Binary Black Holes
A GENERIC Approach
Ref Bari
Advisor: Prof. Brendan Keith

Approach
Approach
Approach
Approach
Approach
✅ Unaligned Spins
✅ Inclined
✅ Dissipation
Keplerian Approximation
Simple!
Circular Orbits
Weak Field Limit

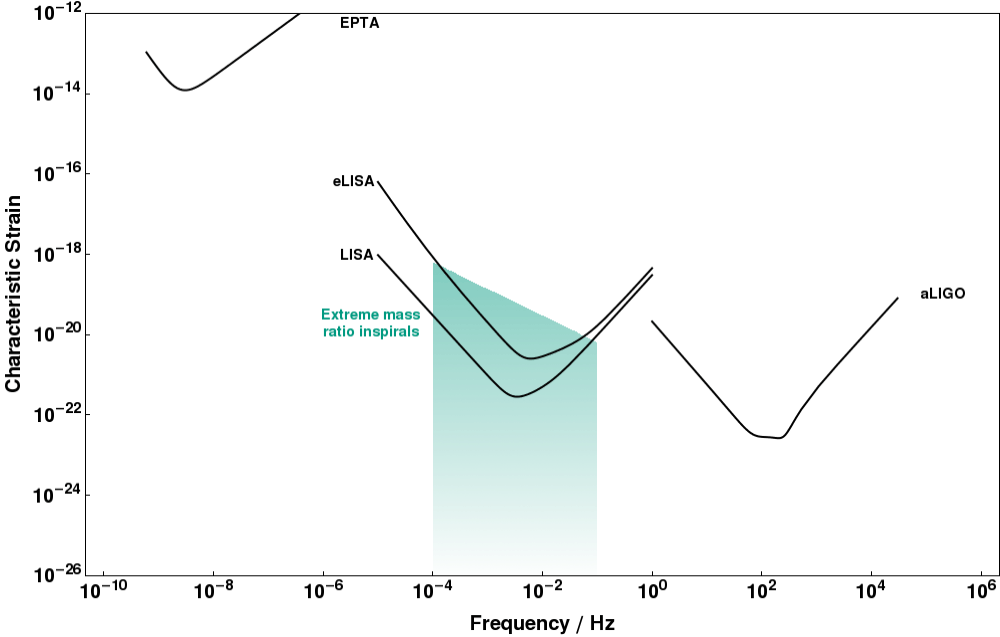
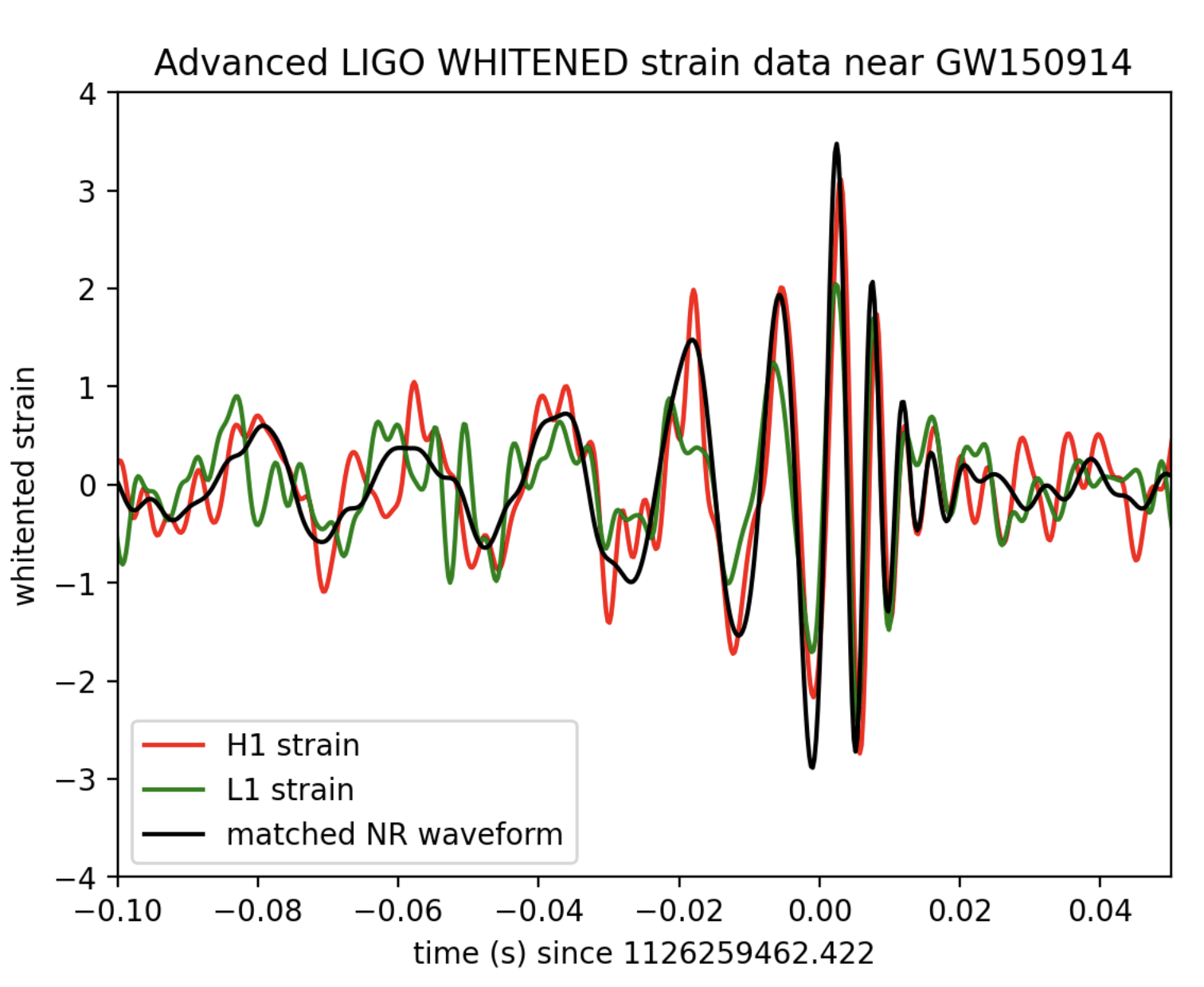
The basic physics of the binary black hole merger GW150914
Keplerian Approximation
No Precession
Only Circular Orbits
Weak Field Limit

The basic physics of the binary black hole merger GW150914 (LIGO & VIRGO Collaborations, 2016)
Limiting Case
Keplerian Approximation
Simple!
Circular Orbits
Weak Field Limit
Peters (1964)
Quadrupole Model
More Complex
Eccentric Orbits
Weak Field Limit

The basic physics of the binary black hole merger GW150914
Gravitational Radiation and the Motion of Two Point Masses

Any Mass Ratio!
Keplerian Approximation
Simple!
Circular Orbits
Weak Field Limit
Peters (1964)
Quadrupole Model
More Complex
Eccentric Orbits
Weak Field Limit

The basic physics of the binary black hole merger GW150914
Gravitational Radiation and the Motion of Two Point Masses (Peters, 1964)

Any Mass Ratio!
Keplerian Approximation
Simple!
Circular Orbits
Weak Field Limit
Peters (1964)
Quadrupole Model

The basic physics of the binary black hole merger GW150914
Gravitational Radiation and the Motion of Two Point Masses (Peters, 1964)

Keplerian Approximation
Peters (1964)
Quadrupole Model
Cutler & Poisson (1994)
Dissipation Model
Simple!
More Complex
Eccentric Orbits
Weak Field Limit
Circular Orbits
Weak Field Limit
Complicated!
Any eccentricity!
Any distance!

