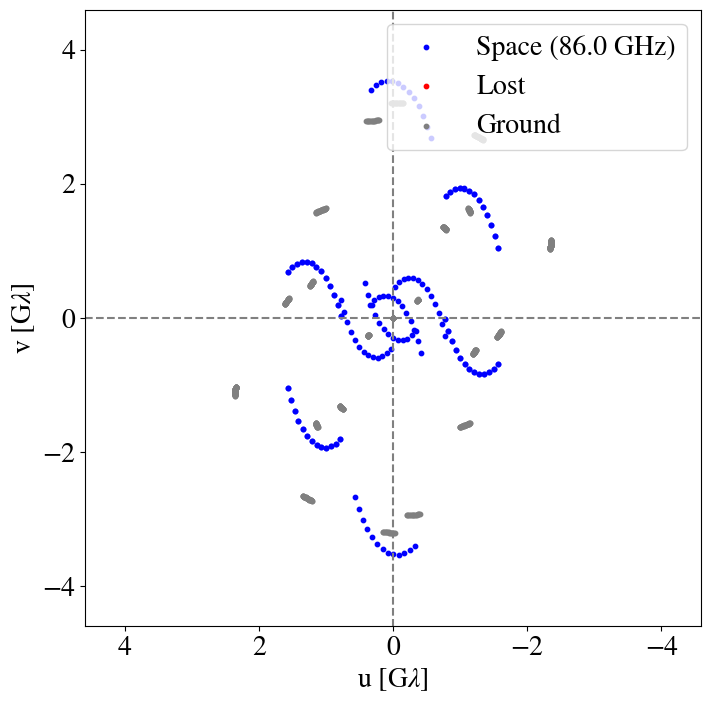
8:00
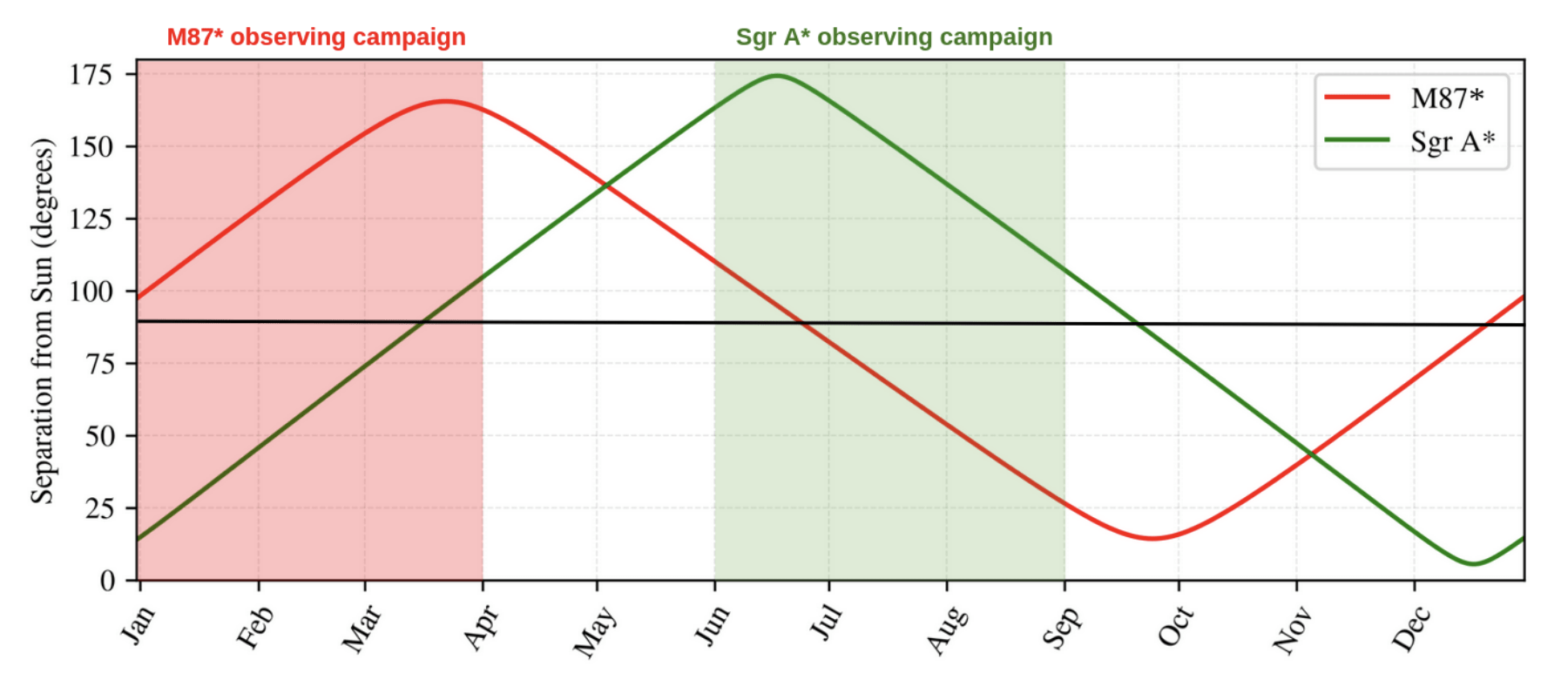


Sgr A*


10:15
11:00

8:00




T-REX
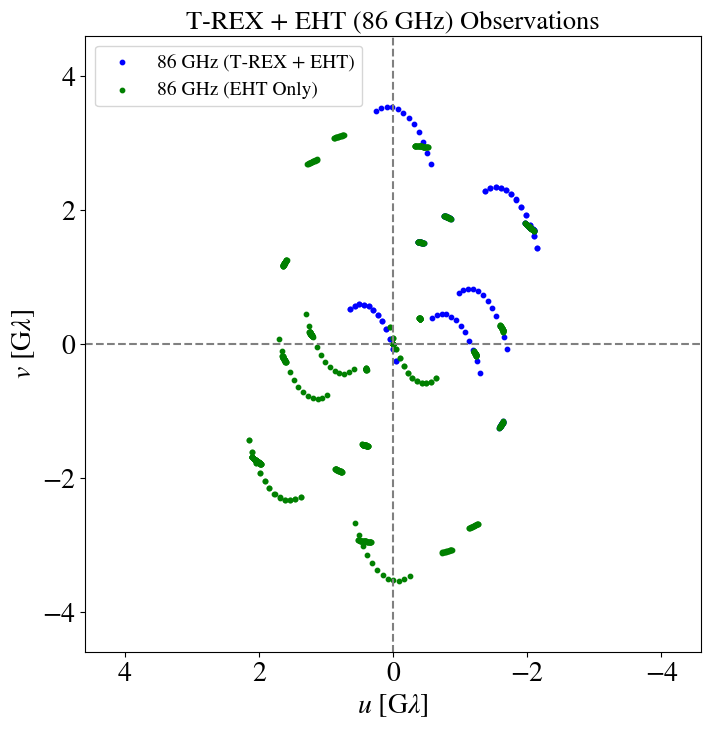
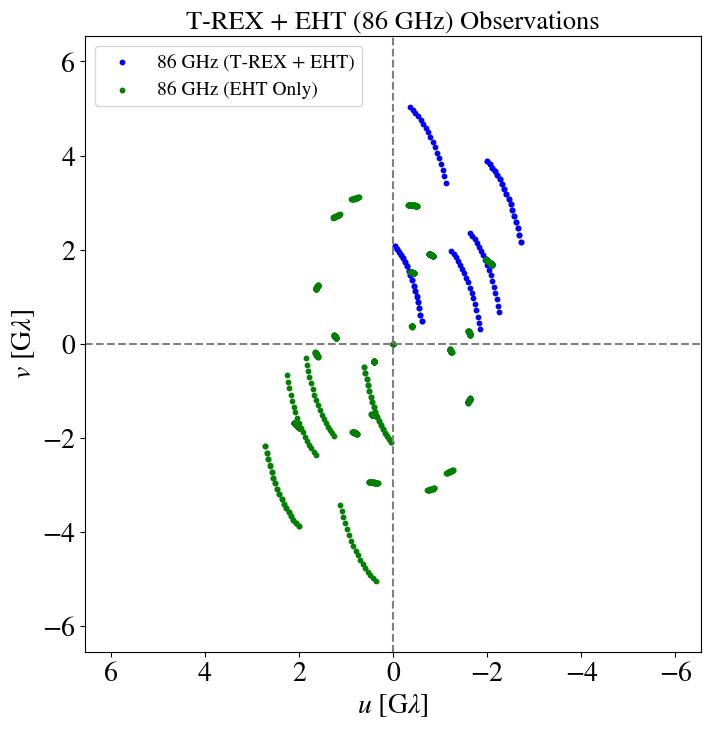
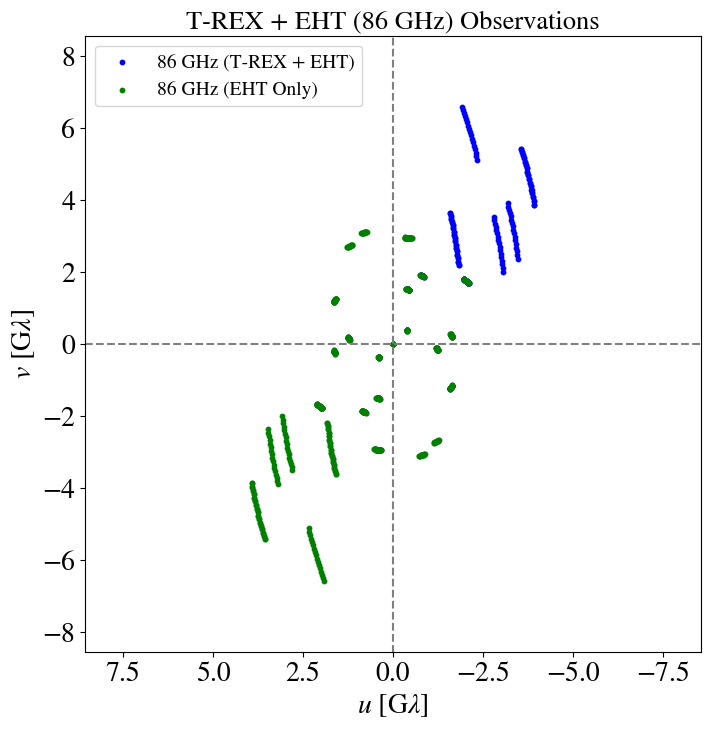
















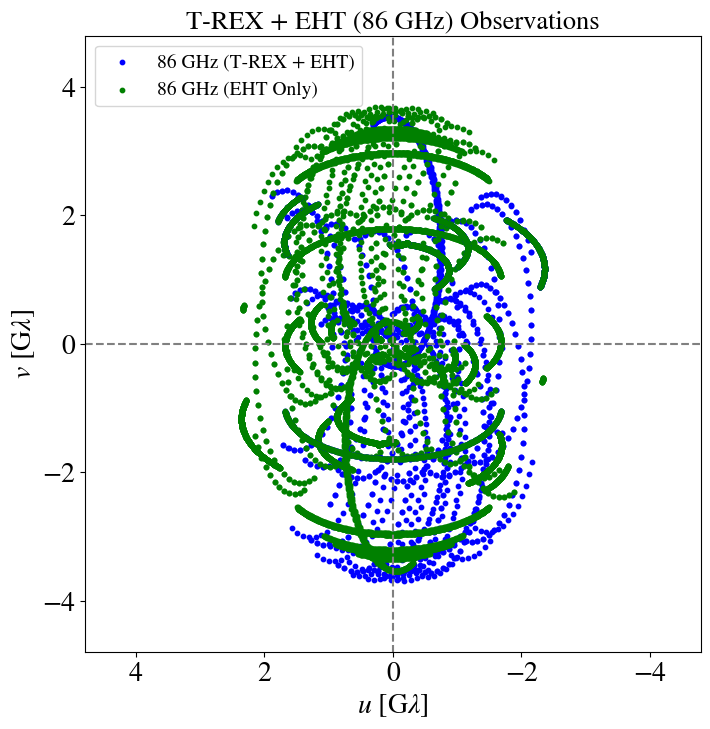
























T-REX
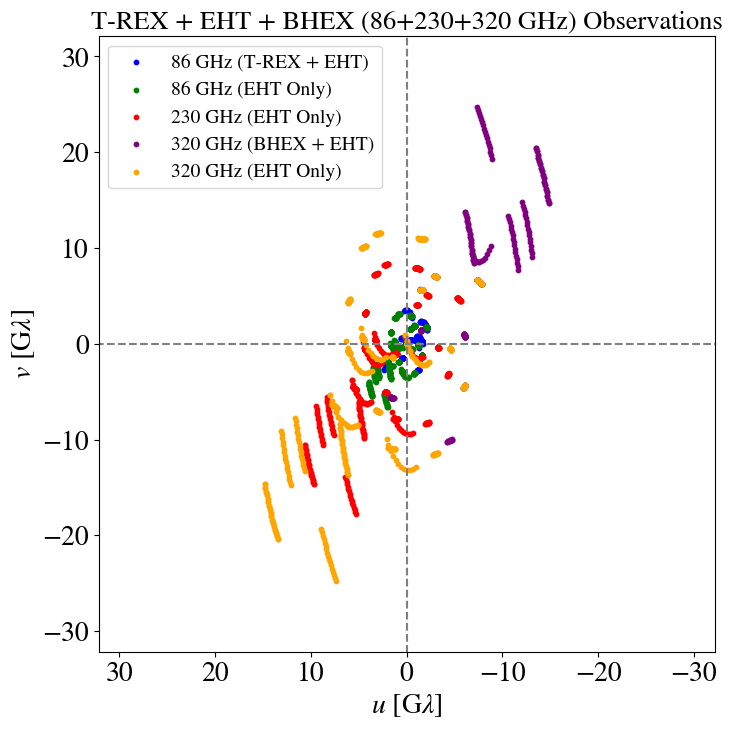
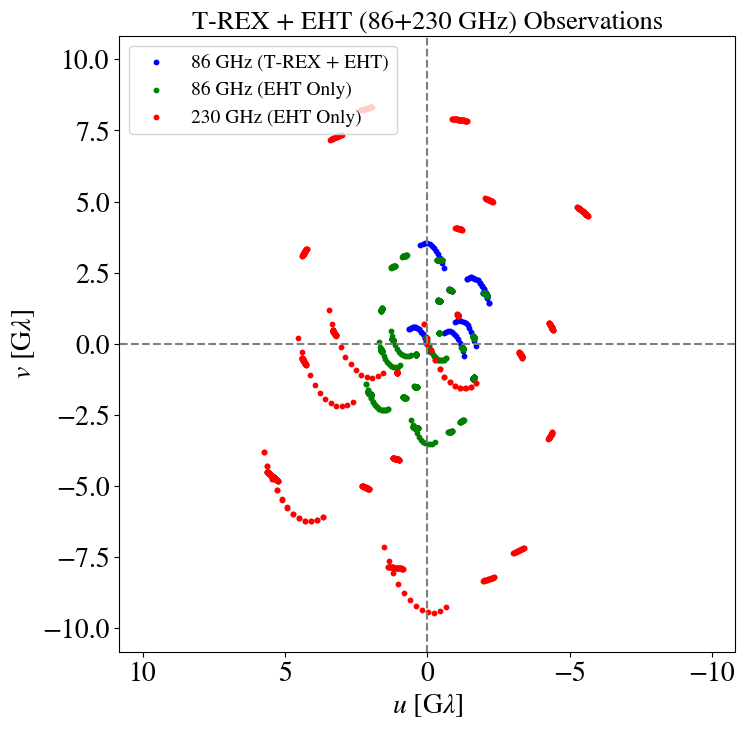
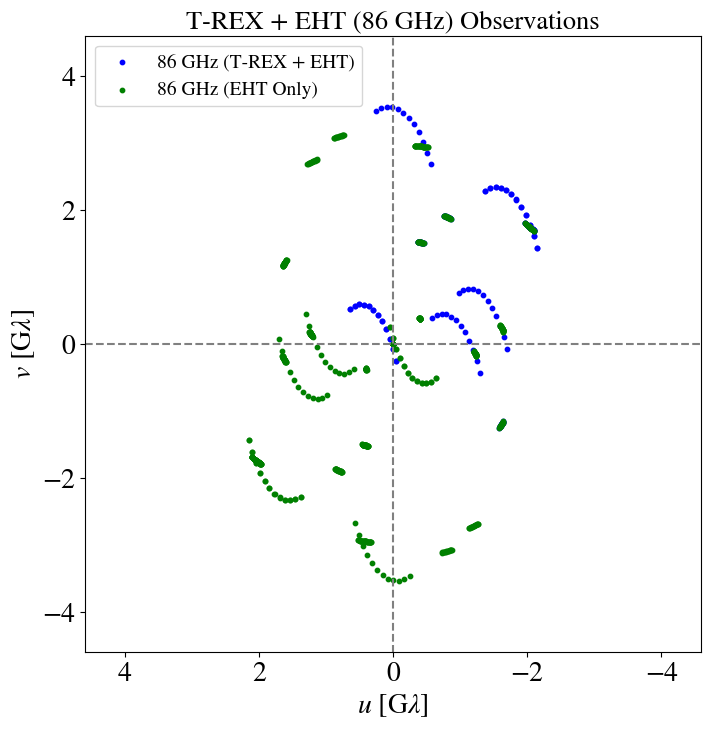