The basic physics of the binary black hole merger GW150914
Gravitational Radiation and the Motion of Two Point Masses


Gravitational radiation reaction for bound motion around a Schwarzschild black hole
Any Mass Ratio!
Only EMRIs
Keplerian Approximation
Peters (1964)
Quadrupole Model
Cutler & Poisson (1994)
Dissipation Model
Simple!
More Complex
Eccentric Orbits
Weak Field Limit
Circular Orbits
Weak Field Limit
Complicated!
Any eccentricity!
Any distance!

The basic physics of the binary black hole merger GW150914
Gravitational Radiation and the Motion of Two Point Masses


Gravitational radiation reaction for bound motion around a Schwarzschild black hole (Cutler et. al., 1994)
Simple!
Circular Orbits
Weak Field Limit
Only EMRIs
Keplerian Approximation
Peters (1964)
Quadrupole Model
Cutler & Poisson (1994)
Dissipation Model
Simple!
More Complex
Eccentric Orbits
Weak Field Limit
Circular Orbits
Weak Field Limit
Complicated!
Any eccentricity!
Any distance!

The basic physics of the binary black hole merger GW150914
Gravitational Radiation and the Motion of Two Point Masses


Gravitational radiation reaction for bound motion around a Schwarzschild black hole (Cutler et. al., 1994)
Simple!
Circular Orbits
Weak Field Limit
Only EMRIs
Keplerian Approximation
Peters (1964)
Quadrupole Model
Cutler & Poisson (1994)
Dissipation Model

The basic physics of the binary black hole merger GW150914
Gravitational Radiation and the Motion of Two Point Masses


Gravitational radiation reaction for bound motion around a Schwarzschild black hole (Cutler et. al., 1994)
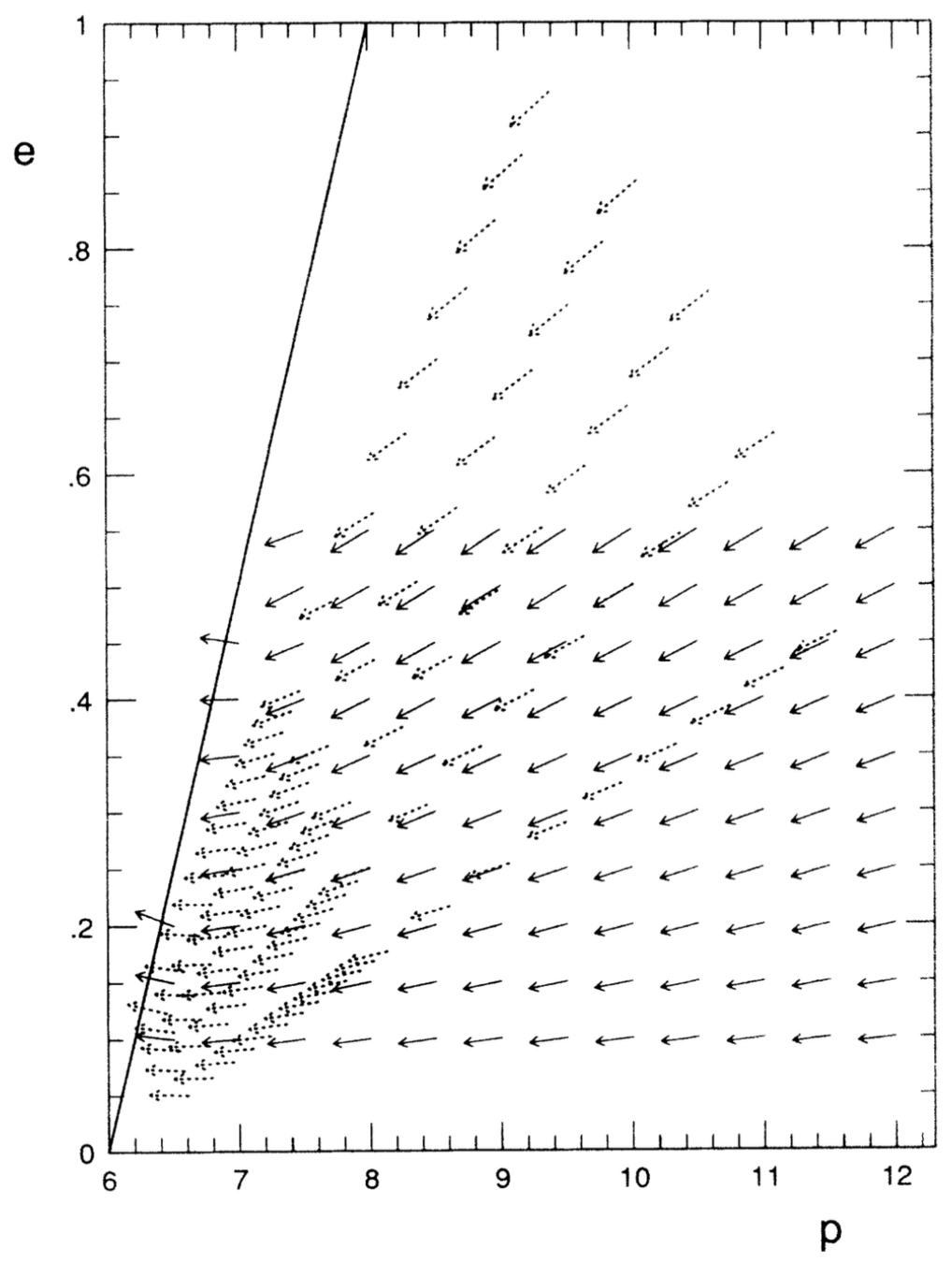
Keplerian Approximation
Peters (1964)
Quadrupole Model
Cutler & Poisson (1994)
Dissipation Model

The basic physics of the binary black hole merger GW150914
Gravitational Radiation and the Motion of Two Point Masses


Simple!
More Complex
Eccentric Orbits
Circular Orbits
Weak Field Limit
Simple!
Circular Orbits
Weak Field Limit