T-REX







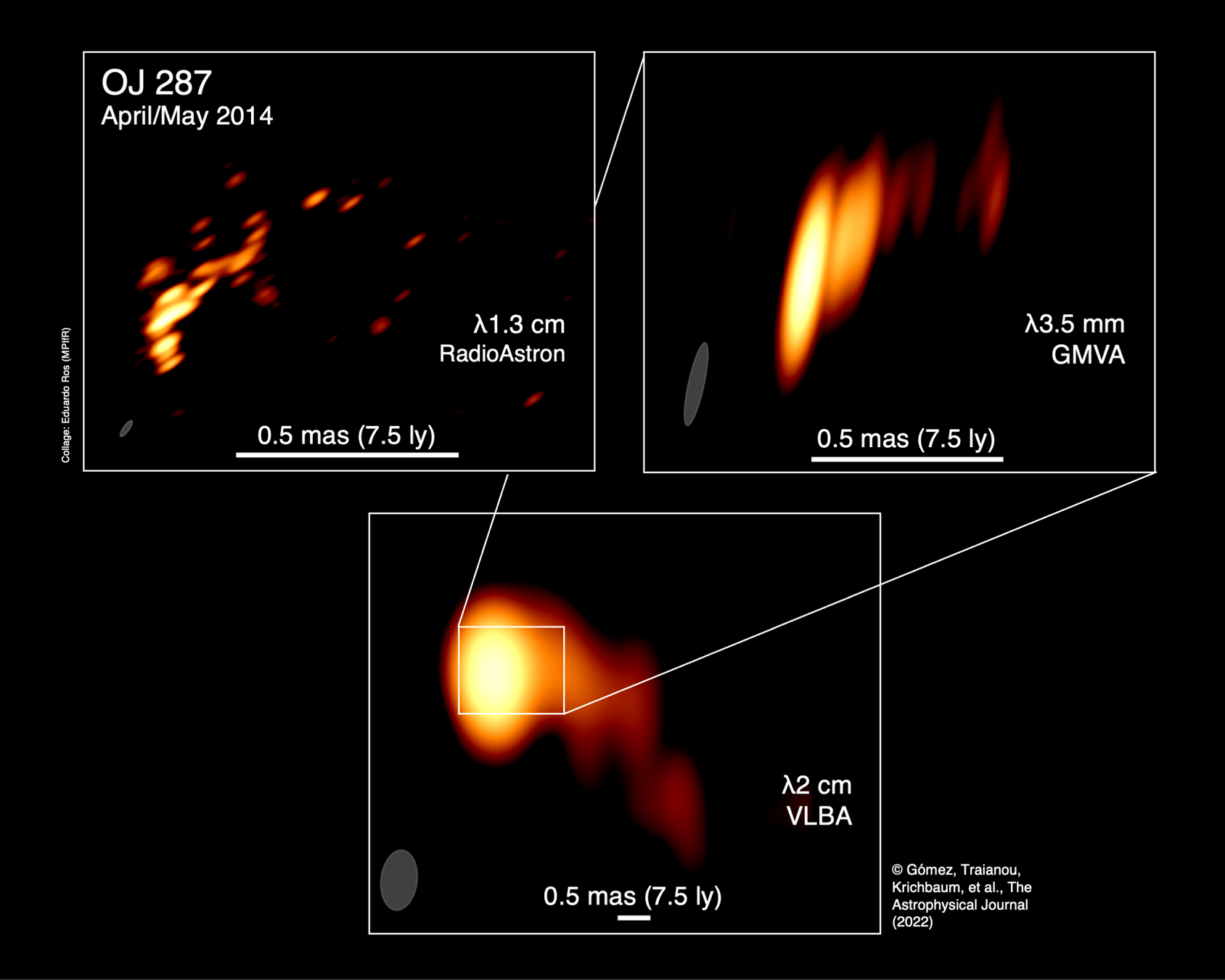
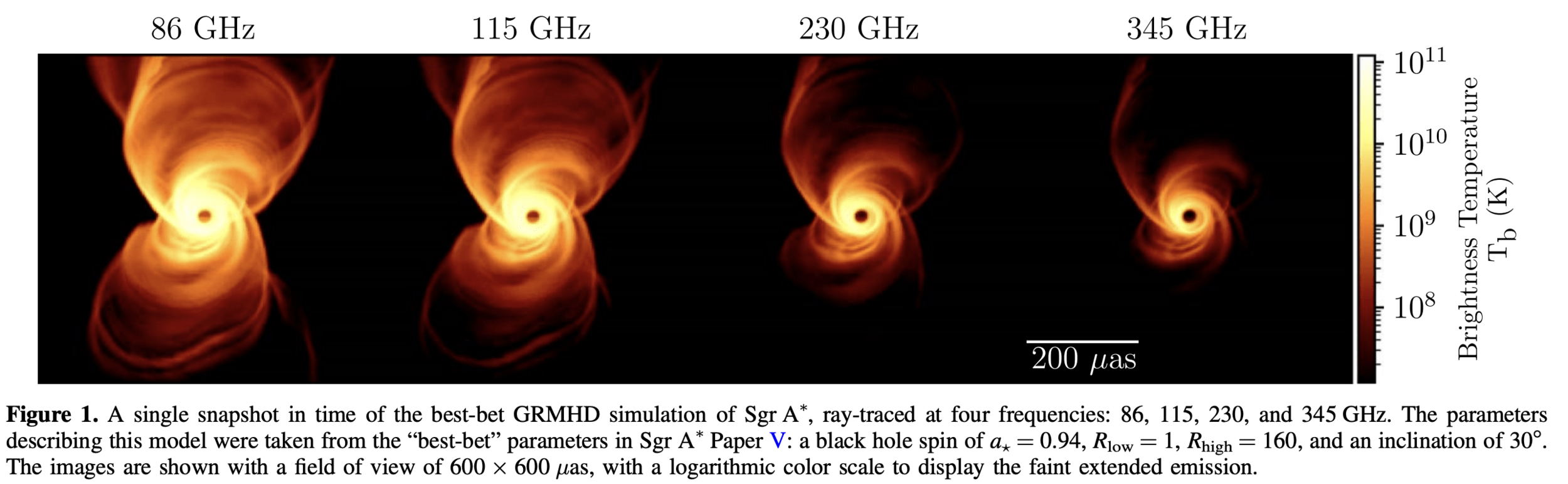
"Imaging the event horizon of M87* from space on different timescales" Shlentsova et. al. ApJ 2024

- Introduction
- What is a black hole?
- How do you image a black hole?
- How do you record a black hole?
- T-REX Primary Science Objectives
- T-REX (u,v) Coverage
- T-REX Engineering Challenges
- T-REX SWaPC Requirements
- T-REX Concept of Operations
- T-REX Timeline & Funding Deadlines


T-REX

T-REX




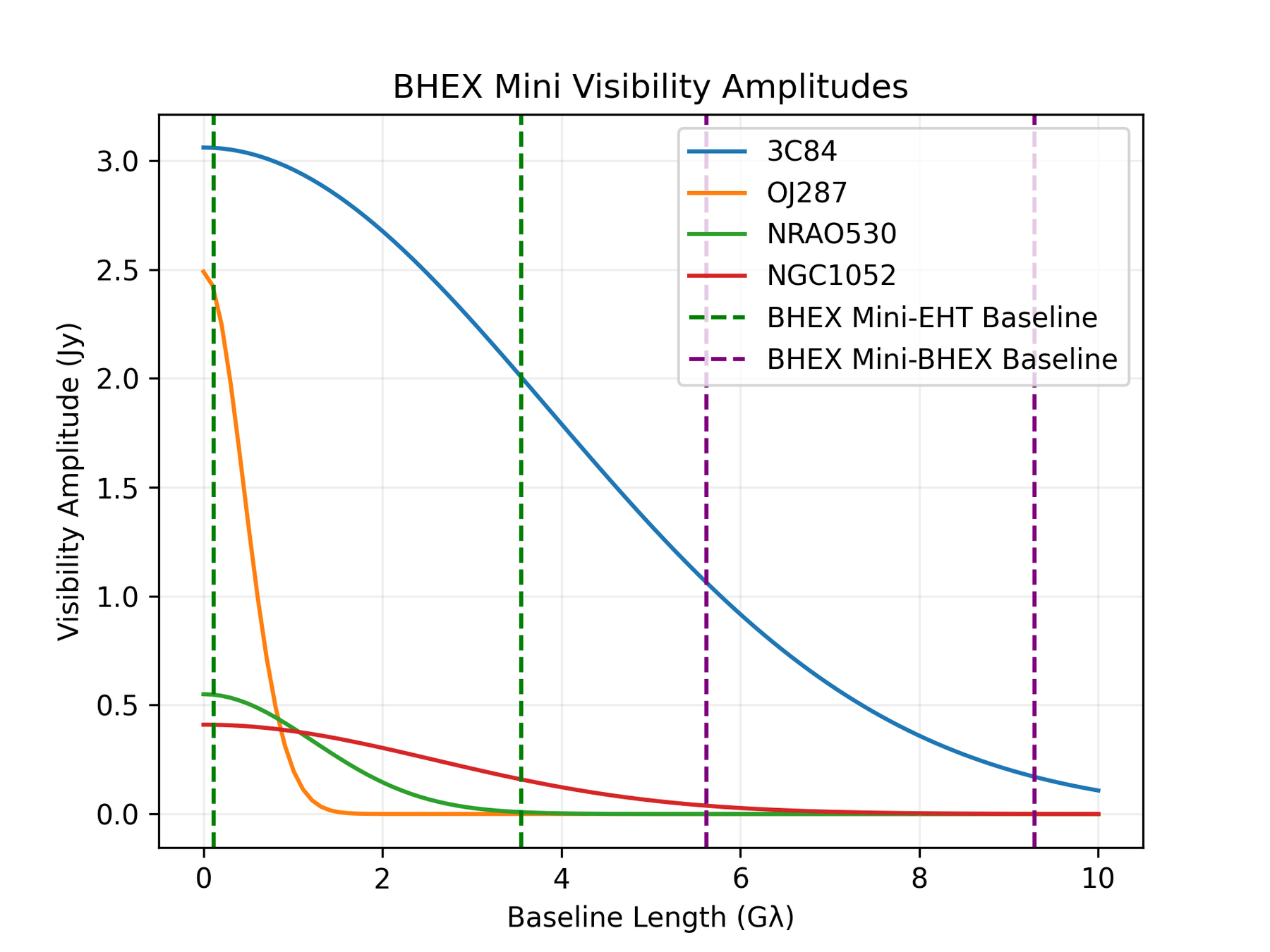
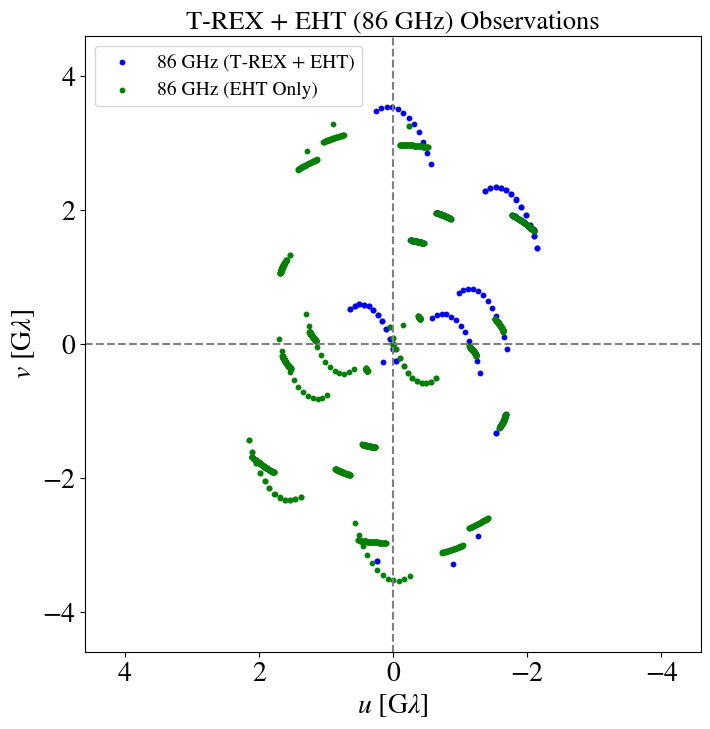
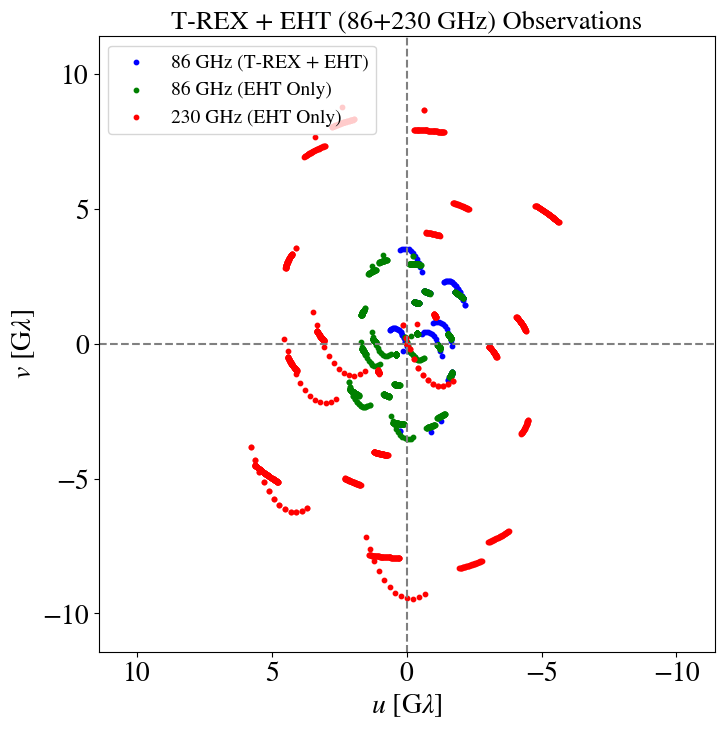
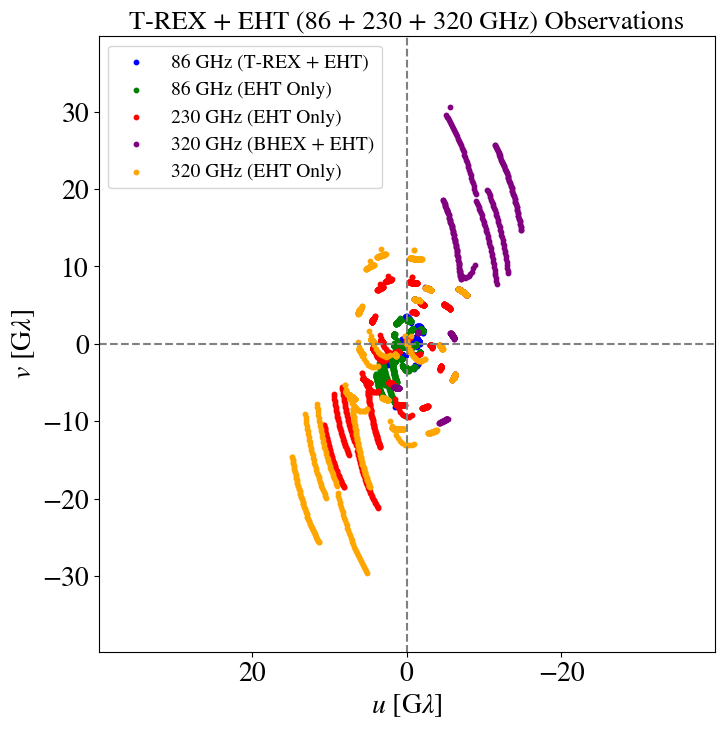
Rapid (u,v) coverage
Decreased signal loss
Decreased radiation environment



Infrared Thermal Emissions
Limited Ground Coverage
Aggressive Slew Rate Required
Potential Reduced ISM Scattering





mm-wavelength angular resolution
Dual-baseline capability



T-REX




Rapid (u,v) coverage
Decreased signal loss
Decreased radiation environment



Infrared Thermal Emissions
Limited Ground Coverage
Aggressive Slew Rate Required
Potential Reduced ISM Scattering





mm-wavelength angular resolution
Dual-baseline capability



T-REX




Rapid (u,v) coverage





T-REX





Rapid (u,v) coverage


T-REX







Rapid (u,v) coverage


T-REX




Rapid (u,v) coverage


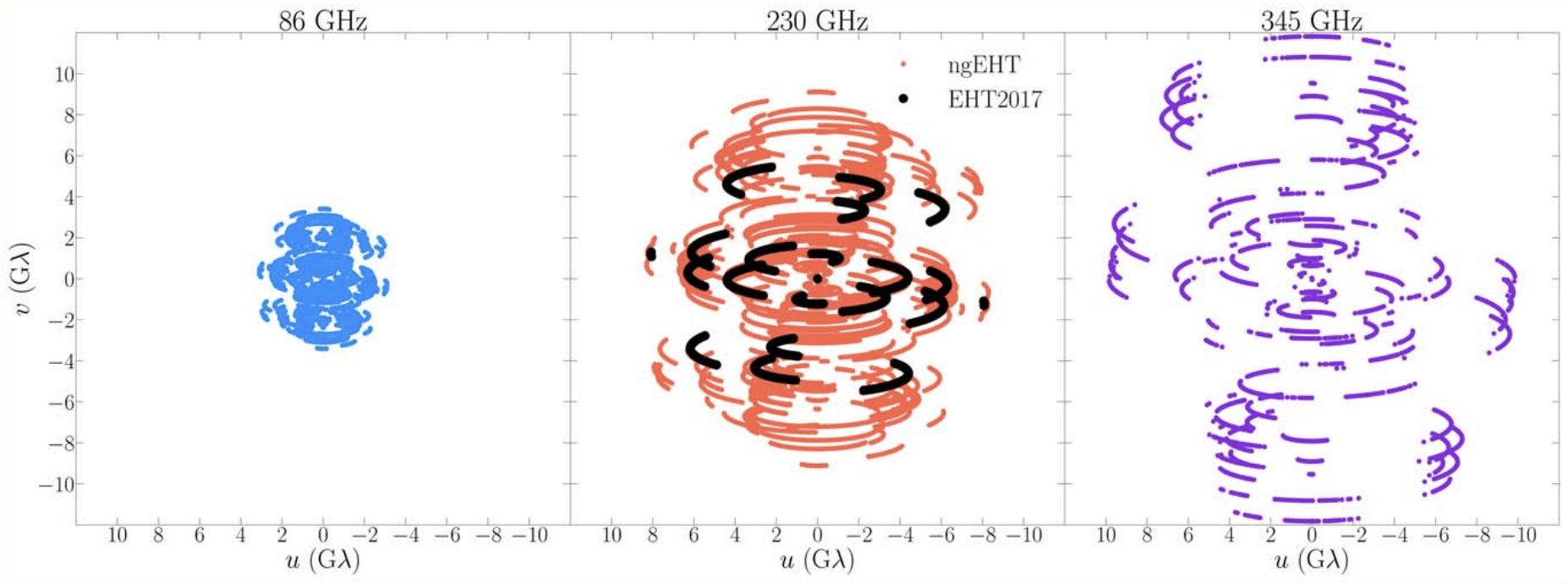
Multifrequency Black Hole Imaging for the Next-generation Event Horizon Telescope (Chael et. al., 2023, ApJ)

T-REX




Rapid (u,v) coverage
Decreased signal loss
Decreased radiation environment



Infrared Thermal Emissions
Limited Ground Coverage
Aggressive Slew Rate Required
Potential Reduced ISM Scattering





mm-wavelength angular resolution
Dual-baseline capability



T-REX




Decreased signal loss




Distance: How much distance did the signal travel through free space? (LEO vs. MEO!)

T-REX




Rapid (u,v) coverage
Decreased signal loss
Decreased radiation environment



Infrared Thermal Emissions
Limited Ground Coverage
Aggressive Slew Rate Required
Potential Reduced ISM Scattering





mm-wavelength angular resolution
Dual-baseline capability



T-REX




Rapid (u,v) coverage
Decreased signal loss
Decreased radiation environment



Infrared Thermal Emissions
Limited Ground Coverage
Aggressive Slew Rate Required
Potential Reduced ISM Scattering





mm-wavelength angular resolution
Dual-baseline capability



T-REX




Potential Reduced ISM Scattering



Prospects of Detecting a Jet in Sagittarius A* with VLBI (Chavez et. al., ApJ 2024)


T-REX




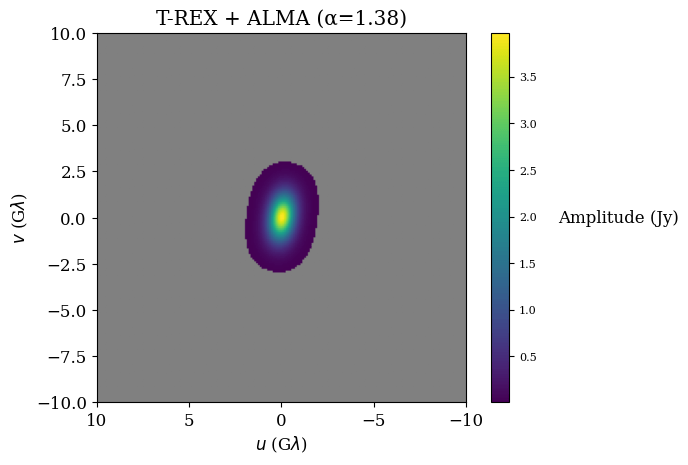
T-REX




Potential Reduced ISM Scattering


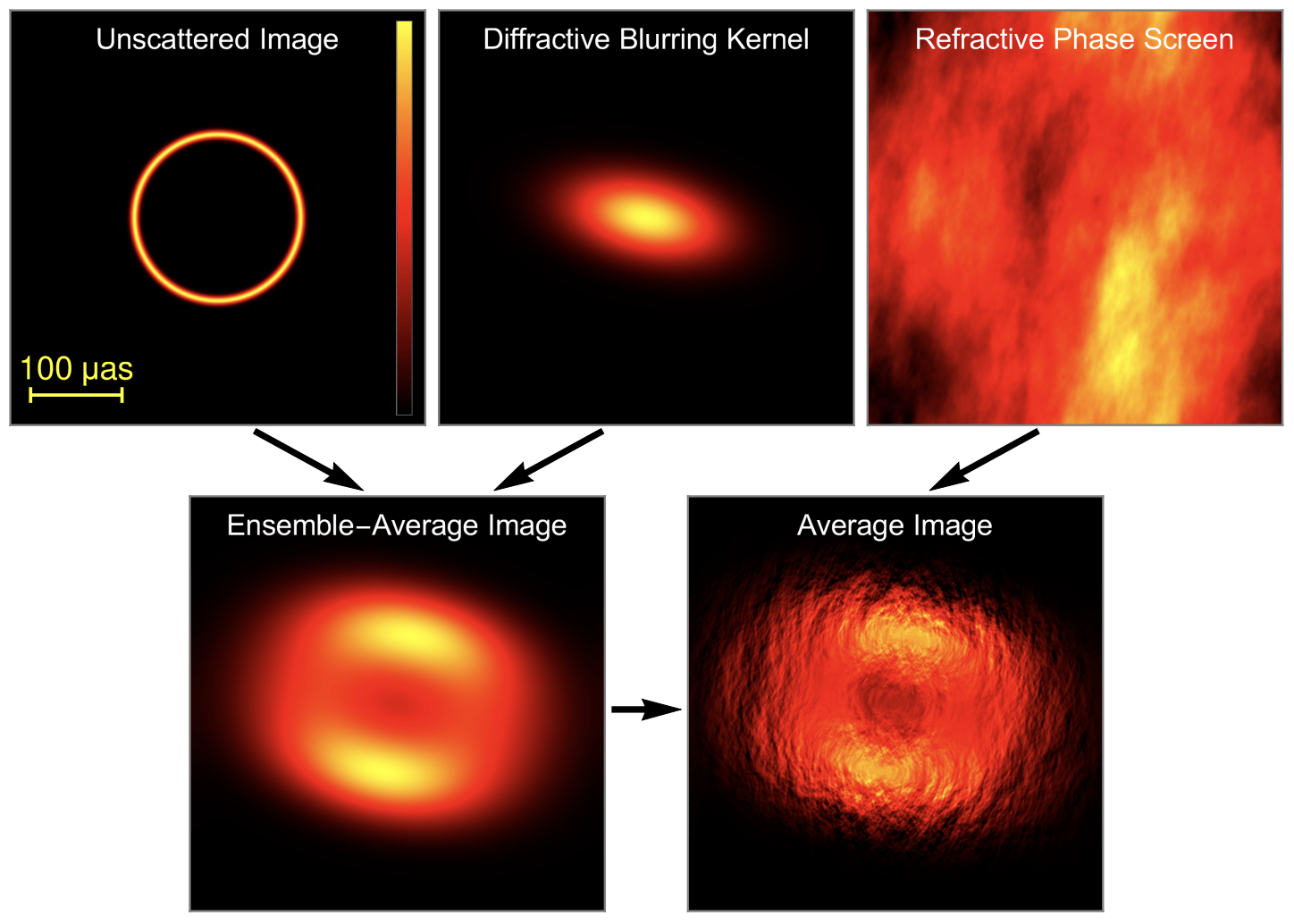
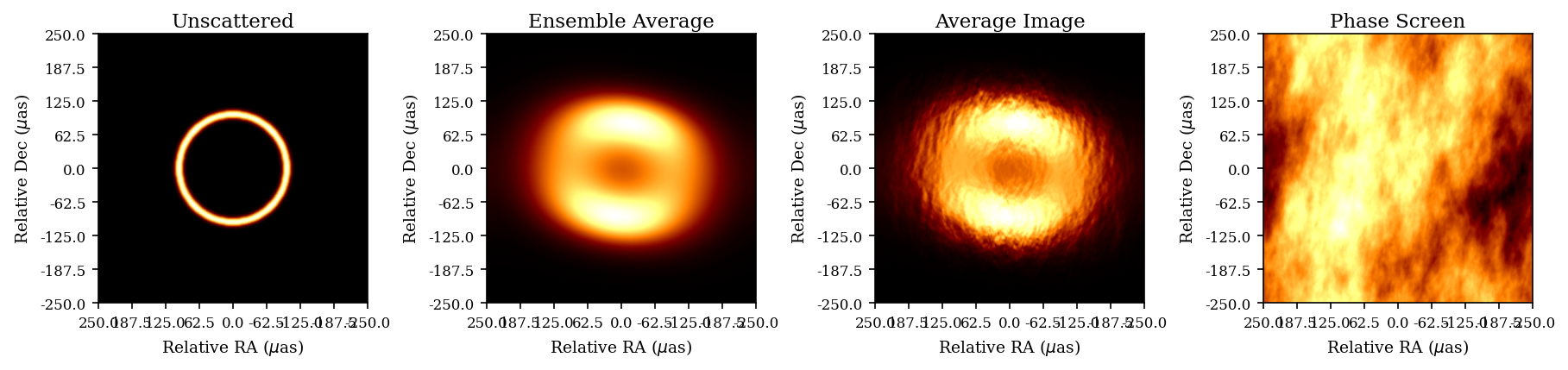
Orbit design for mitigating interstellar scattering effects in Earth-space VLBI observations of Sgr A* (Aditya Tamar, Ben Hudson, Daniel C.M. Palumbo, A&A, 2025)