More Complex
Eccentric Orbits
Weak Field Limit


More Complex
Eccentric Orbits
Weak Field Limit

Condition for Bound Orbits

Condition for Bound Orbits
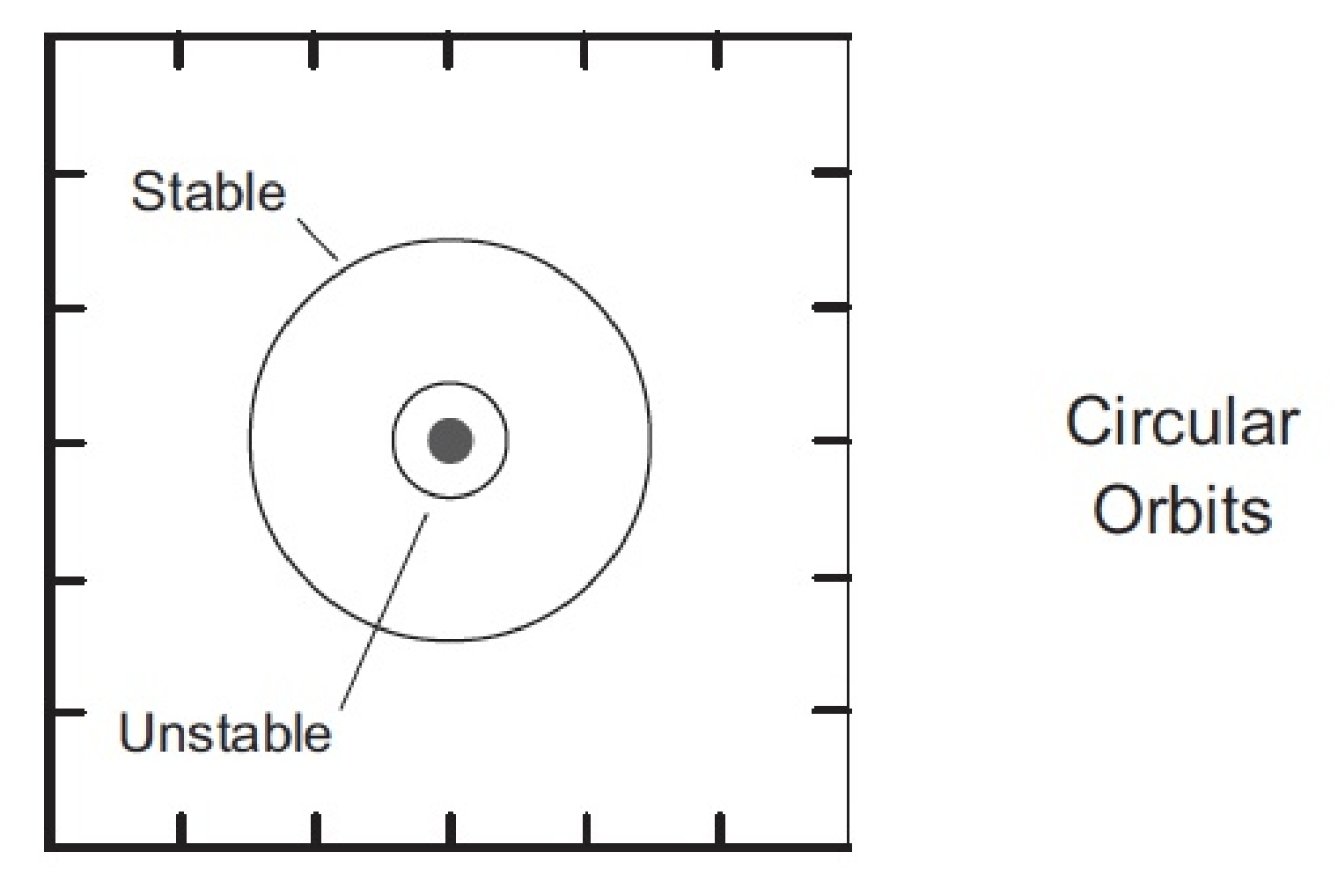
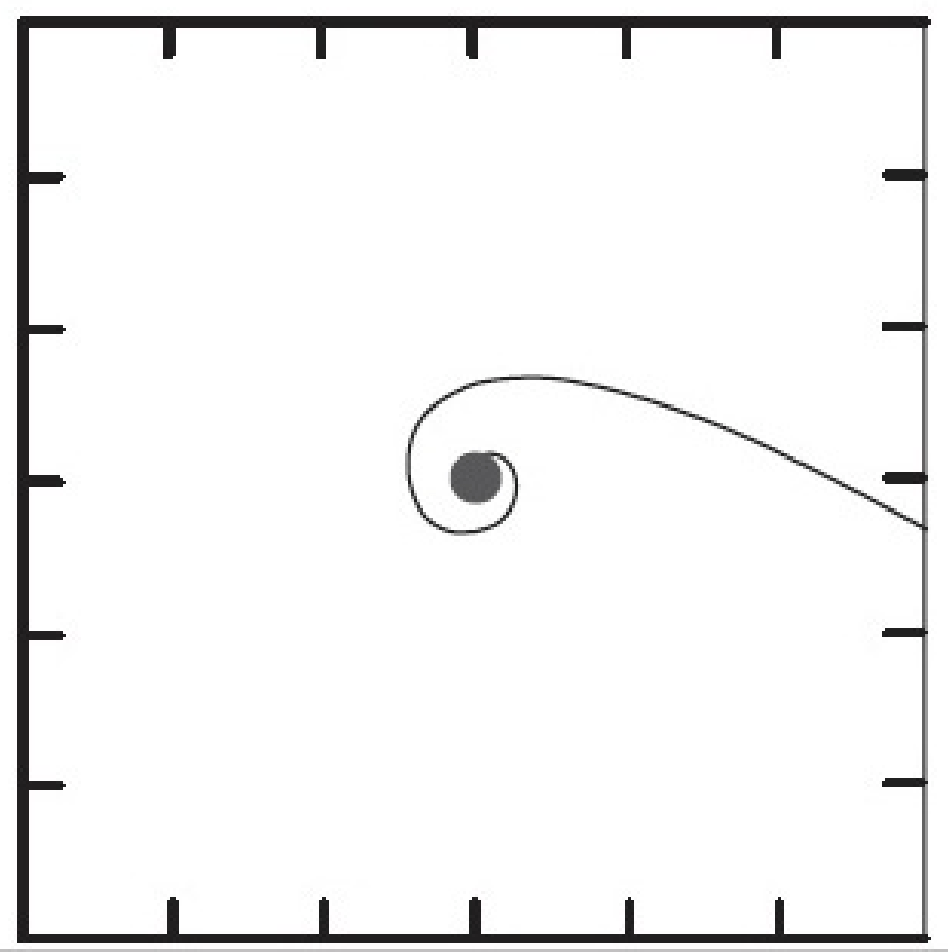

Stable Circular Orbits
Unstable Circular Orbits
Eccentric Orbits
Stable Circular Orbits
Unstable Circular Orbits
Eccentric Orbits


Stable Circular Orbits
Unstable Circular Orbits
Eccentric Orbits

Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
-
Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