T-REX




Potential Reduced ISM Scattering





T-REX




Rapid (u,v) coverage
Decreased signal loss
Decreased radiation environment



Infrared Thermal Emissions
Limited Ground Coverage
Aggressive Slew Rate Required
Potential Reduced ISM Scattering





mm-wavelength resolution
Dual-baseline capability



T-REX




Rapid (u,v) coverage
Decreased signal loss
Decreased radiation environment



Infrared Thermal Emissions
Limited Ground Coverage
Aggressive Slew Rate Required
Potential Reduced ISM Scattering





mm-wavelength resolution


T-REX




Rapid (u,v) coverage
Decreased signal loss
Decreased radiation environment



Infrared Thermal Emissions
Limited Ground Coverage
Aggressive Slew Rate Required
Potential Reduced ISM Scattering





mm-wavelength resolution
Dual-baseline capability



T-REX





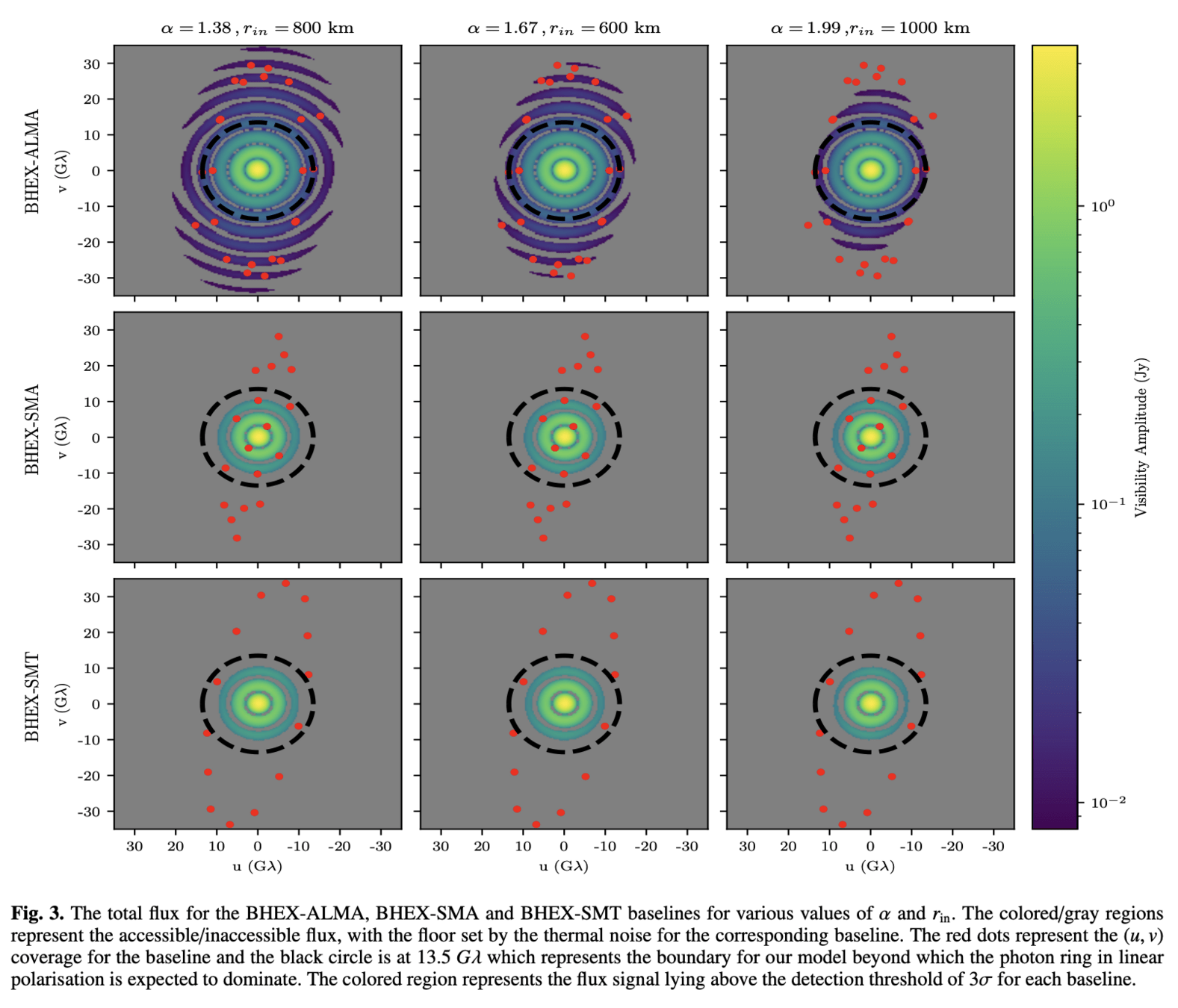
Dual-baseline capability



Rapid coverage of (u,v) plane
Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO
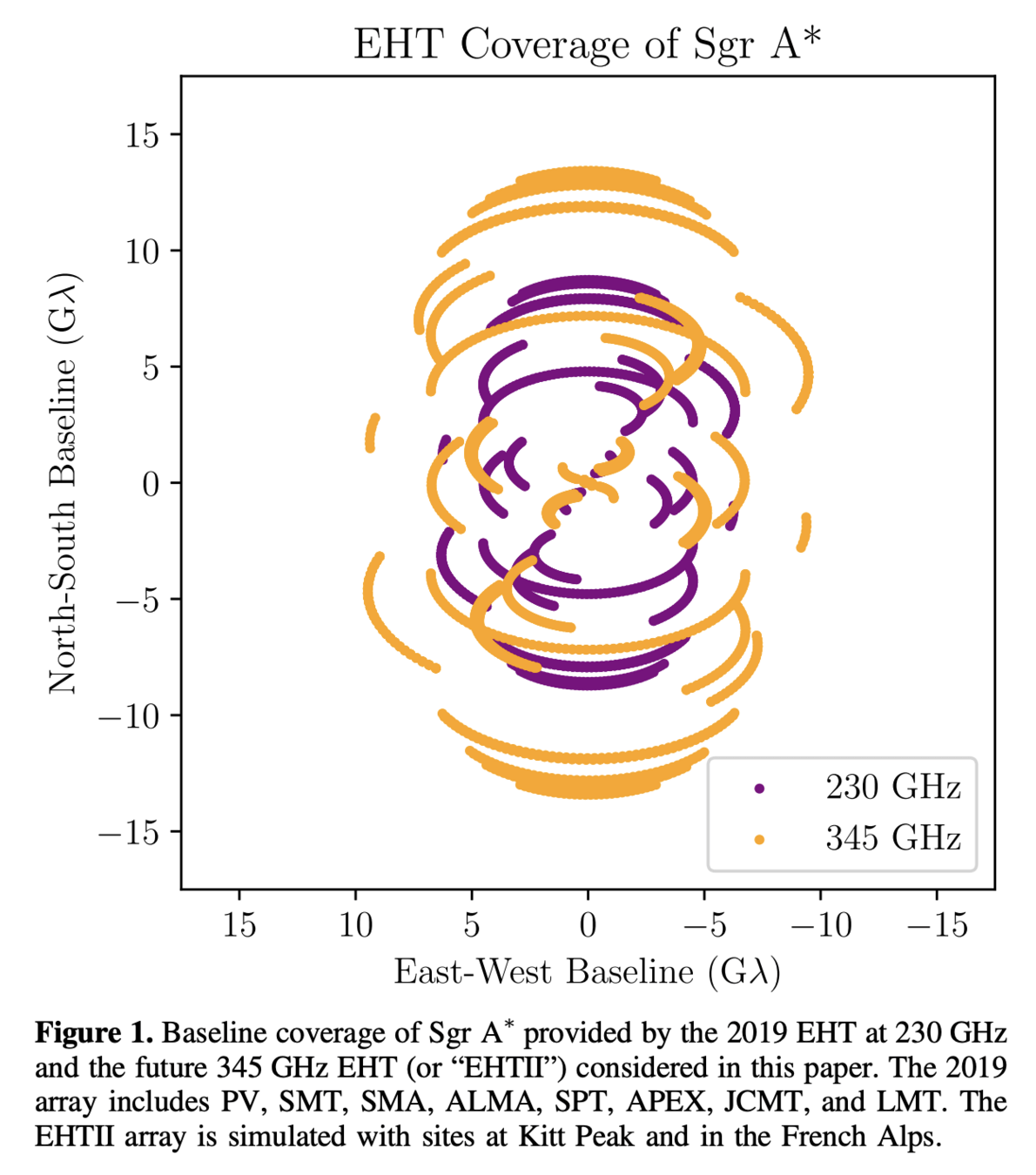
Metrics and Motivations for Earth–Space VLBI: Time-resolving Sgr A* with the Event Horizon Telescope (Palumbo et. al., ApJ 2019)

T-REX





Dual-baseline capability



Decreased signal loss from LEO
Decreased radiation environment in LEO vs. MEO


Metrics and Motivations for Earth–Space VLBI: Time-resolving Sgr A* with the Event Horizon Telescope (Palumbo et. al., ApJ 2019)

T-REX





Dual-baseline capability




T-REX




Rapid (u,v) coverage
Decreased signal loss
Decreased radiation environment



Infrared Thermal Emissions
Limited Ground Coverage
Aggressive Slew Rate Required
Potential Reduced ISM Scattering





mm-wavelength resolution
Dual-baseline capability



T-REX




Infrared Thermal Emissions



T-REX




Rapid (u,v) coverage
Decreased signal loss
Decreased radiation environment



Infrared Thermal Emissions
Limited Ground Coverage
Aggressive Slew Rate Required
Potential Reduced ISM Scattering





mm-wavelength resolution
Dual-baseline capability



T-REX




Limited Ground Coverage


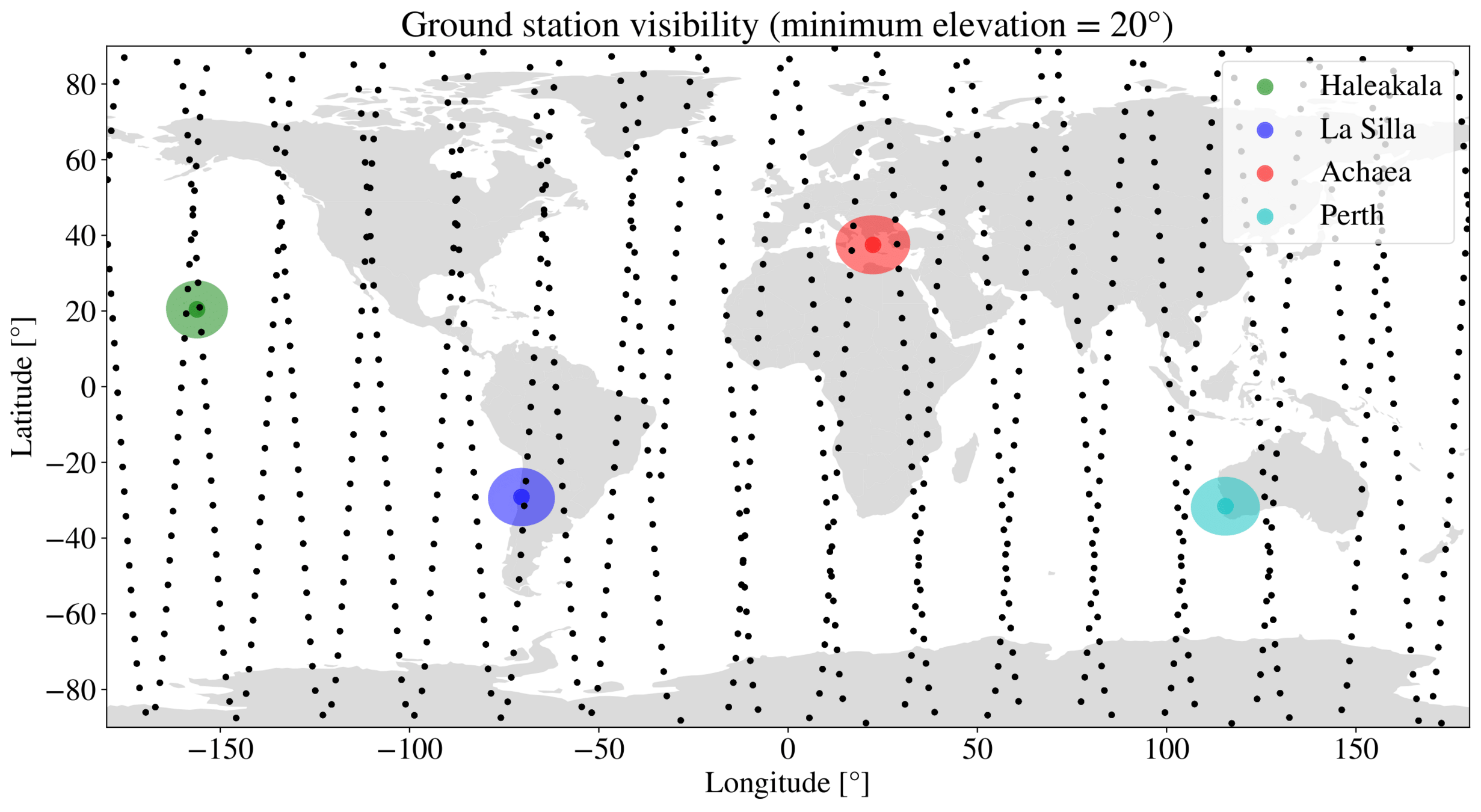


T-REX




Limited Ground Coverage


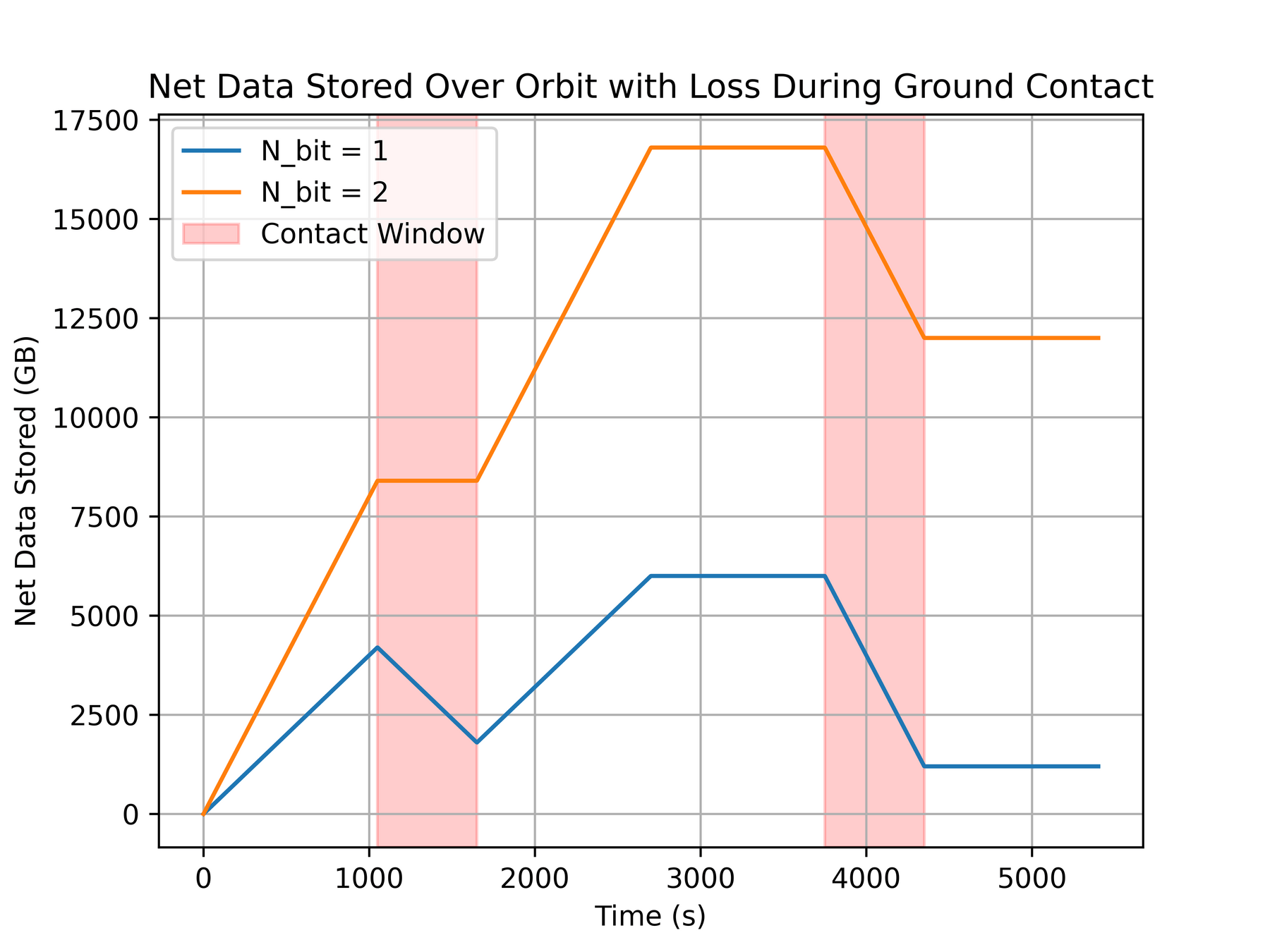
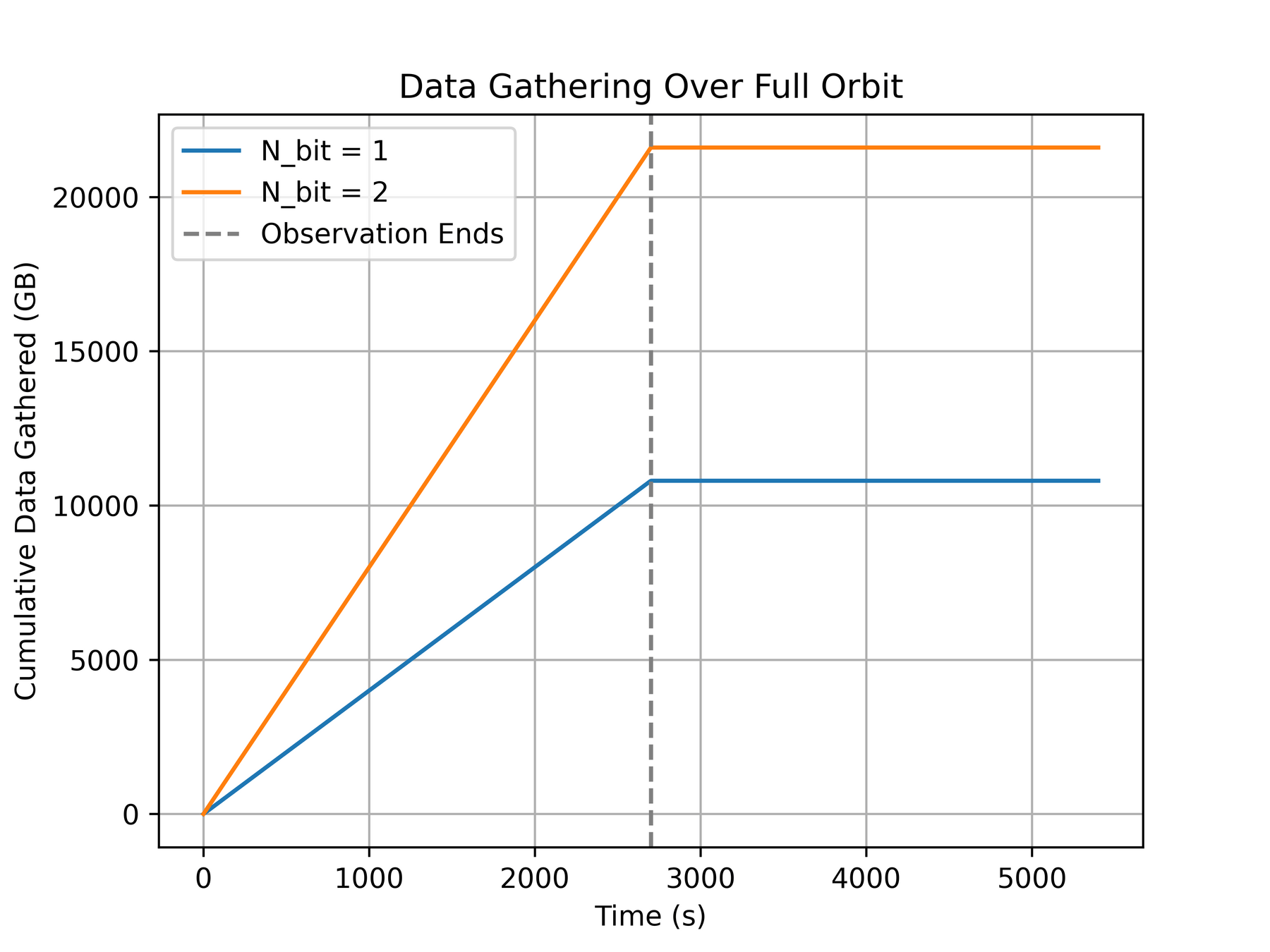

T-REX




Limited Ground Coverage



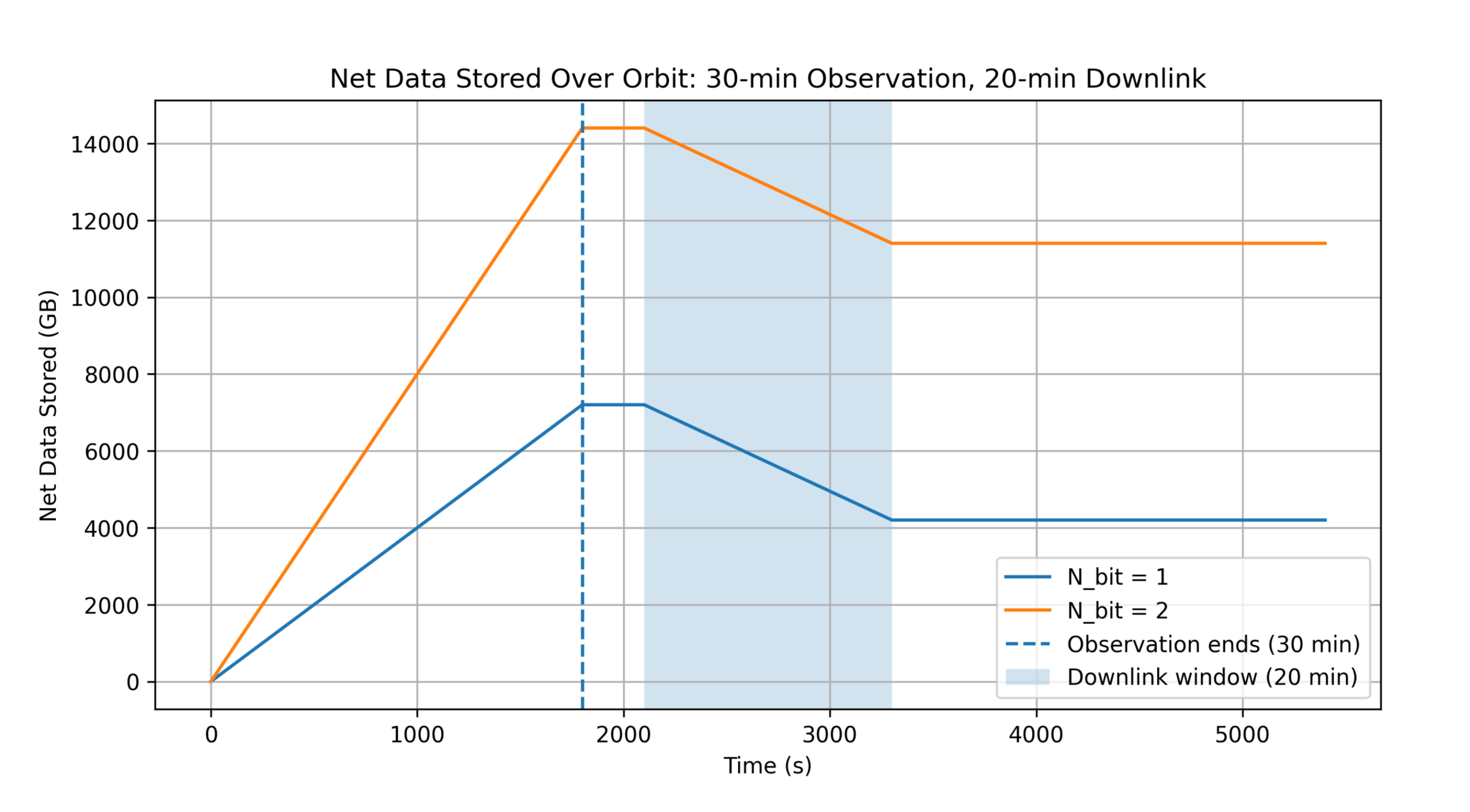
T-REX




Rapid (u,v) coverage
Decreased signal loss
Decreased radiation environment



Infrared Thermal Emissions
Limited Ground Coverage
Aggressive Slew Rate Required
Potential Reduced ISM Scattering





mm-wavelength resolution
Dual-baseline capability



T-REX




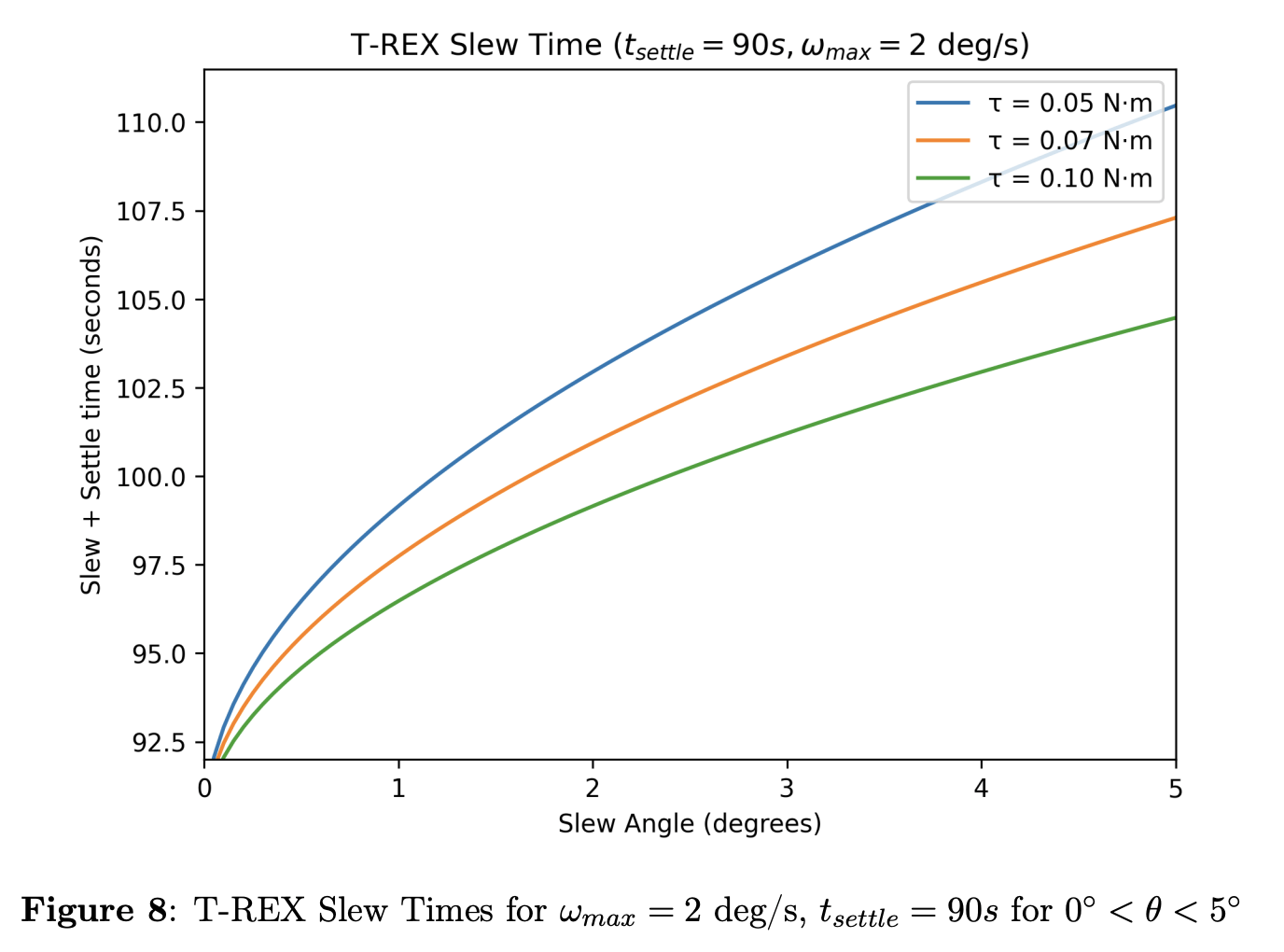
Aggressive Slew Rate Required



- Introduction
- What is a black hole?
- How do you image a black hole?
- How do you record a black hole?
- T-REX Primary Science Objectives
- T-REX (u,v) Coverage
- T-REX Engineering Challenges
- T-REX SWaPC Requirements
- T-REX Concept of Operations
- T-REX Timeline & Funding Deadlines


T-REX

T-REX SWaPC







Size
Weight
Power
Power
Cost



NASA Pioneers

Aspera

Pandora

StarBurst
PUEO
(Galaxy Evolution via UV)
(Exoplanet Explorer)
(Neutron Stars via Gamma Rays)
(Particle Physics via High-Energy Neutrinos)

Mission Parameters

SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit

Systems Design

SEFD

USO
Data
Orbit

Systems Design


SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit

Systems Design

SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design

SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design

SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design

SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design

SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design

SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design

SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design

SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design

SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design

SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design

SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design

SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design

SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design

SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design

SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design

SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design

SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design

SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design
SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design
SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design
SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design
SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design
SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design
SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