Mission Statement

Mission Statement

Mission Statement

Mission Statement



Mission Statement



Mission Statement

Mission Statement

Mission Statement


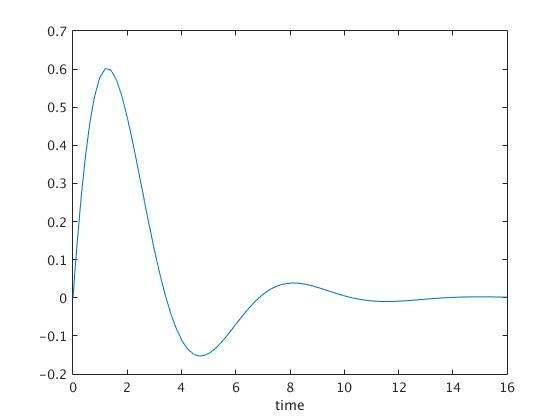
Mission Statement



Mission Statement



Mission Statement


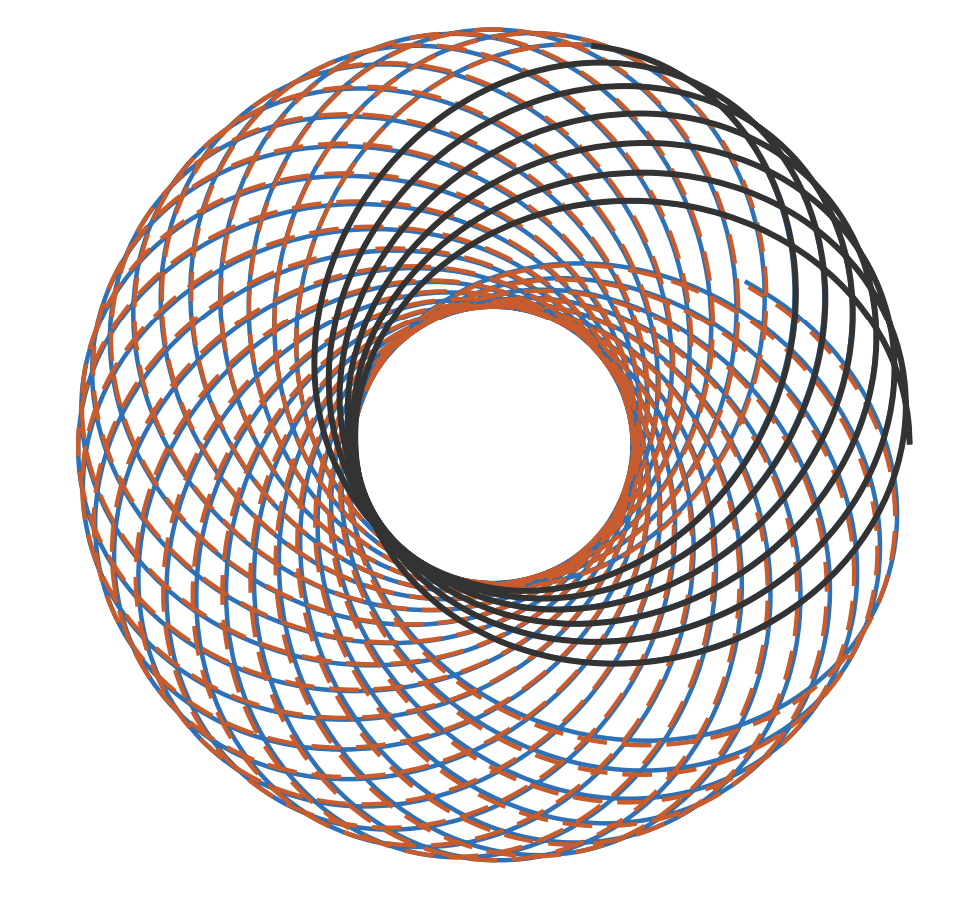
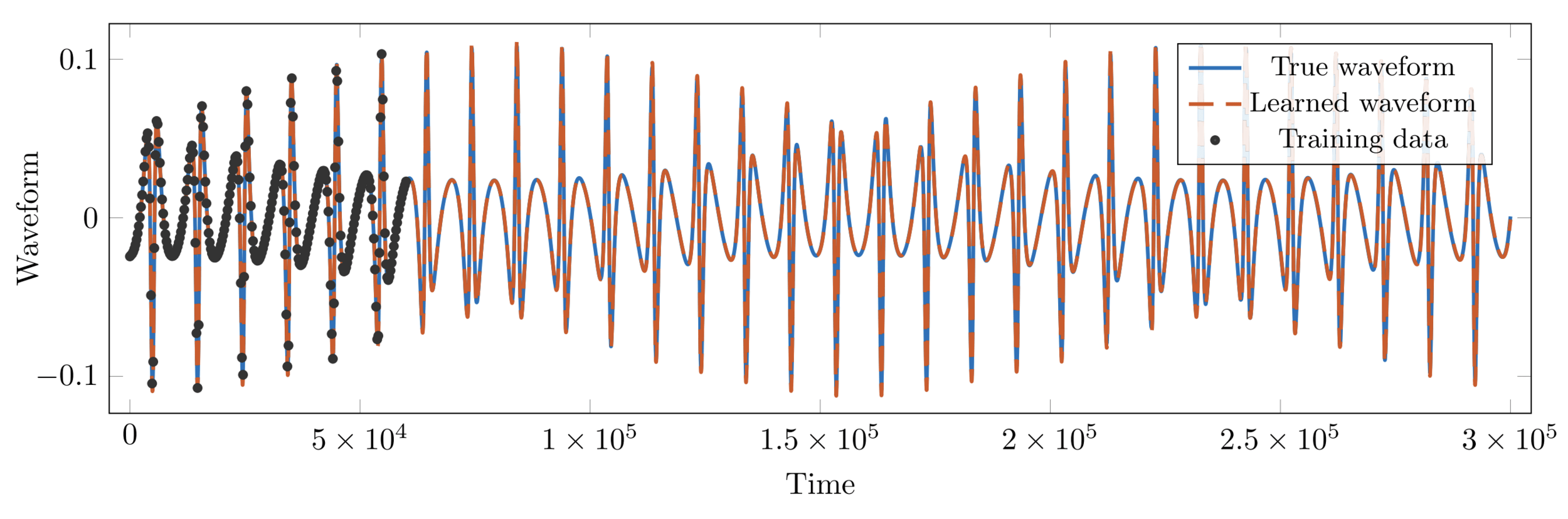
Mission Statement