Systems Design
SEFD
USO
Data
Orbit


T-REX


T-REX
















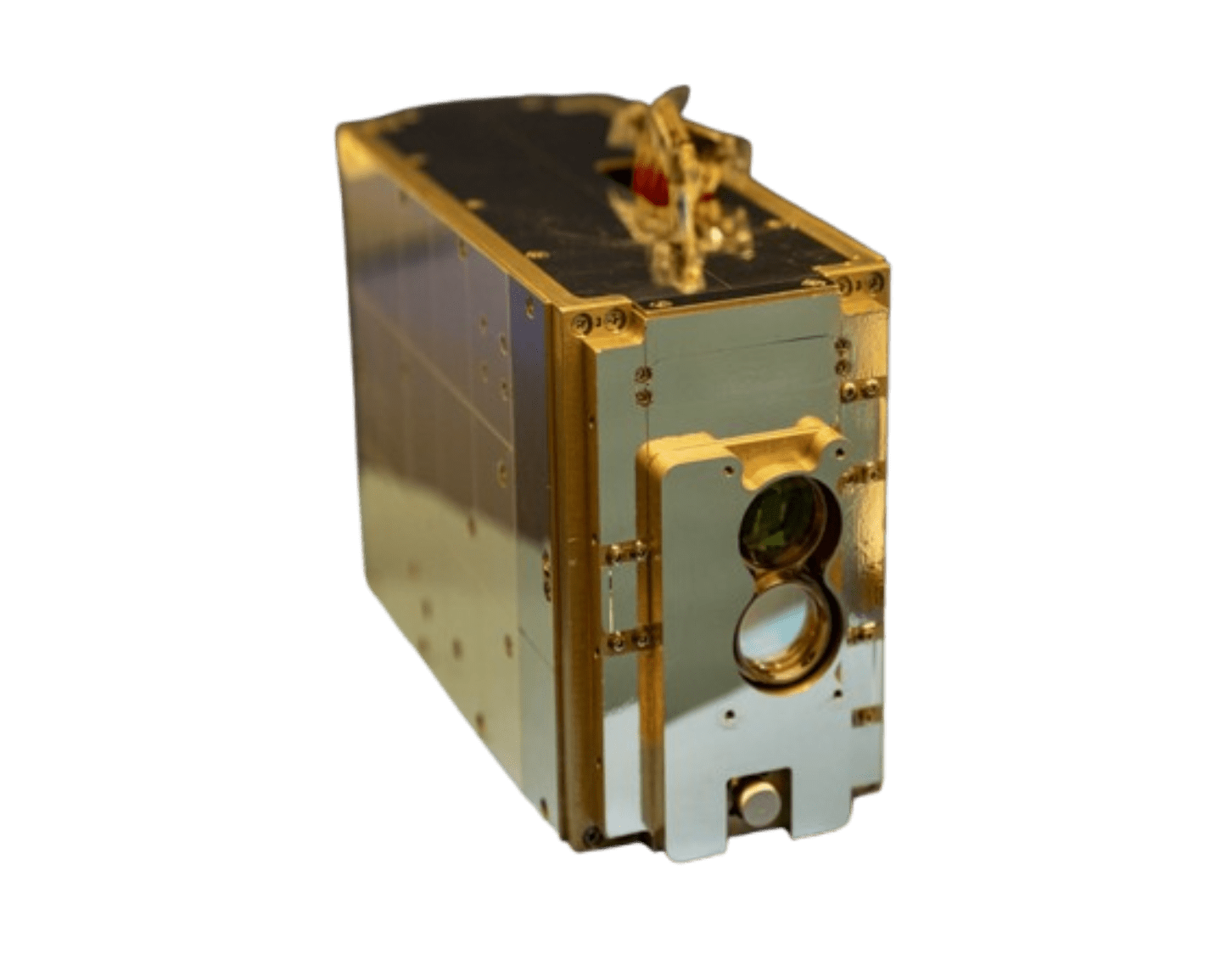
Antenna
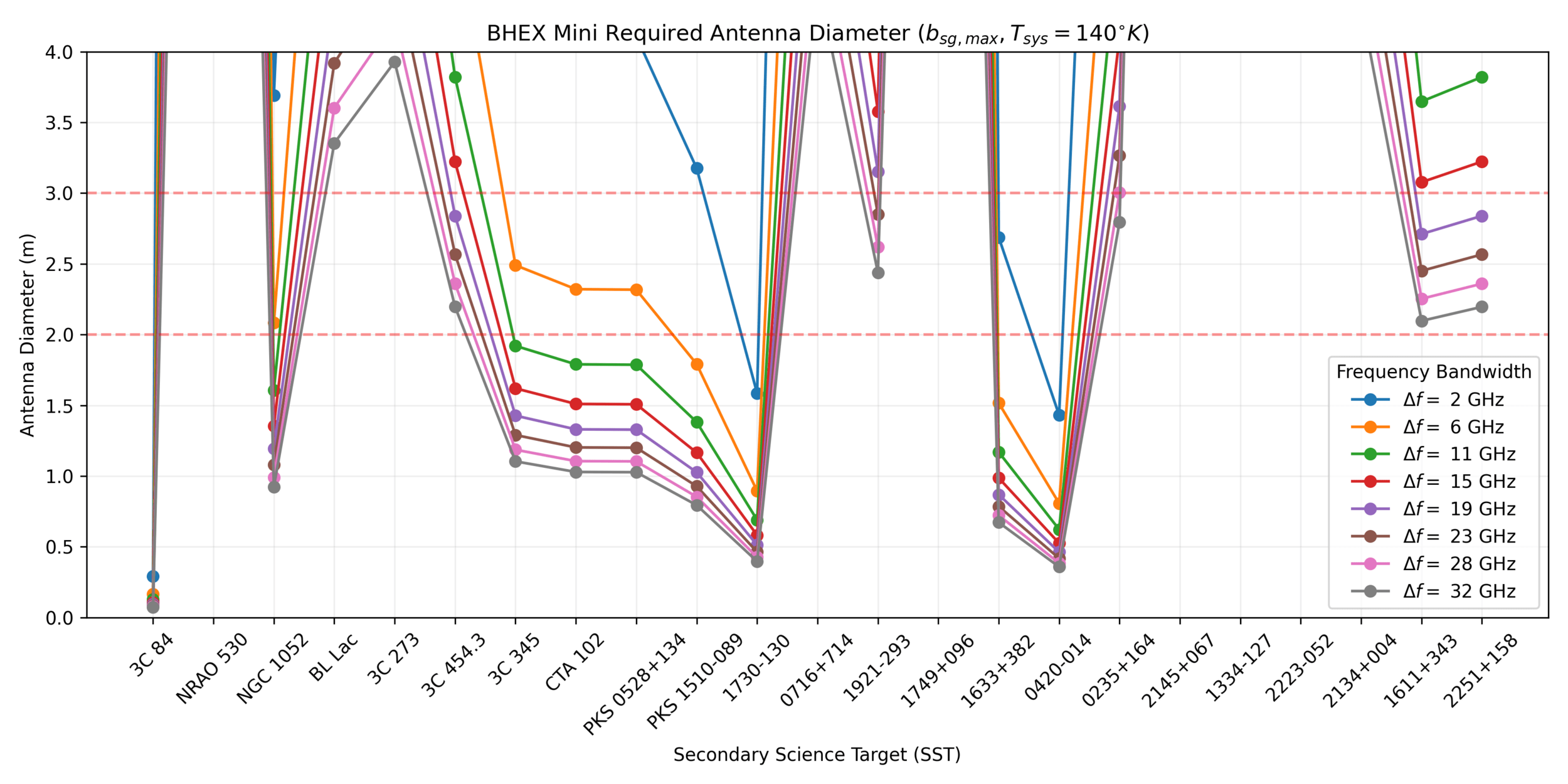
T-REX










Antenna

T-REX











Antenna
T-REX
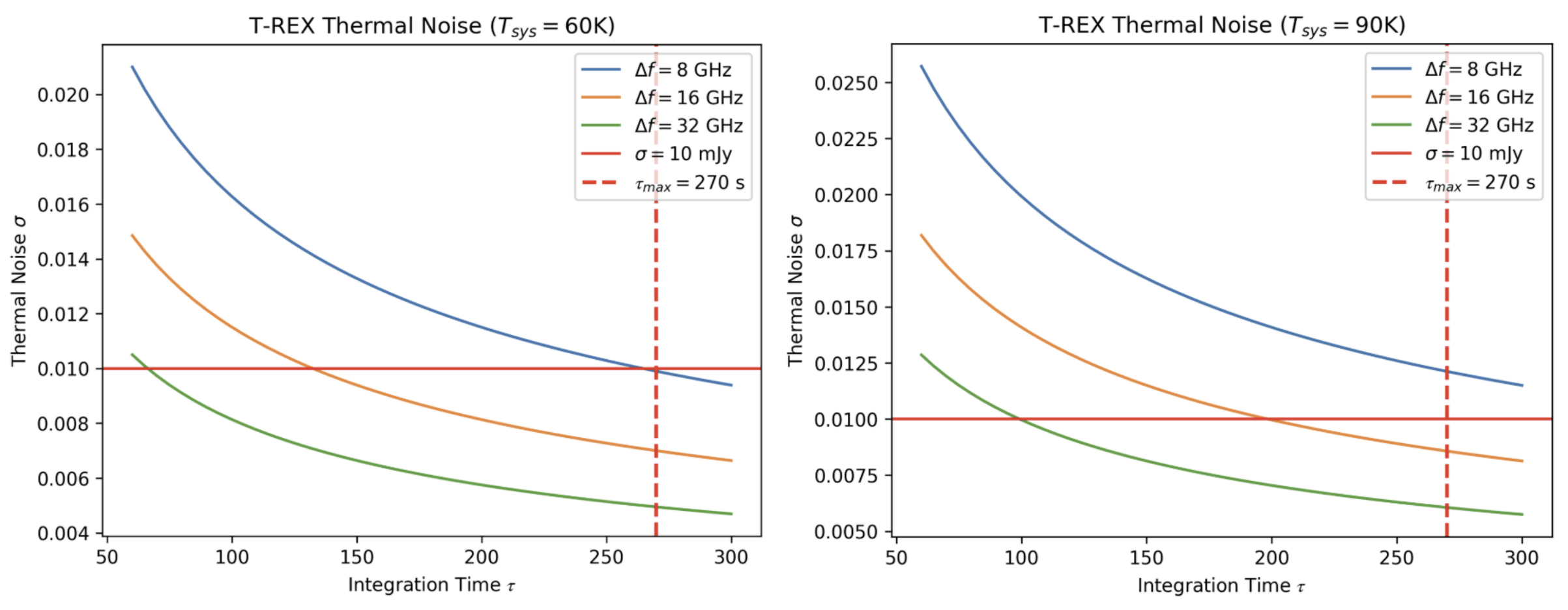


T-REX
















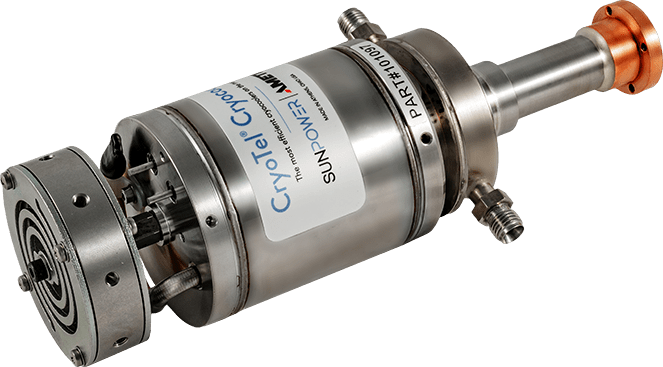
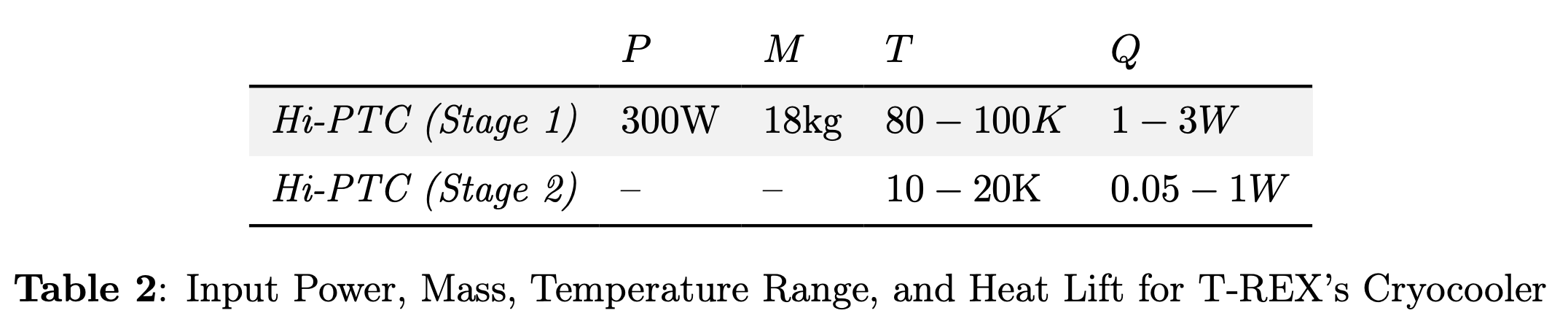
Cryocooler

HiPTC Heat Intercepted Pulse Tube Cooler
T-REX


T-REX










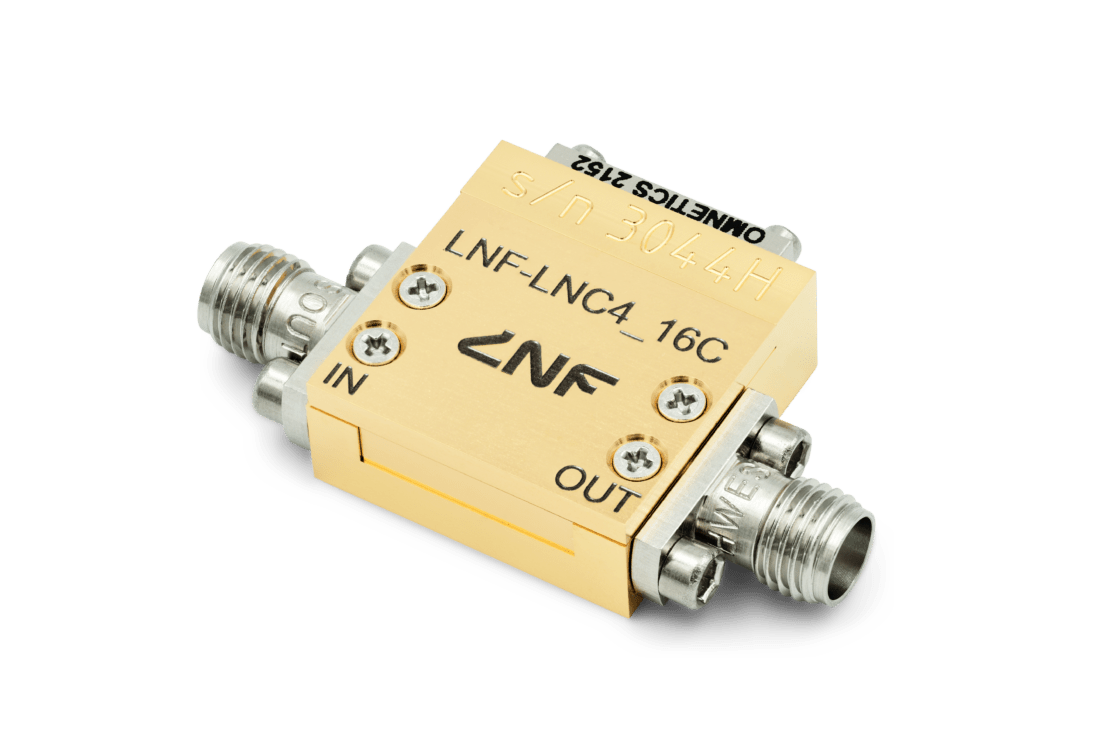
Ultra-Stable Oscillator
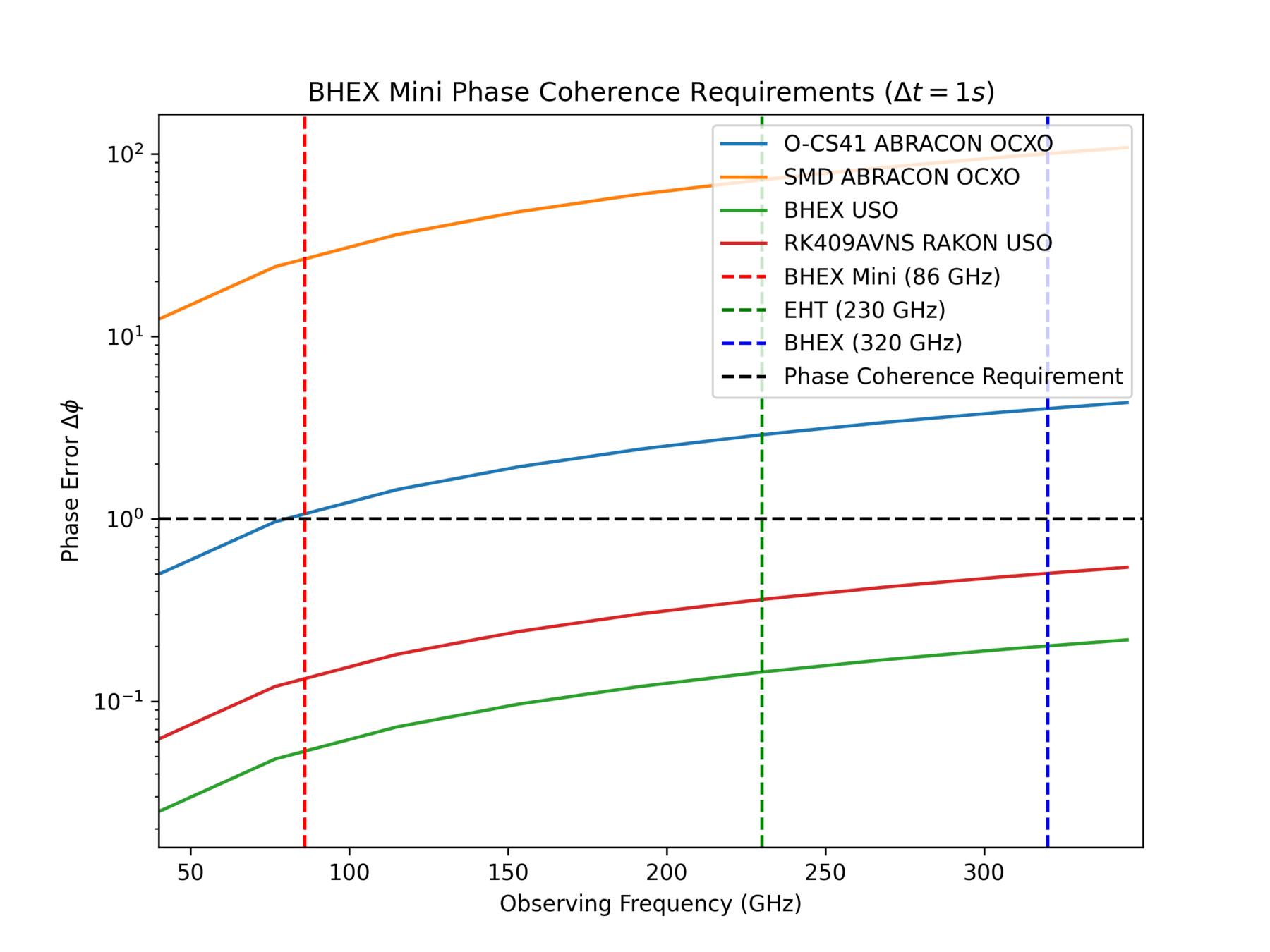
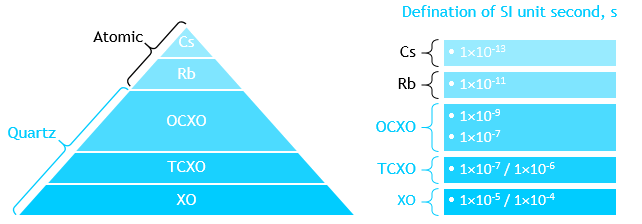
T-REX




Ultra-Stable Oscillator
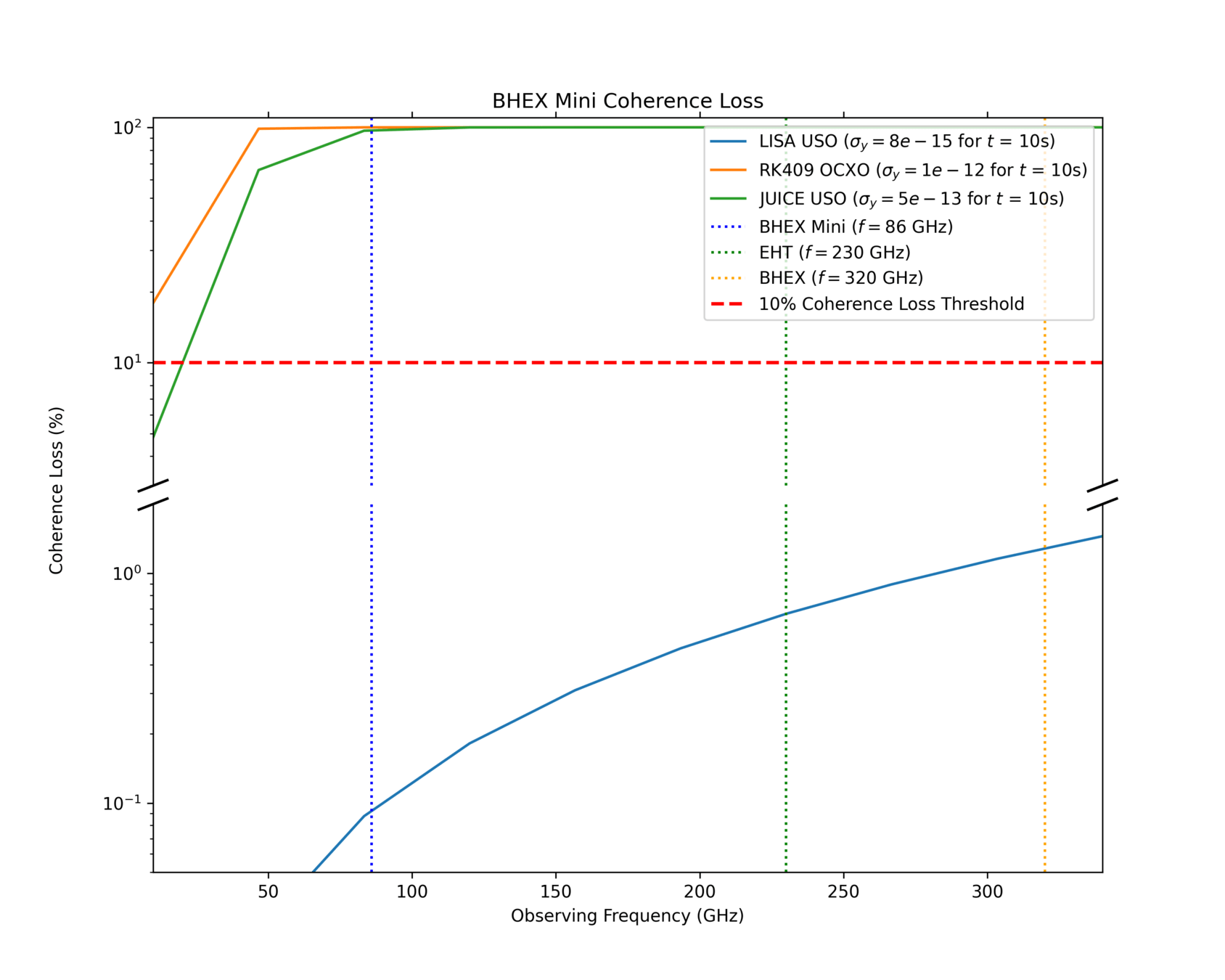
Phase Error
T-REX




Ultra-Stable Oscillator

T-REX




Ultra-Stable Oscillator
Allan Deviation
ABRACON SMD OCXO

T-REX










Digital Backend
T-REX




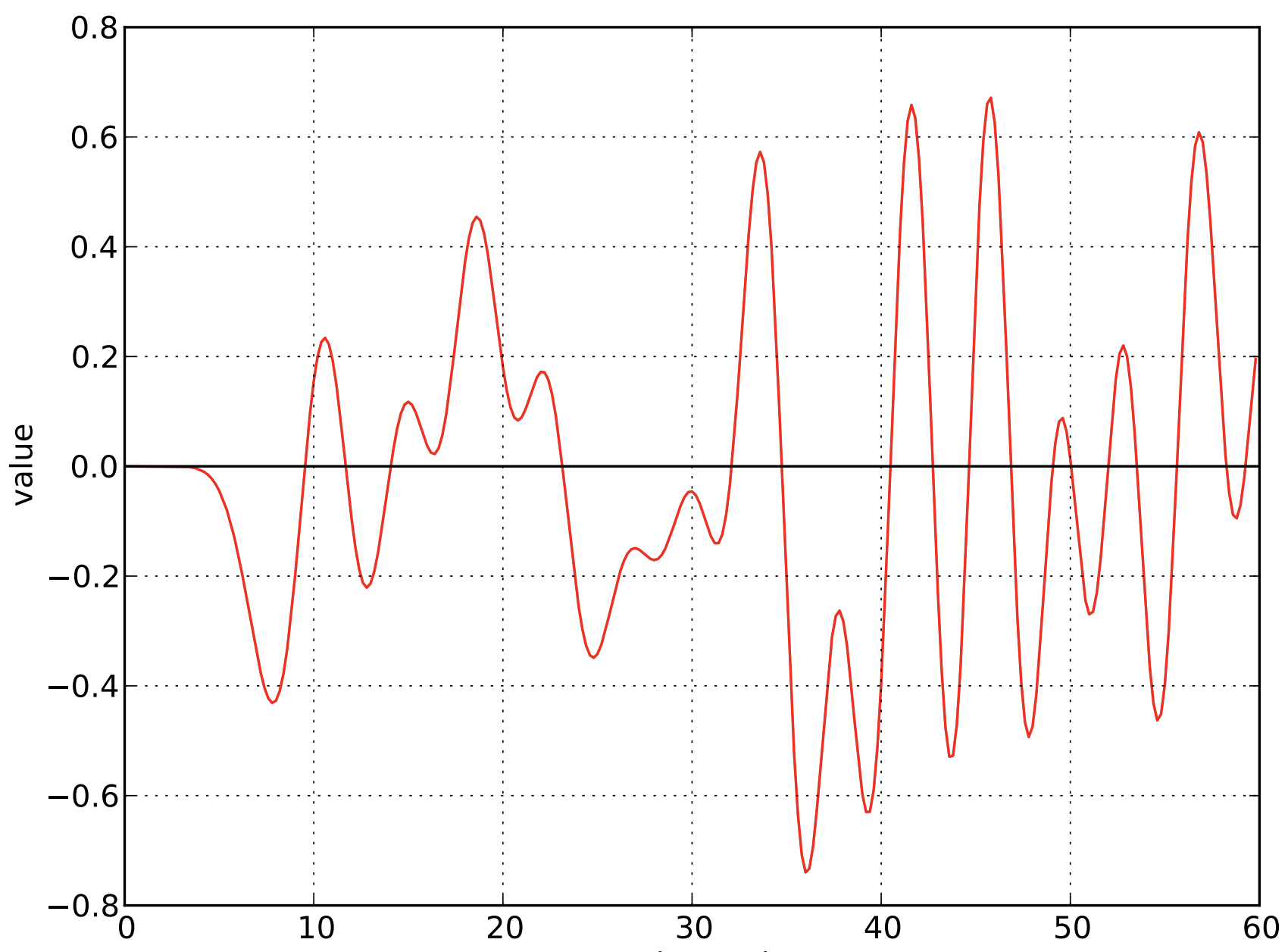
Original Analog Radio Signal
T-REX




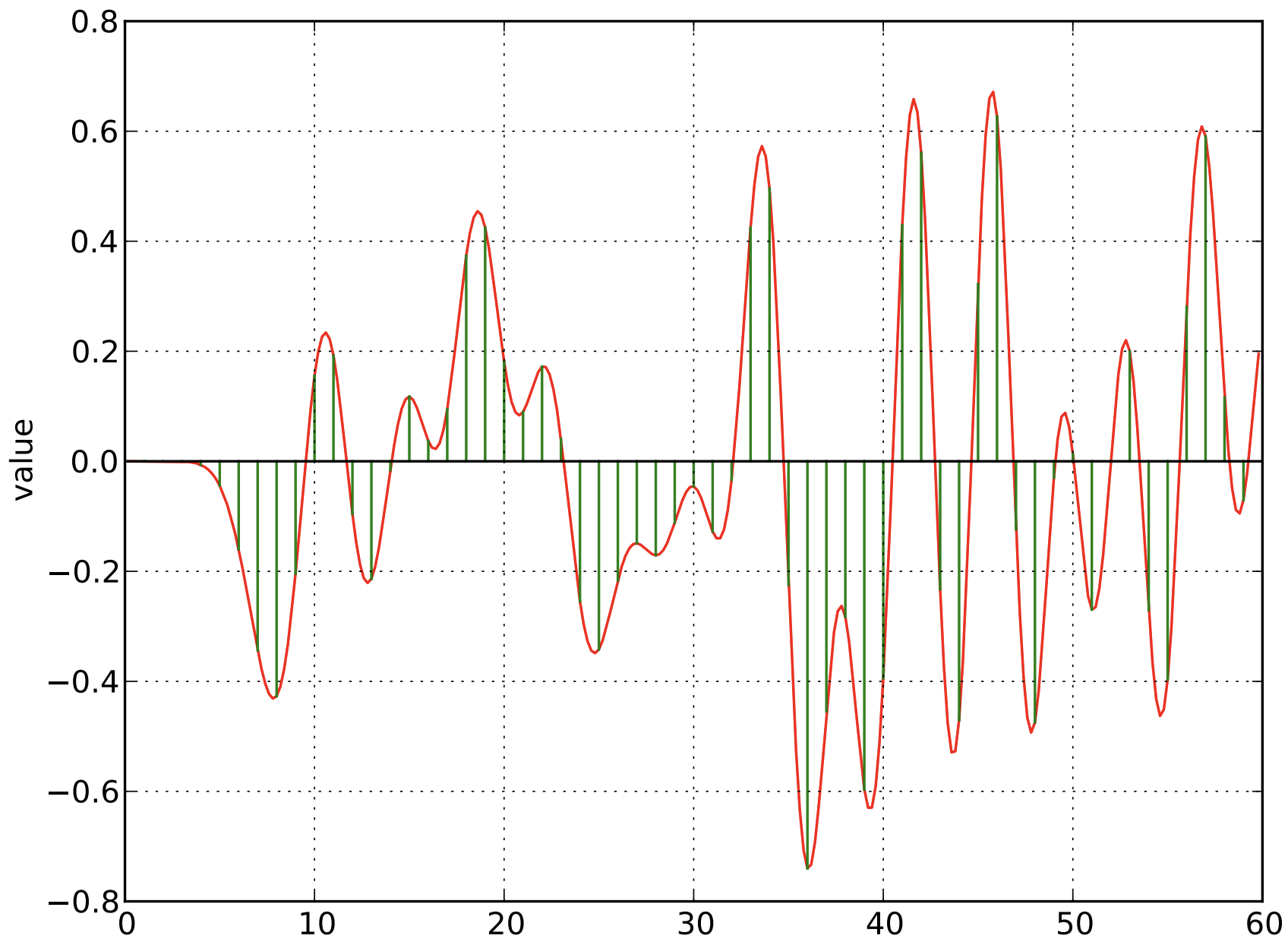
Sample the Signal every Unit Interval
Nyquist-Shannon Sampling Theorem
T-REX