Mission Statement




Mission Statement


Mission Statement

Mission Statement

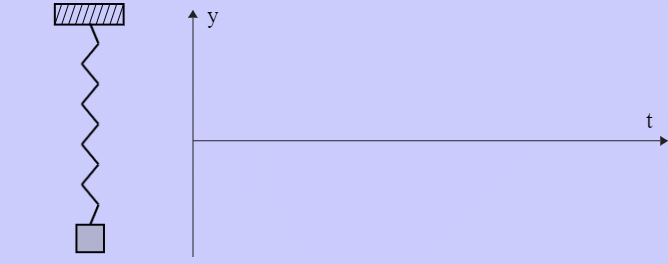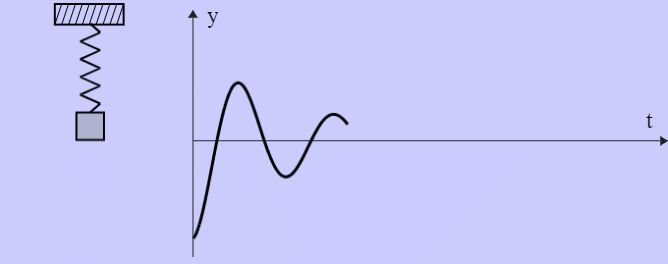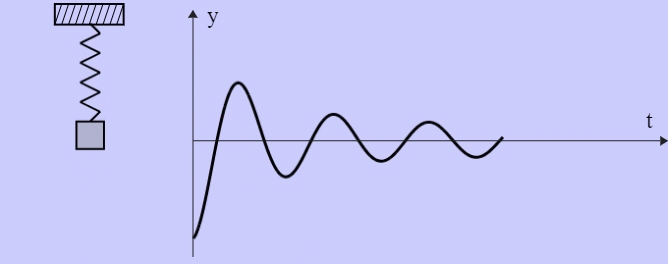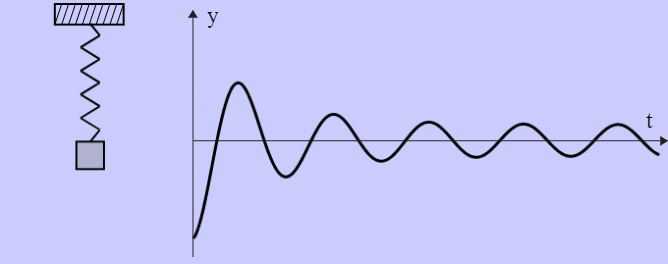
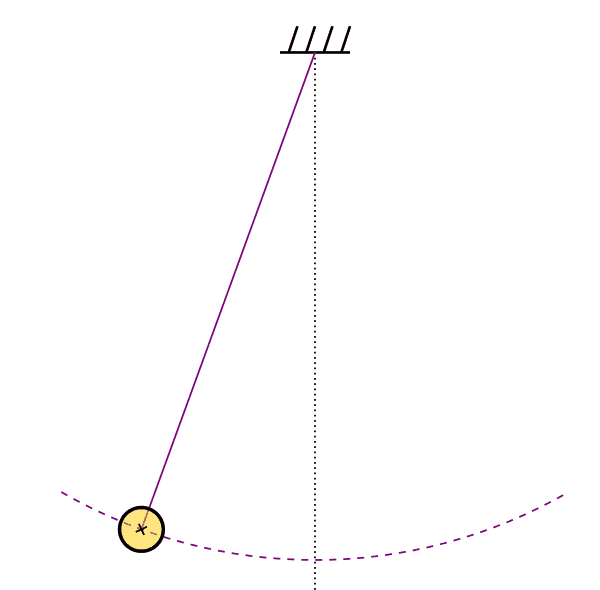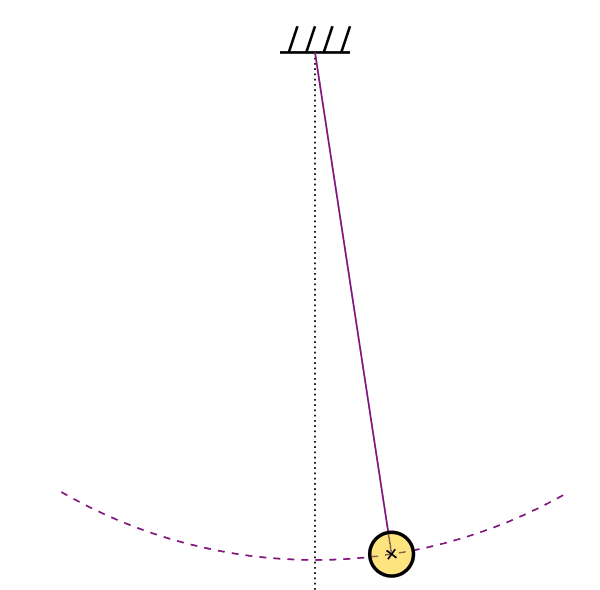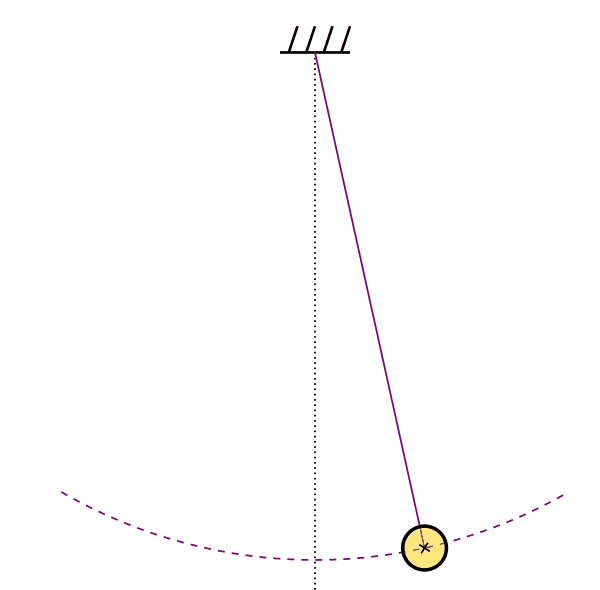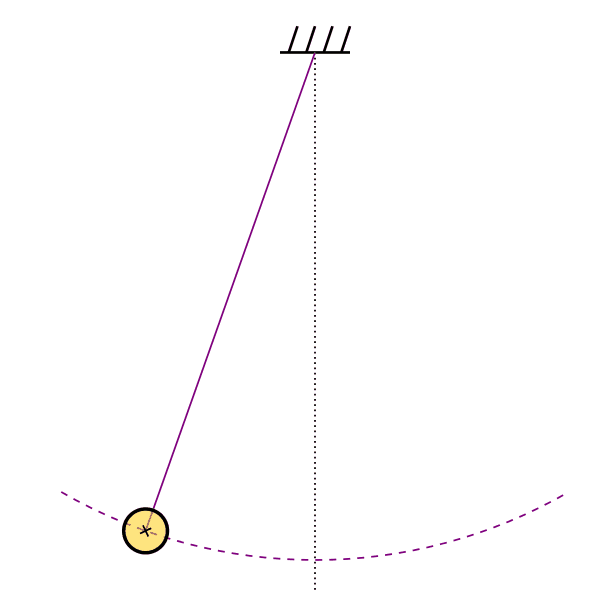
Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
-
Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
-
Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