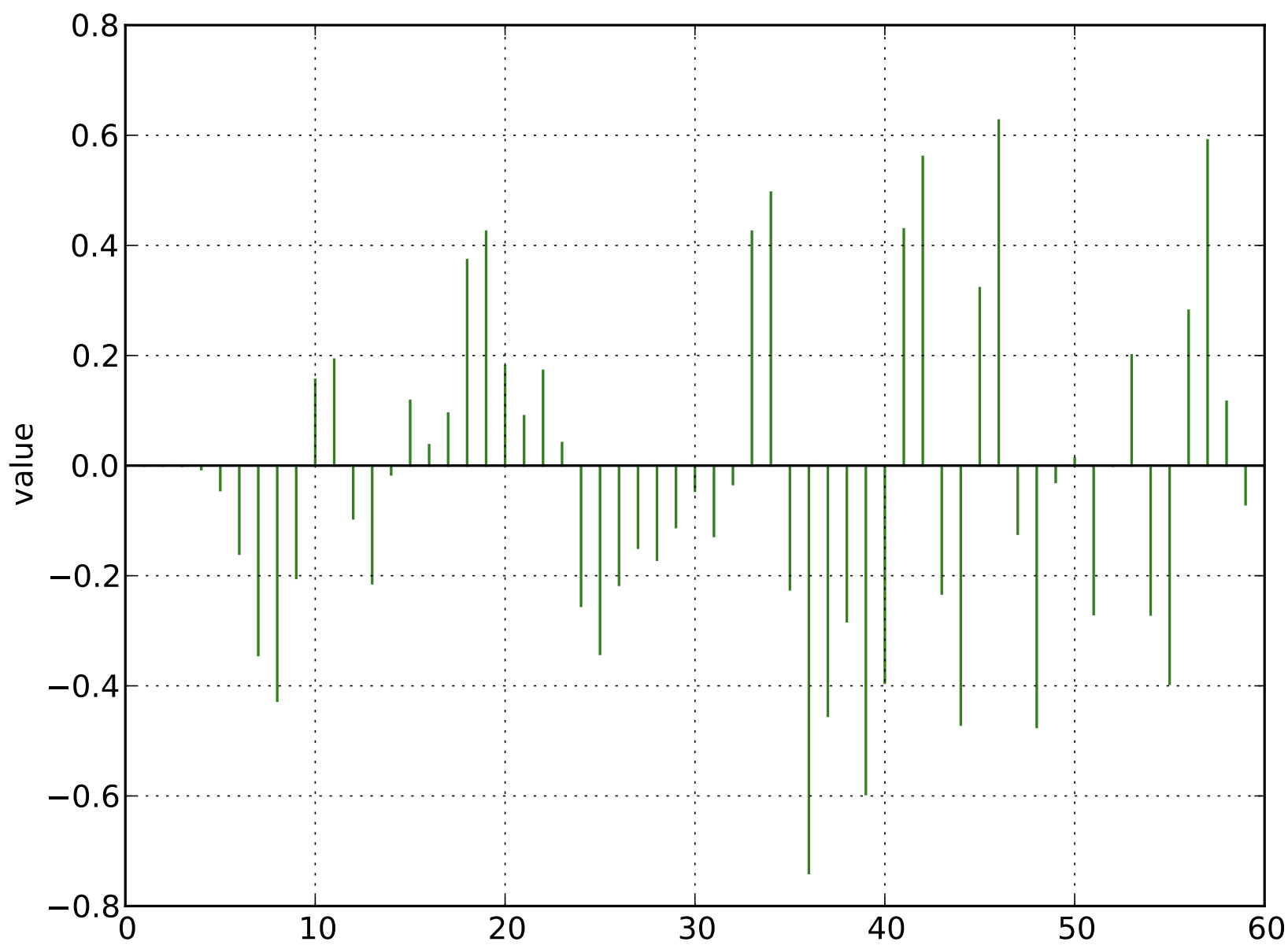
Retain only the samples and record the sign of the voltage for each sample
T-REX




Reconstruct the original signal
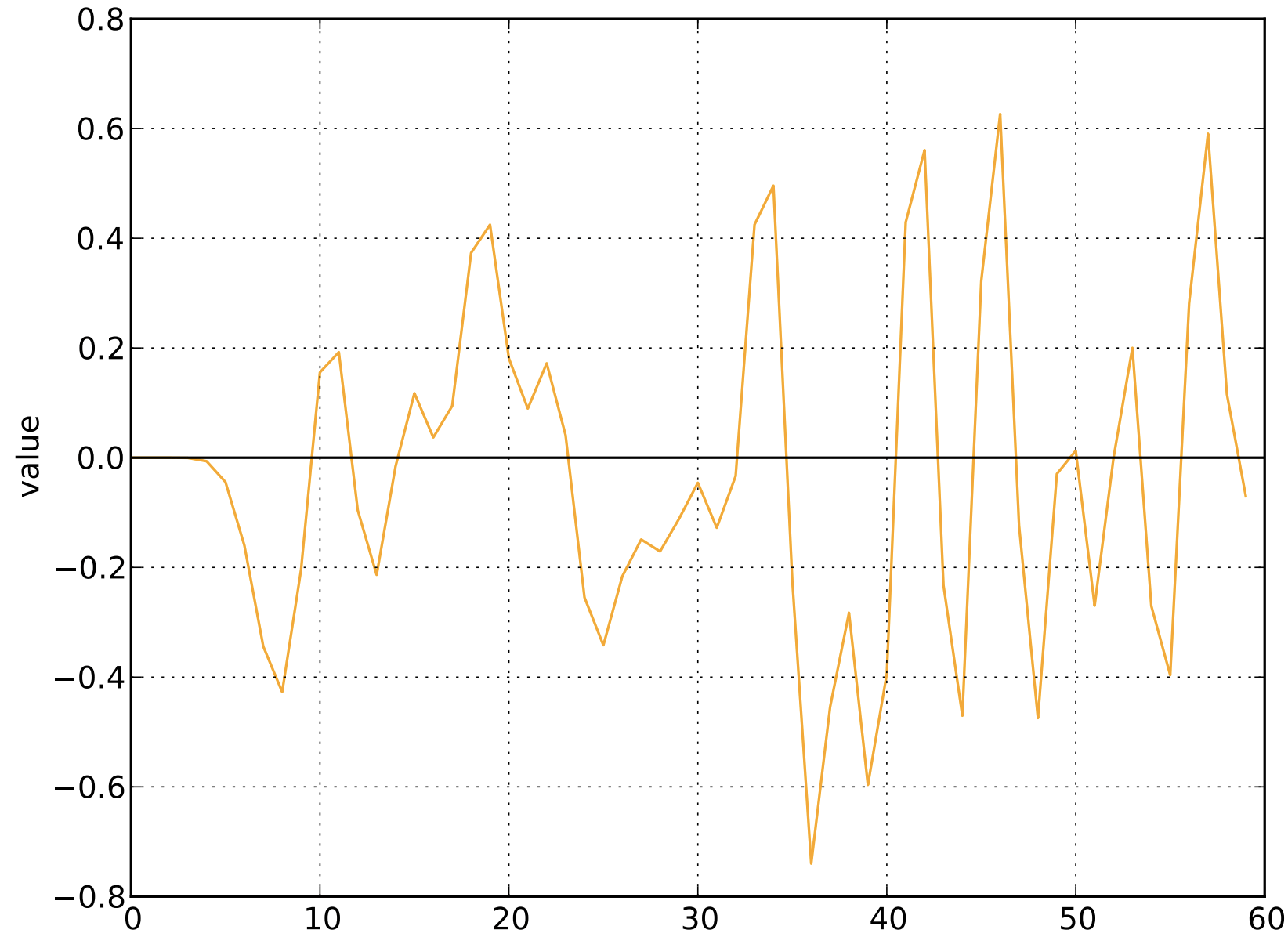
T-REX


T-REX








T-REX



- Introduction
- What is a black hole?
- How do you image a black hole?
- How do you record a black hole?
- T-REX Primary Science Objectives
- T-REX (u,v) Coverage
- T-REX Engineering Challenges
- T-REX SWaPC Requirements
- T-REX Concept of Operations
- T-REX Timeline & Funding Deadlines

T-REX


T-REX ConOps

Optical Terminals
RF Tracking Stations


VLBI Ground Stations






T-REX Data Center



T-REX ConOps

- Introduction
- What is a black hole?
- How do you image a black hole?
- How do you record a black hole?
- T-REX Primary Science Objectives
- T-REX (u,v) Coverage
- T-REX Engineering Challenges
- T-REX SWaPC Requirements
- T-REX Concept of Operations
- T-REX Timeline & Funding Deadlines

T-REX


- Email BHEX Team
Jan 2025
T-REX


- Email BHEX Team
Jan 2025
T-REX


- Email BHEX Team
Jan 2025


T-REX


- Email BHEX Team
Jan 2025
Feb 2025
- Literature Review


T-REX


- Email BHEX Team
Jan 2025
Feb 2025
Mar 2025
- Literature Review
- Advised on BHEX Mini by Prof. Rick Fleeter
- Submit to Rhode Island Space Grant


Rick Fleeter
T-REX


- Email BHEX Team
Jan 2025
Feb 2025
Mar 2025
- Literature Review
Apr 2025
- Ivy Space Conference
- Ben Hudson (BHEX, KISPE)
- Luke Anderson (Orion Space Systems)

Ben Hudson
Luke Anderson
- Advised on BHEX Mini by Prof. Rick Fleeter
- Submit to Rhode Island Space Grant
T-REX


- Email BHEX Team
Jan 2025
Feb 2025
Mar 2025
- Literature Review
Apr 2025
May 2025
- Ivy Space Conference
- Ben Hudson (BHEX, KISPE)
- Luke Anderson (Orion Space Systems)
- Trained ~6 undergraduates to run simulations on BHEX Mini
- Jeffrey Olson (Cryocooler Engineer, Lockheed Martin

Jeffrey Olson
- Advised on BHEX Mini by Prof. Rick Fleeter
- Submit to Rhode Island Space Grant
T-REX


Jun 2025
Jul 2025
- Completed Antenna SWaPC Requirements
- Obtained Preliminary Grant Funding from Nelson Center
- Began correspondence with NASA JPL on Ultrastable Oscillators
- Constrained BHEX Mini SWaPC Requirements
- Approved by Brown Division of Research as PI for BHEX Mini
- Submitted to NASA NIAC Phase I Solicitation
- Accepted to SmallSat Europe 2026






Todd Ely
Joseph Lazio
Eric Burt
- Email BHEX Team
Jan 2025
Feb 2025
Mar 2025
- Literature Review
Apr 2025
May 2025
Jun 2025
Jul 2025
- Ivy Space Conference
- Ben Hudson (BHEX, KISPE)
- Luke Anderson (Orion Space Systems)
- Trained ~6 undergraduates to run simulations on BHEX Mini
- Jeffrey Olson (Cryocooler Engineer, Lockheed Martin)
- Rejected from RISG
- Completed Antenna SWaPC Requirements
- Obtained Preliminary Grant Funding from Nelson Center
- Began correspondence with NASA JPL on Space-Space VLBI
- Constrained BHEX Mini SWaPC Requirements
- Approved by Brown Division of Research as PI for BHEX Mini
- Submitted to NASA NIAC Phase I Solicitation
- Accepted to SmallSat Europe 2026

- Advised on BHEX Mini by Prof. Rick Fleeter
- Submit to Rhode Island Space Grant
Feb 2025
Mar 2025
- Literature Review
Apr 2025
May 2025
Jun 2025
Jul 2025
- Ivy Space Conference
- Ben Hudson (BHEX, KISPE)
- Luke Anderson (Orion Space Systems)
- Trained ~6 undergraduates to run simulations on BHEX Mini
- Jeffrey Olson (Cryocooler Engineer, Lockheed Martin)
- Rejected from RISG
- Completed Antenna SWaPC Requirements
- Obtained Preliminary Grant Funding from Nelson Center
- Began correspondence with NASA JPL on Space-Space VLBI
- Rejected from International Astronautical Congress
- Constrained BHEX Mini SWaPC Requirements
- Approved by Brown Division of Research as PI for BHEX Mini
- Submitted to NASA NIAC Phase I Solicitation
- Accepted to SmallSat Europe 2026
- Advised on BHEX Mini by Prof. Rick Fleeter
- Submit to Rhode Island Space Grant
- Meeting with MIT Lincoln Labs (8/15)
- Colloquium at Princeton IAS (9/04)
- Michael Johnson Colloquium at Brown (PI, BHEX) (9/22)
- Assemble Science/Engineering Leadership Team for NASA / CSA
Aug 2025
Sep 2025
- Accepted as NASA NIAC Finalist
- Accepted to 10th International VLBI Conference (Sweden)
- Accepted to Gravitational Wave Conference (Georgia Tech)



💰Funding Deadlines

June
💰Funding Deadlines
$5,000

-
Brown Nelson Grants
- Submitted: June 30
- Decision: Sep 15

July
💰Funding Deadlines
$5,000


$175,000
-
Brown Nelson Grants
- Submitted: June 30
- Decision: Sep 15
-
NASA NIAC Phase I
- Submitted: July 15
- Decision: Sep 6

Aug
💰Funding Deadlines
$5,000


$175,000
>$4M

-
Brown Nelson Grants
- Submitted: June 30
- Decision: Sep 15
-
NASA NIAC Phase I
- Submitted: July 15
- Decision: Sep 6
-
Templeton Grant
- Submitted: Aug 15
- Decision: Oct 10

Sep
💰Funding Deadlines
$5,000


$175,000
>$4M


-
Brown Nelson Grants
- Submitted: June 30
- Decision: Sep 15
-
NASA NIAC Phase I
- Submitted: July 15
- Decision: Sep 6
-
Templeton Grant
- Submitted: Aug 15
- Decision: Oct 10
-
AAS Splinter Meeting
- Submitted: Sep 25
- Decision: Oct 30

Oct
💰Funding Deadlines
$5,000


-
NASA NIAC Phase I
- Submitted: July 15
- Decision: Sep 6
$175,000
-
Brown Nelson Grants
- Submitted: June 30
- Decision: Sep 15
>$4M

-
Templeton Grant
- Submitted: Aug 15
- Decision: Oct 10

-
AAS Abstracts
- Submitted: Sep 25
- Decision: Oct 30

-
CSA FAST Grant
- Submitted: Oct 26
- Decision: Dec 15
>$400,000

- Introduction
- What is a black hole?
- How do you image a black hole?
- How do you record a black hole?
- T-REX Primary Science Objectives
- T-REX (u,v) Coverage
- T-REX Engineering Challenges
- T-REX SWaPC Requirements
- T-REX Concept of Operations
- The Request


T-REX