Introduction to GENERIC

G
E
N
E
R
I
C
Introduction to GENERIC

G
E
N
E
R
I
C
eneral
quation for
on
quilibrium
eversible
rreversible
oupling


Introduction to GENERIC

Introduction to GENERIC

"reversible"
"irreversible"
Introduction to GENERIC

"reversible"
"irreversible"
Introduction to GENERIC

"reversible"
"irreversible"
Introduction to GENERIC

Equilibrium
Inequilibrium
Introduction to GENERIC

Equilibrium
Inequilibrium
Introduction to GENERIC

Equilibrium
Inequilibrium
Conservative Dynamics
Introduction to GENERIC

Equilibrium
Inequilibrium
Dissipative Dynamics
Introduction to GENERIC

Equilibrium
Inequilibrium
Introduction to GENERIC

Equilibrium
Inequilibrium
Introduction to GENERIC

Equilibrium
Inequilibrium
Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
-
Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
- Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

Examples of GENERIC




Examples of GENERIC


State Variables
State Variables
Examples of GENERIC


State Variables
Energy
Energy
Examples of GENERIC


State Variables
Energy
Energy
Entropy
Energy
Energy
Entropy
Examples of GENERIC


State Variables
Energy
Energy
Entropy
Entropy
Examples of GENERIC


Examples of GENERIC


Examples of GENERIC


Examples of GENERIC


Examples of GENERIC


Examples of GENERIC


Examples of GENERIC




Examples of GENERIC




Examples of GENERIC




Examples of GENERIC







Examples of GENERIC




Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
- Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
-
Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)

GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)

GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)

GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)

GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)

GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)


GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)



GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)



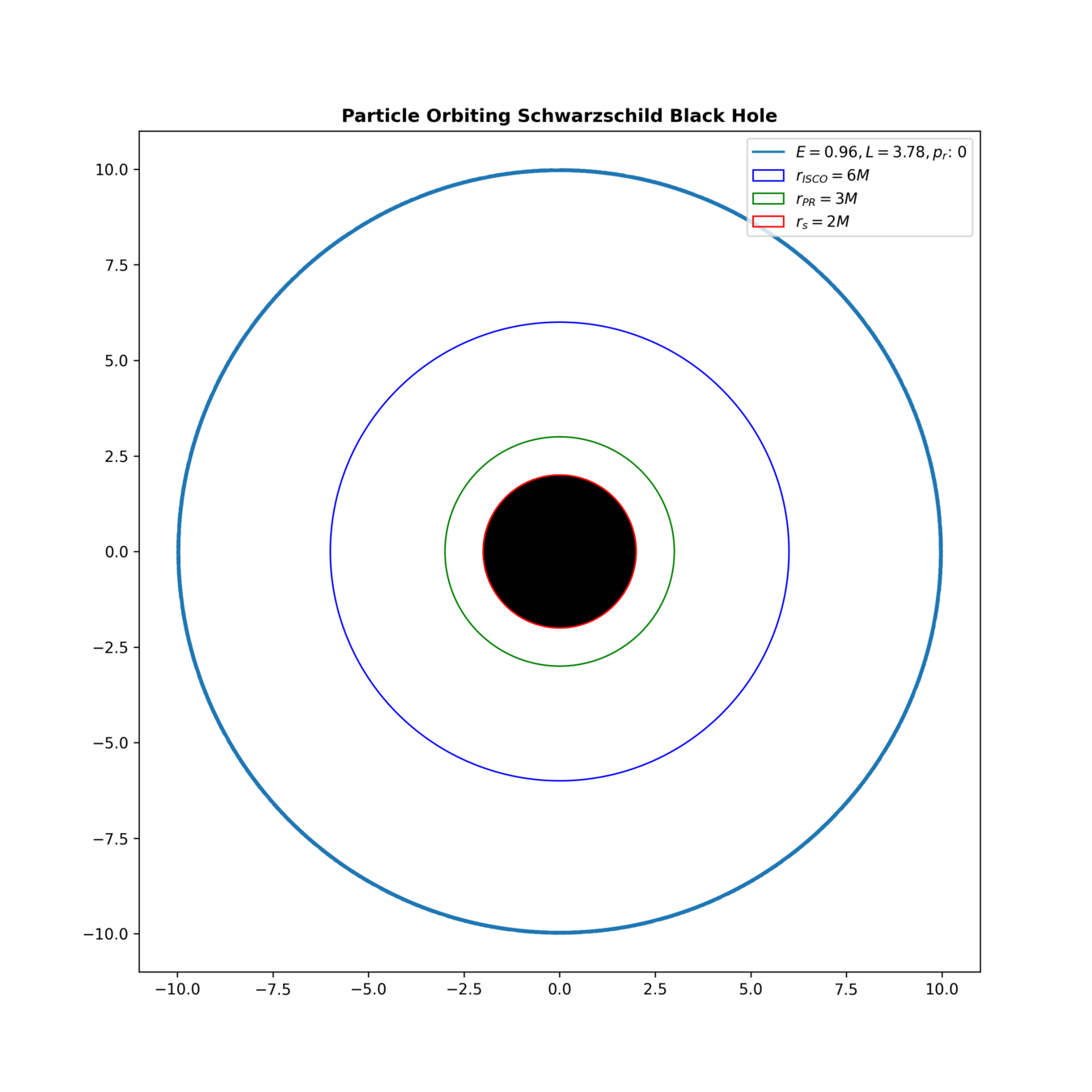
GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)




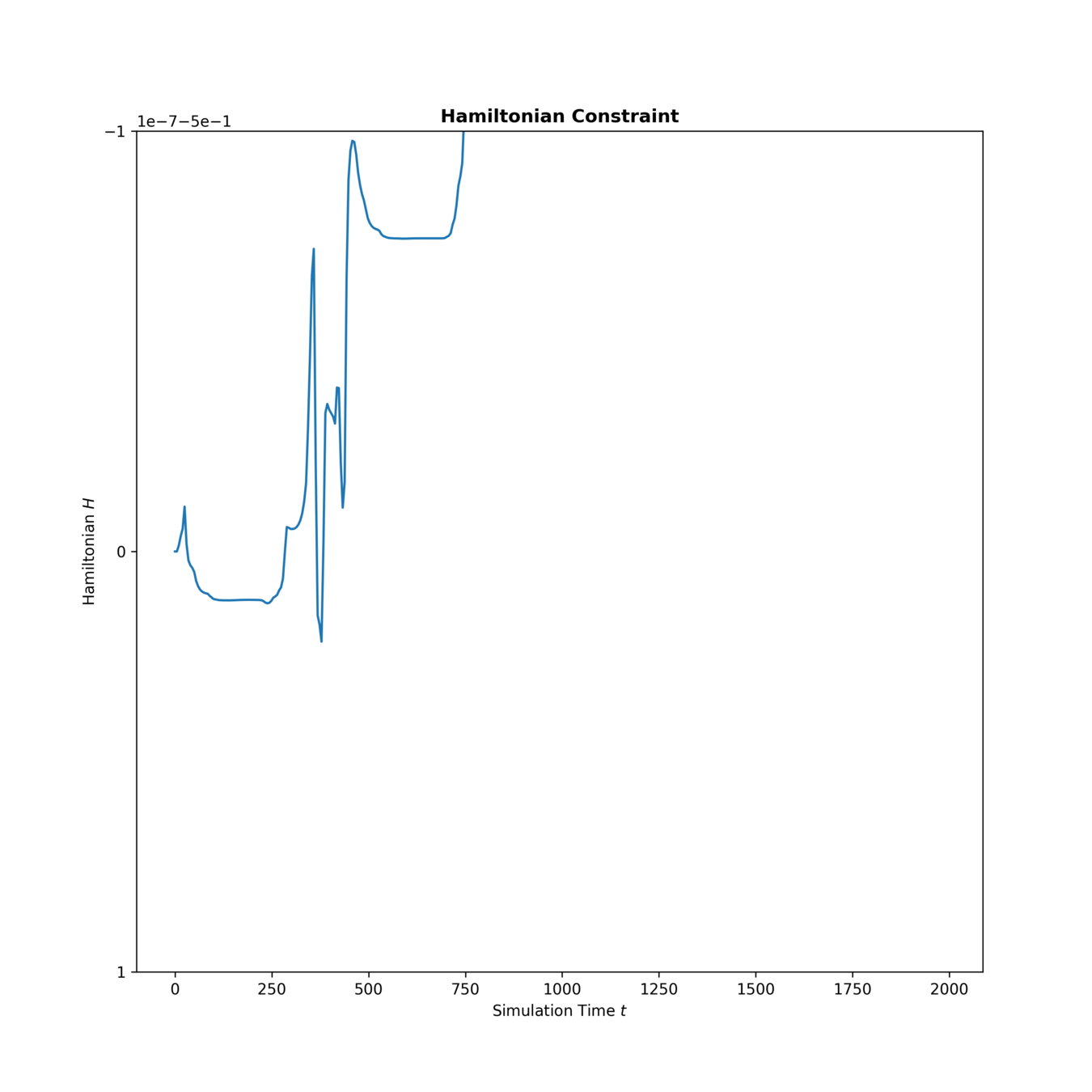
GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)





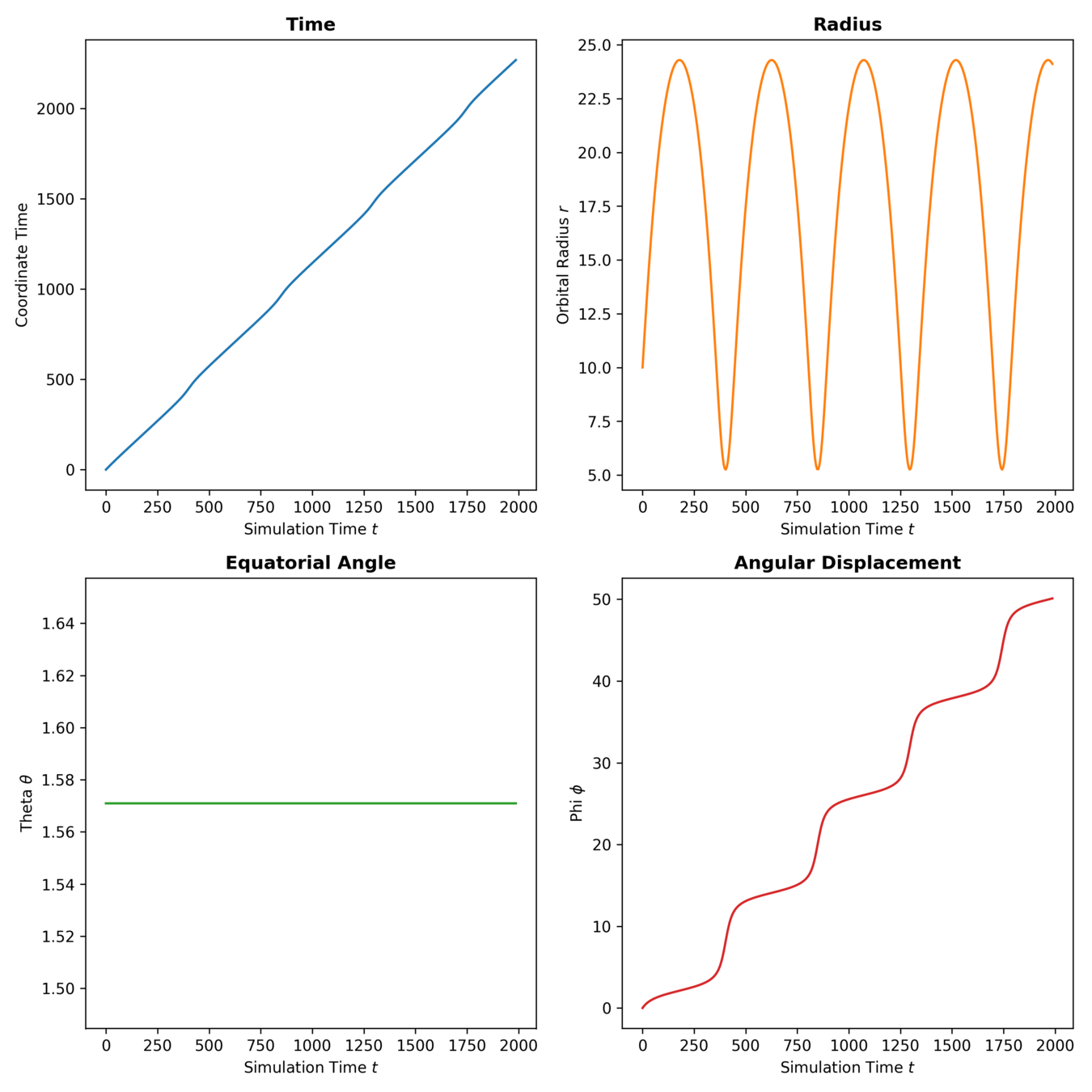
GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)





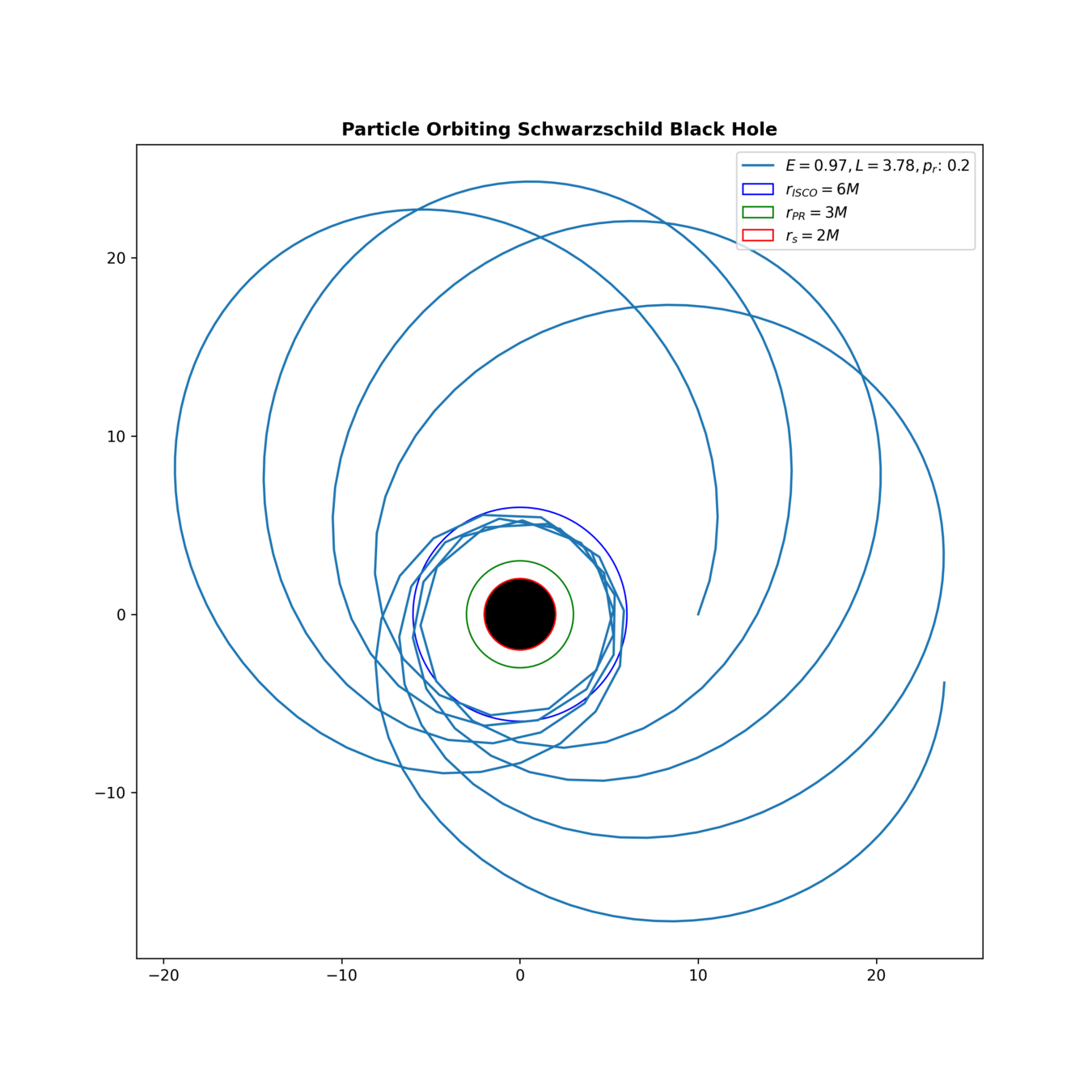

GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)







GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)







Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
-
Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

Binary Black Holes
- Neural ODE DynAMO Proposal Goal
- Introduction to GENERIC Formalism
-
Examples of GENERIC
- Damped Harmonic Oscillator
- Thermolastic Double Pendulum
- Two Boxes Exchanging Energy
- GENERIC for Black Holes (No Dissipation)
- GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

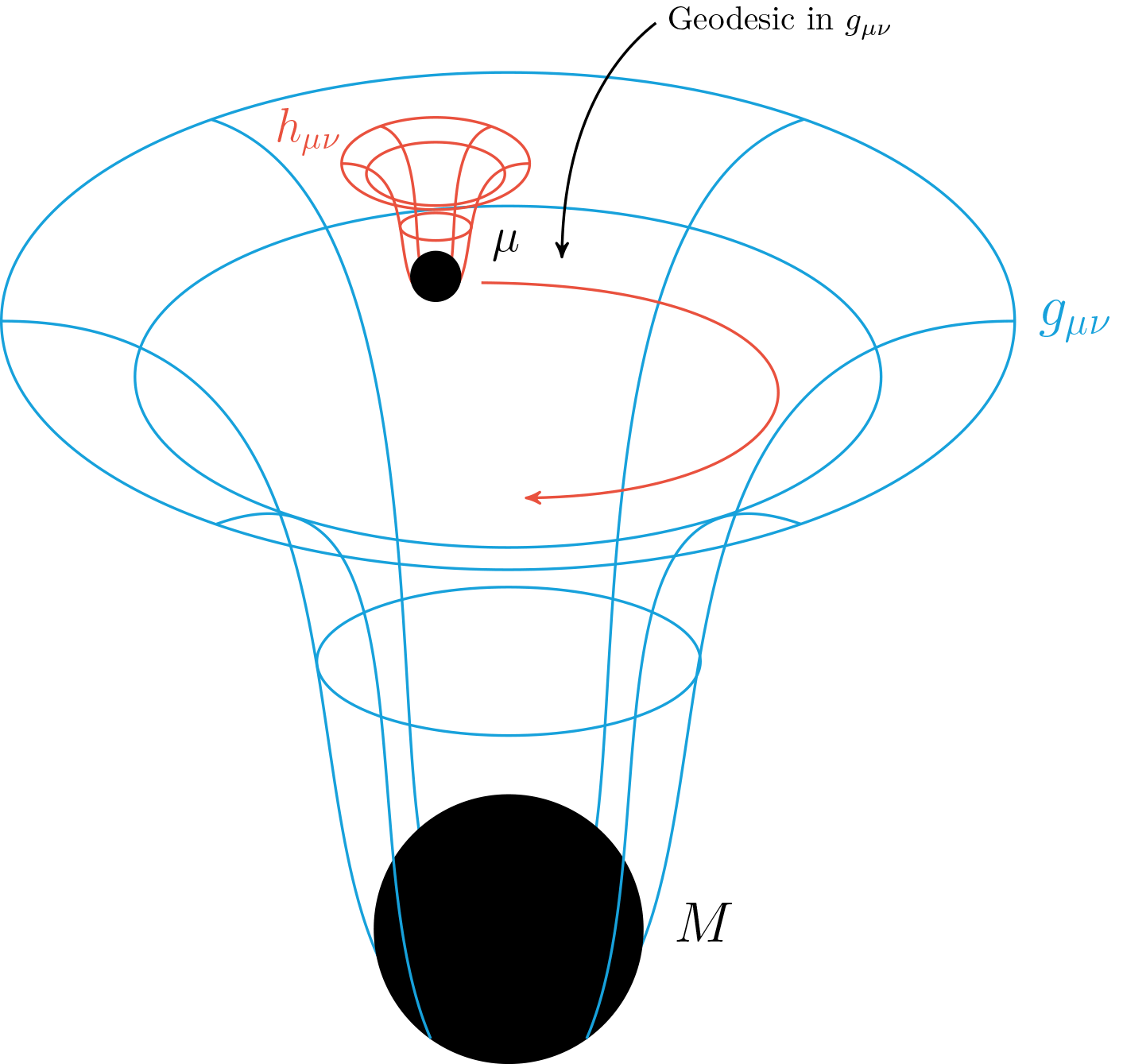
GENERIC for Black Holes (Gravitational Waves)

Binary Black Holes | 06/12 Update
By Ref Bari
Binary Black Holes | 06/12 Update
- 96



